Key Takeaways
- A category manager plays a critical role in optimizing procurement and supply chain activities within specific product categories, driving cost savings, improving supplier relationships, and enhancing product quality.
- To be effective in this role, category managers need to possess a range of skills and qualifications, including strategic thinking, data analysis, communication, and leadership.
- Effective category management can offer significant benefits to businesses, including cost savings, increased profitability, better supplier relationships, improved product quality, and greater flexibility and adaptability.
Category management is a critical function for businesses looking to optimize their procurement process and drive greater profitability.
Category managers are responsible for overseeing the procurement of goods and services within specific categories, and play a crucial role in managing supplier relationships, identifying market trends, and negotiating contracts.
In today’s fast-paced business environment, category management has become an increasingly important function for businesses looking to stay competitive and drive growth.
By leveraging data and insights to make more informed purchasing decisions, category managers can help businesses save money, improve product quality and innovation, and build stronger supplier relationships.
In this article, we’ll provide an in-depth look at what a category manager is, what they do, and why they are so important for businesses of all sizes.
We’ll explore the key responsibilities of a category manager, as well as the skills and qualifications required to excel in this critical role.
Additionally, we’ll examine the benefits of effective category management, and provide examples of how category management is being used in different industries to drive business success.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of what a category manager is, and the value they can bring to your organization.
Whether you’re a business owner, procurement professional, or simply interested in learning more about this critical function, this article is the ultimate guide to category management and its role in driving business success.
Before we venture further into this article, we like to share who we are and what we do.
About 9cv9
9cv9 is a business tech startup based in Singapore with a strong presence all over the world.
With over six years of startup and business experience, and being highly involved in connecting with thousands of companies and startups, the 9cv9 team has listed some important learning points in this overview of what do category managers do.
If you are looking for a category manager job, then we are keen to speak to you. Register and complete your profile here.
If your company needs recruitment and headhunting services, you can use 9cv9 headhunting and recruitment services to hire top talents and candidates. Find out more here, or send over an email to [email protected].
What is a Category Manager and What Do They Do?
- What is Category Management?
- Career Paths of a Category Manager
- Key Responsibilities of a Category Manager
- Skills and Qualifications Required For A Category Manager
- Salaries and Benefits of a Category Manager
- Examples of Category Management in Different Industries
- Benefits of Effective Category Management
1. What is Category Management?

Category management is a strategic approach to procurement and supply chain management that involves the management and optimization of product categories within a business.
Category management is used by businesses to help streamline their procurement process, improve supplier relationships, and drive greater profitability.
At its core, category management involves the use of data and insights to better understand the products and services being procured by a business.
Category managers are responsible for overseeing the procurement of goods and services within specific categories, such as office supplies, IT equipment, or marketing services.
By analyzing market trends, supplier performance, and other key data points, category managers can develop strategies to optimize the procurement process and drive better business outcomes.
This may involve negotiating more favorable pricing with suppliers, consolidating suppliers to reduce complexity, or sourcing alternative products that offer greater value.
In addition to procurement optimization, category management can also help businesses improve product quality and innovation.
By working closely with suppliers and monitoring market trends, category managers can identify new product opportunities and help drive innovation within their businesses.
Overall, category management is a critical function for businesses looking to optimize their procurement process and drive greater profitability.
By leveraging data and insights to make more informed purchasing decisions, category managers can help businesses save money, improve product quality and innovation, and build stronger supplier relationships.
2. Career Paths of a Category Manager
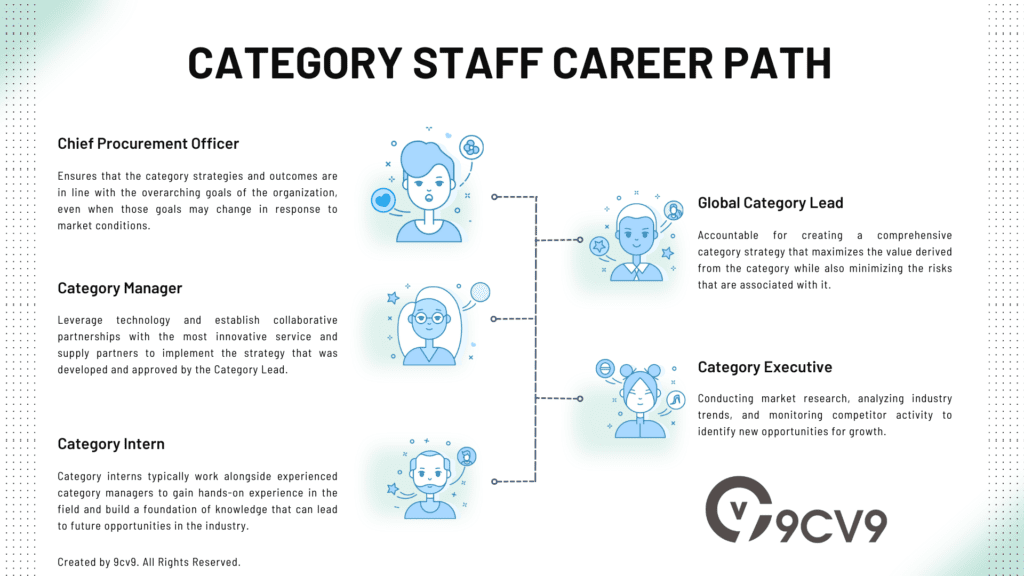
There are several different career paths that a Category Manager can pursue within the field of category management.
One possible path is to move up the ranks within the same company, taking on progressively higher-level roles such as Senior Category Manager, Director of Category Management, Vice President of Category Management, or even Chief Procurement Officer.
Another option is to specialize in a specific area within category management, such as pricing, promotions, or supply chain management. This could lead to roles such as Pricing Manager, Promotions Manager, or Supply Chain Manager.
A third career path could be to transition to a related field such as sales or marketing, leveraging the skills and knowledge gained from category management to excel in these areas.
Ultimately, the career path of a Category Manager will depend on individual interests, goals, and opportunities available in the industry.
3. Key Responsibilities of a Category Manager

The key responsibilities of a category manager may vary depending on the business and industry but generally include:
- Identifying and analyzing market trends: Category managers are responsible for monitoring market trends within their specific product category. This may involve analyzing sales data, reviewing industry reports, and attending industry events to stay up-to-date on the latest trends.
- Developing category strategies: Based on their analysis of market trends and supplier performance, category managers develop strategies to improve the performance of their product category. This may involve negotiating more favorable pricing with suppliers, consolidating suppliers to reduce complexity, or sourcing alternative products that offer greater value.
- Managing supplier relationships: Category managers are responsible for building and maintaining strong relationships with suppliers. This may involve negotiating contracts, resolving disputes, and monitoring supplier performance to ensure they are meeting the needs of the business.
- Managing the procurement process: Category managers are responsible for overseeing the procurement process within their product category. This may involve creating purchase orders, managing inventory levels, and ensuring that deliveries are made on time.
- Managing budgets and expenses: Category managers are responsible for managing budgets and expenses related to their product category. This may involve developing and managing a budget for the category, monitoring spending, and identifying opportunities to reduce costs.
- Monitoring and reporting on category performance: Category managers are responsible for monitoring the performance of their product category and reporting on key metrics such as sales, inventory levels, and supplier performance. This information is used to inform business decisions and identify opportunities for improvement.
The key responsibilities of a category manager involve managing supplier relationships, optimizing the procurement process, and driving better business outcomes within their specific product category.
By leveraging data and insights to make more informed decisions, category managers can help businesses save money, improve product quality and innovation, and build stronger supplier relationships.
4. Skills and Qualifications Required For A Category Manager
The skills and qualifications required for a category manager may vary depending on the business and industry but generally include:
- Strong analytical skills: Category managers must be able to analyze data and identify trends within their product category. This requires strong analytical skills and the ability to use tools such as spreadsheets and data visualization software.
- Negotiation skills: Category managers must be able to negotiate with suppliers to ensure the best possible pricing and terms. This requires strong negotiation skills and the ability to build strong relationships with suppliers.
- Project management skills: Category managers must be able to manage multiple projects simultaneously, ensuring that they are completed on time and within budget. This requires strong project management skills and the ability to work well under pressure.
- Communication skills: Category managers must be able to communicate effectively with internal stakeholders and suppliers. This requires strong communication skills and the ability to clearly articulate complex ideas.
- Strategic thinking: Category managers must be able to think strategically and develop long-term plans to optimize their product category. This requires strong strategic thinking skills and the ability to balance short-term needs with long-term goals.
- Bachelor’s degree: Most category manager positions require a bachelor’s degree in business, supply chain management, or a related field. Some employers may also require a master’s degree or additional certifications.
- Relevant experience: Category managers typically have several years of experience in procurement, supply chain management, or a related field. This experience helps them develop the skills and knowledge needed to excel in their role as a category manager.
The skills and qualifications required for a category manager involve a combination of analytical, negotiation, project management, communication, and strategic thinking skills.
A bachelor’s degree in business or a related field and relevant experience in procurement or supply chain management is also typically required.
5. Salaries and Benefits of a Category Manager
The salaries and benefits of a Category Manager can vary depending on various factors such as the industry, location, company size, experience, and education. In general, a Category Manager can expect to earn a competitive salary along with various benefits.
According to Indeed, the average base salary for a Category Manager in the United States is around $6,718 per Month.
In addition to the base salary, Category Managers may also receive various benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid time off, bonuses, and stock options. These benefits can vary from company to company and may also depend on the specific role and level of the Category Manager.
Category Managers can expect to receive a competitive salary along with a range of benefits that can vary based on the specific job and company.
6. Examples of Category Management in Different Industries
Category management is a strategic approach to managing procurement and supply chain activities within a specific product category.
While the key principles of category management are similar across industries, the specific application of those principles can vary depending on the industry.
Examples of category management in different industries:
- Retail Industry: In the retail industry, category management is often used to manage the supply chain for specific product categories such as clothing, electronics, or home goods. Retailers work with suppliers to ensure they are providing the best quality products at the most competitive prices. They also use data analytics to monitor trends and optimize their product assortments.
- Healthcare Industry: In the healthcare industry, category management is used to manage the procurement of medical supplies and equipment. Hospitals work with suppliers to ensure they are providing the best quality products at the most competitive prices. They also use data analytics to monitor trends and optimize their inventory levels.
- Food Industry: In the food industry, category management is used to manage the procurement of ingredients and finished products. Food manufacturers work with suppliers to ensure they are providing the best quality ingredients at the most competitive prices. They also use data analytics to monitor trends and optimize their product assortments.
- Manufacturing Industry: In the manufacturing industry, category management is used to manage the procurement of raw materials and components. Manufacturers work with suppliers to ensure they are providing the best quality materials at the most competitive prices. They also use data analytics to monitor trends and optimize their inventory levels.
- Energy Industry: In the energy industry, category management is used to manage the procurement of equipment and supplies used in the production and distribution of energy. Energy companies work with suppliers to ensure they are providing the best quality equipment and supplies at the most competitive prices. They also use data analytics to monitor trends and optimize their procurement activities.
Overall, category management is a valuable approach to managing procurement and supply chain activities in a variety of industries.
By working closely with suppliers and using data analytics to monitor trends and optimize inventory levels, businesses can improve the quality and competitiveness of their products while reducing costs and increasing efficiencies.
7. Benefits of Effective Category Management
Effective category management can offer a number of benefits to businesses across industries. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Improved cost savings: Effective category management can lead to significant cost savings for businesses. By optimizing procurement and supply chain activities within a specific product category, businesses can negotiate better pricing with suppliers, reduce waste and excess inventory, and improve overall efficiencies.
- Increased profitability: Cost savings resulting from effective category management can directly contribute to increased profitability for businesses. By reducing costs and increasing efficiencies, businesses can generate more revenue and improve their bottom line.
- Better supplier relationships: Category management involves working closely with suppliers to ensure they are providing the best quality products and services at the most competitive prices. By building strong supplier relationships, businesses can improve their negotiating power and gain access to new products and innovations.
- Improved product quality: By carefully managing their product categories, businesses can ensure they are providing the best quality products to their customers. This can lead to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty, as well as improved brand reputation.
- Greater flexibility and adaptability: Effective category management allows businesses to be more agile and adaptable to changes in the market. By constantly monitoring trends and optimizing their inventory levels, businesses can quickly respond to shifts in demand and adjust their product assortments as needed.
Eective category management can offer significant benefits to businesses, including cost savings, increased profitability, better supplier relationships, improved product quality, and greater flexibility and adaptability.
By adopting a strategic approach to managing their procurement and supply chain activities within specific product categories, businesses can improve their competitive position and drive long-term success.
Conclusion
A category manager is a critical role in any business that wants to optimize its procurement and supply chain activities within specific product categories.
From identifying and selecting suppliers to negotiating contracts and managing inventory levels, category managers play a crucial role in driving cost savings, improving supplier relationships, and enhancing product quality.
To be effective in this role, category managers need to possess a range of skills and qualifications, including strategic thinking, data analysis, communication, and leadership.
They must also be able to collaborate effectively with cross-functional teams and build strong relationships with suppliers.
While the specific responsibilities of a category manager can vary depending on the industry and the size of the organization, the key principles of category management remain the same.
By adopting a strategic approach to managing their procurement and supply chain activities within specific product categories, businesses can drive cost savings, improve efficiencies, and gain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
If you are interested in pursuing a career in category management, there are many resources available to help you get started.
From online courses and certifications to professional associations and networking events, there are many opportunities to build your skills and connect with other professionals in the field.
Category management is a critical function for any business that wants to optimize its procurement and supply chain activities and drive long-term success.
By understanding the role of a category manager and the key principles of category management, businesses can position themselves for growth and profitability in today’s dynamic marketplace.
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your jobseeker friends and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the 9cv9 Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.
People Also Ask
What is a typical day for a category manager?
A typical day of a category manager involves analyzing market trends, monitoring sales data, and working with suppliers to ensure product availability and quality. They also negotiate contracts, manage inventory levels, and collaborate with cross-functional teams such as marketing and sales to develop promotional strategies. Additionally, they may attend industry events and conferences to stay up-to-date on market developments and network with potential suppliers. Overall, a category manager’s day is fast-paced and requires strong analytical, communication, and project management skills.
What are the 3 types of category management?
The three types of category management are Strategic, Tactical, and Operational.
- Strategic category management involves long-term planning and focuses on identifying opportunities for growth and innovation within a category. It involves analyzing market trends, consumer behavior, and supplier capabilities to develop a category strategy that aligns with the overall business strategy.
- Tactical category management focuses on executing the category strategy through day-to-day operations such as supplier selection, pricing negotiations, and promotional planning. It involves monitoring sales data, managing inventory levels, and ensuring product availability and quality.
- Operational category management involves managing the ongoing relationships with suppliers and ensuring compliance with contracts and regulations. It also involves analyzing supplier performance and identifying opportunities for improvement or cost savings.































![Writing A Good CV [6 Tips To Improve Your CV] 6 Tips To Improve Your CV](https://blog.9cv9.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/2020-06-02-2-100x70.png)


