Key Takeaways
- Employers in Vietnam must comply with regulations on minimum wage requirements, working hours and overtime, employee benefits and protections, workplace health and safety, termination and severance pay, and hiring foreign nationals.
- Staying up-to-date on the latest labor laws and seeking legal advice when necessary is essential to avoid legal and financial consequences.
- By creating a positive work environment and fostering employee satisfaction, employers can go above and beyond compliance with regulations and contribute to a thriving and sustainable economy in Vietnam.
Vietnam is one of the fastest-growing economies in Southeast Asia, with a young and dynamic workforce that is driving growth in various industries.
Vietnam’s economy demonstrated robust growth in 2022, expanding at a rate of 8.02%, which is the fastest annual pace since 1997.
This impressive growth was supported by strong domestic retail sales and exports, which have helped to drive the country’s economic activity.
The growth rate of 8.02% significantly exceeded the official growth target of 6.0%-6.5%, which indicates the economy’s resilience and adaptability, even amidst challenging global circumstances.
This growth rate is particularly noteworthy, given that in the previous year, Vietnam’s economy experienced a growth rate of just 2.58%, due to the adverse impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on the economy and factory activity.
These impressive figures underscore Vietnam’s emergence as a dynamic and rapidly growing economy in the Southeast Asia region.
And, companies and startups are looking toward Vietnam as the next frontier market to invest, and hire strong talents for their operations.
As an employer operating in Vietnam, it is crucial to understand the labor laws in the country to ensure compliance, avoid legal issues, and maintain a positive work environment for employees.
However, navigating Vietnam’s labor laws can be a daunting task, with a complex system of regulations and governing bodies that can be difficult to comprehend.
This blog post aims to provide employers in Vietnam with a comprehensive guide to the country’s labor laws.
From minimum wage requirements to employee benefits and protections, this guide will cover everything you need to know as an employer in Vietnam.
We will also explore the latest changes and updates to labor laws in Vietnam, as well as provide practical tips on how to ensure compliance with these regulations.
Understanding Vietnam’s labor laws is crucial for employers to maintain a healthy and positive work environment.
By complying with these regulations, employers can avoid legal issues and protect their employees’ rights and interests.
Moreover, understanding Vietnam’s labor laws can help employers attract and retain top talent, as employees are more likely to choose companies that prioritize their welfare and well-being.
In the following sections, we will provide an overview of Vietnam’s labor law system, discuss minimum wage requirements, working hours and overtime regulations, employee benefits and protections, workplace health and safety regulations, employment termination and severance pay, and regulations for hiring foreign nationals.
By the end of this blog post, you will have a better understanding of Vietnam’s labor laws and how to ensure compliance as an employer operating in the country.
Before we venture further into this article, we like to share who we are and what we do.
About 9cv9
9cv9 is a business tech startup based in Singapore and Vietnam with a strong presence all over the world.
With over six years of startup and business experience, and being highly involved in connecting with thousands of companies and startups, the 9cv9 team has listed some important learning points in this overview of Vietnamese Labor Law from the perspective of an Employer.
If your company needs hiring and corporate services, you can use 9cv9 highly acclaimed services. Book a consultation slot here, or send over an email to [email protected].
Vietnam’s Labor Laws: What You Need to Know as an Employer (Updated in 2023)
- Overview of Vietnam’s Labor Laws
- Minimum Wage Requirements in Vietnam
- Working Hours and Overtime Regulations
- Employee Benefits and Protections
- Workplace Health and Safety Regulations
- Employment Termination and Severance Pay
- Hiring Foreign Nationals in Vietnam
1. Overview of Vietnam’s Labor Laws

Vietnam’s labor laws are designed to protect the rights and interests of employees, ensuring that they are treated fairly and provided with safe working conditions.
The legal framework governing labor laws in Vietnam is relatively complex, with several governing bodies responsible for implementing and enforcing these regulations.
The main labor code that is currently the most up-to-date is the “Labor Code 2019“.
The primary governing body responsible for labor laws in Vietnam is the Ministry of Labor, Invalids and Social Affairs (MOLISA).
MOLISA oversees the development and implementation of labor policies and regulations, as well as the enforcement of labor laws.
Other governing bodies involved in labor laws in Vietnam include the General Confederation of Labor, which represents the interests of workers, and the Vietnam Chamber of Commerce and Industry, which represents the interests of employers.
Vietnam’s labor laws cover a wide range of areas, including minimum wage requirements, working hours, employee benefits and protections, workplace health and safety regulations, and employment termination and severance pay.
These regulations apply to all employers operating in Vietnam, regardless of the industry or sector.
To comply with Vietnam’s labor laws, employers must ensure that their employees are provided with fair working conditions and wages, including adequate social insurance and other benefits.
Employers must also adhere to regulations related to working hours, overtime pay, and annual leave, as well as ensure that their workplace meets health and safety standards.
Overall, understanding and complying with Vietnam’s labor laws is essential for employers operating in the country.
Failure to comply with these regulations can result in legal issues, financial penalties, and damage to the employer’s reputation.
Employers should stay informed and up-to-date on the latest labor laws and regulations to ensure compliance and maintain a positive and healthy work environment for their employees.
2. Minimum Wage Requirements in Vietnam

Minimum wage requirements in Vietnam are set by the government and revised annually.
The minimum wage rate varies by region, with higher rates in urban areas compared to rural areas.
The minimum wage rate is determined by the National Wage Council, which considers a range of factors, including inflation, economic growth, and the cost of living.
As of January 1, 2023, the minimum wage in Vietnam ranges from VND 3,250,000 (approximately USD 139) to VND 4,680,000 (approximately USD 199) per month, depending on the region.
The highest minimum wage rates are in urban areas such as Ho Chi Minh City and Hanoi, while the lowest rates are in rural areas.

Employers in Vietnam are required to pay their employees at least the minimum wage rate set by the government.
Here is the information about the minimum hourly wage, mainly for part-time jobs and roles.
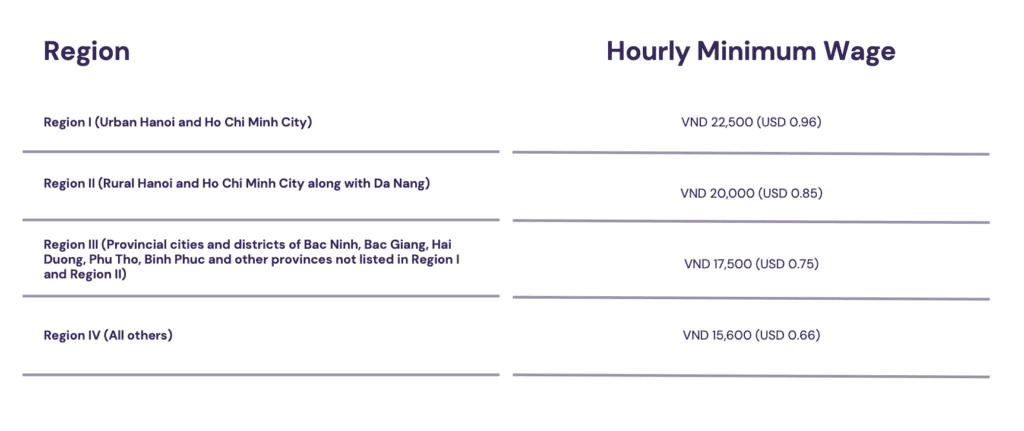
Wages that are paid daily or on a weekly basis, must not be lower than the minimum wage when converted to monthly or hourly rates.
Failure to comply with minimum wage requirements can result in legal issues and financial penalties.
In addition, the minimum wage number serves as an important component to calculate the social contribution for all enterprises (i.e., the maximum social contribution is 20 times the common minimum wage).
Employers should also consider providing their employees with benefits such as health insurance, social insurance, and other incentives to attract and retain top talent.
Employers should also be aware that the minimum wage rate is subject to change, and they should stay up-to-date on the latest regulations to ensure compliance.
Also, employers should ensure that their employee’s wages are paid on time and in full and that all payroll records are accurate and up-to-date.
Minimum wage requirements in Vietnam are an important aspect of labor laws that employers must comply with.
Employers should stay informed about the latest regulations and ensure that they are paying their employees fairly and in compliance with the law.
Providing fair wages and benefits can help employers attract and retain top talent, leading to a more positive and productive work environment.
3. Working Hours and Overtime Regulations

Working hours and overtime regulations are an essential part of Vietnam’s labor laws that employers must comply with.
These regulations aim to ensure that employees are not overworked and are compensated fairly for any additional work beyond regular working hours.
According to Vietnam’s labor laws, the standard working hours cannot exceed eight hours per day and cannot exceed 48 hours per week.
Standard working hours cannot exceed eight hours per day and cannot exceed 48 hours per week
– Vietnam Working Hours
If both the employer and employee come to an agreement regarding overtime, the maximum limit for overtime is 12 hours per day, 40 hours per month, and 200 hours per year.
Under some special cases, the maximum overtime hours can exceed 200 hours in one year, but not more than 300 hours in one year.
This regulation applies to a range of sectors, occupations, and cases, including:
a) The production and processing of export-oriented textiles, garments, leather, footwear, electronics, and agricultural, forestry, salt, and aquatic products.
b) The production and supply of electricity, telecommunications, and oil refining, as well as water supply and drainage.
c) In situations where work requires workers with high-level technical and professional qualifications that are not available in sufficient numbers in the labor market.
d) When urgent work must be completed due to seasonal factors, the availability of raw materials or products, unforeseen factors caused by weather, natural disasters, fire, sabotage, lack of electricity, raw materials, or technical problems with production lines.
e) Other cases specified by the Government of Vietnam.
If any of the situations prevail as per above, the employer must notify the specialized labor agency of the Provincial People’s Committee in writing.
Overtime Pay
If employees work beyond their regular working hours, they are entitled to overtime pay.
The overtime pay rate is at least 150% of the regular hourly rate for work done on weekdays and Saturdays and at least 200% of the regular hourly rate for work done on Sundays or holidays.
On public holidays, New Year holidays (such as their annual Tet holidays), and paid leave days, the extra overtime pay is equal to at least 300%, excluding the wage for public holidays, New Year holidays, and paid leave days if the worker receives a daily wage.
Employers must also provide employees with at least one day off per week, preferably on Sundays.
Employers must maintain accurate records of their employees’ working hours and overtime, including start and finish times, breaks, and rest periods.
Failure to comply with working hours and overtime regulations can result in legal issues and financial penalties.
In addition to complying with working hours and overtime regulations, employers must also ensure that their employees are not subject to any form of forced labor, including excessive overtime.
Employers must provide their employees with a safe and healthy work environment and take measures to prevent workplace accidents and injuries.
Complying with working hours and overtime regulations is an essential part of being a responsible employer in Vietnam.
Employers must ensure that they comply with these regulations, provide their employees with fair compensation for additional work, and maintain accurate records of their employees’ working hours and overtime.
Doing so will help create a positive work environment and foster a more productive workforce.
4. Employee Benefits and Protections

Employee benefits and protections are an essential aspect of Vietnam’s labor laws.
Employers are required to provide their employees with certain benefits and protections, which can help attract and retain top talent and create a more positive work environment.
One of the key benefits that employers must provide is statutory social security.
Read more on our recent written guide “The Ultimate Guide to Social Insurance in Vietnam: Everything You Need to Know” to understand more details on Vietnam’s statutory social insurance.
There are 3 main components of statutory social security:
- Social Insurance
- Health Insurance
- Unemployment Insurance
Social Insurance
Social insurance is a form of social protection that provides employees with financial support in case of sickness, maternity, retirement, and other life events.
Employers must contribute to their employees’ social insurance funds, and employees are also required to make contributions.
In Vietnam, employers are required by law to enroll their foreign staff in the country’s social insurance system.
This is in accordance with the provisions set out in the Labor Code of Vietnam.
Social insurance contributions must be paid monthly on behalf of foreign employees by their employers, and the payments must be made to the provincial Department of Labor, Invalids, and Social Affairs (DoLISA).
Health Insurance
In addition to social insurance, employers must also provide their employees with health insurance.
Health insurance covers the cost of medical treatment and hospitalization and is mandatory for all employees in Vietnam.
Employers must contribute to their employees’ health insurance funds, and employees are also required to make contributions.
Unemployment Insurance
Employers must also comply with other benefits and protections, such as paid leave, maternity leave, and occupational safety and health regulations.
Female employees are entitled to maternity leave of up to six months, and employers are required to provide a safe and healthy work environment that complies with occupational safety and health regulations.
In summary, these are the updated rates of social, health, and unemployment insurance.
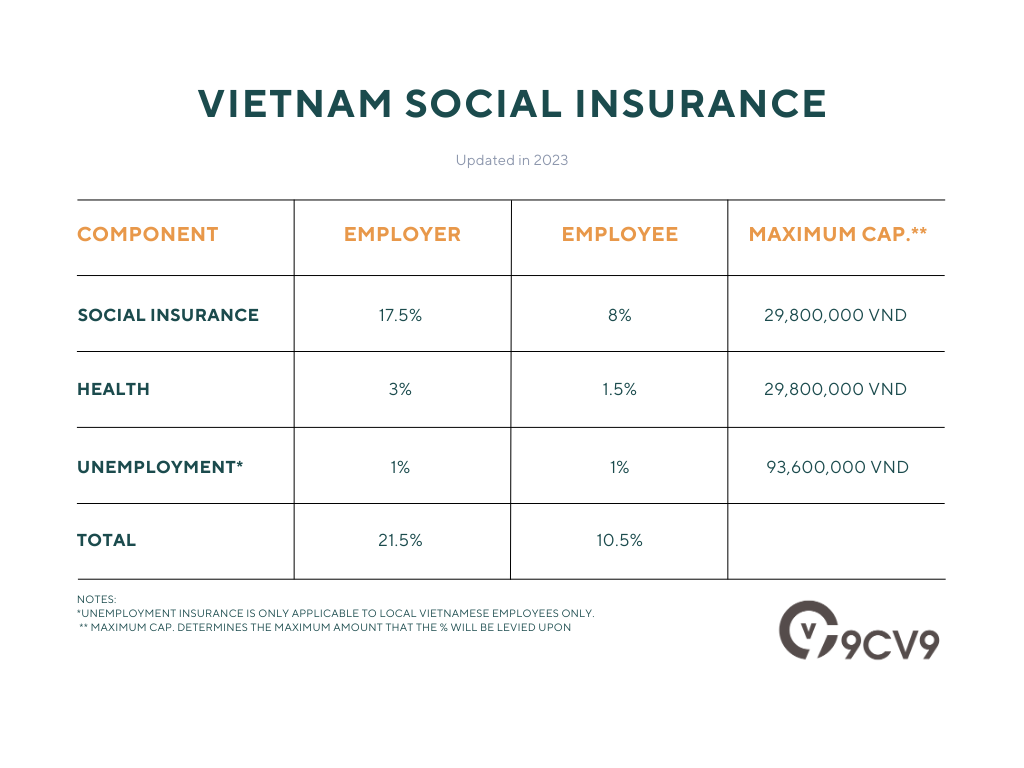
Furthermore, employers must also comply with anti-discrimination and equal opportunity laws.
Discrimination based on gender, race, ethnicity, religion or other factors is strictly prohibited under Vietnam’s labor laws.
Employers must provide equal opportunities for all employees, regardless of their background or personal characteristics.
Employers who fail to comply with employee benefits and protections can face legal issues and financial penalties.
Therefore, it is essential for employers to stay up-to-date on the latest regulations and ensure that they provide their employees with fair compensation and a safe and healthy work environment.
Employee benefits and protections are an essential part of Vietnam’s labor laws that employers must comply with.
Providing social insurance, health insurance, paid leave, and complying with occupational safety and health regulations can help create a positive work environment and attract and retain top talent.
Employers must also comply with anti-discrimination and equal opportunity laws to ensure a fair and inclusive workplace.
5. Workplace Health and Safety Regulations

Workplace health and safety regulations are a crucial part of Vietnam’s labor laws, aimed at ensuring that employees work in a safe and healthy environment.
Employers must comply with a range of regulations to prevent accidents and injuries in the workplace.
The Ministry of Labor, Invalids, and Social Affairs (MOLISA) is responsible for developing and enforcing workplace health and safety regulations in Vietnam.
Employers must comply with the Occupational Safety and Health Law, which outlines the requirements for workplace safety, including providing training, personal protective equipment (PPE), and emergency response plans.
Employers must identify and evaluate the workplace hazards that their employees may face, and implement appropriate measures to eliminate or control those hazards.
Employers must also provide their employees with adequate training and education on workplace safety, including the use of equipment and machinery, handling hazardous materials, and emergency procedures.
In addition to implementing measures to prevent accidents and injuries, employers must also have an emergency response plan in place in case of workplace incidents.
This includes procedures for reporting accidents or injuries, providing first aid, and transporting injured employees to medical facilities.
Employers must also comply with regulations related to workplace hygiene and sanitation.
This includes providing clean drinking water, adequate ventilation, and proper waste disposal facilities.
Failure to comply with workplace health and safety regulations can result in legal issues and financial penalties.
Employers must ensure that they comply with all regulations to create a safe and healthy work environment for their employees.
Workplace health and safety regulations are a critical aspect of Vietnam’s labor laws.
Employers must comply with regulations related to workplace safety, including identifying and controlling workplace hazards, providing training and education, and implementing emergency response plans.
Employers must also comply with regulations related to workplace hygiene and sanitation.
Ensuring a safe and healthy work environment can help prevent accidents and injuries and create a more productive workforce.
6. Employment Termination and Severance Pay
Employment termination and severance pay are important aspects of Vietnam’s labor laws that employers must comply with.
Terminating an employee’s employment contract is only allowed under certain conditions and procedures, and employers must provide severance pay to eligible employees upon termination.
Employers can terminate an employee’s employment contract under several circumstances, including mutual agreement, completion of a specific task or term, or due to employee misconduct or poor performance.
However, termination must follow a specific process and be based on valid reasons.
Employers must provide written notice to employees before terminating their contracts, stating the reasons for termination and the date of termination.
Employers must also provide employees with an opportunity to explain themselves and contest the reasons for termination if they wish to do so.
In addition to complying with the termination process, employers must also provide severance pay to eligible employees upon termination.
The amount of severance pay depends on the length of employment and the reason for termination.
The Labor Code sets out a specific formula for calculating severance pay, which is based on the employee’s monthly salary, length of employment, and reason for termination.
Employees who are terminated due to business restructuring, technological changes, or economic difficulties may be eligible for additional severance pay.
This is known as redundancy pay and is calculated separately from regular severance pay.
Failure to comply with employment termination and severance pay regulations can result in legal issues and financial penalties.
Employers must ensure that they follow the appropriate procedures and provide eligible employees with the appropriate severance pay.
Employment termination and severance pay are important aspects of Vietnam’s labor laws that employers must comply with.
Employers must follow the appropriate procedures when terminating employees’ contracts and provide eligible employees with severance pay.
Failure to comply with regulations can result in legal and financial consequences, so it is essential for employers to stay up-to-date on the latest regulations and ensure that they comply with them.
7. Hiring Foreign Nationals in Vietnam
Hiring foreign nationals in Vietnam is a process that requires employers to comply with several regulations and obtain necessary permits and documents.
Vietnam’s labor laws outline the requirements for hiring foreign nationals and provide guidelines for employers to follow.
Employers who wish to hire foreign nationals must obtain a work permit for the employee from the Department of Labor, Invalids, and Social Affairs.
The work permit is valid for up to two years and can be renewed upon expiration.
To obtain a work permit, employers must demonstrate that the position cannot be filled by a local worker and that the foreign national has the necessary skills and qualifications for the position.
Employers must also provide evidence of their financial capacity and that they have appropriate facilities and equipment to support the employee.
Employers must also comply with regulations related to foreign national taxation and social insurance contributions.
Foreign nationals who work in Vietnam are subject to the same tax and social insurance regulations as local workers, and employers must deduct the appropriate amounts from their salaries and contribute to the relevant funds.
Employers must also ensure that foreign nationals have appropriate visas and residence permits. The employer must obtain a temporary residence card for the employee within 90 days of their arrival in Vietnam.
Failure to comply with regulations related to hiring foreign nationals can result in legal and financial consequences. Employers must ensure that they follow the appropriate procedures and obtain all necessary permits and documents to hire foreign nationals legally.
In conclusion, hiring foreign nationals in Vietnam is a process that requires employers to comply with several regulations and obtain necessary permits and documents.
Employers must obtain a work permit for the employee, comply with tax and social insurance regulations, and ensure that the employee has appropriate visas and residence permits.
Failure to comply with regulations can result in legal and financial consequences, so it is essential for employers to stay up-to-date on the latest regulations and ensure that they comply with them.
Conclusion
Vietnam’s labor laws are designed to protect the rights of employees and ensure fair treatment in the workplace.
As an employer in Vietnam, it is essential to understand and comply with the regulations to avoid legal and financial consequences.
Minimum wage requirements, working hours and overtime regulations, employee benefits and protections, workplace health and safety regulations, and employment termination and severance pay are some of the key aspects of Vietnam’s labor laws that employers must comply with.
To ensure compliance with the regulations, employers should stay up-to-date on the latest laws and regulations and seek legal advice when necessary.
Employers must also maintain accurate records and documentation to demonstrate compliance.
In addition to complying with the regulations, employers can also go above and beyond to create a positive work environment and foster employee satisfaction.
This can include providing additional benefits and perks, implementing flexible working arrangements, and promoting a culture of respect and inclusivity in the workplace.
By understanding and complying with Vietnam’s labor laws, employers can create a fair and productive workplace that benefits both employees and the company.
It is a shared responsibility to ensure that the rights and well-being of employees are respected and upheld, and by doing so, we can contribute to a thriving and sustainable economy in Vietnam.
We hope that this article has provided valuable insights into Vietnam’s labor laws and the key aspects that employers need to know.
By staying informed and taking action to comply with the regulations, employers can build a strong and successful business that benefits everyone involved.
If you need help, 9cv9 Corporate Team stands ready to deliver the best and the most affordable trading company registration and compliance services. Book a free consultation slot here.
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your sales friends and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the 9cv9 Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.






























![Writing A Good CV [6 Tips To Improve Your CV] 6 Tips To Improve Your CV](https://blog.9cv9.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/2020-06-02-2-100x70.png)


