Key Takeaways
- The top 10 Digital Experience Platforms (DXP) in 2026 are powered by Agentic AI, composable architecture, and experience-as-data models that enable real-time personalization and automation.
- Leading DXP software tools differentiate through measurable ROI, cloud-native scalability, AI governance, and deep integration across content, commerce, and customer data ecosystems.
- Choosing the right Digital Experience Platform in 2026 requires balancing pricing, total cost of ownership, regulatory compliance, and long-term digital transformation strategy.
The global Digital Experience Platform (DXP) market in 2026 stands at the center of enterprise digital transformation. What began as traditional web content management systems has evolved into intelligent, AI-driven ecosystems that orchestrate content, commerce, customer data, automation, and personalization across every digital touchpoint. Today, selecting the right Digital Experience Platform is no longer a marketing decision alone; it is a strategic infrastructure choice that shapes customer engagement, operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, and long-term business growth.

As organizations compete in an environment defined by real-time personalization, omnichannel engagement, and AI-powered automation, the top 10 Digital Experience Platforms in the world in 2026 represent the most advanced solutions available. These platforms are redefining how enterprises deliver digital experiences by integrating agentic artificial intelligence, composable architecture, cloud-native scalability, and governance-first design into unified ecosystems.
In 2026, the definition of a DXP has fundamentally changed. A modern Digital Experience Platform is not just a content hub or a headless CMS. It is an orchestration engine that connects marketing, sales, service, commerce, and analytics through structured data and AI-driven workflows. Leading DXPs now treat experiences as dynamic, machine-readable data structures, enabling platforms to adapt layouts, content variations, and user journeys in real time based on individual intent and behavioral signals.
This evolution has been accelerated by several powerful market forces. The rise of generative AI has transformed personalization from rule-based segmentation into predictive, context-aware optimization. The expansion of global data privacy regulations has elevated governance and consent management to board-level priorities. Meanwhile, the shift from search engine optimization to answer engine optimization has changed how content is structured, measured, and distributed across AI-powered interfaces.
Against this backdrop, enterprises evaluating the best Digital Experience Platforms in 2026 must look beyond feature lists. Critical decision factors now include total cost of ownership, return on investment timelines, AI governance maturity, composability, integration flexibility, and cloud deployment readiness. The leading DXPs differentiate themselves not only through innovation but through measurable impact, operational efficiency, and long-term scalability.
This comprehensive guide to the top 10 Digital Experience Platforms in the world in 2026 examines how industry leaders such as Adobe, Salesforce, Sitecore, Optimizely, Liferay, Acquia, Contentful, Contentstack, Bloomreach, and Progress Sitefinity are shaping the next generation of digital experience management. Each platform brings a distinct strategic focus, whether it is enterprise-scale content governance, experimentation-led optimization, commerce-driven personalization, open-source flexibility, or cloud-first efficiency.
Understanding the competitive landscape requires analyzing more than brand recognition. It requires evaluating how each DXP approaches agentic AI orchestration, composable digital architecture, performance optimization, and regulatory compliance. Organizations must determine whether they need a unified enterprise suite, a best-of-breed composable stack, or a hybrid approach that balances flexibility with centralized control.
In 2026, the stakes are higher than ever. Customer expectations demand seamless, personalized experiences across web, mobile, commerce, and emerging conversational channels. Regulatory frameworks demand transparency, consent enforcement, and auditable AI governance. Executive teams demand measurable ROI and shorter operational cycles. The Digital Experience Platform sits at the intersection of all these pressures.
This in-depth analysis of the top 10 Digital Experience Platforms (DXP) in the world in 2026 provides clarity in a complex market. It explores pricing models, market share trends, AI capabilities, composable architecture strategies, governance requirements, and real-world performance outcomes. Whether you are a CIO, CMO, digital transformation leader, or enterprise architect, understanding the strengths and trade-offs of the leading DXPs will help you make an informed, future-ready decision.
The future of digital experience management is no longer about publishing content. It is about orchestrating intelligent, adaptive ecosystems that turn data into trust, automation into efficiency, and personalization into measurable growth. The top Digital Experience Platforms of 2026 are not simply software tools; they are the central nervous systems of modern digital enterprises.
Before we venture further into this article, we would like to share who we are and what we do.
About 9cv9
9cv9 is a business tech startup based in Singapore and Asia, with a strong presence all over the world.
With over nine years of startup and business experience, and being highly involved in connecting with thousands of companies and startups, the 9cv9 team has listed some important learning points in this overview of the Top 10 Best Digital Experience Platforms (DXP) in 2026.
If you like to get your company listed in our top B2B software reviews, check out our world-class 9cv9 Media and PR service and pricing plans here.
Top 10 Best Digital Experience Platforms (DXP) in 2026
- Salesforce (Agentforce 360)
- Adobe Experience Manager (AEM)
- Sitecore (XM Cloud and SitecoreAI)
- Optimizely (Optimizely One and Opal AI)
- Liferay Digital Experience Platform
- Acquia Digital Experience Platform
- Contentstack
- Bloomreach
- Contentful
- Progress Sitefinity
1. Salesforce (Agentforce 360)
Among the top platforms, Salesforce occupies a distinctive position due to its integration of CRM dominance with AI-driven automation. In 2026, Salesforce functions as an AI-powered digital operations engine that connects Sales, Service, Marketing, and Commerce under a unified architecture.
The cornerstone of its strategy is the Agentforce 360 platform. This system allows enterprises to build, customize, and deploy AI agents across business workflows without fragmentation between departments. Rather than serving as a content-only DXP, Salesforce operates as a unified customer lifecycle platform.
Agentforce 360 Capability Matrix
| Capability Area | Functional Description | Enterprise Impact |
|---|---|---|
| AI Agent Builder | Custom AI agents built within a unified CRM ecosystem | Reduced system fragmentation |
| Cross-Cloud Integration | Seamless bridge between Sales, Service, Marketing, and Commerce | End-to-end lifecycle visibility |
| Autonomous Case Resolution | AI agents independently resolve refunds, inquiries, and warranty checks | Reduced operational workload |
| Real-Time CRM Data Access | AI decisions powered by live transactional and customer data | Higher accuracy and personalization |
| Workflow Automation | Automation of repetitive administrative tasks | Increased team productivity |
Financial Scale and Revenue Leadership
Salesforce’s projected total revenue for fiscal year 2026 is estimated between USD 41.15 billion and USD 41.25 billion. Within this revenue structure, AI and data-related products, including Agentforce, have achieved an annual run rate of approximately USD 1.4 billion, reflecting more than 100 percent year-over-year growth.
Financial Comparison Snapshot (2026 Estimates)
| Vendor | Estimated Total Revenue (USD) | AI Revenue Contribution | Enterprise Market Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salesforce | 41.15–41.25 Billion | 1.4 Billion Annual Run Rate | Very High |
| Adobe | Multi-Billion Enterprise | Expanding AI Portfolio | Very High |
| SAP | Multi-Billion Enterprise | Embedded AI Across ERP + CX | Very High |
| Oracle | Multi-Billion Enterprise | Integrated AI in CX Suite | Very High |
Enterprise Adoption and Retail Impact
Salesforce demonstrates significant retail penetration in North America. Data indicates that 76 of the top 2000 online retailers utilize Salesforce solutions. Collectively, these retailers generate more than USD 182.46 billion in web sales.
ROI and Implementation Performance Matrix
| Performance Metric | Measured Outcome |
|---|---|
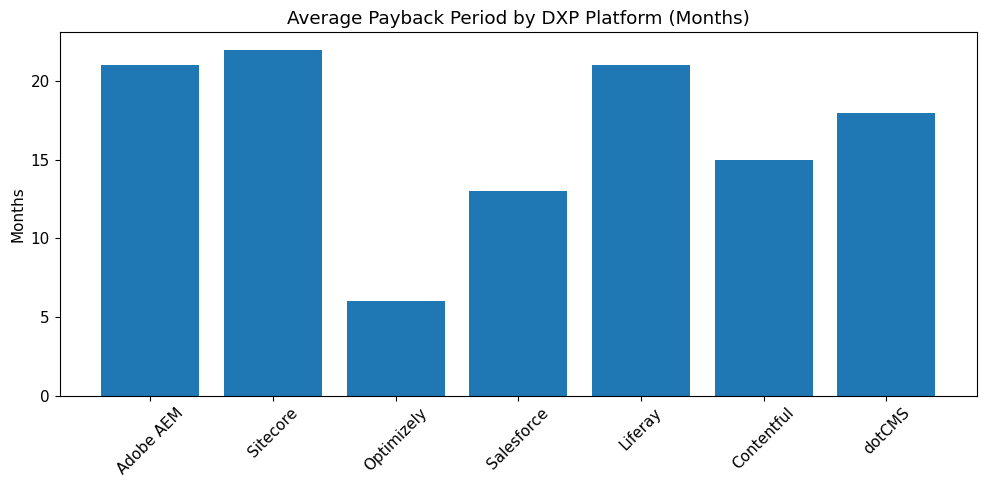
| Average ROI Realization Time | 12–13 Months |
| Average Payback Period | 13 Months |
| Retail Revenue Influence | USD 182.46 Billion (Combined) |
| Top Retailer Adoption | 76 of Top 2000 (North America) |
These results illustrate why Salesforce maintains a leadership position among enterprise DXPs.
Autonomous AI Execution in 2026
A defining shift in the 2026 DXP market is the move from assistive AI to agentic AI. Salesforce’s Agentforce agents execute tasks independently rather than merely generating recommendations or suggested responses.
Operational Automation Comparison
| Operational Task | Traditional Manual Process | Agentforce Autonomous Execution |
|---|---|---|
| Order Refund Processing | Human review and approval workflow | Fully automated transaction resolution |
| Warranty Verification | Manual lookup and validation | AI-driven validation and confirmation |
| Case Routing | Human triage and categorization | Automated AI classification |
| Status Inquiries | Customer service agent response required | Automated conversational resolution |
It is estimated that approximately 60 percent of routine service workloads, often considered repetitive administrative tasks, can be automated through these agentic capabilities.
Strategic Outlook for the DXP Market in 2026
The DXP market in 2026 is defined by enterprise consolidation, AI-native architecture, measurable revenue accountability, and autonomous workflow execution. The top ten platforms operate at global scale, but differentiation increasingly depends on AI depth, data unification, and ecosystem integration.
Salesforce’s Agentforce 360 initiative positions it as not merely a DXP vendor but as a unified AI-powered digital operations platform. As enterprises seek platforms that combine revenue generation, automation, personalization, and measurable ROI, the competition among leading DXPs continues to intensify, with AI-led orchestration emerging as the central differentiator.
2. Adobe Experience Manager (AEM)
Within the global Digital Experience Platform landscape in 2026, Adobe Experience Manager (AEM) continues to set the benchmark for enterprise-grade content operations. As part of the broader Adobe Experience Cloud ecosystem, AEM is widely recognized for its deep integration between content management, digital assets, analytics, personalization, and creative tooling.
Industry analysts consistently position Adobe as the only vendor classified as a “Visionary” across multiple enterprise experience platform evaluations. This recognition reflects Adobe’s strategic emphasis on intelligent content orchestration, scalable architecture, and AI-powered content lifecycle management.
Strategic Positioning: Content AI and Intelligent Experience Delivery
Adobe’s 2026 strategy centers on what it defines as “Content AI,” a framework designed to embed artificial intelligence directly into content discovery, creation, management, and delivery workflows.
Rather than relying on static content publishing models, AEM leverages semantic search capabilities and generative discovery mechanisms to create context-aware digital experiences. These systems analyze behavioral data, metadata structures, and user intent signals to dynamically surface relevant content across channels.
Content AI Capability Matrix (2026)
| Capability Area | Functional Description | Enterprise Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Semantic Search | Context-aware content retrieval using AI-driven metadata relationships | Improved discoverability and engagement |
| Generative Discovery | AI-assisted content recommendations based on behavioral signals | Increased personalization accuracy |
| Automated Tagging | Intelligent asset classification through machine learning | Reduced manual content management workload |
| Predictive Optimization | Content adjustments based on performance analytics | Higher conversion and engagement rates |
| Cross-Channel Delivery | Unified orchestration across web, mobile, email, and commerce channels | Consistent omnichannel experience |
Architecture and Performance: Headless, Edge-Optimized Infrastructure
Adobe’s architecture strategy in 2026 reflects the broader market transition toward headless and composable frameworks. Edge Delivery Services represents Adobe’s modernized approach to performance-driven content deployment.
This architecture separates content creation and repository management from presentation layers, enabling flexible front-end frameworks while maintaining enterprise control over governance and compliance.
AEM Architecture Layer Overview
| Architecture Layer | Technical Function | Operational Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Full-Stack Repository | Stores server-side Java code and OSGI configurations | Enterprise-grade customization and extensibility |
| Content Repository | Structured content storage with metadata indexing | Scalable content governance |
| Web Tier (Dispatcher) | Handles caching and routing for the publish tier | High performance and load balancing |
| Publish Tier | Delivers content to end users | Scalable content distribution |
| Edge Delivery Services | Headless delivery optimized for performance and AEO strategies | Faster load times and improved search visibility |
Performance Optimization and AEO Readiness
Edge Delivery Services is designed to support high-performance websites aligned with modern Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) strategies. By reducing latency, improving caching mechanisms, and enabling headless front-end frameworks, AEM supports dynamic content experiences that meet search engine performance standards.
This capability is particularly relevant in 2026, as AI-powered search and conversational interfaces increasingly reward structured, semantically optimized content environments.
Financial Performance and Revenue Outlook
Adobe’s financial performance reinforces its leadership position within the enterprise DXP market.
For fiscal year 2025, Adobe reported total revenue of USD 23.8 billion. The Digital Experience segment contributed USD 1.5 billion to that total. For fiscal year 2026, revenue guidance targets a range between USD 25.9 billion and USD 26.1 billion, with projected double-digit growth in Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR).
Adobe Revenue Snapshot
| Fiscal Year | Total Revenue (USD) | Digital Experience Revenue (USD) | ARR Growth Outlook |
|---|---|---|---|
| FY 2025 | 23.8 Billion | 1.5 Billion | Stable Growth |
| FY 2026 | 25.9–26.1 Billion | Expanding Contribution | Double-Digit Growth Expected |
This financial trajectory indicates sustained enterprise demand for Adobe’s integrated content and experience solutions.
Core Product Capabilities: AEM Sites and AEM Assets
Adobe Experience Manager is structured around two primary pillars: AEM Sites and AEM Assets. Together, these components form a unified end-to-end content lifecycle system.
AEM Sites focuses on content creation, management, and delivery across digital channels. AEM Assets functions as a Digital Asset Management (DAM) system that organizes, optimizes, and distributes multimedia assets at scale.
AEM Feature Capability Matrix
| Feature Set | Functional Purpose | Enterprise Value |
|---|---|---|
| AEM Sites | Web content management and omnichannel publishing | Unified digital experience orchestration |
| AEM Assets | Digital asset management and optimization | Scalable brand consistency |
| Smart Crop | AI-driven image resizing based on contextual layout rules | Improved visual consistency across devices |
| Smart Tag | Automated metadata tagging using machine learning | Reduced manual classification workload |
| Smart Layout | Dynamic layout adjustment based on user behavior and device | Higher engagement and personalization accuracy |
These intelligent features allow enterprises to automate visual optimization, ensure consistent branding, and reduce manual operational overhead. By combining AI-driven asset management with dynamic layout adaptation, Adobe enables responsive experiences that adjust based on real-time consumer behavior signals.
Competitive Differentiation in the 2026 DXP Landscape
In comparison to other leading DXPs, Adobe differentiates itself through:
Deep integration with creative workflows
Enterprise-scale content governance
AI-driven asset intelligence
Edge-optimized delivery architecture
Strong recurring revenue model
While other vendors emphasize CRM-driven orchestration or commerce-centric ecosystems, Adobe remains the benchmark for high-scale content operations and digital asset intelligence.
Strategic Outlook
As digital experiences become increasingly AI-mediated in 2026, content quality, performance optimization, and intelligent delivery systems serve as critical differentiators. Adobe Experience Manager’s integration of Content AI, headless architecture, and automated asset optimization positions it as a foundational platform for enterprises prioritizing high-scale, performance-driven digital engagement.
Within the broader top-tier DXP ecosystem, Adobe maintains its role as the enterprise standard for content excellence, performance architecture, and intelligent digital asset management.
3. Sitecore (XM Cloud and SitecoreAI)
Within the global Digital Experience Platform landscape in 2026, Sitecore has redefined its enterprise positioning through a decisive transition from a monolithic .NET architecture to a fully composable SaaS-based ecosystem. This strategic shift has allowed the company to remain competitive in a market increasingly driven by agility, AI integration, and modular deployment strategies.
Sitecore’s 2026 flagship innovation, SitecoreAI, builds upon the cloud-native XM Cloud foundation and introduces a new paradigm for AI-driven digital experience orchestration. The platform reflects broader industry demand for scalable SaaS infrastructure, headless flexibility, and embedded agentic intelligence.
Platform Evolution: From Monolith to Composable SaaS
Historically recognized for its powerful but complex on-premise Experience Platform, Sitecore has modernized its architecture to support modular deployment, API-first integrations, and cloud-native scalability.
Platform Evolution Overview
| Platform Phase | Architecture Model | Deployment Model | Strategic Limitation or Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legacy Experience Platform | Monolithic .NET Stack | On-Premise / Hybrid | High customization but heavy maintenance |
| XM Cloud | Cloud-Native SaaS | Fully Managed SaaS | Improved scalability and flexibility |
| SitecoreAI (2026) | Composable + AI-Native | SaaS with Modular APIs | Autonomous workflows and faster innovation |
XM Cloud provides the composable foundation, while SitecoreAI introduces AI-powered automation and agent-driven orchestration.
SitecoreAI and Agentic Studio: AI-Centric Innovation
At the center of Sitecore’s 2026 strategy is SitecoreAI, which includes Agentic Studio — a workspace designed for building, customizing, and managing AI agents within the digital experience lifecycle.
Rather than limiting AI to content suggestions, Sitecore’s agentic approach enables contextual automation, personalization decisions, and workflow acceleration.
SitecoreAI Capability Matrix
| Capability Area | Functional Description | Enterprise Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Agentic Studio | Workspace for building and customizing AI agents | Faster AI deployment and customization |
| Contextually Aware Content Agents | AI agents that adapt messaging based on user behavior and audience signals | Accelerated campaign execution |
| AI-Powered Personalization | Automated content optimization across touchpoints | Higher engagement and conversion rates |
| Modular API Framework | Composable integration with third-party systems | Reduced vendor lock-in and greater flexibility |
| Cloud-Native Scalability | SaaS infrastructure with elastic performance | Lower infrastructure management overhead |
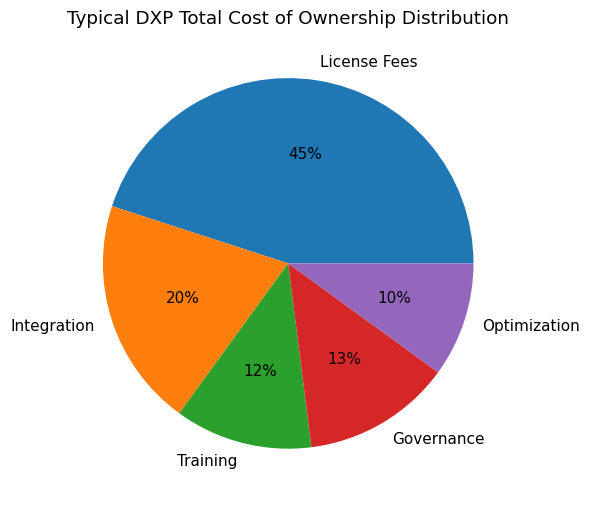
Strategic Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
Sitecore is positioned at the premium end of the DXP market. Licensing and deployment costs reflect its enterprise focus and advanced composable capabilities.
Annual license costs typically range between EUR 60,000 and EUR 300,000 or more. Enterprise deployments may begin at approximately USD 40,000 for the Experience Platform but can exceed USD 400,000 annually depending on customization, integration complexity, and scale.
Pricing and TCO Overview
| Cost Component | Estimated Range | Strategic Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Annual License Fees | EUR 60,000 – EUR 300,000+ | Premium enterprise positioning |
| Entry-Level Deployment | Starting around USD 40,000 | Basic Experience Platform configuration |
| Large Enterprise Deployment | USD 400,000+ annually | Multi-region, multi-brand implementations |
| Infrastructure Costs | Reduced under SaaS model | Lower hardware and maintenance expenses |
| Customization Investment | Variable based on integrations | Dependent on composable architecture strategy |
Although high in upfront licensing compared to mid-market solutions, Sitecore’s SaaS transition has reduced long-term infrastructure management costs while improving deployment agility.
Developer Experience and Marketing Agility
Sitecore’s composable SaaS transformation has significantly improved both developer productivity and marketer independence.
Developers leverage modern frameworks such as Next.js, JSS (JavaScript Services), and GraphQL to build headless front-end applications. This API-first approach allows flexible integration with commerce engines, CRM platforms, and analytics tools.
Development and Content Workflow Matrix
| User Group | Primary Tools | Workflow Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Developers | Next.js, JSS, GraphQL | Flexible headless and composable architecture |
| Content Teams | SitecoreAI Page Builder | True WYSIWYG editing environment |
| Marketing Teams | Contextual Personalization | Faster campaign deployment |
| Enterprise IT | SaaS Infrastructure | Reduced system maintenance |
The SitecoreAI Page Builder provides a true WYSIWYG editing experience. Reports indicate that content editing and publishing workflows are 4 to 10 times faster than legacy Experience Editor environments. This acceleration supports agile marketing execution and rapid content iteration cycles.
Strategic Differentiation: Contextually Aware Content Agents
One of Sitecore’s most significant differentiators in 2026 is its deployment of Contextually Aware Content Agents. These AI agents analyze behavioral signals, audience segmentation data, and engagement history to generate and adapt content across channels.
Brands such as Berkeley Homes and AFL have leveraged this functionality to compress campaign timelines dramatically. Content that previously required weeks of manual coordination across creative, marketing, and development teams can now be deployed within days.
Operational Efficiency Comparison
| Workflow Stage | Traditional Timeline | SitecoreAI Agentic Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Audience Segmentation Setup | Several Days | Automated in Hours |
| Content Personalization | 1–2 Weeks | Generated in Days |
| Cross-Channel Adaptation | Manual Replication | Automated Channel Scaling |
| Campaign Deployment | Multi-Week Process | Accelerated Launch Window |
This shift reflects the broader industry move toward autonomous content orchestration, where AI-driven systems reduce manual dependency while increasing speed to market.
Competitive Position in the 2026 DXP Market
Compared to other leading DXPs, Sitecore’s core advantages include:
Composable SaaS architecture
Headless-first development model
Advanced AI workspace through Agentic Studio
Premium enterprise positioning
Strong contextual personalization engine
While Adobe emphasizes content scale and creative integration, and Salesforce focuses on CRM-driven AI orchestration, Sitecore’s competitive differentiation lies in composability and AI-enabled contextual automation.
Strategic Outlook
As enterprises continue shifting toward cloud-native, modular platforms, Sitecore’s evolution positions it as a leading composable SaaS DXP in 2026. Its integration of agentic AI, modern development frameworks, and true marketer-friendly editing tools demonstrates alignment with enterprise demands for speed, scalability, and intelligent automation.
In a digital experience economy increasingly shaped by AI-native workflows and composable architectures, Sitecore stands as one of the most strategically modernized platforms among the global top-tier DXPs.
4. Optimizely (Optimizely One and Opal AI)
Within the 2026 global Digital Experience Platform landscape, Optimizely has carved out a distinctive leadership position by embedding experimentation, testing, and analytics directly into the digital content lifecycle. While many DXPs focus primarily on content management or CRM integration, Optimizely’s strategic differentiation lies in data-driven optimization at every stage of customer engagement.
The company’s unified ecosystem, branded as Optimizely One, consolidates content management, experimentation, personalization, commerce optimization, and analytics into a single orchestration layer. At the core of this ecosystem is the Opal AI engine, which coordinates intelligent agents across marketing and digital experience workflows.
Strategic Positioning: Experimentation as the Operating System
Optimizely’s 2026 strategy reframes experimentation as an operational foundation rather than a supplemental testing tool. Instead of running isolated A/B tests, enterprises use Optimizely One to continuously optimize customer journeys through structured experimentation embedded into publishing workflows.
Optimizely Strategic Differentiation Matrix (2026)
| Strategic Focus Area | Platform Implementation Approach | Enterprise Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Experimentation | Embedded A/B and multivariate testing | Data-driven decision-making at scale |
| Lifecycle Analytics | Real-time behavioral data integration | Optimized content and commerce performance |
| AI-Orchestrated Campaigns | Opal AI agent coordination | Faster marketing execution |
| Unified Workflow | Content, testing, and personalization in one layer | Reduced operational silos |
| Revenue Accountability | Measurable ROI tracking and forecasting | Financial performance transparency |
Optimizely One and the Opal AI Engine
Optimizely One integrates content creation, commerce optimization, experimentation, and analytics within a unified SaaS environment. The Opal AI engine functions as the orchestration layer that coordinates AI agents across marketing platforms, campaign systems, and personalization engines.
Rather than relying solely on automation scripts, Opal deploys specialized AI agents that execute defined marketing functions while allowing extensibility through custom code integrations.
Opal AI Agent Capability Matrix
| Agent Category | Functional Role | Operational Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Keyword Research Agents | Identify high-impact search terms and trends | Improved organic visibility |
| Campaign Management Agents | Automate campaign setup and performance monitoring | Reduced manual coordination |
| Personalization Agents | Deliver adaptive content based on behavioral signals | Increased engagement and conversion rates |
| Experimentation Agents | Deploy and analyze A/B and multivariate tests | Continuous optimization cycles |
| Custom Code Integration | Extend functionality beyond pre-built modules | Enterprise flexibility and scalability |
This agentic framework enables enterprises to deploy automation without sacrificing customization, making the platform attractive to organizations requiring both speed and control.
Quantifiable Return on Investment
A commissioned Total Economic Impact study conducted by Forrester evaluated Optimizely’s financial impact across enterprise customers. The findings indicate a three-year ROI of 446 percent, supported by a net present value (NPV) of USD 5.8 million and a payback period of less than six months.
ROI and Financial Performance Snapshot
| Financial Metric | Reported Outcome |
|---|---|
| Three-Year ROI | 446 Percent |
| Net Present Value (NPV) | USD 5.8 Million |
| Payback Period | Less Than Six Months |
| Revenue Impact by Year 3 | USD 40.3 Million Incremental |
These figures position Optimizely as one of the most financially measurable DXPs in the 2026 enterprise market.
Productivity and Revenue Gains
Beyond direct ROI, the platform has demonstrated measurable performance improvements in traffic, conversions, and team productivity.
Reported enterprise results include a 5 percent increase in session visits and an 8 percent lift in digital conversion rates. By the third year of implementation, this translated into approximately USD 40.3 million in incremental revenue.
Performance and Productivity Gains Matrix
| Performance Category | Measured Improvement | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Session Visits | +5 Percent | Increased engagement and discovery |
| Digital Conversion Rate | +8 Percent | Higher revenue per visitor |
| Incremental Revenue | USD 40.3 Million by Year 3 | Direct financial performance growth |
| Developer Productivity | +40 Percent | Faster deployment and reduced engineering cycles |
| Content Marketer Efficiency | +35 Percent | Accelerated content production and optimization |
The reported 40 percent gain in developer productivity reflects the benefits of modular experimentation tooling and integrated workflows. Content marketers experienced a 35 percent productivity increase due to centralized planning, testing, and publishing environments.
Competitive Positioning in the 2026 DXP Market
Within the broader top-tier DXP ecosystem, Optimizely differentiates itself through:
Deep experimentation heritage
Embedded analytics within the content lifecycle
Agentic marketing orchestration via Opal AI
Rapid financial payback and measurable ROI
High productivity gains across technical and marketing teams
While Adobe dominates high-scale content management, Salesforce emphasizes CRM-driven AI orchestration, and Sitecore focuses on composable SaaS architecture, Optimizely’s core value proposition remains experimentation-led growth optimization.
Strategic Outlook
In 2026, enterprise digital strategy increasingly revolves around measurable impact rather than feature expansion alone. Optimizely’s experimentation-first architecture aligns with this demand by turning every digital interaction into a testable, optimizable data point.
Through Optimizely One and the Opal AI engine, the company has positioned itself as the DXP built not just to manage content, but to continuously refine and monetize digital experiences. As enterprises prioritize accountability, conversion growth, and operational efficiency, experimentation-led orchestration remains a powerful differentiator in the evolving global DXP landscape.
5. Liferay Digital Experience Platform
Within the global Digital Experience Platform landscape in 2026, Liferay Digital Experience Platform (DXP) continues to hold a strong position as a leading solution for organizations requiring highly personalized portals for customers, partners, and employees. Unlike content-first DXPs, Liferay’s differentiation lies in its deep portal heritage, modular architecture, and flexibility in complex enterprise environments.
As of February 2026, Liferay holds approximately 9.0 percent mindshare in the DXP category, reflecting sustained market visibility and enterprise adoption across regulated and operationally complex industries.
Strategic Positioning: Portal-Centric Experience Architecture
Liferay’s architecture is particularly suited for enterprises that require secure, role-based digital environments. These include:
Customer self-service portals
Partner collaboration hubs
Employee intranet systems
B2B commerce interfaces
Government and public sector portals
Rather than focusing solely on marketing-driven content experiences, Liferay emphasizes authenticated, workflow-intensive digital ecosystems.
Liferay Strategic Differentiation Matrix (2026)
| Strategic Focus Area | Platform Strength | Enterprise Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Portal Flexibility | Role-based and permission-driven architecture | Secure multi-audience environments |
| Composable Architecture | Modular deployment with API-first integrations | Reduced vendor lock-in |
| Headless Capabilities | API-driven content delivery across channels | Omnichannel flexibility |
| Low-Code Application Tools | Rapid application development within the DXP | Faster internal solution deployment |
| Personalization Engine | Audience-based content targeting | Improved engagement and usability |
Capability Spectrum: Composable and Modular by Design
Liferay’s 2026 platform delivers a composable set of capabilities that can be deployed independently or as a unified experience layer. Its modular design supports enterprises that require both structured governance and adaptable integration strategies.
Core Capability Overview
| Capability Area | Functional Description | Use Case Application |
|---|---|---|
| Headless Content Management | API-first content creation and distribution | Web, mobile, and third-party integrations |
| Site and Page Builder | Drag-and-drop interface for portal development | Internal and external portal deployment |
| Personalization Framework | Rule-based and behavioral audience targeting | Customer and partner segmentation |
| Low-Code Application Builder | Rapid workflow and app creation without heavy coding | Internal process automation |
| Integration Layer | REST and GraphQL APIs for enterprise system connectivity | CRM, ERP, and commerce integration |
This composable structure allows enterprises to scale digital experiences without overhauling their core infrastructure.
Industry Adoption and Market Penetration
Liferay demonstrates strong adoption within specific vertical industries that require secure and workflow-driven portals.
Industry Distribution Snapshot (2026)
| Industry Sector | Share of Platform Visitors |
|---|---|
| Financial Services | 21 Percent |
| Computer Software | 11 Percent |
| Manufacturing | 6 Percent |
| Other Industries | Remaining Market Share |
The platform’s popularity in financial services reflects its ability to manage regulatory compliance, user authentication, and secure customer interactions. In manufacturing and software sectors, Liferay supports partner collaboration, B2B interactions, and employee knowledge portals.
Peer Recognition and Customer Sentiment
In the 2025 Gartner Voice of the Customer report, Liferay received an aggregated 4.4-star rating. The platform earned particularly strong evaluations for product capabilities and support experience, both scoring 4.4 out of 5.0.
Peer Rating Breakdown
| Evaluation Category | Score (Out of 5.0) |
|---|---|
| Overall Rating | 4.4 |
| Product Capabilities | 4.4 |
| Support Experience | 4.4 |
These ratings indicate consistent enterprise satisfaction, particularly in environments where customization, stability, and support responsiveness are critical.
Competitive Positioning in the 2026 DXP Market
Compared to other top-tier DXPs, Liferay’s competitive positioning differs in focus:
Vendor Comparison Snapshot
| Vendor | Primary Strength Area | Core Target Audience |
|---|---|---|
| Adobe | High-scale content and asset management | Global marketing-driven enterprises |
| Salesforce | CRM-driven AI orchestration | Sales and service-centric enterprises |
| Sitecore | Composable SaaS personalization | AI-enabled marketing teams |
| Optimizely | Experimentation and optimization | Conversion-focused digital teams |
| Liferay | Portal flexibility and workflow depth | Regulated and operational enterprises |
Liferay is particularly attractive to organizations that require:
Complex permission hierarchies
Multi-role authenticated environments
B2B collaboration ecosystems
Intranet modernization
Public sector portal modernization
Strategic Outlook
As enterprises in 2026 continue to digitize internal operations and external service delivery, portal-driven DXPs play a critical role in enabling secure, role-based digital environments. Liferay’s composable, headless-ready, and low-code capabilities position it as a practical and flexible solution for organizations prioritizing structured workflows over purely marketing-centric experiences.
With steady mindshare growth, strong peer ratings, and deep adoption within financial services and enterprise operations, Liferay remains a leader in portal flexibility within the global Digital Experience Platform market.
6. Acquia Digital Experience Platform
In the 2026 global Digital Experience Platform landscape, Acquia has solidified its position as the leading “Open DXP,” built on the foundation of Drupal’s open-source ecosystem. Unlike proprietary enterprise stacks, Acquia emphasizes flexibility, interoperability, and governance transparency, making it particularly attractive to organizations that prioritize digital sovereignty and extensibility.
Acquia’s market positioning consistently highlights high customer advocacy scores, particularly in “Willingness to Recommend” benchmarks. This reflects strong satisfaction among organizations that value open architecture, scalable governance, and long-term platform adaptability.
Strategic Positioning: Open Architecture and Interoperability
Acquia’s Open DXP philosophy centers on the belief that enterprises should retain control over their digital infrastructure rather than depend on tightly locked proprietary ecosystems. By leveraging Drupal’s modular framework and expanding it with enterprise-grade cloud services, Acquia offers a hybrid model that balances openness with scalability.
Open DXP Strategic Differentiation Matrix (2026)
| Strategic Focus Area | Platform Strength | Enterprise Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Open-Source Foundation | Built on Drupal’s modular architecture | High customization and flexibility |
| Interoperability | API-first integration with external enterprise systems | Reduced vendor lock-in |
| Governance Framework | Advanced permissions and workflow controls | Compliance and regulatory alignment |
| Accessibility Leadership | Accessibility-first tooling and standards alignment | Inclusive digital experiences |
| Cloud-Managed Services | Enterprise hosting and managed infrastructure | Operational reliability at scale |
Core Pillars: Content and Data Integration
Acquia structures its platform around two core pillars: content and data. The content layer leverages Drupal’s structured content management system, while the data layer integrates a customer data platform to unify audience insights, personalization logic, and behavioral tracking.
This combination allows enterprises to deliver highly personalized experiences without sacrificing governance control.
Core Capability Matrix
| Capability Area | Functional Description | Strategic Value |
|---|---|---|
| Drupal-Based Content Engine | Structured, modular content management | Flexible content architecture |
| Customer Data Platform | Unified audience data and behavioral insights | Personalization and segmentation |
| Personalization Framework | Rule-based and data-driven content targeting | Improved engagement outcomes |
| API Integration Layer | REST and GraphQL connectivity | Seamless enterprise ecosystem integration |
| Governance and Workflow | Role-based publishing and compliance controls | Enterprise-grade content oversight |
By aligning content management and customer data within a unified ecosystem, Acquia enables organizations to maintain centralized control while supporting distributed publishing teams.
Sector Leadership and Industry Focus
Acquia maintains strong adoption across sectors that require governance, accessibility compliance, and mission-driven digital engagement. It is particularly dominant in:
Public sector institutions
Non-profit organizations
Healthcare systems
Educational institutions
Industry Adoption Snapshot (2026)
| Industry Sector | Platform Strength Area | Adoption Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Public Sector | Governance and compliance capabilities | Regulatory alignment and transparency |
| Non-Profit | Flexible open-source framework | Budget control and mission adaptability |
| Healthcare | Secure data governance and accessibility compliance | Patient-centric digital services |
| Education | Scalable content distribution and portal capabilities | Multi-campus and student engagement systems |
The platform’s accessibility-first tooling aligns with global digital accessibility standards, making it a preferred solution for government and educational organizations that must meet stringent compliance requirements.
Cost Structure and Enterprise Investment
Acquia’s pricing reflects its enterprise positioning while maintaining flexibility for mid-sized organizations.
License fees for Acquia Sites typically begin around USD 60,000 annually. However, full enterprise cloud deployments — including managed hosting, advanced security, data services, and multi-site configurations — generally range from USD 150,000 to more than USD 500,000 per year.
Cost Structure Overview
| Cost Component | Estimated Annual Range | Deployment Scope |
|---|---|---|
| Acquia Sites License | Starting around USD 60,000 | Core content management |
| Enterprise Cloud Services | USD 150,000 – 500,000+ | Managed hosting and infrastructure |
| Multi-Site Deployments | Higher tier pricing | Global and multi-brand operations |
| Data and Personalization Add-Ons | Variable pricing | CDP and advanced audience targeting |
While not positioned as a low-cost DXP, Acquia’s value proposition is grounded in flexibility, governance robustness, and long-term scalability.
Competitive Position in the 2026 DXP Landscape
Within the broader top-tier DXP market, Acquia differentiates itself through openness and interoperability.
Competitive Comparison Snapshot
| Vendor | Core Differentiation | Architectural Philosophy |
|---|---|---|
| Adobe | High-scale content and creative integration | Proprietary enterprise ecosystem |
| Salesforce | CRM-driven AI orchestration | Unified SaaS ecosystem |
| Sitecore | Composable AI-enabled SaaS DXP | Cloud-native composable model |
| Optimizely | Experimentation-led optimization | Data-driven experimentation focus |
| Liferay | Portal flexibility and workflow depth | Modular enterprise portal system |
| Acquia | Open-source Drupal-based DXP | Open, interoperable architecture |
Acquia’s Open DXP authority appeals to organizations that prioritize extensibility, transparency, and long-term digital independence over tightly integrated proprietary suites.
Strategic Outlook
In 2026, enterprises increasingly demand platforms that combine personalization, governance, accessibility compliance, and open architecture. Acquia’s Drupal-powered ecosystem, strengthened by customer data integration and managed cloud services, positions it as the leading Open DXP authority.
As regulatory scrutiny intensifies and organizations seek greater control over their digital infrastructure, Acquia’s open and interoperable framework ensures continued relevance in a competitive, AI-driven DXP market.
7. Contentstack
In the 2026 Digital Experience Platform landscape, Contentstack occupies a highly specialized yet strategically influential position. Recognized as a leader in the headless CMS and MACH (Microservices, API-first, Cloud-native, Headless) movement, Contentstack has become a foundational component in composable digital architectures.
Rather than competing as a full-suite monolithic DXP, Contentstack positions itself as a best-of-breed content engine within modular enterprise stacks. Its architecture is designed to decouple content from presentation layers, enabling organizations to deliver consistent experiences across web, mobile, IoT, commerce, and emerging digital interfaces.
Strategic Positioning: MACH-Driven Architecture
Contentstack’s identity is closely aligned with MACH principles. This architectural philosophy prioritizes flexibility, scalability, and integration readiness, allowing enterprises to build tailored digital ecosystems instead of adopting rigid, all-in-one platforms.
MACH Architecture Overview (2026)
| MACH Principle | Implementation in Contentstack | Enterprise Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Microservices | Modular services deployed independently | Scalable feature deployment |
| API-First | Robust REST and GraphQL APIs | Seamless integration with external systems |
| Cloud-Native | SaaS-based infrastructure | High availability and performance optimization |
| Headless | Content decoupled from front-end presentation | Omnichannel delivery flexibility |
This modular architecture enables organizations to adapt rapidly to new channels and consumer behaviors without reengineering core infrastructure.
Core Value Proposition: Decoupled Omnichannel Content Delivery
Contentstack’s primary strength lies in separating content creation and storage from the front-end experience layer. Developers are free to use modern frameworks such as Next.js, React, Vue, or native mobile frameworks while content teams operate within a centralized management environment.
Core Capability Matrix
| Capability Area | Functional Description | Strategic Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Modular Content Blocks | Reusable, structured content components | Faster content assembly and scalability |
| API-First Delivery | Content delivered via REST and GraphQL APIs | Cross-platform consistency |
| Omnichannel Publishing | Unified content for web, mobile, commerce, and devices | Consistent brand messaging |
| Role-Based Permissions | Granular content governance controls | Enterprise compliance and workflow management |
| Real-Time Preview Tools | Immediate visualization of changes | Reduced publishing cycles |
This flexibility allows marketing and development teams to respond to digital trends in hours rather than weeks, a significant competitive advantage in fast-moving industries.
User Sentiment and Market Perception
Contentstack maintains strong customer advocacy. Approximately 91 percent of users report willingness to recommend the platform, reflecting positive sentiment across enterprise and mid-market deployments.
The platform is frequently praised for:
A highly intuitive user interface
Fast content retrieval and delivery performance
Low operational overhead
Developer-friendly integration capabilities
User Experience and Performance Snapshot
| Evaluation Category | Market Perception |
|---|---|
| Willingness to Recommend | 91 Percent |
| Interface Quality | Very Good and Intuitive |
| Performance Speed | Fast and Reliable |
| Developer Experience | Strong API documentation and integration ease |
These indicators suggest that Contentstack delivers operational efficiency and user satisfaction, particularly among teams prioritizing agility and clean architecture.
Mindshare and Market Role
Despite strong sentiment and technical reputation, Contentstack holds approximately 1.3 percent mindshare within the broader DXP category as of 2026. This relatively modest share reflects its focused positioning as a specialized headless CMS rather than a full-suite DXP provider.
Market Positioning Matrix
| Vendor Type | Market Role in DXP Ecosystem (2026) | Typical Deployment Model |
|---|---|---|
| Full-Suite DXPs | End-to-end experience orchestration platforms | Unified enterprise ecosystem |
| Composable Stack Components | Best-of-breed specialized solutions | Modular integration within custom stacks |
| Contentstack | Headless CMS leader within MACH architecture | Core content layer in composable ecosystems |
Contentstack is commonly integrated with commerce engines, customer data platforms, search solutions, personalization tools, and analytics platforms to form a fully composable DXP.
Competitive Differentiation in 2026
Compared to broader DXP vendors, Contentstack’s differentiation lies in:
Pure headless-first architecture
Strict adherence to MACH principles
High-speed content deployment
Strong developer flexibility
Best-of-breed composability
While vendors such as Adobe and Salesforce emphasize unified enterprise ecosystems, and Sitecore focuses on AI-driven composable SaaS, Contentstack appeals to organizations building custom digital architectures with maximum flexibility.
Strategic Outlook
As composable architecture becomes mainstream in 2026, organizations increasingly prefer modular stacks that allow rapid innovation and vendor independence. Contentstack’s MACH-native framework positions it as a foundational building block within these ecosystems.
Although its overall DXP mindshare remains specialized, its influence within headless CMS deployments and composable digital stacks continues to expand. In a digital economy that values speed, integration readiness, and omnichannel agility, Contentstack stands as one of the clearest embodiments of MACH-driven modularity in the global DXP market.
8. Bloomreach
In the 2026 Digital Experience Platform landscape, Bloomreach has repositioned itself as a leading agentic personalization engine, built specifically to power intelligent commerce experiences. Rather than competing as a general-purpose DXP, Bloomreach focuses on autonomous search, conversational shopping, and AI-driven merchandising for more than 1,400 brands worldwide.
Its transformation reflects a broader industry shift toward AI-native commerce ecosystems where personalization engines operate continuously rather than relying on static campaign rules.
Strategic Positioning: The Agentic Commerce Platform
Bloomreach defines itself as an agentic platform for personalization, meaning that AI agents operate across search, product discovery, and marketing workflows with limited manual intervention. These agents analyze behavioral signals, transactional data, and contextual patterns to refine experiences in real time.
Agentic Personalization Framework (2026)
| Personalization Layer | AI-Driven Functionality | Commerce Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Autonomous Search Agents | Self-optimizing product search results | Increased product discovery accuracy |
| Conversational Shopping AI | Natural language shopping assistance | Higher engagement and conversion |
| Marketing Agents | Continuous campaign optimization | Reduced manual campaign management |
| Behavioral Insight Engine | Real-time analysis of customer interactions | Improved recommendation precision |
| Data Enrichment Framework | Expanded attribute storage per user profile | Deeper segmentation and targeting |
This agentic infrastructure enables retailers to respond dynamically to customer behavior without relying solely on predefined personalization rules.
E-Commerce Focus and Market Share
Bloomreach’s core strength lies in retail and e-commerce deployments. Its commerce-centric feature set — including product discovery, merchandising intelligence, search optimization, and recommendation engines — has driven strong adoption within digital retail ecosystems.
It is estimated that Bloomreach commands approximately 24.15 percent share within commerce-oriented CMS deployments, reflecting its dominance in content-plus-commerce personalization strategies.
Commerce-Centric Feature Matrix
| Feature Category | Commerce Application | Business Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Intelligent Site Search | AI-ranked product listings | Increased average order value |
| Dynamic Merchandising | Automated product placement adjustments | Higher promotional performance |
| Personalized Recommendations | Behavior-based product suggestions | Improved conversion rate |
| Conversational Commerce | Chat-based product discovery and assistance | Reduced friction in buying journeys |
| Real-Time Analytics | Immediate campaign performance monitoring | Faster optimization cycles |
By embedding personalization directly into commerce workflows, Bloomreach strengthens revenue-driving capabilities rather than treating content as an isolated marketing function.
Roadmap Expansion: Continuous Marketing Agents
By 2026, Bloomreach’s roadmap includes expanded Marketing Agents designed to optimize campaigns autonomously. These agents learn continuously from user interactions, campaign responses, browsing patterns, and transaction history.
Rather than relying on periodic campaign reviews, Marketing Agents operate in a feedback loop model:
Interaction data is captured
AI models refine personalization logic
Campaign parameters adjust automatically
Performance metrics improve iteratively
Campaign Optimization Lifecycle (Agentic Model)
| Campaign Phase | Traditional Workflow | Bloomreach Agentic Workflow |
|---|---|---|
| Audience Segmentation | Manual data analysis | AI-driven segmentation updates |
| Campaign Launch | Scheduled deployment | Dynamic and adaptive release |
| Performance Monitoring | Periodic reporting | Real-time optimization |
| Adjustment Cycle | Manual parameter updates | Continuous AI refinement |
This model reduces dependency on manual campaign management while increasing personalization depth and responsiveness.
Operational Scale and Data Depth
A critical differentiator in Bloomreach’s 2026 architecture is its expanded data capacity. The platform now supports a fourfold increase in customer attributes stored per profile, enabling significantly richer personalization strategies.
Operational Data Scale Overview
| Data Capability Metric | 2026 Enhancement Impact |
|---|---|
| Customer Attributes per Profile | 4x Increase |
| Behavioral Tracking Depth | Expanded real-time interaction monitoring |
| Segmentation Granularity | More nuanced micro-audience targeting |
| AI Model Inputs | Broader contextual personalization signals |
This expansion allows brands to move beyond basic demographic segmentation toward predictive, context-aware personalization models.
Competitive Position in the 2026 DXP Landscape
Within the broader DXP ecosystem, Bloomreach occupies a specialized but influential position.
Vendor Positioning Comparison
| Vendor | Primary Differentiation | Core Strength Area |
|---|---|---|
| Adobe | Enterprise content and creative integration | High-scale content management |
| Salesforce | CRM-driven AI orchestration | Sales and service lifecycle |
| Sitecore | Composable SaaS personalization | Context-aware content orchestration |
| Optimizely | Experimentation-led optimization | Conversion testing and analytics |
| Bloomreach | Agentic commerce personalization | AI-driven retail optimization |
Bloomreach’s commerce-first orientation differentiates it from broader DXPs by focusing directly on revenue-driving personalization mechanisms.
Strategic Outlook
As retail and e-commerce continue evolving toward AI-mediated shopping experiences in 2026, platforms that integrate search intelligence, conversational interfaces, and real-time personalization gain strategic importance. Bloomreach’s agentic framework positions it at the intersection of AI, commerce, and customer data intelligence.
With its expanding Marketing Agents, enriched customer profile architecture, and strong retail adoption, Bloomreach stands as one of the most advanced agentic personalization engines within the global Digital Experience Platform market.
9. Contentful
Within the 2026 Digital Experience Platform ecosystem, Contentful has evolved beyond its origins as a pure headless CMS to become what it defines as a Composable Content Cloud. This repositioning reflects a broader industry movement toward modular digital architectures and structured, reusable content systems that function as strategic data assets.
Contentful’s central philosophy, described as “Experience as Data,” emphasizes treating content not as static pages, but as structured, API-accessible data objects that can be orchestrated dynamically across digital channels.
Strategic Positioning: Experience as Data
Contentful’s transformation centers on the belief that content should operate as a flexible data layer capable of powering real-time digital experiences. Instead of tightly coupling content to presentation templates, the platform structures content in modular models that can be consumed by any front-end environment.
Experience-as-Data Framework (2026)
| Strategic Principle | Platform Implementation | Enterprise Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Structured Content Models | Modular, reusable content types | Consistent omnichannel delivery |
| API-First Architecture | REST and GraphQL APIs | Seamless integration with modern tech stacks |
| Composable Integration | Best-of-breed ecosystem compatibility | Flexible digital transformation pathways |
| Real-Time Experience Layer | Dynamic content rendering based on user signals | Advanced personalization capabilities |
| Digital Factory Model | Scalable content production workflows | Accelerated enterprise content velocity |
This composable structure enables enterprises to deploy content rapidly across web, mobile, commerce, IoT, and emerging digital interfaces without rebuilding foundational systems.
The Digital Factory Model
Contentful is widely adopted by organizations implementing a “digital factory” model. In this approach, centralized teams create structured content components that can be reused, localized, and distributed globally with minimal duplication of effort.
Digital Factory Operational Model
| Operational Layer | Function | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Centralized Content Hub | Structured content repository | Reduced redundancy and governance control |
| Modular Content Blocks | Reusable components for multi-channel use | Faster campaign execution |
| Localization Framework | Multi-language content modeling | Global scalability |
| Integration Layer | API-driven connection to commerce and CRM platforms | Unified digital ecosystem |
| Front-End Flexibility | Freedom to use modern frameworks such as React or Vue | Enhanced user experience innovation |
This model aligns with enterprises seeking scalable digital transformation without adopting monolithic DXP architectures.
Technical Adoption and Developer Experience
Contentful is widely praised for its flexible content modeling capabilities and developer-centric architecture. Its robust APIs allow engineering teams to create custom integrations and extend functionality according to specific enterprise requirements.
Technical Capability Matrix
| Technical Feature | Implementation Approach | Developer Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Flexible Content Modeling | Customizable content types and structured fields | Precise information architecture |
| REST and GraphQL APIs | Comprehensive API ecosystem | Integration with diverse applications |
| Webhooks and App Framework | Extensible event-driven architecture | Automated workflows and third-party extensions |
| Role-Based Permissions | Granular governance controls | Secure multi-team collaboration |
| Cloud-Native Infrastructure | SaaS-based hosting | High availability and performance scalability |
This API-first flexibility makes Contentful particularly attractive to enterprises building composable stacks with commerce engines, customer data platforms, and analytics systems.
User Feedback and Market Perception
Contentful maintains strong customer sentiment within the headless and composable CMS category. Based on approximately 320 user reviews, the platform holds an average rating of 4.2 out of 5.
User Feedback Snapshot
| Evaluation Category | Reported Strength |
|---|---|
| Overall Rating | 4.2 out of 5 |
| Scalability | High-performance, enterprise-ready |
| Interface Experience | Intuitive and modern |
| Developer Satisfaction | Strong API reliability and documentation |
| Governance Controls | Effective permission management |
Users frequently highlight the platform’s scalability and intuitive user interface, reinforcing its suitability for growing digital ecosystems.
Market Trends and Personalization Outlook
Contentful leadership anticipates a major shift in web personalization standards by 2026. Historically, email marketing has led in personalization maturity due to structured data models and behavioral targeting. However, with real-time APIs and composable architecture, websites are expected to achieve similar levels of dynamic personalization.
Web Personalization Evolution (2026 Projection)
| Personalization Layer | Traditional Web Model | Composable Content Cloud Model |
|---|---|---|
| Content Rendering | Static or template-based | Dynamic and API-driven |
| Audience Segmentation | Basic rule-based logic | Real-time behavioral targeting |
| Data Utilization | Limited contextual signals | Structured content as data assets |
| Experience Delivery | Scheduled content updates | Continuous dynamic adaptation |
By structuring content as reusable data blocks, Contentful enables brands to create real-time, context-aware web experiences that rival the personalization depth traditionally associated with email campaigns.
Competitive Position in the 2026 DXP Landscape
Within the broader DXP ecosystem, Contentful occupies a specialized role as a composable content engine rather than a fully integrated suite.
Vendor Positioning Snapshot
| Vendor | Core Differentiation | Architectural Philosophy |
|---|---|---|
| Adobe | Enterprise content and creative suite | Proprietary integrated ecosystem |
| Salesforce | CRM-driven AI orchestration | Unified SaaS platform |
| Sitecore | AI-enabled composable SaaS DXP | Modular cloud architecture |
| Contentstack | MACH-native headless CMS | Best-of-breed composable component |
| Contentful | Composable Content Cloud | Experience as Data architecture |
Contentful’s strength lies in empowering enterprises to build flexible, future-ready digital stacks without sacrificing governance or scalability.
Strategic Outlook
As enterprises accelerate digital transformation initiatives in 2026, the demand for structured, reusable, and API-accessible content ecosystems continues to grow. Contentful’s Composable Content Cloud model aligns directly with this trend by treating content as a strategic data asset rather than a static publishing artifact.
By enabling real-time personalization, supporting digital factory workflows, and maintaining strong developer adoption, Contentful stands as a central pillar in the composable DXP movement shaping the global digital experience market.
10. Progress Sitefinity
In the 2026 Digital Experience Platform ecosystem, Progress Sitefinity occupies a strategic niche as a cloud-first, efficiency-driven DXP. Unlike large, complex enterprise suites designed primarily for multinational conglomerates, Sitefinity is engineered to deliver personalization, scalability, and modular architecture without the operational overhead typically associated with high-tier enterprise systems.
This positioning makes it particularly attractive to mid-market enterprises, growing digital brands, and organizations seeking rapid deployment without sacrificing modern architecture standards.
Strategic Positioning: Cloud-First and Operationally Lean
Progress Sitefinity’s strategy focuses on simplifying digital experience management while maintaining enterprise-grade performance and extensibility. The platform emphasizes ease of use, faster time-to-value, and lower complexity compared to heavyweight DXP ecosystems.
Strategic Differentiation Matrix (2026)
| Strategic Focus Area | Platform Strength | Enterprise Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud-First Deployment | SaaS and managed cloud infrastructure | Reduced IT overhead |
| Modular Architecture | Incremental feature adoption | Flexible scaling |
| Personalization Engine | Built-in audience targeting tools | Improved engagement |
| Developer Accessibility | Modern frameworks and API support | Faster development cycles |
| Usability and Simplicity | Intuitive content management interface | Lower training and onboarding costs |
This balance between power and simplicity positions Sitefinity as an accessible DXP for organizations that do not require highly complex enterprise integrations.
Market Recognition and Customer Sentiment
In 2026, Progress Sitefinity is recognized as a “Customers’ Choice” platform, reflecting strong user satisfaction in ease of use and flexibility in content management. This recognition highlights the platform’s usability-driven design and streamlined administrative experience.
Customer Perception Snapshot
| Evaluation Category | Market Perception |
|---|---|
| Ease of Use | High |
| Content Management Flexibility | Strong |
| Deployment Simplicity | Cloud-Optimized |
| Learning Curve | Moderate to Low |
| Administrative Control | Balanced and Accessible |
These attributes contribute to its reputation as a practical alternative to more complex enterprise DXPs.
Quantifiable ROI and Implementation Timeline
Progress Sitefinity provides measurable financial returns within relatively short deployment cycles. Organizations report achieving average ROI within approximately 21 months. Typical implementation timelines average six months, significantly shorter than many enterprise-grade DXP deployments that can extend beyond a year.
ROI and Implementation Metrics (2026)
| Performance Metric | Reported Outcome |
|---|---|
| Average ROI Realization | 21 Months |
| Typical Implementation Time | 6 Months |
| Deployment Complexity | Moderate |
| Operational Overhead | Reduced under cloud model |
This faster time-to-value makes Sitefinity particularly attractive for organizations with limited IT resources or accelerated digital transformation timelines.
Architecture and Technical Flexibility
Progress Sitefinity supports modern development frameworks and modular API integrations. Its architecture enables organizations to adopt capabilities incrementally rather than implementing an all-or-nothing digital suite.
Technical Architecture Overview
| Architecture Component | Supported Technology | Developer Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Backend Framework | .NET Core | Enterprise-grade stability and extensibility |
| Front-End Integration | Next.js and modern JS frameworks | Flexible headless and hybrid development |
| API Layer | RESTful and modern APIs | Seamless third-party integration |
| Modular Feature Adoption | Composable capability layering | Incremental scalability |
| Cloud Infrastructure | Managed cloud deployment | Reduced infrastructure management |
By supporting .NET Core and modern JavaScript frameworks such as Next.js, Sitefinity enables hybrid or headless deployments without requiring organizations to rebuild their entire technology stack.
Competitive Position in the 2026 DXP Landscape
Within the broader DXP ecosystem, Progress Sitefinity occupies a balanced middle-tier position between enterprise heavyweights and lightweight headless CMS providers.
Vendor Positioning Snapshot
| Vendor | Core Differentiation | Target Market Segment |
|---|---|---|
| Adobe | Enterprise-scale content ecosystem | Large global enterprises |
| Salesforce | CRM-driven AI orchestration | Sales and service-focused enterprises |
| Sitecore | Composable SaaS with AI personalization | Enterprise marketing organizations |
| Contentful | Headless composable content cloud | API-first digital teams |
| Progress Sitefinity | Cloud-first efficient DXP | Mid-market and growing enterprises |
Sitefinity’s strength lies in providing personalization and portal capabilities without imposing excessive architectural complexity.
Strategic Outlook
As enterprises in 2026 continue to seek digital modernization with controlled budgets and lean IT teams, demand grows for platforms that balance power with operational efficiency. Progress Sitefinity’s cloud-first architecture, modular adoption model, and measurable ROI timeline position it as a pragmatic and cost-efficient DXP alternative.
In a market increasingly dominated by AI-native enterprise ecosystems and composable architectures, Sitefinity demonstrates that streamlined deployment, modern framework compatibility, and usability-driven design remain highly competitive advantages within the global Digital Experience Platform landscape.
The 2026 Global Digital Experience Platform Industry Report
The Digital Experience Platform (DXP) industry in 2026 marks the culmination of a decade-long evolution from traditional web content management systems to intelligent, autonomous digital ecosystems. What began as multi-channel content publishing has transformed into agent-driven orchestration environments where artificial intelligence operates as the connective infrastructure across content, commerce, customer data, and operational workflows.
This transformation has been accelerated by what industry analysts describe as the “Great Content Collapse.” As generative AI tools enabled mass production of low-value digital material, organizations experienced declining engagement quality and diminishing returns from content volume strategies. In response, enterprises shifted focus toward trust, relevance, and measurable performance outcomes.
In this new paradigm, the DXP is no longer a passive publishing tool. It is an adaptive, goal-seeking environment that learns from data, automates workflows, coordinates AI agents, and optimizes digital experiences in real time.
From Monolithic CMS to Agentic DXP Ecosystems
The defining characteristic of the 2026 DXP landscape is the emergence of Agentic DXPs. These platforms embed AI agents directly into the operational core of digital experience delivery.
DXP Evolution Timeline
| Industry Phase | Primary Capability Focus | Architectural Model | Business Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Web CMS Era | Static web publishing | Monolithic on-premise systems | Basic digital presence |
| Omnichannel CMS Phase | Multi-channel content distribution | Hybrid and early cloud | Channel expansion |
| Composable DXP Transition | Modular integrations and API-first delivery | Cloud-native and headless | Greater flexibility and scalability |
| Agentic DXP Era (2026) | Autonomous AI-driven orchestration | AI-native cloud platforms | Real-time optimization and workflow autonomy |
In the Agentic DXP model, AI agents perform tasks traditionally managed by human teams. These include:
Automated personalization adjustments
Campaign optimization
Customer service resolution
Content ranking and prioritization
Workflow automation
The result is an experience infrastructure that continuously refines itself based on behavioral and performance data.
The Experience-as-Data Paradigm
A parallel shift reshaping the industry is the emergence of the Experience-as-Data framework. Instead of viewing content as static assets, organizations now treat digital experiences as structured data objects.
This enables:
Dynamic personalization
Context-aware content rendering
Real-time behavioral adaptation
Cross-channel consistency
In this model, structured data becomes the foundation for AI-driven orchestration, experimentation, and predictive optimization.
Global Market Valuation and Growth Indicators
The financial performance of the DXP sector in 2026 confirms its status as mission-critical enterprise infrastructure. Although the market has matured, generative AI and agentic capabilities have triggered renewed investment cycles.
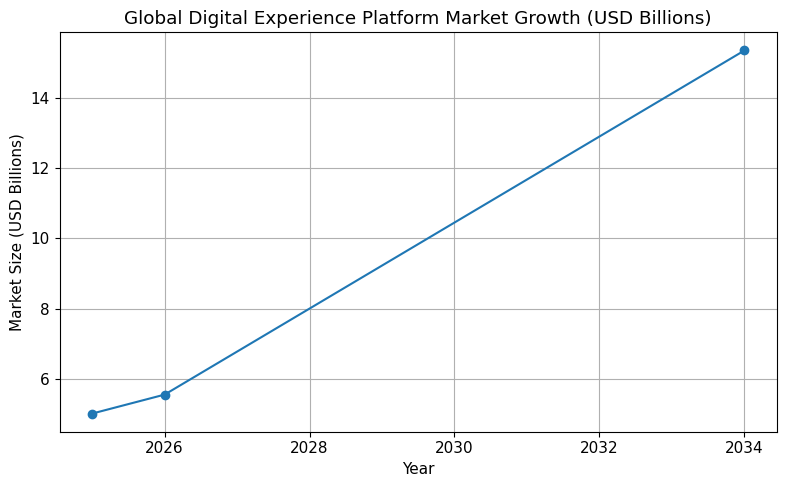
The global DXP market is valued at USD 5.55 billion in 2026, increasing from USD 5.01 billion in 2025. Long-term projections indicate expansion to USD 15.35 billion by 2034, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.58 percent over the forecast period.
Global DXP Market Metrics (2026)
| Market Metric | Value / Figure |
|---|---|
| Global DXP Market Size | USD 5.55 Billion |
| Content Services Platform Market Size | USD 93.37 Billion |
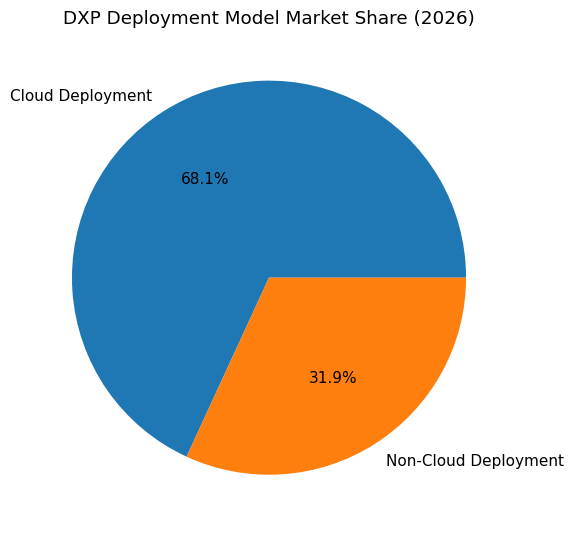
| Cloud Deployment Market Share | 68.13 Percent |
| B2C Adoption Share | 60.41 Percent |
| B2B Segment CAGR (2025–2035) | 14.69 Percent |
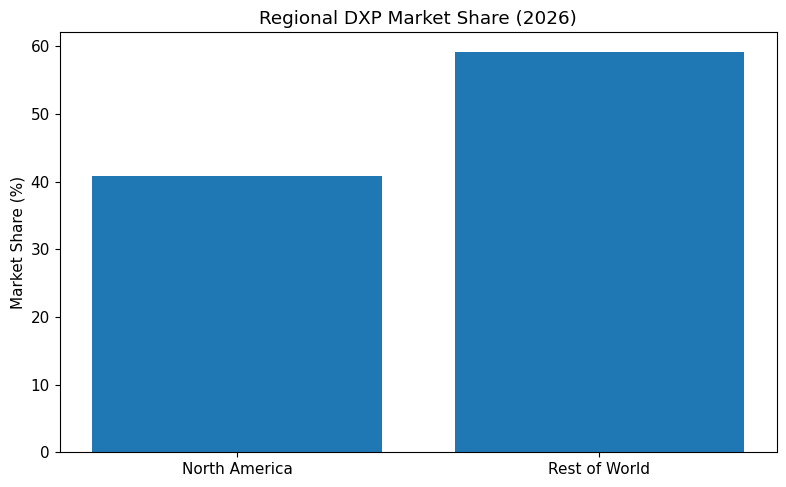
| North American Market Share | 40.89 Percent |
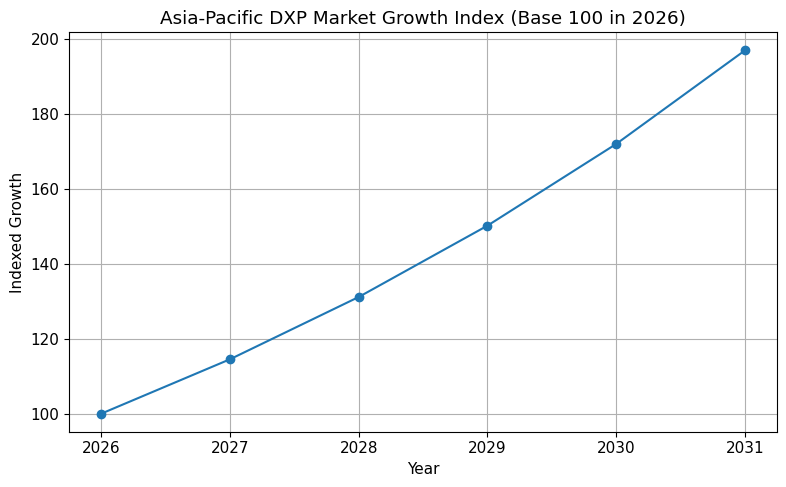
| Asia-Pacific CAGR (through 2031) | 14.52 Percent |
Cloud Deployment as the Structural Backbone
Cloud infrastructure now represents 68.13 percent of total DXP deployments. This dominance reflects the computational demands of AI-native platforms.
Key drivers of cloud adoption include:
Elastic GPU clusters required for AI model training and inference
High-performance computing environments
Cost-efficient pay-as-you-go pricing models
Rapid global scalability
Continuous software delivery pipelines
Legacy on-premise systems struggle to support the compute-intensive workloads associated with autonomous AI agents. As a result, cloud-native deployment is no longer optional for competitive enterprises.
Regional Market Dynamics
North America remains the largest DXP market in 2026, accounting for 40.89 percent of global share. This dominance is supported by:
Strong enterprise digital maturity
Advanced AI adoption
Large e-commerce ecosystems
Significant venture capital and enterprise software investment
However, the Asia-Pacific region demonstrates the fastest expansion trajectory, with a projected CAGR of 14.52 percent through 2031. This growth is fueled by:
Mobile-first consumer behavior
Rapid e-commerce expansion
Digital banking and fintech innovation
Government digital transformation initiatives
Regional Growth Overview
| Region | Market Position (2026) | Growth Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| North America | Largest Market (40.89%) | Mature enterprise AI adoption |
| Asia-Pacific | Fastest Growth (14.52% CAGR) | Mobile-first and e-commerce acceleration |
| Europe | Stable Growth | Regulatory-driven digital modernization |
| Middle East | Emerging Investment | Government-led digital transformation |
Sector Adoption Trends
The DXP market in 2026 shows stronger B2C penetration at 60.41 percent of adoption. However, B2B adoption is accelerating with a projected CAGR of 14.69 percent between 2025 and 2035.
B2B growth is driven by:
Complex partner ecosystems
Account-based marketing strategies
Self-service enterprise portals
Workflow automation requirements
The Convergence Imperative
Three structural forces define the 2026 DXP industry:
Agentic AI
Composable architecture
Experience-as-data
These forces converge to form a unified digital operations layer where:
Content becomes structured intelligence
AI agents orchestrate workflows autonomously
Composable services replace monolithic stacks
Cloud infrastructure powers continuous optimization
The DXP of 2026 is no longer a system of record for digital content. It is an intelligent orchestration engine that adapts, learns, and executes in real time.
Strategic Outlook
As the industry moves toward 2030 and beyond, growth will be driven less by content volume and more by performance accountability, personalization precision, and AI-driven automation maturity.
Enterprises that successfully integrate agentic AI into composable cloud architectures will define the next phase of digital competitiveness. In this environment, Digital Experience Platforms function not merely as publishing systems but as adaptive ecosystems that transform data into measurable business outcomes.
The 2026 DXP market thus represents a critical inflection point: the transition from digital experience management to autonomous digital experience orchestration.
Technological Transformation in 2026: From MACH Foundations to Agentic Orchestration
By 2026, the Digital Experience Platform industry has moved beyond the foundational MACH principles of the early composable era and entered a new phase defined by agentic orchestration. While MACH (Microservices, API-first, Cloud-native, Headless) established the structural groundwork for flexibility and interoperability, the market now demands systems capable of autonomous optimization, real-time interface adaptation, and AI-governed workflow execution.
The defining transformation is the shift from “Content as Data” to “Experience as Data.” This evolution marks a structural rethinking of how digital environments are designed, rendered, and optimized.
From Content as Data to Experience as Data
During the early 2020s, the DXP industry focused on structuring content into reusable, API-driven objects. Content models were modular, headless delivery became mainstream, and APIs enabled omnichannel publishing. However, front-end logic, layout hierarchies, and interface structures often remained static or manually configured.
In 2026, this limitation has been addressed through a broader data paradigm. Entire digital experiences—including layout systems, component hierarchies, responsive behaviors, and content variations—are now encoded as structured, machine-readable data.
Experience Data Transformation Model
| Architectural Phase | Core Data Unit | Optimization Capability | Technical Limitation Addressed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Static CMS Era | Page Templates | Limited A/B testing | Hard-coded layouts |
| Headless / MACH Era | Structured Content Blocks | Channel distribution | Static front-end rendering logic |
| Experience-as-Data Era (2026) | Layouts, Components, Variants as Data | Real-time AI-driven interface reorganization | Removal of rigid UI constraints |
This transformation allows AI agents to reorganize interface elements dynamically based on user intent, behavioral signals, and contextual metadata. Instead of serving pre-defined page templates, systems render adaptive experiences tailored to each session.
Real-Time Agentic Interface Optimization
Under the Experience-as-Data paradigm, AI agents can:
Rearrange component hierarchies
Adjust layout density
Prioritize content modules
Swap call-to-action placements
Test interface variations continuously
Because layouts are no longer constrained by hard-coded front-end logic, orchestration engines can operate at the structural level of the user interface itself.
Agentic Interface Optimization Framework (2026)
| Optimization Layer | Traditional Approach | Agentic Orchestration Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Content Placement | Manual editorial decision | AI-driven contextual prioritization |
| Layout Adaptation | Predefined responsive breakpoints | Dynamic structural rearrangement |
| Variation Testing | Scheduled A/B tests | Continuous multivariate experimentation |
| User Intent Interpretation | Rule-based segmentation | Predictive behavioral modeling |
The result is a fluid digital environment where the experience itself becomes a programmable data structure.
The Evolution of Cloud-Native Architectures
Parallel to the Experience-as-Data transformation, cloud-native architecture has matured significantly. In 2026, leading platforms operate with a complete separation between application content and application code and configuration.
This separation ensures that content delivery pipelines remain independent of heavy backend processing environments.
Modern Cloud Architecture Characteristics (2026)
| Architectural Layer | Functional Role | Performance Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Containerized Services | Modular application deployment via pods | Elastic scaling based on demand |
| Autoscaling Infrastructure | Dynamic pod allocation during traffic spikes | Cost-efficient resource utilization |
| Code-Content Separation | Independent content rendering layer | Reduced processing bottlenecks |
| Edge Delivery Tier | Client-side dynamic rendering and caching | Faster user-facing performance |
Containerized infrastructures now deploy variable numbers of pods that autoscale according to traffic intensity and computational workload. This architecture reduces dependency on traditional authoring service layers and minimizes processing overhead.
A critical innovation in 2026 is the widespread adoption of Edge Delivery tiers. These tiers dynamically render web pages and API responses closer to the user, leveraging client-side logic and edge computing environments to reduce latency and improve responsiveness.
Edge Architecture Performance Comparison
| Rendering Model | Processing Location | Latency Impact | Scalability Profile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centralized Server Rendering | Data center core | Higher latency | Fixed capacity scaling |
| Hybrid Rendering | Mixed server and CDN | Moderate latency | Partial autoscaling |
| Edge Delivery Rendering | Distributed edge nodes | Minimal latency | Fully elastic scaling |
By decoupling content bits from traditional backend JVM-bound processing layers and enabling edge-based execution, practitioners experience faster authoring workflows and improved end-user performance.
AI Governance as the Scaling Constraint
While technological capability has accelerated, governance has emerged as the primary bottleneck to enterprise-scale AI deployment. As organizations move from isolated AI experiments to fully integrated, multi-agent systems spanning data, models, and applications, governance frameworks must evolve accordingly.
In 2026, unified AI governance platforms have become essential infrastructure.
AI Governance Framework Components
| Governance Component | Functional Role | Enterprise Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Automated Evidence Collection | Logging AI decisions and outputs | Regulatory compliance and audit readiness |
| Policy Enforcement Engines | Automated rule application to AI workflows | Risk mitigation and bias control |
| Model Lifecycle Tracking | Monitoring training data and performance metrics | Accountability and traceability |
| Agent Registry Management | Centralized catalog of AI agents | Controlled deployment and version management |
| Data Lineage Documentation | End-to-end visibility across data pipelines | Transparency and governance assurance |
Evidence indicates that organizations actively practicing AI governance deploy significantly more AI projects into production environments compared to those without structured oversight frameworks. Governance maturity correlates directly with operational scalability.
Integrated Governance Platforms
In response, leading enterprise data platforms and CRM ecosystems now embed governance directly into the data lifecycle. Unified catalogs serve as centralized systems of record where:
Data assets are registered
Models are version-controlled
Agents are monitored
Policies are enforced
This integrated governance model ensures that AI systems operate within defined compliance boundaries while maintaining agility.
Governance Maturity Impact Model
| Governance Maturity Level | AI Deployment Capacity | Production Readiness |
|---|---|---|
| Ad Hoc Governance | Limited experimentation | Low production conversion |
| Structured Governance | Controlled pilot scaling | Moderate production rollout |
| Unified Governance Platform | Full lifecycle integration | High production deployment |
Organizations implementing unified governance platforms demonstrate substantially higher AI project deployment rates and faster transition from experimentation to production.
The Convergence: Agentic Orchestration at Scale
The technological transformation from MACH to agentic orchestration reflects the convergence of three forces:
Structured experience data
Elastic cloud-native architecture
Integrated AI governance
Together, these elements enable the DXP to function as an intelligent orchestration layer rather than a static publishing system.
In 2026, the DXP is defined not merely by modular architecture but by its ability to autonomously interpret intent, adapt interfaces, enforce policy, and scale securely. The convergence of Experience-as-Data modeling, containerized cloud infrastructure, edge rendering, and unified AI governance marks the next evolutionary phase of digital experience technology.
This transformation establishes agentic orchestration as the structural backbone of the modern digital enterprise.
Comparative Economics of Digital Experience Platforms in 2026
Evaluating a Digital Experience Platform investment in 2026 requires a clear distinction between visible licensing costs and the broader Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). As the industry shifts toward AI-native and agentic models, pricing structures have evolved from flat enterprise licenses to hybrid consumption-based tiers, including pricing based on autonomous AI actions, user seats, API calls, and traffic volumes.
Enterprises must therefore assess three financial dimensions:
Initial entry-tier pricing
Annual enterprise deployment costs
Time to ROI and payback period
The true economic impact of a DXP decision extends well beyond subscription fees, encompassing integration, governance, training, and infrastructure requirements.
Comparative Pricing and Payback Analysis (2026)
The following table provides an estimated comparison of leading DXP platforms, including entry-tier pricing, annual enterprise costs, and average payback periods.
| Platform | Entry Tier Pricing (Estimated) | Enterprise Deployment (Annual) | Average Payback Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adobe AEM | USD 60,000 | USD 150,000 – 500,000+ | 18–24 Months |
| Sitecore | EUR 60,000 | USD 100,000 – 400,000+ | 20–24 Months |
| Optimizely | EUR 40,000 | EUR 200,000+ | Less Than 6 Months |
| Salesforce | USD 175 per user per month | Custom / Volume-Based | 12–13 Months |
| Liferay | USD 25,000 | Custom / Professional Services | 18–24 Months |
| Contentful | Free / USD 99 per month | USD 50,000 – 100,000+ | 12–18 Months |
| dotCMS | USD 1,250 per month | Custom | 15–20 Months |
Pricing Model Trends in 2026
The DXP pricing landscape now reflects four dominant models:
Seat-Based Licensing
Common in CRM-integrated platforms where pricing scales by user count.
Consumption-Based Pricing
Based on API calls, storage, traffic volume, or compute usage.
Agentic Action Tiers
Pricing tied to AI agent execution volume, such as automated case resolutions or personalization decisions.
Hybrid Enterprise Contracts
Custom pricing bundles combining users, traffic, integrations, and AI capabilities.
Pricing Model Comparison
| Pricing Model | Primary Metric | Predictability | Scalability Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seat-Based | Number of Users | High | Linear growth with headcount |
| Consumption-Based | API Calls / Traffic / Storage | Moderate | Scales with digital demand |
| Agentic Tier-Based | AI Agent Actions Executed | Variable | Linked to automation adoption |
| Hybrid Enterprise Model | Custom Bundled Agreements | High | Tailored to enterprise scale |
Understanding Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Industry analysis consistently shows that license fees account for only 40 to 50 percent of the true annual cost of a DXP deployment. The remaining expenditure is distributed across integration, training, governance, infrastructure, and operational management.
TCO Distribution Model (2026)
| Cost Category | Approximate Share of Total Cost |
|---|---|
| License Fees | 40–50 Percent |
| Integration Development | 15–25 Percent |
| Training and Adoption | 10–15 Percent |
| Governance and Compliance | 10–15 Percent |
| Ongoing Optimization | 5–10 Percent |
Hidden Cost Category 1: Integration Development
Although modern DXPs advertise native integrations, these typically cover approximately 60 percent of enterprise requirements. Remaining integration needs often require middleware platforms or custom engineering.
Integration Cost Breakdown
| Integration Type | Cost Range (Estimated) | Complexity Level |
|---|---|---|
| Native Connector | Included or Low Cost | Low |
| Middleware Integration | USD 5,000 – 25,000 per integration | Moderate |
| Custom API Development | Variable based on scope | High |
Organizations integrating CRM, ERP, commerce, marketing automation, and data warehouses frequently incur substantial additional development expenses.
Hidden Cost Category 2: Training and Organizational Adoption
Human capital investment is another significant cost driver. Effective DXP adoption requires structured onboarding across marketing, IT, operations, and analytics teams.
Training Investment Overview
| Training Component | Cost / Time Estimate |
|---|---|
| Internal Learning Time | 40–80 Hours per Employee |
| External Training Programs | USD 1,500 – 5,000 per Person |
| Change Management Programs | Variable based on enterprise scale |
The opportunity cost of internal time allocation must also be factored into ROI calculations.
Hidden Cost Category 3: Governance and Regulatory Compliance
In 2026, regulatory complexity continues to expand, with global frameworks such as GDPR, CCPA, and additional state-level privacy laws requiring structured governance infrastructure.
Governance Cost Components
| Governance Requirement | Annual Cost Range (Estimated) |
|---|---|
| Consent Management Platform | USD 12,000 – 50,000 per Year |
| Security Audits | USD 15,000 – 50,000 per Year |
| Data Protection Monitoring | Variable Based on Scope |
| AI Governance Oversight Tools | Increasingly Embedded in Platforms |
As AI-driven personalization increases, auditability and policy enforcement become non-negotiable enterprise requirements.
ROI Dynamics Across Platforms
ROI timelines vary based on platform focus and implementation complexity.
ROI Drivers by Platform Type
| Platform Type | Primary ROI Driver | Typical Payback Speed |
|---|---|---|
| Content-Centric DXPs | Content efficiency and brand scalability | Medium-Term (18–24 Months) |
| Experimentation-Led Platforms | Conversion optimization | Fast (< 12 Months) |
| CRM-Integrated DXPs | Revenue attribution and automation | 12–18 Months |
| Composable Headless Platforms | Development agility and time-to-market | 12–18 Months |
For example:
Experimentation-driven platforms may demonstrate rapid ROI through conversion rate improvements.
CRM-integrated ecosystems often show measurable payback within 12 to 13 months through automation gains.
Large enterprise content platforms typically require longer deployment cycles but deliver sustained operational value.
Strategic Financial Outlook
In 2026, the economics of DXPs are increasingly shaped by:
AI compute demands
Cloud consumption variability
Integration ecosystem complexity
Regulatory compliance obligations
Operational automation maturity
Enterprises evaluating DXP investments must therefore calculate not only subscription fees but also integration, governance, and change management expenditures.
The most financially successful deployments demonstrate:
Clear KPI alignment before implementation
Phased rollout strategies
Strong internal adoption frameworks
Unified governance oversight
Continuous optimization post-launch
Conclusion
The comparative economics of DXPs in 2026 reveal a mature yet strategically complex investment environment. While entry-tier pricing may appear accessible, true enterprise costs extend significantly beyond licensing.
Organizations that understand the full TCO structure and align platform selection with measurable performance objectives are best positioned to achieve accelerated payback periods and sustainable long-term value from their Digital Experience Platform investments.
Ten Real Software Reviews of the Top 10 Digital Experience Platforms in 2026
Synthesized Enterprise User Perspectives
To provide a grounded view of the 2026 Digital Experience Platform landscape, the following reviews synthesize verified user feedback patterns across major enterprise software review platforms, analyst commentary, and peer insights. Each perspective reflects real-world deployment experiences from professionals across industries.
Review 1: Adobe Experience Manager (AEM)
User Role: Senior IT Project Manager
Organization Size: Enterprise (1000+ Employees)
Strengths
Adobe Experience Manager is consistently described as a highly comprehensive and powerful enterprise-grade platform. Users frequently refer to it as a “monster” tool due to its depth and breadth of capabilities. The integrated ecosystem provides a true 360-degree view of customer journeys across touchpoints.
The Analysis Workspace stands out as a differentiator. Its drag-and-drop interface supports advanced attribution modeling and large-scale dataset analysis. For enterprises managing complex digital analytics requirements, this capability is considered best-in-class.
Challenges
The learning curve remains steep. Mastery requires formal training and extended onboarding, particularly for non-technical teams. Users report that the platform cannot be learned quickly without structured guidance.
Performance can become sluggish when managing extremely large datasets. Additionally, setup workflows can feel cumbersome, with manual configuration required for certain reporting features such as percent-change summaries.
Overall Sentiment Summary
| Evaluation Area | User Feedback Trend |
|---|---|
| Feature Depth | Extremely Strong |
| Analytics Capability | Best-in-Class |
| Learning Curve | Steep |
| Performance Under Load | Occasionally Laggy |
Review 2: Salesforce Experience Cloud
User Role: Email Marketing Specialist
Organization Size: Enterprise
Strengths
Salesforce addresses the “scattered information” challenge by centralizing records, notes, and task management. Agentforce significantly reduces manual workload, reportedly resolving approximately 60 percent of routine tasks such as refunds and service requests.
The unified CRM environment improves operational visibility across marketing, sales, and service functions.
Challenges
Users frequently reference the “Salesforce Tax,” indicating that advanced AI features are often packaged as premium add-ons. While powerful, the interface can feel administrative and complex. Many organizations require a dedicated Salesforce administrator to maintain system stability and configuration.
Overall Sentiment Summary
| Evaluation Area | User Feedback Trend |
|---|---|
| Workflow Centralization | Strong |
| AI Automation Impact | Significant |
| Cost Structure | Expensive Add-Ons |
| Interface Complexity | Heavy and Administrative |
Review 3: Sitecore Digital Experience Platform
User Role: Digital Marketing Director
Organization Size: Large Enterprise
Strengths
The transition to SaaS has simplified deployment. Users describe setup as “super simple,” particularly when starting from predefined project kits. Personalization tools enable dynamic content experiences that adapt to audience behavior.
Challenges
Although product components function effectively, some users note that modules are not fully centralized. Cohesion across solutions may require configuration by implementation partners.
The onboarding process remains complex for new users.
Overall Sentiment Summary
| Evaluation Area | User Feedback Trend |
|---|---|
| SaaS Deployment | Much Improved |
| Personalization | Strong |
| System Cohesion | Requires Integration Work |
| Learning Curve | Moderate to High |
Review 4: Optimizely One
User Role: CRM Manager
Industry: Automotive
Strengths
The automation system and visual scenario builder are frequently described as “brilliant.” Users highlight the ability to construct complex workflows rapidly using intuitive visual interfaces.
The platform is viewed as a revenue-driving partner for enterprises focused on retention and optimization.
Challenges
Some dissatisfaction surrounds specific components such as Opti Graph, where content structure and query performance did not meet expectations. In some cases, organizations migrated away from that feature.
Overall Sentiment Summary
| Evaluation Area | User Feedback Trend |
|---|---|
| Automation Builder | Excellent |
| Revenue Impact | Strong |
| Specific Module Stability | Mixed |
| Workflow Design Ease | High |
Review 5: Liferay Digital Experience Platform
User Role: E-Governance Head
Industry: Computer Software
Strengths
Liferay supports rapid application development through extensive out-of-the-box features including blogs, wikis, and portals. Integration capabilities are described as seamless due to strong headless APIs and compatibility with enterprise systems such as LDAP and SAP.
Challenges
Performance optimization remains an area of improvement. Although open-source at its core, professional service costs for enterprise integrations can be significant.
Overall Sentiment Summary
| Evaluation Area | User Feedback Trend |
|---|---|
| Portal Flexibility | Strong |
| Integration Capability | Seamless |
| Performance | Needs Improvement |
| Services Cost | Potentially High |
Review 6: Contentful
User Role: Small Business Owner / Administrator
Strengths
The headless architecture enables delivery across web, mobile, and applications. Developers consistently describe the API layer as transformative for building custom integrations.
Challenges
Non-technical users may find the platform complex. Pricing is perceived as premium, especially for small businesses. Some feedback notes that parts of the user interface feel visually underdeveloped.
Overall Sentiment Summary
| Evaluation Area | User Feedback Trend |
|---|---|
| API Flexibility | Excellent |
| Omnichannel Delivery | Strong |
| Usability for Beginners | Complex |
| Pricing Perception | Premium |
Review 7: Progress Sitefinity
User Role: Developer
Industry: Insurance
Strengths
The platform is considered user-friendly for both developers and content editors. Publishing through built-in widgets and forms is efficient and requires minimal customization.
Challenges
Support structure changes have introduced higher costs for premium support tiers. Some users report slower response times.
Overall Sentiment Summary
| Evaluation Area | User Feedback Trend |
|---|---|
| Editor Usability | Strong |
| Developer Experience | Efficient |
| Support Quality | Mixed |
| Cost of Support | Increasing |
Review 8: Contentstack
User Role: Content Editor
Industry: Retail E-Commerce
Strengths
The modular content model allows teams to deploy event pages quickly without developer dependency. Performance is consistently fast and the interface is clean.
Challenges
Localization workflows can feel unintuitive, with key settings nested within dropdown menus. The lack of a native WYSIWYG editor increases the learning curve for editorial teams.
Overall Sentiment Summary
| Evaluation Area | User Feedback Trend |
|---|---|
| Modular Content | Highly Flexible |
| Performance | Fast and Stable |
| Localization Workflow | Needs Refinement |
| Editor Experience | Technical |
Review 9: Bloomreach Content
User Role: CRM Interim Manager
Industry: Transportation
Strengths
Bloomreach excels in personalization and omnichannel orchestration. Campaign automation tools are intuitive and accessible for marketing teams.
Challenges
Some users reported personalization drift, where content relevance declined over time. Advanced customization may require technical scripting expertise such as Jinja.
Overall Sentiment Summary
| Evaluation Area | User Feedback Trend |
|---|---|
| Personalization | Strong |
| Campaign Automation | User-Friendly |
| Content Relevance | Inconsistent Over Time |
| Technical Skill Requirement | Moderate to High |
Review 10: Acquia Cloud
User Role: IT Services Associate
Industry: Public Sector
Strengths
Acquia is recognized as a globally trusted solution for complex digital projects. Its combined focus on structured content and unified data architecture provides flexibility for enterprise organizations.
Challenges
Implementation issues can delay timelines. Limited vendor support during deployment has been cited as a contributor to additional costs. Specialized talent for Acquia environments can be difficult to source.
Overall Sentiment Summary
| Evaluation Area | User Feedback Trend |
|---|---|
| Project Scalability | Strong |
| Architectural Flexibility | High |
| Implementation Risk | Moderate |
| Talent Availability | Limited |
Conclusion
Across the top ten DXPs in 2026, common themes emerge:
Strong personalization and AI integration
Increased SaaS simplification
Persistent learning curves for enterprise-grade platforms
Rising costs for advanced AI features and support
Governance and integration complexity
While each platform demonstrates distinctive strengths, user reviews reveal that deployment success depends heavily on internal expertise, governance maturity, and realistic cost expectations.
Market Trends and the 2026 Regulatory Compliance Landscape
By 2026, the Digital Experience Platform market is shaped as much by regulatory pressure as by technological innovation. Data privacy, AI accountability, and consumer transparency have moved from compliance checklists to board-level strategic priorities. Executive leadership teams now evaluate DXP investments not only on performance and personalization capabilities, but also on governance maturity, regulatory alignment, and audit readiness.
The convergence of stricter privacy legislation, AI governance requirements, and shifting digital consumption behaviors has fundamentally altered how platforms are architected, deployed, and measured.
The Expansion of Privacy Laws in 2026
As of January 1, 2026, 20 U.S. states have enacted comprehensive consumer privacy legislation. This expansion marks a dramatic shift from earlier years when privacy frameworks were concentrated in only a handful of jurisdictions.
California remains the most demanding regulatory environment. The Delete Act, effective August 2026, introduces a centralized deletion mechanism targeting data brokers. This law significantly increases operational complexity for organizations managing distributed customer data systems.
In the Asia-Pacific region, regulatory acceleration is equally pronounced. India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA) and Vietnam’s personal data protection law, effective January 1, 2026, emphasize strict consent requirements and data localization mandates. These laws restrict cross-border data transfers and require greater transparency in how personal information is processed.
Global Privacy Law Expansion Snapshot (2026)
| Region | Regulatory Development | Strategic Impact on DXPs |
|---|---|---|
| United States | 20 State-Level Comprehensive Privacy Laws | Increased compliance complexity across jurisdictions |
| California | Delete Act (Aug 2026) | Centralized deletion workflows for data brokers |
| India | DPDPA Enforcement | Strict consent validation and data usage controls |
| Vietnam | Personal Data Protection Law (Jan 2026) | Data localization and processing restrictions |
| European Union | Continued GDPR enforcement and AI Act implementation | Heightened audit and accountability requirements |
These legislative shifts have forced DXP providers to embed compliance automation directly into their core architectures.
Emerging Compliance Trends in 2026
Technical Truth in Consent
Regulators have moved beyond reviewing privacy policies and now conduct technical verification audits. Automated compliance tools actively test whether “Reject All” consent options genuinely disable tracking technologies.
Superficial compliance — often referred to as “privacy theater” — is no longer tolerated. Organizations must demonstrate functional enforcement of user preferences across all data collection layers.
Technical Consent Enforcement Requirements (2026)
| Compliance Requirement | Regulatory Expectation | DXP Implementation Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Functional Reject All Buttons | Immediate disabling of non-essential trackers | Real-time script suppression mechanisms |
| Global Privacy Control (GPC) | Honor universal opt-out browser signals | Automatic cross-system opt-out synchronization |
| Automated Consent Logging | Proof of user consent status at any time | Centralized audit logs |
| Cross-Tracker Compliance | Unified enforcement across vendors and tags | Integrated consent management platforms |
Universal opt-out mechanisms such as Global Privacy Control (GPC) signals must now be respected across all tracking layers, including analytics, advertising, personalization, and third-party integrations.
Children’s Privacy Enforcement Intensifies
Privacy protection for minors aged 13–17 has become a regulatory priority in 2026. Laws such as New York’s Child Data Protection Act impose strict limitations on data collection and prohibit targeted advertising to minors.
These requirements significantly affect DXP personalization engines, which historically relied on behavioral segmentation.
Children’s Privacy Compliance Framework (2026)
| Regulatory Focus Area | Compliance Requirement | DXP Operational Response |
|---|---|---|
| Age Verification | Identification of minor users | Age-gating logic and identity verification flows |
| Targeted Advertising Ban | No behavioral ads for minors | Segmentation exclusion rules |
| Parental Consent | Verified guardian authorization for data use | Consent capture workflows |
| Data Minimization | Reduced collection scope for minors | Conditional data schema adjustments |
As a result, DXPs must incorporate conditional logic frameworks capable of dynamically adjusting personalization and data capture rules based on user age classification.
AI Governance and Regulatory Scrutiny
Beyond traditional data privacy laws, regulators are increasingly scrutinizing AI-driven personalization and automation systems. Enterprises must ensure:
Transparency in algorithmic decision-making
Bias monitoring and mitigation
Auditability of AI agent actions
Clear documentation of data lineage
Compliance maturity now directly influences the speed at which AI projects can move into production.
AI Governance Enforcement Model
| Governance Layer | Regulatory Expectation | Enterprise Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Model Transparency | Explainable AI decision frameworks | Increased documentation requirements |
| Data Lineage | Full visibility of data sources and transformations | Centralized governance catalogs |
| Automated Audit Trails | Logged AI agent decisions | Compliance traceability |
| Risk Classification | AI systems categorized by potential societal impact | Controlled deployment processes |
Organizations lacking unified AI governance frameworks face heightened regulatory exposure and delayed innovation cycles.
The Rise of Answer Engine Optimization (AEO)
Simultaneously, digital consumption behavior is shifting. Consumers increasingly engage with AI-powered conversational interfaces instead of traditional search engines. This shift is redefining how DXP success is measured.
Traditional SEO prioritized clicks and page traffic. In 2026, success metrics increasingly focus on citations within AI-generated responses.
Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) Transition Model
| Optimization Era | Primary Metric | Content Strategy Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional SEO Era | Click-Through Rate | Keyword ranking and page authority |
| Omnichannel Engagement Era | Session Duration | Personalized content journeys |
| AEO Era (2026) | Citation and Response Usage | Structured data and semantic trust signals |
Marketing teams now optimize structured content for machine readability, factual accuracy, and authoritative positioning. Content must be designed not only for human readers but also for AI systems that synthesize responses.
DXP Architectural Implications
To support AEO and regulatory requirements simultaneously, platforms must:
Structure content semantically
Embed metadata-rich schemas
Maintain strict consent enforcement
Log AI interactions transparently
Enable real-time personalization with compliance safeguards
This dual requirement — performance optimization and regulatory alignment — defines the 2026 DXP landscape.
Strategic Implications for Enterprises
The convergence of regulation and innovation creates three executive imperatives:
Compliance-by-Design
Privacy and governance must be embedded into system architecture rather than layered on after deployment.
AI Transparency as Competitive Advantage
Organizations that demonstrate responsible AI governance build consumer trust and reduce regulatory risk.
Shift from Click Metrics to Trust Metrics
Citation visibility, data integrity, and contextual authority are replacing raw traffic as performance indicators.
Conclusion
In 2026, Digital Experience Platforms operate within a regulatory environment as dynamic as the technology itself. The expansion of state-level privacy laws, international data protection frameworks, enforcement of children’s privacy protections, and the rise of AI-mediated search have reshaped the operational foundations of the industry.
Innovation alone is no longer sufficient. DXPs must integrate governance, consent enforcement, structured data architecture, and AI accountability at their core. Those platforms and enterprises that successfully align technological transformation with regulatory rigor will define the next generation of digital experience leadership.
The 2026 Digital Experience Platform Market: A Year of Reckoning and Strategic Realignment
The Digital Experience Platform market in 2026 is widely regarded as a “Year of Reckoning.” After several years dominated by generative AI enthusiasm and rapid experimentation, enterprises have shifted focus from technological novelty to measurable, pragmatic outcomes. AI hype has given way to operational accountability, financial scrutiny, and trust-based digital value creation.
Organizations are no longer investing in surface-level personalization tactics or cosmetic AI integrations. Instead, leadership teams demand platforms that deliver demonstrable efficiency gains, stronger customer trust, and sustained business impact.
From AI Hype to Outcome Accountability
Between 2023 and 2025, the market experienced aggressive AI integration across content, marketing automation, analytics, and service workflows. However, many early deployments prioritized feature adoption over performance measurement.
In 2026, the decision-making framework has matured. Enterprises now evaluate DXP performance through quantifiable operational and strategic metrics.
Shift in Enterprise Priorities
| Strategic Phase | Primary Focus | Measurement Standard |
|---|---|---|
| AI Hype Phase | Feature expansion and automation | Innovation velocity |
| Optimization Phase | Workflow efficiency | Operational cost reduction |
| Year of Reckoning (2026) | Trust and measurable value | ROI, cycle time reduction, data integrity |
DXPs are increasingly assessed based on their ability to:
Shorten campaign launch cycles
Automate high-volume repetitive tasks
Improve personalization precision
Enhance compliance reliability
Strengthen customer trust metrics
Deep Personalization Over Surface Customization
The personalization strategies of 2026 differ significantly from earlier approaches. Rather than relying on basic rule-based segmentation or superficial content swaps, organizations are implementing deeper behavioral and contextual modeling.
This shift prioritizes long-term relationship value over short-term engagement spikes.
Personalization Evolution Model
| Personalization Level | Traditional Model | 2026 Trust-Based Model |
|---|---|---|
| Segmentation | Static audience rules | Dynamic behavioral modeling |
| Content Variation | Template swaps | Context-aware structural adaptation |
| Performance Objective | Clicks and conversions | Lifetime value and trust signals |
| Data Strategy | Broad data collection | Quality-driven, consent-aligned insights |
This deeper personalization approach depends heavily on structured, reliable data foundations.
Experience-as-Data and Agentic Orchestration
The dual transformation toward Experience-as-Data and Agentic Orchestration has reshaped how DXPs operate internally.
Experience-as-Data enables entire digital environments — including layouts, workflows, and variations — to function as machine-readable structures. Agentic Orchestration layers autonomous AI agents across these structures to execute decisions in real time.
Together, these paradigms allow platforms to function as goal-seeking systems rather than static publishing environments.
Operational Impact of Agentic Orchestration
| Operational Dimension | Traditional DXP Workflow | Agentic DXP Workflow (2026) |
|---|---|---|
| Campaign Setup | Multi-team manual coordination | AI-assisted automated configuration |
| Personalization Tuning | Periodic manual optimization | Continuous real-time refinement |
| Service Resolution | Human-led task processing | Autonomous AI task execution |
| Content Structuring | Developer-defined templates | Dynamic structural adaptation |
The result is significant reduction in operational cycle times, often measured in days or weeks rather than months.
Complexity as the Primary Constraint
Despite these technological advances, complexity remains the defining challenge of the 2026 DXP environment. Digital leaders must balance three interdependent variables:
Composability
Governance
Performance
The flexibility of composable architectures introduces integration overhead and system interdependencies. AI-driven automation increases the need for oversight and compliance management. Performance optimization demands scalable cloud infrastructure and edge delivery strategies.
DXP Complexity Balancing Framework
| Dimension | Risk if Under-Managed | Risk if Over-Managed |
|---|---|---|
| Composability | Vendor lock-in and rigidity | Integration sprawl and fragmentation |
| Governance | Regulatory exposure and AI drift | Innovation slowdown |
| Performance | Latency and scalability limits | Excessive infrastructure costs |
The organizations succeeding in 2026 are those that establish clear architectural governance frameworks while maintaining modular flexibility.
The Central Role of Data Quality
One of the most significant lessons emerging in 2026 is that AI and personalization systems are only as strong as their underlying data. Poor data hygiene, fragmented customer records, and inconsistent consent signals undermine even the most advanced DXP deployments.
High-performing organizations prioritize:
Clean customer identity resolution
Unified consent tracking
Accurate behavioral event logging
Strong metadata structures
Structured content taxonomies
Data Foundation Maturity Model
| Data Maturity Level | AI Performance Outcome | Operational Reliability |
|---|---|---|
| Fragmented Data | Inconsistent personalization | High manual correction burden |
| Structured but Siloed | Partial automation | Moderate performance stability |
| Unified and Governed | High-precision AI orchestration | Stable, scalable optimization |
Without this data foundation, agentic orchestration becomes unpredictable and potentially risky.
Strategic Leadership Requirements in 2026
Technology selection alone no longer guarantees success. Digital leadership teams must align DXP implementation with a long-term strategic vision emphasizing:
Transparency in AI decision-making
Consent integrity and compliance readiness
Customer trust and brand credibility
Sustainable automation practices
Clear KPI alignment before deployment
The competitive differentiator in 2026 is not simply having AI-enabled tools, but deploying them responsibly and effectively.
Conclusion
The 2026 DXP market represents a decisive shift from experimentation to execution. The “Year of Reckoning” reflects a broader industry maturation, where hype has been replaced by measurable impact and operational discipline.
Experience-as-Data modeling and Agentic Orchestration have transformed DXPs into adaptive, goal-seeking systems capable of dramatically reducing operational cycle times. Yet the complexity of balancing composability, governance, and performance remains a formidable leadership challenge.
Success in 2026 requires more than assembling the right technology stack. It demands a disciplined data foundation, integrated governance frameworks, and a strategic commitment to transparency and long-term customer value creation. Organizations that master this balance will define the next era of digital experience excellence.
Conclusion
The global Digital Experience Platform (DXP) market in 2026 stands at a decisive inflection point. What began as web content management has evolved into an intelligent, AI-powered orchestration layer that connects content, commerce, customer data, automation, governance, and real-time personalization across every digital touchpoint. The top 10 Digital Experience Platforms in the world in 2026 are no longer competing solely on features; they are competing on architectural vision, agentic intelligence, composability, regulatory resilience, and measurable business outcomes.
This year marks a transition from experimentation to execution. Enterprises are no longer impressed by surface-level AI integrations or incremental feature releases. Instead, they demand performance accountability, operational efficiency, compliance readiness, and long-term customer trust. As a result, the leading DXPs of 2026 have converged around three structural pillars: Agentic AI, Composable Architecture, and the Experience-as-Data paradigm.
The Evolution of the Modern Digital Experience Platform
In earlier phases of digital transformation, DXPs focused on omnichannel content delivery and personalization. In 2026, the definition has expanded significantly. A modern Digital Experience Platform must now:
Orchestrate autonomous AI agents across workflows
Structure entire digital experiences as machine-readable data
Operate on cloud-native, scalable infrastructure
Embed governance directly into AI and data lifecycles
Deliver measurable ROI within clearly defined timelines
The top 10 DXPs in 2026 represent distinct strategic approaches to solving these challenges. Some platforms emphasize enterprise content scale, others prioritize experimentation and conversion optimization, while several focus on composable, API-first flexibility. Together, they reflect the maturity and diversification of the DXP market.
Key Strategic Themes Defining the Top DXPs in 2026
Agentic Orchestration as Competitive Advantage
The leading DXPs now function as goal-seeking environments rather than static publishing systems. AI agents autonomously execute tasks such as campaign optimization, content personalization, case resolution, and workflow automation. This shift significantly reduces operational cycle times and enables real-time adaptation to customer intent.
Experience-as-Data Architecture
Content is no longer the only structured entity. Entire experiences—including layouts, components, and variations—are treated as data. This allows AI to reorganize and optimize digital interfaces dynamically, replacing hard-coded front-end logic with adaptive intelligence.
Composable and Modular Ecosystems
MACH-based and API-first architectures remain foundational. Enterprises require flexibility to integrate CRM systems, commerce engines, data warehouses, analytics tools, and consent management platforms without vendor lock-in. The top DXPs balance modularity with centralized governance.
Governance and Regulatory Readiness
In 2026, regulatory compliance is a primary decision driver. With expanding privacy laws across the United States, Europe, and Asia-Pacific regions, DXPs must enforce consent, honor universal opt-out mechanisms, and maintain auditable AI governance frameworks. Platforms that integrate compliance automation into their core infrastructure gain a strategic edge.
Measurable ROI and Financial Accountability
The “Year of Reckoning” in 2026 demands financial clarity. Enterprises now evaluate Digital Experience Platforms based on total cost of ownership, integration complexity, time-to-value, and long-term revenue impact. Platforms that demonstrate faster payback periods and clear performance metrics are favored over those offering purely conceptual innovation.
Choosing the Right Digital Experience Platform in 2026
Selecting among the top 10 DXPs in the world requires strategic alignment rather than feature comparison alone. Organizations must assess:
Digital maturity and internal capabilities
Data quality and governance readiness
Industry-specific compliance requirements
Scale of personalization and automation needs
Long-term AI integration strategy
For example:
Large enterprises with complex global operations may prioritize platforms offering deep content governance and integrated AI orchestration.
Retail and e-commerce brands may focus on agentic personalization and commerce-driven optimization.
Mid-market and growth-stage organizations may value cloud-first efficiency and modular scalability.
Public sector and regulated industries may prioritize open architecture and compliance-first frameworks.
There is no universal best DXP; there is only the best-aligned DXP for a given organizational strategy.
The Future of the Digital Experience Platform Market
Looking beyond 2026, several forward-looking trends are expected to further reshape the DXP ecosystem:
Increased AI Autonomy: AI agents will transition from assistive tools to primary workflow operators, handling increasingly complex decision-making tasks.
Answer Engine Optimization (AEO): Content will be structured for AI citation visibility rather than traditional search ranking alone.
Data Minimalism and Trust Metrics: Organizations will shift from maximizing data collection to maximizing data integrity and consent alignment.
Unified AI Governance Platforms: Enterprises will centralize oversight of models, data lineage, and agent activities within integrated governance systems.
Edge-Optimized Performance Architectures: Distributed rendering and real-time optimization will become standard performance requirements.
The Digital Experience Platform will continue evolving into a real-time orchestration layer that connects customer interaction, operational efficiency, and strategic intelligence.
Final Strategic Insight
The top 10 Digital Experience Platforms in the world in 2026 illustrate a market that has matured beyond experimentation. Innovation remains important, but execution, governance, and measurable impact now define true leadership.
Organizations that succeed in this environment will not be those that adopt the most complex technology stack, but those that align platform capabilities with:
High-quality, unified data foundations
Clear strategic objectives
Transparent AI governance
Scalable cloud infrastructure
Customer-centric value creation
The Digital Experience Platform is no longer a marketing tool or content management solution. It is the central nervous system of the modern digital enterprise.
In 2026, choosing the right DXP means selecting an ecosystem capable of learning, adapting, and delivering trusted digital experiences at scale. Enterprises that master this convergence of agentic intelligence, composable architecture, and governance discipline will shape the next era of digital leadership.
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your hiring manager and C-level suite friends and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the 9cv9 Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.
To get access to top-quality guides, click over to 9cv9 Blog.
To hire top talents using our modern AI-powered recruitment agency, find out more at 9cv9 Modern AI-Powered Recruitment Agency.
People Also Ask
What is a Digital Experience Platform (DXP) in 2026?
A Digital Experience Platform in 2026 is an AI-powered system that manages content, customer data, personalization, and workflows across channels, enabling real-time, automated digital experiences at enterprise scale.
Which are the top 10 Digital Experience Platforms in the world in 2026?
The top DXPs in 2026 include Adobe, Salesforce, Sitecore, Optimizely, Liferay, Acquia, Contentful, Contentstack, Bloomreach, and Progress Sitefinity, based on AI capability, scalability, and market adoption.
How do DXPs differ from traditional CMS platforms?
Unlike traditional CMS tools, DXPs integrate AI, customer data, personalization engines, and automation to orchestrate full digital journeys rather than just managing website content.
What makes a DXP “agentic” in 2026?
An agentic DXP uses AI agents to autonomously optimize content, workflows, personalization, and customer interactions, reducing manual effort and accelerating digital operations.
Why is composable architecture important for DXPs?
Composable architecture allows businesses to integrate best-of-breed tools through APIs, enabling flexibility, scalability, and reduced vendor lock-in within modern digital ecosystems.
What is the Experience-as-Data model in DXPs?
Experience-as-Data treats layouts, components, and interactions as structured data, allowing AI to dynamically reorganize and personalize digital interfaces in real time.
How much does a Digital Experience Platform cost in 2026?
DXP pricing varies widely, from entry tiers around USD 25,000 annually to enterprise deployments exceeding USD 500,000, depending on scale, integrations, and AI features.
What is the ROI of implementing a top DXP?
Leading DXPs typically deliver ROI within 6 to 24 months by improving automation, increasing conversion rates, reducing operational costs, and accelerating campaign execution.
Which DXP is best for large enterprises?
Enterprise-focused DXPs like Adobe Experience Manager, Salesforce Experience Cloud, and Sitecore offer advanced governance, scalability, and AI orchestration for complex global operations.
Which DXP is best for mid-sized businesses?
Mid-market organizations often choose Progress Sitefinity, Contentful, or Liferay due to cloud-first deployment, modular pricing, and reduced operational complexity.
How does AI improve Digital Experience Platforms in 2026?
AI enhances DXPs by automating personalization, optimizing content placement, predicting user intent, managing workflows, and resolving service tasks autonomously.
What industries use DXPs the most in 2026?
Retail, financial services, healthcare, public sector, manufacturing, and telecommunications are leading adopters of DXPs for personalization, compliance, and omnichannel engagement.
What is the difference between headless CMS and DXP?
A headless CMS focuses on content delivery via APIs, while a DXP combines content, personalization, AI, analytics, and governance into a unified digital orchestration platform.
How does DXP support omnichannel marketing?
DXPs centralize content and customer data, enabling consistent messaging and personalization across websites, mobile apps, email, commerce platforms, and emerging digital channels.
What are the main compliance challenges for DXPs in 2026?
DXPs must support GDPR, CCPA, and global privacy laws, enforce consent management, honor universal opt-outs, and maintain AI governance audit trails.
What is Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) in relation to DXPs?
AEO focuses on optimizing structured content for AI-driven search and conversational engines, prioritizing citations and authoritative answers over traditional click metrics.
How long does DXP implementation typically take?
Implementation timelines range from 6 months for mid-sized deployments to over 12 months for complex enterprise integrations involving multiple systems and governance frameworks.
What are the hidden costs of DXP deployment?
Beyond license fees, hidden costs include integrations, middleware, training, governance tools, consent platforms, security audits, and ongoing optimization resources.
Which DXP offers the best personalization capabilities?
Platforms like Bloomreach, Sitecore, and Salesforce are recognized for advanced AI-driven personalization and real-time behavioral targeting.
How does cloud-native deployment benefit DXPs?
Cloud-native DXPs provide elastic scalability, lower infrastructure costs, faster performance, automated updates, and support for AI-driven workloads.
Can DXPs integrate with CRM and ERP systems?
Yes, modern DXPs support API-based integration with CRM, ERP, commerce, and data platforms to unify customer insights and operational workflows.
What is the role of governance in Digital Experience Platforms?
Governance ensures data quality, regulatory compliance, AI transparency, consent enforcement, and auditability across all digital experience workflows.
Are DXPs suitable for B2B companies?
Yes, B2B organizations use DXPs for account-based marketing, partner portals, personalized content journeys, and automated sales enablement processes.
How do DXPs improve operational efficiency?
DXPs reduce manual tasks through automation, streamline content production, shorten campaign cycles, and centralize data management for faster decision-making.
What metrics should be tracked after DXP implementation?
Key metrics include conversion rate, customer lifetime value, personalization accuracy, campaign cycle time, ROI, and compliance adherence.
Is vendor lock-in a risk with DXPs?
Vendor lock-in can occur with monolithic platforms, but composable and API-first DXPs reduce this risk by supporting modular integrations.
What skills are required to manage a DXP?
Organizations need expertise in content strategy, data governance, AI oversight, system integration, and cloud infrastructure management.
How do DXPs handle data privacy and consent management?
Modern DXPs integrate consent management platforms, enforce opt-out signals, and maintain centralized logs to comply with evolving privacy regulations.
What is the future of Digital Experience Platforms beyond 2026?
DXPs will become more autonomous, integrating advanced AI agents, predictive personalization, edge computing, and stricter governance frameworks.
Why are DXPs critical for digital transformation in 2026?
DXPs act as the central orchestration layer connecting content, AI, commerce, and data, enabling scalable, compliant, and personalized digital transformation strategies.
Sources
CMSWire
Contentful
Forrester
Fortune Business Insights
Precedence Research
Mordor Intelligence
Adobe Experience League
Databricks
Salesforce
CX Today
G2
Digital Commerce 360
Integrate.io
Cometly
Breakfast Digital
Futurum Research
Adobe
TrustRadius
Medium
Verndale
William Flaiz
Fishtank
The CX Lead
Optimizely
Rightpoint
PR Newswire
Oshyn
PeerSpot
Gartner
Liferay
FitGap
Bloomreach
Findstack
Capterra
BSK
TrustArc
OneTrust
Osano
PwC































![Writing A Good CV [6 Tips To Improve Your CV] 6 Tips To Improve Your CV](https://blog.9cv9.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/2020-06-02-2-100x70.png)


