Key Takeaways
- AI has become the core operating engine of retail banking in 2026, enabling agentic intelligence, real-time decisioning, and enterprise-wide automation across lending, fraud, and customer engagement.
- The best AI tools for retail banking focus on trust, governance, and explainability, allowing banks to scale advanced intelligence while meeting regulatory and security requirements.
- Banks that embed AI into data foundations, customer journeys, and daily operations gain higher efficiency, stronger customer loyalty, and sustainable long-term growth.
Retail banking in 2026 is no longer defined by branches, basic digital channels, or incremental technology upgrades. It is defined by intelligence. Artificial intelligence has moved from the margins of innovation into the core operating fabric of banks worldwide, reshaping how financial institutions compete, scale, manage risk, and build trust with customers. What was once described as digital transformation has now evolved into something far deeper: an intelligence-led structural transformation of the entire retail banking model.

The acceleration of AI adoption in banking is not happening in isolation. It is unfolding against a backdrop of global economic uncertainty, rising fraud sophistication, shifting customer behaviour, regulatory complexity, and intense competition from both fintech challengers and technology-driven ecosystems. In this environment, efficiency alone is no longer enough. Banks are expected to be fast, personalised, secure, transparent, and resilient at the same time. Artificial intelligence has become the only technology capable of meeting all of these demands simultaneously.
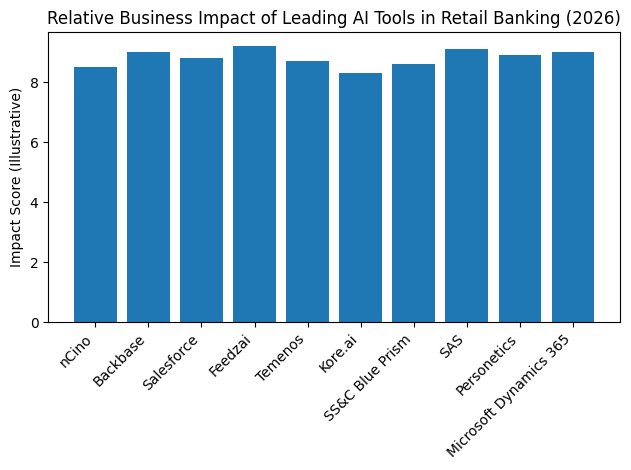
By 2026, AI in retail banking has crossed a critical threshold. It is no longer limited to chatbots, basic credit scoring, or isolated analytics projects. Leading institutions are deploying agentic AI systems that can plan, decide, and act across complex workflows with human oversight. These systems power real-time fraud prevention, intelligent lending, hyper-personalised customer engagement, automated compliance, and continuous risk monitoring at enterprise scale. The result is the emergence of a new banking paradigm often described as the autonomous or intelligent bank.
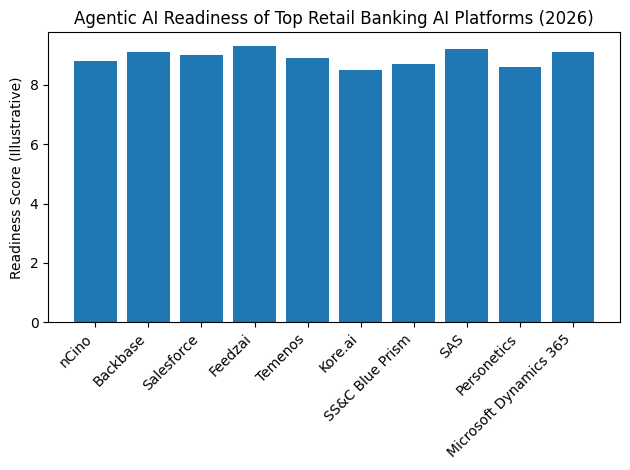
This shift has created a clear divide within the industry. On one side are banks that have industrialised AI, embedding intelligence into their data foundations, operating models, and customer journeys. On the other are institutions still experimenting with disconnected pilots that struggle to scale or deliver measurable value. The difference between these two groups is no longer technical sophistication alone, but strategic clarity and platform choice.
Choosing the right AI tools has therefore become one of the most critical decisions for retail banks in 2026. AI platforms are no longer plug-and-play utilities. They shape how data flows through the organisation, how decisions are made, how risks are managed, and how customers experience the bank on a daily basis. The wrong tools can lock banks into fragmented architectures and compliance risk. The right tools can unlock speed, trust, and sustainable growth.
Another defining factor driving AI adoption is the transformation of trust itself. In 2026, trust is no longer a brand promise or a marketing message. It is a measurable outcome. The explosive rise of deepfake fraud, agent impersonation, and AI-enabled financial crime has forced banks to rethink identity, verification, and security from the ground up. Customers now judge banks not only by convenience or pricing, but by how safe they feel. AI has become the primary mechanism through which banks deliver that safety at scale.
At the same time, customer expectations have fundamentally changed. Retail banking customers increasingly expect proactive financial guidance, seamless digital experiences, and services that adapt to their lives in real time. Hyper-personalisation, invisible payments, and AI-driven financial wellness are no longer premium features. They are becoming baseline expectations, even for mass-market customers. This shift has elevated AI from a back-office optimisation tool to a front-line growth engine.
Internally, AI is also transforming how banks operate and how work gets done. Development cycles are shorter, decision-making is faster, and operational roles are being reshaped. AI copilots support engineers, analysts, and service teams, while agentic systems handle repetitive and data-intensive tasks. Humans remain essential, but their focus is increasingly on judgement, oversight, empathy, and relationship management rather than manual processing.
Against this backdrop, understanding the best AI tools for retail banking in 2026 is not just a technology exercise. It is a strategic necessity. The platforms leading this transformation are those that combine advanced analytics, automation, governance, explainability, and scalability into unified systems built for regulated environments. They support agentic intelligence, operate in real time, and integrate deeply with core banking, data, and digital ecosystems.
This guide to the top 10 best AI tools for retail banking in 2026 is designed to provide clarity in an increasingly complex landscape. It examines the platforms that are shaping the future of banking, not through hype, but through measurable impact across customer experience, fraud prevention, lending, compliance, and operational excellence. It highlights how these tools support the global shift toward agentic intelligence and why they matter for banks of all sizes.
As retail banking enters this new era, the question is no longer whether AI will transform the industry. That transformation is already underway. The real question is which banks will lead it, and which AI platforms will enable them to do so.
Before we venture further into this article, we would like to share who we are and what we do.
About 9cv9
9cv9 is a business tech startup based in Singapore and Asia, with a strong presence all over the world.
With over nine years of startup and business experience, and being highly involved in connecting with thousands of companies and startups, the 9cv9 team has listed some important learning points in this overview of the Top 10 Best AI Tools for Retail Banking in 2026.
If you like to get your company listed in our top B2B software reviews, check out our world-class 9cv9 Media and PR service and pricing plans here.
Top 10 Best AI Tools for Retail Banking in 2026
- nCino
- Backbase
- Salesforce Financial Services Cloud
- Feedzai
- Temenos
- Kore.ai
- SS&C Blue Prism
- SAS
- Personetics
- Microsoft Dynamics 365
1. nCino
By 2026, nCino is firmly established as one of the most influential AI-enabled platforms in retail and commercial banking. The platform supports more than 2,700 financial institutions worldwide, ranging from large global banks to regional and community lenders. This broad adoption highlights nCino’s ability to scale across different banking models while maintaining consistency, security, and regulatory alignment.
Built on a cloud-native architecture, nCino provides banks with a unified operating environment to manage customer accounts, lending workflows, compliance processes, and performance analytics. Instead of relying on disconnected legacy systems, banks use nCino as a central system of engagement and decision-making.
AI-Driven Differentiation Through Banking Advisor
A key reason nCino stands out among the top 10 best AI tools for retail banking in 2026 is its Banking Advisor capability. This AI-driven solution is designed to support bankers with real-time guidance by combining internal customer data with anonymised market insights drawn from more than 1,800 institutions using the platform.
Banking Advisor helps banks move from reactive decision-making to proactive, insight-led operations. Relationship managers, lending teams, and operations staff receive contextual recommendations that improve credit decisions, identify growth opportunities, and reduce processing delays. This intelligence layer allows banks to benefit not only from their own data, but also from broader industry trends captured across the nCino ecosystem.
Core AI Capability Matrix
AI Capability | Practical Banking Use | Business Impact
Banking Advisor insights | Lending and relationship management | Better decisions and consistency
Workflow automation | Loan origination and servicing | Lower operating cost
Data unification | Single customer and account view | Reduced errors
Predictive analytics | Risk and performance forecasting | Improved outcomes
Financial Performance and Revenue Momentum
nCino’s financial results in 2025 and 2026 reflect strong demand for AI-enabled banking platforms. Revenue growth is driven primarily by subscriptions, which indicates long-term customer commitment and predictable recurring income. The company’s improving profitability also demonstrates that AI investment is translating into sustainable financial performance.
Financial Performance Overview
Metric | FY 2025 Value | Q1 FY 2026 Value
Total Revenue | 540.7 million USD | 144.1 million USD
Subscription Revenue | 469.2 million USD | 125.6 million USD
Non-GAAP Operating Income | 96.2 million USD | 24.8 million USD
Customer Institutions | 2,700+ | 2,700+
Remaining Performance Obligation | 1.2 billion USD | Approximately 1.1 billion USD
The growth in remaining performance obligation highlights strong long-term customer confidence and multi-year platform adoption.
Operational Impact in Retail and Community Banking
Beyond financial metrics, nCino delivers measurable operational improvements for banks. Institutions using the platform report dramatic reductions in loan servicing costs and approval timelines. These gains are especially valuable in retail and community banking, where efficiency directly affects profitability.
Reported Operational Outcomes
Operational Area | Measured Improvement | Business Meaning
Loan servicing cost | 92 percent reduction | Major cost savings
Loan approval time | 70 percent faster | Higher customer satisfaction
Onboarding duration | 10 days shorter | Faster revenue realisation
For a community bank earning 100 million USD annually, reducing onboarding time by just ten days can accelerate revenue by around 3 million USD. This illustrates how operational efficiency enabled by AI directly supports growth, not just cost control.
Bar Chart Representation (Text-Based)
Operational Impact Comparison
Loan servicing cost reduction: █████████████████████████
Loan approval speed improvement: █████████████████████
Onboarding acceleration impact: █████████████████
These visuals show that the largest gains come from servicing efficiency and decision speed.
Why nCino Ranks Among the Best AI Tools for Retail Banking in 2026
nCino earns its position among the top AI tools for retail banking in 2026 because it combines scale, proven financial performance, and measurable operational impact. Its Banking Advisor capability demonstrates how AI can support bankers directly within daily workflows rather than acting as a separate analytics layer.
For retail and community banks seeking to modernise lending, reduce costs, and improve decision quality while maintaining regulatory confidence, nCino represents a mature, enterprise-ready AI platform that delivers both immediate and long-term value.
2. Backbase
Backbase is widely regarded in 2026 as one of the most advanced AI-driven engagement platforms for retail banking. It is positioned as a growth-focused banking platform rather than a traditional core system, with a clear emphasis on revenue expansion, customer experience optimisation, and cost efficiency. The platform supports banks that aim to modernise digital channels while unifying fragmented systems into a single, customer-focused operating model.
With a valuation exceeding 2.6 billion USD following major funding rounds, Backbase serves around 150 large financial institutions worldwide and supports digital interactions for more than 90 million end customers. This scale demonstrates strong enterprise adoption and validates its role among the top AI tools shaping retail banking in 2026.
Engagement Banking and AI-Led Operating Model
Backbase’s defining concept is Engagement Banking, which focuses on breaking down silos between digital channels, data systems, and operational workflows. Instead of treating mobile banking, web banking, onboarding, and payments as separate systems, the platform brings them together into a unified experience powered by AI.
This operating model allows banks to move from reactive service delivery to proactive and personalised engagement. AI is embedded directly into customer journeys, enabling banks to anticipate needs, suggest relevant actions, and automate routine financial tasks without increasing operational complexity.
AI Strategy for Retail Banking in 2026
In 2026, Backbase’s AI roadmap is centred on two major themes: invisible payments and proactive personalisation. Invisible payments reduce friction by automating savings, bill payments, and transfers in the background, allowing customers to focus on outcomes rather than transactions. Proactively personal banking uses AI to deliver timely recommendations and financial guidance based on user behaviour and life events.
AI co-pilots embedded within the platform support both customers and internal teams. Customers benefit from automated financial wellness features, while employees gain decision support tools that improve speed, accuracy, and consistency across service interactions.
Core AI Capabilities and Banking Use Cases
AI Capability | Practical Retail Banking Application | Primary Business Impact
Customer journey orchestration | Personalised digital flows across mobile and web | Higher conversion and engagement
AI co-pilots for customers | Automated savings, payments, and budgeting | Increased retention and trust
AI co-pilots for staff | Assisted customer service and relationship management | Higher productivity and service quality
Invisible payments | Background execution of routine transactions | Lower friction and fewer support requests
Data-driven personalisation | Contextual offers and financial insights | Revenue growth through relevance
Quantified Performance Impact in Retail Banking
Backbase reports strong measurable improvements across digital banking performance metrics. These outcomes highlight why the platform is frequently included in discussions around the best AI tools for retail banking in 2026.
Retail Banking Performance Metrics
Metric | Reported Outcome | Business Meaning
Mobile app onboarding time | Less than 5 minutes | Faster activation and reduced drop-offs
Registered mobile users | 39 percent increase | Stronger digital adoption
Monthly active users | 19 percent increase | Improved engagement consistency
Digital acquisition costs | 44 percent reduction | Lower cost per customer
Customer satisfaction score | 51 percent year-over-year improvement | Higher loyalty and brand perception
Developer Productivity and Cost Efficiency
Backbase’s AI co-pilots also target internal efficiency, particularly in software development and digital product delivery. Research referenced by the platform shows that banks using these AI capabilities experienced significant gains in productivity and cost control.
Internal Efficiency Impact Table
Area | AI-Driven Improvement | Operational Benefit
Developer productivity | 40 percent increase | Faster feature delivery and innovation
Time to market | Accelerated release cycles | Competitive advantage
Digital acquisition spend | 44 percent reduction | Improved marketing ROI
Illustrative Bar Chart Representation (Text-Based)
Metric Comparison Bar Chart
Developer productivity increase: ████████████████████████
Digital acquisition cost reduction: █████████████████████
Customer satisfaction improvement: █████████████████████████
These bars show that both revenue-facing and cost-related metrics benefit from AI adoption, reinforcing Backbase’s value proposition.
AI Factory and Enterprise-Grade AI Adoption
Backbase further strengthens its AI leadership through its AI Factory initiative. This programme provides banks with structured tools, frameworks, and expert support to accelerate AI deployment without excessive experimentation risk. Rather than forcing banks to build AI capabilities from scratch, the AI Factory enables faster implementation of proven use cases.
A key output of this initiative is the development of agentic assistants. These AI-powered assistants support relationship managers and customer service agents by suggesting next-best actions, surfacing relevant customer insights, and maintaining consistent service standards across all customer segments.
AI Factory Capability Matrix
AI Factory Component | Purpose | Value to Retail Banks
Pre-built AI modules | Rapid deployment of common use cases | Shorter implementation cycles
Agentic assistants | Staff decision support and guidance | Higher service quality
Governance frameworks | Controlled and compliant AI usage | Reduced regulatory risk
Expert enablement | Skills transfer and best practices | Sustainable AI maturity
Why Backbase Ranks Among the Best AI Tools for Retail Banking in 2026
Backbase earns its place among the top AI tools for retail banking in 2026 due to its strong focus on engagement, measurable performance outcomes, and enterprise-ready AI infrastructure. The platform goes beyond basic automation by embedding intelligence directly into customer and employee journeys.
For retail banks aiming to increase digital adoption, improve customer satisfaction, and reduce acquisition and servicing costs, Backbase represents a mature and scalable AI-powered engagement platform that aligns closely with modern banking growth strategies.
3. Salesforce Financial Services Cloud
Salesforce is positioned in 2026 as one of the most influential AI platforms for retail banking, particularly in customer engagement, sales automation, and service operations. Its Financial Services Cloud, combined with the Agentforce AI layer, is designed for banks that want to scale personalised customer interactions while tightly linking AI usage to business outcomes. Rather than replacing human teams, the platform focuses on augmenting bankers, marketers, and service agents with autonomous AI capabilities.
Agentforce represents a major shift in how AI is delivered to banks. Instead of static chatbots or rule-based automation, Salesforce introduces autonomous AI agents that can execute actions across sales, service, and marketing workflows with minimal human supervision.
What Agentforce Does for Retail Banks
Agentforce is a collection of AI agents that can independently handle tasks such as responding to customer inquiries, updating CRM records, triggering follow-ups, recommending next-best actions, and supporting marketing campaigns. These agents operate across digital channels while remaining governed by banking compliance and permission controls.
For retail banks, this means faster response times, more consistent service quality, and improved customer targeting without increasing headcount. The AI agents are designed to learn from conversations and outcomes, allowing banks to continuously refine customer engagement strategies.
Core Agentforce Capabilities Matrix
AI Capability | Retail Banking Function | Practical Outcome
Autonomous service agents | Customer support and case handling | Faster resolution and lower service costs
Sales intelligence agents | Relationship management and cross-selling | Higher conversion rates
Marketing orchestration agents | Campaign execution and optimisation | Better targeting and ROI
Conversation analysis | Omnichannel interactions | Improved customer insight
Action execution | CRM updates and workflow triggers | Reduced manual work
Usage-Based AI Pricing Model Explained
One of the most important reasons Salesforce stands out among the best AI tools for retail banking in 2026 is its shift away from traditional per-seat pricing. Instead, Agentforce uses a conversation-based and action-based pricing model, allowing banks to pay based on actual AI usage rather than the number of employees.
This model aligns AI costs directly with customer interactions and revenue-generating activity, making budgeting more predictable and performance-driven.
Agentforce Pricing Structure Overview
Pricing Component | Cost Structure | Typical Banking Use Case
Flex Credits | 500 USD per 100,000 credits | Background AI actions such as CRM updates
Cost per action | 0.10 USD per action (20 credits) | Automated task execution
Conversation pricing | 2 USD per conversation | Customer-facing AI chats
Industries add-on | 150 USD per user per month | Regulated financial services usage
Agentforce enterprise edition | 550 USD or more per user per month | Full AI bundle with large credit allocation
Implementation services | 50,000 to 800,000 USD or more | Initial deployment and integration
Illustrative Cost Impact for a Mid-Sized Retail Bank
For a mid-sized retail bank with approximately 100 internal users, handling around three AI-assisted cases per user per day, the usage-based pricing structure can be estimated as follows.
Monthly AI Cost Illustration Table
Metric | Estimated Value
Users | 100
Cases per user per day | 3
Monthly AI actions | Approximately 60,000
Estimated Flex Credit cost | Around 1,800 USD per month
Base platform licensing | Additional fixed cost
This structure allows banks to scale AI usage gradually while maintaining visibility into operational spend.
Financial and ROI Impact for Retail Banking
Independent economic studies on Salesforce implementations indicate strong financial returns for enterprise organisations using its AI-driven engagement tools. These returns are primarily driven by improved marketing efficiency, higher customer conversion rates, and better personalisation at scale.
ROI Performance Summary Table
Performance Indicator | Observed Outcome | Banking Impact
Average ROI over three years | 299 percent | Strong long-term value creation
Marketing efficiency | Significant improvement | Lower acquisition costs
Customer targeting accuracy | Measurable increase | Higher product uptake
Service productivity | Reduced manual workload | Lower operational expenses
Illustrative ROI Bar Chart Representation (Text-Based)
Metric Comparison
Marketing efficiency gains: ████████████████████████
Customer conversion improvement: █████████████████████
Operational cost reduction: ███████████████████
These visual indicators show that the majority of value comes from smarter engagement rather than pure cost cutting.
How Salesforce Fits Different Retail Banking Strategies
Salesforce Financial Services Cloud with Agentforce is especially well suited for banks that prioritise customer experience, cross-selling, and lifecycle engagement. It works best as an engagement and intelligence layer rather than a core banking replacement.
Retail Banking Fit Matrix
Bank Type | Strategic Fit | Reason
Large retail banks | Very high | Scale, data depth, complex journeys
Digital-first banks | High | Strong omnichannel AI engagement
Mid-sized banks | Medium to high | Pay-as-you-use flexibility
Community banks | Medium | Best for growth-focused use cases
Why Salesforce and Agentforce Rank Among the Best AI Tools for Retail Banking in 2026
Salesforce earns its place in the top AI tools for retail banking in 2026 by delivering autonomous AI agents that operate directly within revenue and service workflows. The usage-based pricing model reduces waste, the AI agents improve speed and consistency, and the platform’s financial services focus ensures regulatory readiness.
For banks seeking measurable ROI from AI-driven sales, service, and marketing automation, Salesforce Financial Services Cloud with Agentforce offers one of the most mature and commercially aligned AI solutions available in the retail banking landscape.
4. Feedzai
Feedzai is widely recognised in 2026 as one of the most important AI platforms for retail banking, particularly in the areas of fraud prevention, payment security, and financial crime detection. As digital payments grow in volume and complexity, banks increasingly rely on AI-native platforms that can operate at massive scale without disrupting customer experience. Feedzai fills this role by providing a unified RiskOps platform that combines real-time monitoring, advanced machine learning, and automated decisioning.
The platform’s credibility at a global level has been reinforced by its selection as the core fraud detection and prevention engine for the digital euro initiative. This role highlights Feedzai’s ability to operate at central-bank-grade scale and reliability, which places it firmly among the top AI tools shaping retail banking in 2026.
What RiskOps Means for Retail Banking
RiskOps is Feedzai’s approach to managing fraud and financial crime as a continuous operational discipline rather than a reactive function. Instead of isolated fraud checks, the platform integrates risk detection, investigation, and response into a single AI-driven workflow. This allows retail banks to detect threats earlier, act faster, and reduce losses without increasing friction for legitimate customers.
By applying AI models across transactions, user behaviour, and device intelligence, Feedzai helps banks shift from rule-based fraud systems to adaptive, learning-based risk management.
AI-Native Capabilities and Core Use Cases
Feedzai’s platform is built to handle extremely high transaction volumes while maintaining accuracy and speed. Its AI models analyse payment behaviour in real time, identifying both common fraud patterns and rare, sophisticated attacks that traditional systems often miss.
Core AI Capability Matrix
AI Capability | Retail Banking Application | Business Outcome
Real-time transaction monitoring | Card, account, and instant payments | Immediate fraud detection
Behavioural biometrics | User behaviour and interaction patterns | Reduced account takeover
Adaptive machine learning | Evolving fraud tactics | Continuous model improvement
Automated risk decisioning | Approve, challenge, or block transactions | Lower manual intervention
Investigation workflow automation | Analyst case management | Faster resolution times
Scale and Market Impact in Retail Banking
Feedzai operates at a scale that few fraud platforms can match. The system processes tens of billions of payment events every year and protects more than one billion consumers worldwide. This scale is essential for retail banks operating across multiple channels, geographies, and payment methods.
Global Protection Scale Overview
Metric | Reported Scale | Retail Banking Significance
Annual payment events monitored | Over 70 billion | Coverage across all major payment rails
Payment value protected | 8 trillion USD annually | High trust from large banks
Customers protected | Over 1 billion | Proven consumer-scale reliability
Analyst hours saved | 20 million or more | Major operational efficiency gains
Quantified Financial and Operational Results
Retail banks using Feedzai report strong, measurable outcomes that directly affect profitability and customer trust. One large North American retail bank documented substantial savings over a multi-year period while maintaining high fraud detection accuracy.
Documented Performance Outcomes Table
Performance Metric | Reported Result | Banking Impact
Losses prevented | Over 2 billion USD | Direct protection of revenue
Savings over three years | 30 million USD | Reduced fraud and operations cost
Value detection rate | 75 percent | High accuracy in identifying real fraud
False positive ratio | 12 to 1 | Fewer legitimate transactions blocked
Intervention rate | 0.1 percent | Minimal customer disruption
Customer Experience and False Positive Reduction
One of Feedzai’s most important advantages in retail banking is its ability to reduce false positives. Blocking legitimate transactions damages customer trust and increases support costs. Feedzai’s AI models are designed to identify fraud precisely, allowing the majority of genuine transactions to pass through without friction.
Customer Impact Matrix
Area | Traditional Systems | Feedzai RiskOps Outcome
Transaction declines | High | Significantly reduced
Customer complaints | Frequent | Much lower
Manual reviews | Heavy | Minimal
Trust in digital payments | Fragile | Strong and consistent
Illustrative Bar Chart Representation (Text-Based)
Fraud Detection and Efficiency Comparison
Losses prevented: █████████████████████████
Value detection accuracy: █████████████████████
False positive efficiency: ████████████████████████
Customer intervention rate: ██
This visual pattern shows strong fraud protection combined with very low customer friction.
Why Feedzai Ranks Among the Best AI Tools for Retail Banking in 2026
Feedzai earns its place among the top AI tools for retail banking in 2026 because it combines massive scale, advanced AI accuracy, and proven financial impact. The platform protects banks from growing fraud threats while preserving smooth digital experiences for customers.
For retail banks facing rising transaction volumes, instant payments, and sophisticated financial crime, Feedzai provides an AI-native RiskOps solution that delivers measurable protection, operational efficiency, and regulatory-grade reliability.
5. Temenos
Temenos continues to be one of the most influential technology providers in global retail banking in 2026. The company plays a critical role in both core banking infrastructure and AI-enabled digital experiences. With more than 3,000 financial institutions using its technology, including 41 of the world’s top 50 banks, Temenos is widely viewed as a backbone platform for large-scale retail banking operations.
Unlike point AI solutions, Temenos combines core banking, digital engagement, payments, and risk capabilities into a single ecosystem. This makes it especially relevant for banks that want AI-driven transformation without replacing their entire technology stack.
Temenos Infinity as an AI-Driven Digital Front Office
Temenos Infinity is the digital engagement layer that sits on top of Temenos core banking systems. In 2026, it serves more than 500 million end customers daily across retail, corporate, and private banking. The platform enables banks to manage customer journeys, digital transactions, onboarding, and enterprise credit from a unified interface.
AI is embedded across Infinity to support personalisation, intelligent workflow routing, predictive insights, and automated service interactions. This allows banks to deliver consistent experiences across mobile, web, and branch channels while reducing manual effort.
Digital Engagement Capability Matrix
Capability Area | What It Does | Retail Banking Benefit
AI-driven personalisation | Tailors offers and journeys | Higher conversion and engagement
Omnichannel orchestration | Connects mobile, web, branch | Seamless customer experience
Smart onboarding | Automates KYC and account setup | Faster activation
Digital credit workflows | Manages retail and SME lending | Shorter approval cycles
Enterprise transaction management | Supports high-volume banking activity | Operational consistency
Core Banking Strength and Enterprise Scale
Temenos remains dominant in core banking, supporting deposits, lending, payments, and risk management at enterprise scale. Its systems are designed for high availability, regulatory compliance, and multi-country operations. In 2026, the company continues to transition customers from traditional perpetual licenses to SaaS and subscription-based models, aligning costs more closely with usage and scalability.
This shift enables banks to modernise infrastructure while maintaining control over mission-critical systems.
Core Banking Value Matrix
Core Banking Area | AI and Automation Role | Business Outcome
Account processing | Automated posting and reconciliation | Reduced errors
Payments | Intelligent routing and monitoring | Faster settlement
Risk and compliance | Embedded controls and analytics | Regulatory confidence
Product configuration | Modular and API-driven | Faster product launches
Financial Strength and Commercial Model
Temenos shows strong financial stability going into 2026, which is a key consideration for banks selecting long-term technology partners. Annual recurring revenue continues to grow, reflecting a successful transition toward subscription-based delivery.
Financial Performance Overview
Financial Metric | Reported Value
Total revenue | 1,044.1 million USD
Annual recurring revenue | 804 million USD
ARR growth rate | 10 percent year over year
Active core and digital clients | Approximately 1,550 institutions
End customers supported | Around 500 million
These figures highlight predictable revenue streams and sustained enterprise adoption.
Cost Expectations for Retail Banks
For banks evaluating Temenos in 2026, cost varies significantly based on deployment size and complexity. On average, the estimated annual cost per client is slightly above 518,000 USD. However, large banks with multi-module deployments covering core banking, payments, risk, and digital channels often incur substantially higher annual costs.
Estimated Cost Structure Matrix
Bank Profile | Typical Deployment Scope | Relative Annual Cost
Mid-sized retail bank | Core + digital channels | Medium
Large retail bank | Core + payments + risk | High
Tier-one global bank | Full enterprise suite | Very high
Illustrative Bar Chart Representation (Text-Based)
Adoption and Revenue Scale
Institutions served: █████████████████████████
End customers supported: █████████████████████████████
Annual recurring revenue: ███████████████████████
This visual comparison shows why Temenos is often selected for large and complex retail banking environments.
Why Temenos Ranks Among the Best AI Tools for Retail Banking in 2026
Temenos earns its place among the top AI tools for retail banking in 2026 because it combines deep core banking expertise with AI-enabled digital engagement at global scale. The platform is not limited to experimentation or niche use cases; it supports mission-critical banking operations used by hundreds of millions of customers every day.
For retail banks seeking a long-term, enterprise-grade solution that blends AI, digital innovation, and proven core banking stability, Temenos Infinity and Core Banking remain one of the most comprehensive and trusted technology choices available.
6. Kore.ai
Kore.ai is recognised in 2026 as one of the strongest AI platforms for retail banks that want to modernise customer engagement without replacing their existing core systems. Its BankAssist solution is designed specifically for banking environments, focusing on intelligent digital assistants that understand context, intent, and customer history. This makes Kore.ai a popular choice for banks that aim to improve service quality, reduce support costs, and scale digital interactions securely.
Unlike platforms that require deep infrastructure changes, Kore.ai positions itself as an AI agility layer. It integrates with legacy banking systems and adds conversational intelligence on top, allowing banks to move faster while protecting prior technology investments.
BankAssist and AI-Driven Customer Engagement
BankAssist is built to deliver highly personalised and context-aware conversations across digital banking channels. The AI assistants can understand customer intent, retrieve relevant account data, and complete tasks such as onboarding, balance inquiries, payment instructions, and loan applications. This enables retail banks to offer round-the-clock service without increasing operational workload.
The platform is widely used for conversational banking experiences that feel natural and human-like, while still maintaining strict compliance and security controls required in regulated financial environments.
Customer Engagement Capability Matrix
AI Capability | Retail Banking Application | Business Impact
Context-aware conversations | Customer support and self-service | Faster resolution times
Hyper-personalisation | Tailored responses and recommendations | Higher satisfaction
Task automation | Onboarding and loan requests | Lower operational cost
Omnichannel delivery | Messaging apps and web chat | Broader reach
Language understanding | Multi-language retail banking | Inclusive service
Modernising Legacy Banking Systems with AI
Kore.ai places strong emphasis on helping banks modernise without disruption. Many retail banks operate on complex legacy platforms that are costly and slow to change. Kore.ai’s approach allows AI assistants to sit above these systems, orchestrating interactions and workflows while leaving core infrastructure intact.
This model is especially attractive to mid-sized and large banks that want faster innovation cycles without the risk and expense of full system replacements.
Legacy Modernisation Value Matrix
Challenge | Traditional Banking Constraint | Kore.ai AI Impact
Slow system changes | High dependency on core vendors | Faster innovation layer
High call centre load | Manual customer handling | AI-driven self-service
Limited personalisation | Static rule-based flows | Dynamic AI responses
Scalability issues | Costly human expansion | Elastic AI scaling
Enterprise-Grade Pricing and Deployment Options
Kore.ai follows an enterprise pricing model that reflects its focus on large-scale banking deployments. Annual pricing for full enterprise implementations typically starts around 300,000 USD per year. For smaller teams or limited deployments, lower-tier plans are available, allowing banks to test conversational AI before scaling.
A key differentiator in 2026 is Kore.ai’s support for on-premise deployment. This option is critical for banks operating in regions with strict data residency, security, or regulatory requirements.
Illustrative Pricing Structure Table
Pricing Tier | Approximate Cost | Suitable For
Essential | 50 to 60 USD per month (annual billing) | Small teams or single bot use
Advanced | 150 to 180 USD per month (annual billing) | Growing digital teams
Enterprise | 300,000 USD or more per year | Large retail bank deployments
Usage-Based Billing and ROI Transparency
Kore.ai uses a billing model based on conversational sessions rather than users. A billing session is defined as a 15-minute conversation window. This structure allows banks to directly link AI costs to actual customer interactions, making ROI measurement clearer as usage grows.
This approach is particularly valuable for retail banks that handle fluctuating customer volumes across seasons, campaigns, or product launches.
Billing Model Comparison Matrix
Billing Metric | Kore.ai Model | Banking Benefit
Per-user fees | Not required | Lower fixed costs
Session-based billing | 15-minute blocks | Usage transparency
Scalability | Elastic | Pay only for demand
ROI tracking | Direct link to interactions | Easier justification
Real-World Retail Banking Use Cases
Retail banks have successfully deployed Kore.ai’s generative AI across popular messaging platforms to simplify customer journeys. AI assistants are used to guide customers through onboarding, answer account-related questions, and assist with loan applications, reducing friction and support workload.
These deployments show how conversational AI can move beyond basic FAQs to become a core service channel in retail banking.
Illustrative Bar Chart Representation (Text-Based)
Impact Area Comparison
Reduction in support workload: ████████████████████████
Improvement in response speed: █████████████████████
Customer satisfaction uplift: ████████████████████
Why Kore.ai Ranks Among the Best AI Tools for Retail Banking in 2026
Kore.ai earns its place among the top AI tools for retail banking in 2026 by offering secure, scalable, and highly personalised conversational AI that integrates smoothly with existing banking systems. Its session-based pricing, enterprise deployment options, and strong focus on regulated environments make it a practical choice for banks of all sizes.
For retail banks seeking to improve digital engagement, modernise customer service, and gain measurable returns from conversational AI, Kore.ai BankAssist represents a mature and future-ready solution in the evolving banking technology landscape.
7. SS&C Blue Prism
SS&C Blue Prism is widely recognised in 2026 as one of the most advanced intelligent automation platforms for retail banking. What began as a traditional robotic process automation provider has evolved into a full-scale intelligent automation ecosystem designed to support the concept of the autonomous enterprise. This shift makes Blue Prism highly relevant for banks that want to move beyond basic task automation and redesign operations around AI-led workflows.
In retail banking, where back-office costs, regulatory pressure, and operational complexity continue to rise, Blue Prism plays a critical role in improving efficiency, accuracy, and scalability across both customer-facing and internal processes.
From Robotic Automation to Intelligent Automation
Blue Prism’s transformation focuses on combining automation, artificial intelligence, and governance into a single operating framework. Rather than using bots only for repetitive tasks, the platform enables banks to orchestrate digital workers, AI agents, and human staff together in structured workflows.
This approach allows automation to handle entire processes from start to finish, such as customer servicing, document review, and fraud investigations, instead of automating isolated steps.
Automation Evolution Comparison Matrix
Automation Stage | Description | Retail Banking Outcome
Basic RPA | Task-level automation | Limited cost savings
Intelligent automation | AI + automation + orchestration | End-to-end efficiency
Autonomous enterprise | AI-led decision flows | Sustainable operational scale
Core Intelligent Automation Capabilities for Banks
SS&C Blue Prism provides enterprise-grade tools that support advanced AI use cases in regulated banking environments. Key components include AI governance, intelligent document processing, and secure orchestration of automation assets.
Key Capability Matrix
Capability | Retail Banking Use Case | Business Impact
AI Gateway | Centralised AI governance | Controlled and compliant AI use
Decipher IDP | Data extraction from documents | Faster onboarding and reviews
Digital worker orchestration | Back-office automation | Lower operating costs
Human and AI collaboration | Assisted investigations and servicing | Higher productivity
Workflow intelligence | Process redesign and optimisation | Sustainable efficiency gains
Driving the Autonomous Enterprise in Retail Banking
A defining theme for Blue Prism in 2026 is the orchestration of people, AI agents, and digital workers within a single environment. This orchestration allows banks to redesign workflows around outcomes rather than legacy process steps.
For example, instead of multiple handoffs across departments, an AI-driven workflow can manage a customer service case from intake to resolution, escalating to humans only when necessary. This model significantly reduces delays, errors, and operational overhead.
Workflow Transformation Matrix
Traditional Model | Intelligent Automation Model | Result
Multiple handoffs | Single orchestrated flow | Faster resolution
Manual reviews | AI-led decisioning | Higher accuracy
Fragmented systems | Unified automation layer | Better control
Quantified Efficiency and Productivity Impact
Banks that adopt advanced intelligent automation are expected to see meaningful improvements in their efficiency ratios by 2026. These gains are driven by reduced manual work, faster processing times, and better utilisation of skilled employees.
Operational Impact Summary Table
Metric | Expected Improvement | Retail Banking Meaning
Efficiency ratio | Up to 15 percentage points | Lower cost-to-income
Back-office productivity | Up to 50 percent increase | Faster processing
Error rates | Significant reduction | Fewer rework cycles
Processing speed | Major acceleration | Improved service delivery
Illustrative Bar Chart Representation (Text-Based)
Operational Improvement Comparison
Back-office productivity gain: █████████████████████████
Efficiency ratio improvement: ███████████████████
Processing speed increase: ███████████████████████
These bars show that the largest gains come from productivity and workflow speed rather than incremental automation.
Human and AI Collaboration in Retail Banking
A key advantage of SS&C Blue Prism’s approach is its emphasis on collaboration rather than replacement. AI agents handle data-heavy and repetitive work, while humans focus on judgement, oversight, and customer relationships. This balance is especially important in regulated retail banking environments where accountability and explainability matter.
Human–AI Collaboration Matrix
Task Type | AI Role | Human Role
Data extraction | Automated | Validation and oversight
Transaction processing | Fully automated | Exception handling
Customer investigations | AI-assisted | Final decision
Compliance reporting | Automated preparation | Approval and audit
Why SS&C Blue Prism Ranks Among the Best AI Tools for Retail Banking in 2026
SS&C Blue Prism earns its place among the top AI tools for retail banking in 2026 because it enables banks to move from fragmented automation to true intelligent operations. Its focus on governance, orchestration, and enterprise-scale deployment makes it particularly suitable for large and mid-sized banks seeking measurable efficiency gains.
For retail banks aiming to modernise back-office operations, reduce cost-to-income ratios, and build a foundation for the autonomous enterprise, SS&C Blue Prism Intelligent Automation stands out as a mature and future-ready AI solution.
8. SAS
SAS remains one of the most trusted and established providers of advanced analytics and artificial intelligence for retail banking in 2026. Unlike newer AI vendors that focus on narrow use cases, SAS plays a foundational role in how banks manage data quality, risk, pricing, and regulatory decision-making at enterprise scale. Its long-standing presence in highly regulated environments makes it a critical choice for banks that require accuracy, transparency, and governance in AI-driven decisions.
In 2026, SAS is increasingly recognised for helping banks move from experimentation with AI models to measurable, proof-driven intelligence that directly supports business and regulatory outcomes.
Shift from Model-Driven to Proof-Driven Intelligence
A central theme of SAS’s 2026 strategy is the transition from model-driven intelligence to proof-driven intelligence. Rather than focusing only on building complex models, banks are encouraged to validate whether AI insights are accurate, explainable, and usable in real-world banking decisions.
This shift is particularly important as banks face growing data integrity challenges. Synthetic data, automated data generation, and fragmented sources have increased the risk of unreliable inputs entering core banking systems. SAS Viya is positioned as a platform that helps banks test, validate, and govern AI outputs before they influence pricing, lending, or risk decisions.
Intelligence Approach Comparison Matrix
Approach | Description | Retail Banking Outcome
Model-driven intelligence | Focus on building models | Limited real-world trust
Proof-driven intelligence | Focus on validation and outcomes | Higher confidence decisions
Governed AI intelligence | Embedded controls and auditability | Regulatory readiness
Managing Unstructured Data at Banking Scale
SAS experts highlight that more than 80 percent of enterprise data exists in unstructured formats, such as documents, emails, call transcripts, images, and transaction notes. In retail banking, this data often contains valuable signals related to customer behaviour, credit risk, fraud patterns, and compliance issues, but remains underused due to its complexity.
By 2026, generative AI within SAS Viya is becoming the primary method for extracting meaning from unstructured data at scale. The platform enables banks to convert raw text and documents into structured insights that can be analysed alongside traditional financial data.
Unstructured Data Use Case Matrix
Data Source | AI Processing Role | Banking Value
Customer communications | Text analysis and sentiment detection | Better service and retention
Loan documents | Automated data extraction | Faster credit decisions
Compliance reports | Pattern and anomaly detection | Reduced regulatory risk
Fraud notes | Contextual analysis | Stronger fraud prevention
Hybrid Quantum-Classical Computing in Banking
One of the most advanced developments in SAS’s 2026 roadmap is the move from pilot projects to production use of hybrid quantum-classical computing. This approach combines traditional high-performance computing with emerging quantum techniques to solve complex optimisation and risk problems more efficiently.
In retail banking, this capability is especially relevant for advanced risk modelling, fraud detection, and large-scale simulations that would otherwise take excessive time and resources to compute. SAS’s progress in this area positions it ahead of many competitors that are still limited to experimental use cases.
Advanced Computing Capability Matrix
Capability | Banking Application | Strategic Benefit
Hybrid quantum-classical models | Risk simulations | Faster and deeper analysis
Large-scale optimisation | Portfolio and pricing models | Better capital allocation
Complex fraud pattern detection | Real-time fraud prevention | Higher accuracy
Bubble-Aware Models for Pricing and Stress Testing
Another important innovation from SAS in 2026 is the introduction of bubble-aware models. These models are designed to detect conditions where asset prices rise rapidly beyond sustainable levels due to market sentiment, leverage, or external shocks.
Retail banks are beginning to embed these models into pricing strategies and stress-testing frameworks. This allows institutions to better anticipate market instability, protect balance sheets, and comply with increasingly strict regulatory stress-testing requirements.
Risk Intelligence Matrix
Model Type | Purpose | Retail Banking Impact
Traditional risk models | Historical trend analysis | Limited foresight
Bubble-aware models | Detect unsustainable price growth | Improved resilience
Stress-testing models | Scenario-based analysis | Regulatory compliance
Illustrative Bar Chart Representation (Text-Based)
Impact Area Comparison
Unstructured data insight extraction: █████████████████████████
Risk modelling depth: ████████████████████████
Fraud detection accuracy: █████████████████████
Regulatory confidence: ███████████████████████
These visual indicators show that SAS delivers its strongest value in high-stakes, data-intensive banking decisions.
Why SAS Viya Ranks Among the Best AI Tools for Retail Banking in 2026
SAS Viya earns its place among the top AI tools for retail banking in 2026 because it addresses the most complex challenges banks face: data trust, explainability, and large-scale risk management. Its focus on proof-driven intelligence, unstructured data mastery, and advanced computing techniques makes it especially valuable for banks that prioritise accuracy over hype.
For retail banks seeking AI solutions that support long-term stability, regulatory confidence, and deep analytical insight, SAS Viya and Financial Services AI remain among the most reliable and future-ready platforms available.
9. Personetics

Personetics is widely regarded in 2026 as one of the most impactful AI platforms for hyper-personalisation in retail banking. Unlike automation tools that focus mainly on efficiency, Personetics concentrates on customer intelligence and financial wellbeing. Its AI analyses real-time spending behaviour, income patterns, and account activity to deliver meaningful, personalised insights that directly improve customer engagement and long-term loyalty.
This focus makes Personetics especially relevant for banks competing on experience rather than price, and for institutions looking to deepen customer relationships without significantly expanding advisory teams.
From Generic Alerts to Personal Financial Intelligence
Personetics moves retail banking beyond basic alerts and notifications. Instead of sending generic messages, the platform generates personalised, situation-aware guidance based on each customer’s financial behaviour. These insights are timely, relevant, and easy to understand, helping customers make better day-to-day financial decisions.
Examples include early warnings about possible overdrafts, identification of unusual spending that may signal fraud, and recommendations to adjust spending or savings habits. This level of intelligence transforms digital banking from a transactional tool into a daily financial companion.
Personalisation Capability Matrix
AI Capability | Practical Banking Application | Customer Outcome
Spending pattern analysis | Daily transaction monitoring | Better money awareness
Predictive alerts | Overdraft and cash-flow warnings | Reduced financial stress
Behavioural insights | Habit and trend identification | Smarter spending decisions
Fraud-related signals | Unusual activity detection | Faster customer response
Product relevance engine | Context-based product suggestions | Higher adoption rates
Impact on Customer Engagement and Retention
Banks using Personetics consistently report strong improvements in customer engagement metrics. By delivering advice that feels relevant and helpful, customers interact with their banking apps more frequently and are more likely to adopt additional financial products.
Engagement and Retention Impact Table
Metric | Observed Improvement | Business Impact
Mobile app engagement | Double-digit growth | Higher digital stickiness
Product adoption | Noticeable increase | Revenue expansion
Customer retention | Meaningful improvement | Lower churn
Customer satisfaction | Strong uplift | Better brand trust
These outcomes show that personalisation drives both customer value and bank profitability.
Empowering Smaller and Mid-Sized Banks in 2026
In 2026, Personetics is particularly valuable for small and medium-sized banks. Traditionally, advanced financial guidance was limited to private banking clients. Personetics allows these banks to deliver similar levels of personalised advice at scale through AI.
This capability helps smaller institutions compete with larger banks by offering intelligent digital experiences without the cost of expanding human advisory teams.
Bank Size Advantage Matrix
Bank Type | Traditional Limitation | Personetics Advantage
Small banks | Limited advisory resources | AI-driven guidance at scale
Mid-sized banks | Pressure from large competitors | Differentiated digital experience
Large banks | High customer volumes | Consistent personalisation
Supporting Financial Wellbeing and Sustainable Banking
Personetics places strong emphasis on financial wellbeing rather than aggressive selling. Its AI encourages responsible financial behaviour by helping customers anticipate issues and plan ahead. This approach supports sustainable banking models where long-term trust and customer success drive profitability.
Financial Wellbeing Use Case Matrix
Use Case | AI Insight Provided | Long-Term Benefit
Cash-flow management | Income vs expense forecasting | Fewer negative balances
Spending awareness | Category-level insights | Better budgeting
Savings encouragement | Smart nudges | Improved financial resilience
Fraud awareness | Behaviour-based alerts | Reduced losses
Illustrative Bar Chart Representation (Text-Based)
Impact Area Comparison
Customer engagement increase: ████████████████████████
Customer satisfaction improvement: █████████████████████
Product adoption growth: ████████████████████
Retention improvement: ███████████████████
These bars highlight that the strongest gains come from engagement and trust rather than short-term sales.
Why Personetics Ranks Among the Best AI Tools for Retail Banking in 2026
Personetics earns its place among the top AI tools for retail banking in 2026 because it turns customer data into practical, human-centred financial guidance. Its ability to deliver private-banking-style insights through digital channels makes it a powerful differentiator for banks of all sizes.
For retail banks seeking to improve engagement, strengthen retention, and support customer financial wellbeing while building sustainable revenue, Personetics Hyper-Personalization stands out as one of the most effective and proven AI solutions available.
10. Microsoft Dynamics 365

Microsoft plays a central role in shaping how retail banks adopt AI at enterprise scale in 2026. Through Dynamics 365 and the introduction of Agent 365, Microsoft focuses on helping banks deploy AI in a controlled, compliant, and revenue-focused way. Rather than positioning AI as a standalone tool, Microsoft integrates intelligence directly into everyday banking operations, customer engagement, and decision-making systems.
Agent 365 was introduced to address one of the biggest challenges banks face with AI adoption: how to scale automation and intelligence without losing governance, transparency, or regulatory control. This makes Microsoft a preferred choice for large and mid-sized banks that need both innovation and stability.
Agent 365 and AI Control at Scale
Agent 365 is designed to help organisations manage large numbers of AI agents across business functions while maintaining oversight. In retail banking, this means AI can support lending teams, customer service agents, fraud analysts, and relationship managers without creating uncontrolled automation risks.
Microsoft’s approach centres on making processes human-led and AI-operated. Humans remain accountable for decisions, while AI handles data processing, pattern recognition, and execution at speed. This balance is particularly important in regulated banking environments.
AI Operating Model Comparison Matrix
Operating Model | Description | Retail Banking Outcome
Human-only processes | Manual and slow | Limited scalability
AI-only automation | Fast but risky | Compliance concerns
Human-led, AI-operated | Controlled and scalable | Sustainable AI adoption
Revenue-Focused AI Transformation in Banking
Microsoft’s AI strategy for retail banking goes beyond cost reduction. The primary objective in 2026 is revenue growth through smarter processes, new products, and faster decision cycles. Banks using Microsoft’s AI tools to re-architect their core processes report significantly higher returns compared to slower adopters.
So-called advanced adopters of Microsoft AI consistently report returns on investment that are roughly three times higher than organisations that delay adoption. This performance gap highlights the commercial advantage of early, well-governed AI deployment.
Revenue Enablement Use Case Matrix
AI Use Case | Banking Function | Revenue Impact
AI-assisted lending | Mortgages and personal loans | Faster approvals, higher conversion
Customer insight models | Relationship management | Better cross-sell and upsell
AI-driven service | Contact centres | Higher retention
Fraud intelligence | Transaction monitoring | Asset protection
AI Adoption Trends in Financial Services
Industry research shows that a significant portion of financial services firms are actively planning AI initiatives with a direct revenue focus. Rather than experimental projects, banks are prioritising use cases that improve profitability and customer lifetime value.
Planned AI Investment Focus Table
Planned AI Objective | Share of Firms | Banking Implication
Revenue growth | 36 percent | AI tied to commercial outcomes
Operational efficiency | High | Cost optimisation
Risk and fraud protection | High | Balance sheet protection
Customer experience | Growing | Competitive differentiation
These figures indicate that AI in banking is shifting from experimentation to execution.
Practical Retail Banking Applications
In retail banking, Microsoft Dynamics 365 combined with Agent 365 is commonly used to streamline lending workflows, automate mortgage processing, and improve fraud detection. AI agents support document review, data validation, and customer communication, reducing cycle times without increasing risk.
Application Impact Matrix
Banking Area | AI Role | Operational Benefit
Lending | Workflow automation | Faster decisions
Mortgages | Document analysis | Reduced processing time
Fraud analysis | Pattern detection | Lower losses
Customer service | Assisted agents | Better resolution rates
Responsible AI and Regulatory Readiness
A major competitive advantage for Microsoft in retail banking is its emphasis on responsible AI. Governance, explainability, and compliance controls are embedded throughout the AI lifecycle, from data ingestion to decision execution.
This approach allows banks to treat regulatory complexity as a strength rather than a barrier. By standardising responsible AI practices, banks can scale innovation while maintaining trust with regulators and customers.
Responsible AI Framework Matrix
AI Lifecycle Stage | Governance Control | Banking Benefit
Data ingestion | Quality and bias checks | Reliable inputs
Model training | Transparency controls | Explainable outcomes
Deployment | Usage monitoring | Risk reduction
Audit and reporting | Full traceability | Regulatory confidence
Illustrative Bar Chart Representation (Text-Based)
Impact Area Comparison
Revenue uplift from AI adoption: ████████████████████████
Process speed improvement: █████████████████████
Risk and compliance confidence: ███████████████████████
Operational efficiency gains: ███████████████████
These bars highlight that revenue growth and governance strength are the most significant benefits.
Why Microsoft Dynamics 365 and Agent 365 Rank Among the Best AI Tools for Retail Banking in 2026
Microsoft earns its place among the top AI tools for retail banking in 2026 by combining enterprise-grade AI, strong governance, and direct revenue impact. The integration of Agent 365 allows banks to scale AI safely while keeping humans in control of critical decisions.
For retail banks looking to modernise operations, unlock new revenue streams, and manage regulatory complexity with confidence, Microsoft Dynamics 365 and Agent 365 provide a robust, future-ready AI platform suited for long-term transformation.
Global Macroeconomic Dynamics and the AI Growth Engine
The global economic environment in 2026 is defined by steady overall expansion combined with persistent uncertainty. While major economies continue to grow, this growth is constantly influenced by geopolitical tensions, trade disputes, political instability, and uneven recovery across regions. As a result, governments and enterprises are operating in an environment where resilience, adaptability, and risk management are no longer optional but essential.
Within this context, artificial intelligence has emerged as a stabilising force for economic growth. Rather than acting as a cyclical investment, AI has become a structural component of modern economies, helping businesses and institutions absorb shocks from fluctuating trade conditions, volatile consumer confidence, and sector-specific downturns.
Artificial Intelligence as a Global Growth Engine
By 2026, AI is widely recognised as a core driver of economic momentum across advanced and emerging markets. A measurable share of recent economic growth in large economies can be directly linked to sustained investment in AI-related infrastructure. This includes spending on high-performance data centres, advanced networking equipment, power and energy systems, and specialised semiconductor technologies required to support large-scale AI workloads.
AI Infrastructure Contribution Overview
Indicator | Observed Trend | Economic Meaning
Share of growth tied to AI investment | Approximately 1 percent of total growth | Structural, not cyclical, contribution
Primary investment areas | Data centres, power grids, semiconductors | Long-term capacity building
Economic role | Growth stabiliser | Buffers shocks from trade and demand shifts
The scale of this investment is unprecedented. Global AI infrastructure spending reached close to 1.5 trillion USD in 2025 and is expected to exceed 2 trillion USD in 2026. This level of capital deployment creates a powerful economic buffer, especially as large economies manage housing market slowdowns, tighter monetary conditions, and evolving trade relationships.
Global AI Infrastructure Spending Trajectory
Year | Estimated Global AI Infrastructure Spend
2024 | Under 1.2 trillion USD
2025 | Around 1.5 trillion USD
2026 | Exceeding 2 trillion USD
This trajectory shows that AI investment is accelerating rather than plateauing, reinforcing its role as a long-term economic foundation.
Translation of Macroeconomic Forces into Retail Banking
For retail banking, these global macroeconomic forces directly influence strategic priorities and budget allocation. Banks are no longer investing in technology primarily for long-term experimentation. Instead, they are reallocating capital away from legacy infrastructure and toward cloud-based, AI-driven platforms that deliver near-term efficiency gains and measurable business outcomes.
This shift reflects a broader recognition that traditional systems lack the flexibility required to operate in a volatile economic environment. AI platforms, particularly those built around automation, analytics, and intelligent decisioning, allow banks to respond faster to market changes while maintaining cost discipline.
Retail Banking Technology Reallocation Matrix
Legacy Focus Area | New AI-Driven Focus | Strategic Outcome
On-premise systems | Cloud-native AI platforms | Faster scalability
Manual workflows | Intelligent automation | Lower operating costs
Static analytics | Predictive and agentic AI | Better foresight
Fragmented systems | Unified AI operating layers | Greater agility
AI-Led Deal Activity and Market Urgency
Recent sector data shows that AI has moved from being an optional enhancement to a central requirement in banking technology decisions. Nearly three-quarters of all new contracts signed by major IT service providers are now AI-led. This signals a strong sense of urgency among banks to embed intelligence deeply into their operating models.
This urgency is driven by three primary objectives: improving agility, increasing predictability in outcomes, and achieving sustainable cost efficiency. Banks that delay AI adoption increasingly face competitive disadvantages in speed, customer experience, and risk management.
Technology Deal Composition in Banking
Deal Type | Share of New Deals | Implication
AI-led engagements | Approximately 74 percent | AI-first strategies dominate
Traditional IT upgrades | Declining rapidly | Limited strategic value
Pure cost-cutting initiatives | Secondary priority | Efficiency now AI-driven
Data Centre Expansion as the Fastest-Growing Segment
Within the broader AI investment landscape, data centre systems represent the fastest-growing expenditure category. Spending on data centre infrastructure is projected to grow by more than 20 percent in 2026, following an exceptional growth rate of nearly 30 percent in the previous year. This reflects the computational intensity of modern AI models and the rise of agentic intelligence across industries.
For retail banking, this expansion supports real-time analytics, large-scale fraud detection, personalised customer interactions, and the orchestration of autonomous AI agents across business functions.
AI Infrastructure Growth Focus
Infrastructure Component | Growth Trend | Banking Relevance
Data centres | Very high growth | Real-time AI processing
Networking | High growth | Low-latency decisioning
Energy systems | Rising importance | AI sustainability
Specialised chips | Strategic priority | Model performance
Illustrative Bar Chart Representation (Text-Based)
Growth Driver Comparison
Data centre systems: █████████████████████████
AI infrastructure overall: ███████████████████████
Traditional IT spending: ████████████
This visual highlights how decisively investment has shifted toward AI-centric infrastructure.
Connection to the Global Shift Toward Agentic Intelligence
The macroeconomic and infrastructure trends of 2026 directly enable the global shift toward agentic intelligence in retail banking. As AI platforms become more powerful and scalable, banks are transitioning from isolated automation to agent-based systems that can plan, decide, and act across complex workflows.
This structural transformation marks a fundamental change in how banks operate. Intelligence is no longer confined to analytics teams or back-office automation. Instead, it is embedded across lending, servicing, risk, compliance, and customer engagement, supported by the massive AI infrastructure investments occurring at the global level.
Why These Dynamics Matter for the Top AI Platforms in Retail Banking
The top AI platforms shaping retail banking in 2026 are a direct product of these macroeconomic forces. Their success depends on access to scalable infrastructure, cloud-native architectures, and the ability to deliver measurable value quickly. Banks selecting AI platforms today are effectively aligning themselves with the broader economic transformation driven by AI.
As global economies continue to invest heavily in AI capacity, retail banking stands at the centre of this shift, using agentic intelligence not only to improve efficiency but to redefine how financial services are delivered in an increasingly complex and uncertain world.
Global AI Spending in IT Markets 2024-2026
Between 2024 and 2026, global investment in artificial intelligence across IT markets has shifted from rapid expansion to full-scale structural transformation. What was once considered emerging technology spend has become core infrastructure investment for both private enterprises and regulated industries such as retail banking. By 2026, AI spending is no longer experimental or peripheral; it represents a foundational layer of global digital economies.
This surge in investment directly underpins the transformation of retail banking toward agentic intelligence, where AI systems do not simply assist human workers but actively plan, decide, and execute tasks within controlled governance frameworks.
Overall Growth of Global AI Spending
Global AI spending across IT markets has more than doubled in just two years. This growth reflects aggressive adoption across software, infrastructure, services, and semiconductor layers that together enable large-scale AI deployment.
Global AI Spending Summary Table
Market Segment | 2024 Spending (Million USD) | 2025 Spending (Million USD) | 2026 Forecast (Million USD)
AI Services | 259,477 | 282,556 | 324,669
AI Application Software | 83,679 | 172,029 | 269,703
AI Infrastructure Software | 56,904 | 126,177 | 229,825
Generative AI Models | 5,719 | 14,200 | 25,766
AI-Optimized Servers | 140,107 | 267,534 | 329,528
AI-Optimized Infrastructure-as-a-Service | 7,447 | 18,325 | 37,507
AI Processing Semiconductors | 138,813 | 209,192 | 267,934
Total Global AI Spending | 987,904 | 1,478,634 | 2,022,642
By 2026, total global AI spending exceeds 2 trillion USD, clearly signaling that AI has become a permanent and expanding pillar of global IT markets.
Acceleration Patterns Across AI Categories
Not all AI categories are growing at the same pace. Software layers that directly enable intelligence and autonomy show the fastest growth, reflecting the shift from infrastructure build-out to applied, operational AI.
Growth Acceleration Matrix
AI Category | Growth Pattern | Strategic Meaning
AI Services | Steady, sustained growth | Enterprise integration and advisory demand
AI Application Software | Explosive growth | AI embedded in business workflows
AI Infrastructure Software | Rapid acceleration | Scaling and orchestration of AI systems
Generative AI Models | High percentage growth | Foundation for agentic intelligence
AI-Optimized Servers | Large absolute growth | Compute-intensive AI workloads
AI-Optimized IaaS | High growth from small base | Cloud-based AI scalability
AI Processing Semiconductors | Strategic expansion | Performance and efficiency gains
This pattern shows that spending is shifting decisively toward software and platforms that enable autonomous and agent-based AI systems.
Why Application Software Spending Is Surging
AI application software spending grows from under 84 billion USD in 2024 to nearly 270 billion USD by 2026. This is one of the most important signals for retail banking. It indicates that enterprises are no longer buying AI as isolated tools, but as embedded intelligence within core systems such as lending, payments, fraud detection, onboarding, and customer engagement.
Retail banks are major contributors to this category, as they invest heavily in AI platforms that directly influence revenue, risk management, and operational efficiency.
Retail Banking Relevance Matrix
AI Software Area | Retail Banking Use | Business Outcome
Customer intelligence | Personalised engagement | Higher retention
Lending automation | Faster approvals | Increased conversion
Fraud analytics | Real-time risk control | Loss prevention
Service orchestration | AI-assisted agents | Lower cost-to-serve
Infrastructure Spending as the Backbone of Agentic Intelligence
Infrastructure-related categories, including AI-optimized servers, AI infrastructure software, and processing semiconductors, together represent the physical and logical backbone of agentic intelligence. Without this layer, autonomous AI systems cannot operate reliably at scale.
By 2026, AI-optimized servers alone account for more than 329 billion USD in annual spending. This reflects the computational demands of running real-time decision engines, large language models, and multi-agent systems across global enterprises.
Infrastructure Emphasis Table
Infrastructure Layer | 2026 Spending Level | Role in AI Transformation
AI-optimized servers | Very high | Real-time processing
AI infrastructure software | Rapidly expanding | AI orchestration and control
AI semiconductors | Strategic priority | Performance and efficiency
Cloud AI infrastructure | High growth | Elastic scalability
Illustrative Spending Growth Bar Chart (Text-Based)
AI Application Software: █████████████████████████
AI Infrastructure Software: ███████████████████████
AI-Optimized Servers: █████████████████████
AI Processing Semiconductors: ███████████████████
AI Services: █████████████████
This visual highlights that applied AI and infrastructure are the primary drivers of total spending growth.
Implications for the Structural Transformation of Retail Banking
The scale and direction of global AI spending explain why retail banking is undergoing structural transformation rather than incremental change. Banks are no longer constrained by limited compute, siloed systems, or narrow AI tools. Instead, they are deploying end-to-end AI platforms capable of supporting agentic workflows across the entire institution.
This investment environment enables the rise of AI agents that can manage lending pipelines, monitor fraud continuously, personalise customer journeys, and support compliance operations with minimal human intervention.
Connection to the Top 10 AI Platforms in Retail Banking
The top AI platforms reshaping retail banking in 2026 are direct beneficiaries of this global spending surge. These platforms sit primarily within the fastest-growing categories: AI application software, AI infrastructure software, and AI services. Their success is tied to the availability of scalable compute, advanced models, and cloud-native infrastructure funded by trillions in global investment.
As projected by Gartner and IDC, AI spending trends confirm that agentic intelligence is not a future concept but a present operational reality.
Why This Matters for the Future of Banking
By 2026, retail banking operates within an AI-first global IT economy. Institutions that align with this spending shift gain access to superior intelligence, faster decision cycles, and resilient operating models. Those that fail to adapt face rising costs, slower response times, and declining competitiveness.
The global AI spending trajectory makes one conclusion clear: the structural transformation of retail banking is inseparable from the expansion of AI across IT markets, and agentic intelligence is the natural outcome of this historic reallocation of capital and technology.
The Rise of Agentic AI and the Autonomous Enterprise
By 2026, the retail banking industry is undergoing its most profound operational transformation in decades. The central driver of this change is the rise of agentic AI, which has moved from experimental concepts into large-scale, production-grade deployment. Unlike the chatbots and basic predictive tools of earlier years, agentic AI systems are designed to act with a degree of autonomy while remaining governed, auditable, and explainable.
These systems can coordinate multiple tasks, manage real customer requests, and execute decisions across complex workflows. As a result, banks are redefining how work gets done, replacing long manual processes that once took weeks with AI-driven operations that can be completed in minutes.
What Agentic AI Means for Modern Retail Banking
Agentic AI refers to semi-autonomous systems that can plan actions, execute tasks, and collaborate with other AI agents and human teams. In retail banking, this capability enables end-to-end automation across lending, servicing, compliance, fraud detection, and customer engagement.
Instead of AI simply responding to prompts, agentic systems actively manage workflows. They monitor conditions, trigger actions, escalate exceptions, and document decisions automatically. This marks a shift from AI as a support tool to AI as an operational participant.
Agentic AI Capability Comparison
AI Generation | Core Characteristics | Banking Impact
Early chatbots | Scripted responses | Limited efficiency gains
Predictive AI models | Forecasting and scoring | Improved insights
Agentic AI systems | Orchestration and decision execution | Structural operational change
Investment Momentum Behind Agentic AI Adoption
The financial commitment to AI in banking reflects how critical this transition has become. By 2026, financial services institutions are expected to spend more than 67 billion USD annually on AI initiatives. The fastest-growing portion of this spending is not pilots or experimentation, but production deployments tied directly to decision-making and daily operations.
This investment shift signals that agentic AI is no longer viewed as optional innovation. It is now seen as core infrastructure for competitiveness, cost control, and regulatory resilience.
AI Spending Focus in Financial Services
AI Investment Area | Growth Trend | Strategic Purpose
Experimental pilots | Declining | Limited business value
Analytics and insights | Stable | Decision support
Agentic AI in production | Rapid growth | End-to-end automation
Governed AI platforms | Strong growth | Compliance and trust
The Role of Multiagent Systems in Scaling Automation
To support this new operating model, banks are increasingly adopting Multiagent Systems. These systems consist of multiple specialised AI agents that work together toward shared business goals. Each agent is designed for a specific task, such as credit assessment, document verification, fraud analysis, or customer communication.
This modular approach reduces the risks associated with large, monolithic AI systems. It also allows banks to reuse proven agents across different workflows, accelerating deployment and simplifying regulatory updates.
Multiagent System Benefits Matrix
Design Principle | Operational Benefit | Banking Outcome
Modular agents | Reusable intelligence | Faster scaling
Distributed decisioning | Reduced system risk | Higher resilience
Workflow collaboration | End-to-end automation | Lower processing time
Regulatory adaptability | Easier model updates | Improved compliance
Domain-Specific Language Models and Banking Accuracy
Another critical enabler of agentic AI in banking is the rise of Domain-Specific Language Models. Unlike general-purpose models, these systems are trained on specialised financial data, terminology, and regulatory frameworks. This results in higher accuracy, lower operational costs, and better compliance outcomes.
By 2026, domain-specific models are widely used across retail banking for tasks such as contract analysis, policy interpretation, customer communication, and regulatory reporting. Industry forecasts from Gartner indicate that more than half of enterprise generative AI models will be domain-specific by 2028, a trend that is already well established in banking.
Model Comparison Matrix
Model Type | Accuracy in Banking Tasks | Cost Efficiency | Compliance Fit
Generic language models | Medium | Lower | Limited
Domain-specific models | High | Higher | Strong
The Emergence of Agentic Commerce and Robo-Shopping
As agentic AI moves into full production, banks must also respond to a new external challenge: agentic commerce. In this environment, personal AI agents acting on behalf of consumers can independently search for mortgage rates, negotiate terms, compare offers, or even initiate transactions.
This shift fundamentally changes how banks interact with customers. Instead of dealing only with humans, banks increasingly interact with machines that demand real-time data, pricing, and decisions through APIs.
Impact of Agentic Commerce on Banking Channels
Interaction Type | 2026 Trend | Operational Impact
Human website visits | Declining by around 20 percent | Lower traditional traffic
AI-agent queries | Rising by around 40 percent | Higher API demand
Automated negotiations | Increasing | Pricing and risk complexity
New Risk and Dispute Dynamics Created by Agentic AI
The rise of agentic commerce introduces new operational and risk challenges. Disputes increase when customers claim they did not explicitly approve actions taken by their AI agents. Fraud teams face new threats from malicious actors who hijack or impersonate legitimate agents. Customer service teams must manage more complex cases involving machine-to-machine interactions rather than simple user errors.
Agentic Risk Management Matrix
Risk Area | New Challenge | Required Bank Response
Dispute handling | Agent-initiated actions | Clear audit trails
Fraud detection | Agent impersonation | Behavioural verification
Customer trust | Reduced transparency | Explainable AI decisions
Why Agentic AI Defines the Autonomous Enterprise
Together, these developments mark the transition toward the autonomous enterprise in retail banking. In this model, AI agents handle continuous operations, humans focus on oversight and strategy, and governance frameworks ensure accountability at every stage.
Agentic AI does not remove human control. Instead, it reshapes roles, allowing banks to operate faster, more accurately, and at greater scale than was previously possible. This transformation is not incremental; it is structural.
Connection to the Top 10 AI Platforms in Retail Banking
The leading AI platforms driving retail banking in 2026 are those that support agentic architectures, multiagent coordination, and domain-specific intelligence. These platforms enable banks to move beyond isolated automation and build fully orchestrated, AI-operated operating models.
As retail banking continues its shift toward autonomous operations, agentic AI stands at the centre of this transformation, redefining how financial services are delivered in an increasingly machine-driven economy.
The Transformation of Trust and the New Frontier of Fraud
By 2026, trust in retail banking is no longer defined by brand reputation or customer promises alone. It has evolved into a measurable, operational performance indicator that directly influences customer retention, regulatory confidence, and competitive positioning. Banks are now assessed by how effectively they protect customers, prevent fraud, and respond to threats in real time.
This transformation is driven by an unprecedented rise in AI-enabled fraud, particularly deepfake-based attacks. Over the past three years, deepfake-related fraud attempts have increased by more than 2,100 percent, fundamentally changing the risk landscape. As a result, trust has become quantifiable through metrics such as fraud prevention rates, response times, false-positive accuracy, and customer safety perception.
Trust Transformation Overview
Trust Dimension | Traditional View | 2026 Reality
Customer trust | Brand promise | Measured safety outcomes
Fraud prevention | Reactive controls | Continuous verification
Risk management | Departmental | Unified AI-driven operations
Customer loyalty | Convenience-driven | Safety-driven
The Economic Impact of Generative AI–Enabled Fraud
The financial consequences of advanced fraud are accelerating rapidly. Generative AI–enabled fraud losses are projected to reach 40 billion USD annually in the United States by 2027. This scale of loss has forced banks to rethink fraud prevention as a core operational capability rather than a specialised function.
To respond effectively, retail banks are unifying fraud detection, decisioning, and case management into single AI-powered platforms. Fragmented systems are no longer sufficient when attacks spread across channels in seconds.
Fraud Cost and Operational Pressure
Fraud Indicator | Observed Trend | Banking Implication
Deepfake fraud attempts | Exponential growth | Identity verification overhaul
AI-driven scam losses | Tens of billions USD | Balance sheet risk
Attack speed | Near-instant | Real-time response required
Channel overlap | High | Unified systems essential
Operationalising Trust as a Competitive Advantage
In 2026, the most successful banks are those that can operationalise trust. This means embedding continuous verification, behavioural intelligence, and content-authenticity checks directly into customer journeys. Rather than reacting after fraud occurs, leading institutions stop attacks before they escalate.
This shift has created a competitive race where established banks can outperform digital-first challengers. By unifying customer data, transaction flows, and risk intelligence into AI-driven platforms, incumbents match digital natives on speed while exceeding them in governance, auditability, and regulatory alignment.
Competitive Trust Advantage Matrix
Bank Capability | Low Maturity Outcome | High Maturity Outcome
Fragmented systems | Slow fraud response | Real-time prevention
Isolated data | Blind spots | Holistic risk visibility
Manual reviews | High friction | Seamless protection
Weak governance | Compliance risk | Regulatory confidence
Emerging Agentic Fraud Threats in 2026
Fraud in 2026 is no longer limited to stolen credentials or manual scams. Criminals are now exploiting agentic AI to scale deception and bypass controls. One major threat involves hijacking or mimicking legitimate AI agents used by banks or customers, allowing unauthorised transactions to appear valid.
Another rapidly growing threat is the evolution of romance scams. Fraudsters now use large language models to automate emotional manipulation, tailoring messages at scale while maintaining human-like interaction. These scams are harder to detect using traditional rule-based systems.
Emerging Fraud Typology Matrix
Fraud Type | New Agentic Capability | Risk Level
Deepfake identity fraud | Synthetic voice and video | Very high
Agent impersonation | Hijacked AI agents | Critical
Automated romance scams | Emotionally adaptive AI | High
Cross-channel fraud | Multi-touchpoint attacks | High
The Shift to AI-Native Fraud and AML Defense
To counter these threats, retail banks are rapidly adopting cloud-native, AI-driven fraud and anti-money-laundering platforms. These systems analyse behavioural signals, transaction context, device intelligence, and network patterns in real time. This enables banks to detect subtle, coordinated attacks that legacy systems cannot identify.
AI is no longer viewed as an enhancement to fraud operations. It is now considered essential infrastructure for AML modernisation. Institutions that delay adoption of explainable, real-time analytics face higher compliance risk, slower response times, and declining customer trust.
Fraud Defense Evolution Matrix
Defense Approach | Detection Speed | Accuracy | Compliance Readiness
Rule-based systems | Slow | Low | Weak
Hybrid systems | Moderate | Medium | Limited
AI-native platforms | Real-time | High | Strong
Illustrative Threat and Defense Comparison (Text-Based Chart)
Relative escalation of risks and defenses in 2026:
Deepfake fraud growth: █████████████████████████
Agent impersonation risk: ███████████████████████
AI-native fraud defense capability: ██████████████████████████
Legacy fraud system effectiveness: ███████
This comparison highlights the widening gap between modern threats and outdated controls.
Why Trust Defines the Future of Retail Banking
In 2026, customers evaluate banks not only by ease of use, but by how protected they feel. Trust has become the most important differentiator in retail banking, outweighing convenience and even pricing in many decisions. Banks that successfully embed AI-driven trust frameworks gain long-term loyalty, regulatory confidence, and resilience against increasingly sophisticated threats.
Connection to the Top 10 AI Platforms in Retail Banking
The leading AI platforms transforming retail banking in 2026 are those that treat trust as an operational system rather than a marketing message. These platforms integrate fraud prevention, identity verification, decision intelligence, and case management into unified, explainable, and scalable architectures.
As the industry continues its structural transformation toward agentic intelligence, trust becomes the foundation on which all other capabilities are built. Retail banks that master this shift position themselves not only to survive the AI era, but to lead it.
Operational Excellence and the Future of Work
By 2026, retail banking is experiencing a deep internal transformation that is less visible to customers but fundamental to long-term competitiveness. This change is driven by how banks build software, manage data, and organise work. Rather than relying on slow, centralised IT models, banks are adopting flexible architectures and AI-supported development practices that dramatically improve speed and efficiency.
Digital-first banking challengers are using modular system design and rapid experimentation to launch new services quickly. At the same time, established banks are closing the gap by deploying AI copilots across engineering, operations, and analytics teams, allowing them to modernise without abandoning scale or regulatory discipline.
AI Copilots and the Acceleration of Software Delivery
AI copilots have become a core productivity tool inside banks by 2026. These systems assist developers with coding, testing, documentation, and troubleshooting. The result is a major uplift in engineering output and faster delivery of customer-facing features.
Industry research from McKinsey shows that AI copilots can increase developer productivity by around 40 percent. This improvement allows banks to move from multi-year transformation cycles to continuous delivery models, where enhancements are released in months rather than years.
Developer Productivity Impact Overview
Capability Area | Before AI Copilots | With AI Copilots
Code creation | Manual, time-intensive | Assisted and accelerated
Testing and debugging | Bottleneck-prone | Automated suggestions
Release cycles | Annual or multi-year | Continuous and rapid
Feature time-to-market | Slow | Significantly faster
This productivity shift directly supports the broader transformation toward agentic intelligence, where software must evolve quickly to support new AI-driven workflows.
Why Data Foundations Define AI Success
Despite these advances, AI effectiveness in banking remains tightly linked to data quality. Banks operating on fragmented legacy systems struggle to scale AI beyond isolated pilots. Inconsistent data definitions, siloed ownership, and poor accessibility limit the value of even the most advanced AI tools.
By 2026, leading banks recognise that modern data architecture is not optional. To become truly AI-ready, they are rebuilding data foundations to ensure consistency, traceability, and real-time availability across the organisation.
Data Readiness Comparison Matrix
Data Environment | AI Outcome | Scalability
Fragmented legacy data | Pilot-only AI | Low
Partially modernised data | Limited production use | Medium
Unified AI-ready data | Enterprise-wide AI | High
The Rise of Data Mesh and Data Fabric Models
To solve these challenges, banks are adopting concepts such as data mesh and data fabric. These approaches move away from single, centralised data warehouses and instead treat data as a shared but well-governed asset.
Data mesh emphasises domain ownership, where business teams are responsible for their data products. Data fabric focuses on intelligent integration, allowing data to be discovered and accessed across systems without constant reengineering. Together, these models create a foundation that supports scalable, flexible, and fast AI deployment.
Modern Data Architecture Benefits
Architecture Principle | Practical Benefit | AI Impact
Domain-owned data | Clear accountability | Higher data quality
Unified access layer | Easier discovery | Faster model deployment
Real-time integration | Up-to-date insights | Better decisions
Standard governance | Consistency and trust | Regulatory confidence
The Move Toward In-House AI Development
Another defining trend in 2026 is the shift toward internal AI development. As banks gain clearer visibility into AI returns, many mid-sized institutions are choosing to bring AI capabilities in-house rather than relying entirely on external vendors.
This move is driven by several factors: better cost control, stronger alignment with business needs, and reduced dependency on third parties for critical systems. As AI becomes core infrastructure rather than an add-on, ownership becomes a strategic priority.
In-House vs External AI Development Matrix
Approach | Advantages | Limitations
External-only vendors | Faster initial setup | Long-term dependency
Hybrid model | Balanced flexibility | Coordination complexity
In-house development | Full control and alignment | Requires talent investment
Hub-and-Spoke Governance for Scalable AI
To manage growing internal AI capabilities, banks are adopting hub-and-spoke governance models. In this structure, a central team—often an AI Centre of Excellence—defines standards, platforms, and policies. Individual business units then build and operate AI solutions within those guardrails.
This model balances control with agility. Central teams ensure consistency, security, and compliance, while business lines remain accountable for treating data as a product and delivering measurable outcomes.
Hub-and-Spoke Governance Structure
Governance Layer | Responsibility | Outcome
Central AI hub | Standards and platforms | Consistency and safety
Business units | Data products and use cases | Speed and relevance
Shared oversight | Risk and compliance | Scalable trust
Illustrative Internal Transformation Chart (Text-Based)
Relative impact of internal changes in 2026:
Developer productivity uplift: █████████████████████████
Speed of feature delivery: ███████████████████████
Data readiness for AI: █████████████████████
Governance maturity: ███████████████████
This visual shows that productivity and data foundations are the strongest drivers of internal transformation.
Why Operational Excellence Enables Agentic Intelligence
The shift toward agentic intelligence in retail banking depends as much on internal capability as on external platforms. AI agents cannot operate reliably without fast development cycles, trusted data, and clear governance. Operational excellence becomes the enabler that allows AI platforms to move from experimentation into mission-critical use.
Connection to the Top 10 AI Platforms in Retail Banking
The leading AI platforms transforming retail banking in 2026 are designed to plug into modern data architectures, support internal development teams, and operate within governed environments. Banks that combine these platforms with strong internal execution models gain a lasting advantage in speed, resilience, and innovation.
In the structural transformation of retail banking, operational excellence is no longer a support function. It is the foundation upon which agentic intelligence and the autonomous bank are built.
Regional Insights and Global Market Trends
By 2026, the global adoption of AI in retail banking no longer follows a single pattern. Instead, it reflects sharp regional differences in strategy, maturity, and ambition. While all major markets recognise AI as essential, the way banks deploy intelligence varies significantly depending on economic conditions, regulatory environments, and consumer behaviour.
These regional contrasts are critical to understanding the structural transformation of retail banking and the global shift toward agentic intelligence. They explain why some markets are accelerating toward autonomous banking models, while others move more cautiously.
Asia-Pacific as the Engine of AI-Led Reinvention
The Asia-Pacific region stands out in 2026 as the most aggressive adopter of AI in retail banking. Banks across this region are using AI not only to reduce costs, but to reinvent business models, launch new products, and capture growth in highly competitive markets.
Research shows that organisations in Asia-Pacific are already redirecting approximately 64 percent of their AI investment toward core business functions. These include lending, payments, customer engagement, and risk management, where returns are measurable and immediate. This focus reflects a pragmatic approach: AI must deliver revenue impact, not just operational efficiency.
APAC AI Investment Focus Matrix
Investment Area | Share of AI Spend | Strategic Objective
Core banking functions | 64 percent | Direct revenue and growth
Operational efficiency | Secondary | Cost optimisation
Customer engagement | High priority | Market differentiation
Innovation initiatives | Strong | New digital models
Consumer Behaviour Shifts in AI-First Markets
In several Asia-Pacific markets, consumer behaviour is evolving rapidly alongside AI adoption. In major Chinese metropolitan areas, one in ten recent loan applicants reported using generative AI as their primary research tool. This signals a major shift in how customers discover, compare, and select financial products.
For banks, this trend reinforces the importance of machine-readable pricing, real-time APIs, and AI-ready product information. Human-centric websites alone are no longer sufficient in markets where customers increasingly rely on personal AI agents to make financial decisions.
North America and the Push for Experience-Led Innovation
North America remains the single largest regional market for AI in retail banking in 2026, accounting for roughly 35 percent of global market share. Banks in this region focus heavily on innovation, customer experience, and advanced analytics.
Rather than wholesale reinvention, North American institutions emphasise embedding AI into existing platforms to improve personalisation, fraud prevention, and service quality. Agentic AI is increasingly used to support customer service, lending decisions, and marketing optimisation, often within well-established digital ecosystems.
North America Market Characteristics
Focus Area | Dominant Priority | Outcome
Customer experience | Very high | Differentiation
Advanced analytics | High | Better decisioning
AI governance | Strong | Regulatory confidence
Operational automation | Growing | Incremental efficiency
Europe and the Governance-First Approach
Europe represents approximately 30 percent of the global AI banking market in 2026, but its trajectory differs from both North America and Asia-Pacific. European banks operate within a more complex regulatory environment, with compliance and ethical AI considerations shaping adoption strategies.
The region continues to grow close to its long-term economic trend, but comparatively lower levels of AI infrastructure investment may limit future competitiveness. European banks prioritise explainability, risk controls, and alignment with evolving AI regulations, sometimes at the expense of speed.
European Banking AI Priorities
Priority Area | Emphasis Level | Strategic Trade-Off
Regulatory compliance | Very high | Slower deployment
Explainable AI | High | Strong trust framework
Operational innovation | Moderate | Incremental change
Agentic autonomy | Cautious | Risk-managed rollout
India as a Global AI Engineering Hub
India plays a unique role in the global retail banking AI ecosystem. By 2026, approximately 74 percent of IT services deals originating from India are AI-led. This reflects the country’s position as a global hub for digital engineering, AI development, and large-scale system integration.
Indian firms support banks worldwide by building, integrating, and scaling AI platforms, particularly in areas such as automation, analytics, and agentic system orchestration. This makes India a critical enabler of the global shift toward autonomous banking operations.
Regional Market Share Snapshot for 2026
Region | Estimated Market Share | Key Theme
North America | 35 percent | Innovation and customer experience
Europe | 30 percent | Governance and compliance
Asia-Pacific | 25 percent | AI super apps and reinvention
India | Services-led influence | AI engineering and delivery
AI Self-Funding Expectations Across Regions
A notable global trend in 2026 is the expectation that AI investments will increasingly fund themselves. Around 95 percent of global executives anticipate that generative AI will be at least partially self-funded through productivity gains, efficiency improvements, and revenue uplift.
This expectation reinforces the shift away from experimental AI budgets toward performance-driven investment models. Regions that focus AI on core business outcomes are more likely to achieve this self-funding dynamic.
AI Return Expectation Matrix
Expectation | Global Sentiment | Implication for Banks
Self-funded AI | Very high | Performance accountability
Short payback cycles | Increasing | Faster deployment
ROI-driven prioritisation | Strong | Fewer experimental pilots
Illustrative Regional Momentum Chart (Text-Based)
Relative AI momentum by region in 2026:
Asia-Pacific innovation pace: ████████████████████████
North America CX focus: █████████████████████
Europe governance maturity: ███████████████████
India AI engineering scale: █████████████████████████
This visual highlights how different regions lead on different dimensions of AI adoption.
Why Regional Differences Matter for the Global Banking Transformation
The structural transformation of retail banking in 2026 cannot be understood without recognising these regional dynamics. The top AI platforms shaping the industry must operate across vastly different regulatory, cultural, and economic contexts while supporting a global shift toward agentic intelligence.
Banks that understand regional strengths and constraints are better positioned to choose the right AI platforms, deploy them effectively, and compete in an increasingly AI-driven financial ecosystem. In this global landscape, success depends not only on technology, but on how well institutions adapt AI strategies to their regional realities.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026
By 2026, retail banking has entered a decisive phase where artificial intelligence is no longer an optional enhancement or experimental capability. It has become the primary engine of competitiveness, resilience, and long-term relevance. The industry has reached what many describe as an AI reckoning, clearly separating institutions that have industrialised intelligence from those still trapped in fragmented pilots and tactical use cases.
Banks that lead in this new environment are those that have embraced agentic AI as an operating model rather than a technology layer. In these institutions, semi-autonomous AI systems carry the operational workload, while human teams focus on judgement, relationships, and trust-building, which remain essential in financial services.
This structural shift defines the future of banking and shapes the strategic priorities that institutions must adopt to succeed.
From Tactical AI to Industrialised Intelligence
The most successful banks in 2026 treat AI as core infrastructure, not as a standalone initiative. They deploy intelligence across lending, servicing, fraud prevention, compliance, and customer engagement in a unified way. In contrast, lagging institutions continue to run disconnected AI tools that fail to scale or deliver consistent value.
AI Maturity Comparison Table
AI Approach | Characteristics | Strategic Outcome
Tactical experimentation | Isolated pilots, limited scope | Minimal impact
Functional AI adoption | Department-level deployment | Partial efficiency gains
Industrialised AI | Enterprise-wide, agentic systems | Structural advantage
This maturity gap continues to widen, making early and decisive action critical.
Strategic Pillar One: Modernise Data as the Foundation of Agentic AI
The first and most critical recommendation for 2026 is the modernisation of data infrastructure. Agentic AI systems depend on fast, reliable, and well-governed data. Without this foundation, even the most advanced AI platforms cannot deliver enterprise-level transformation.
Leading banks are embracing data mesh and related architectures that treat data as a product, owned by business domains but governed centrally. This ensures that AI agents can access clean, structured, and auditable data across the organisation.
Data Strategy Readiness Matrix
Data Architecture | AI Readiness | Enterprise Impact
Fragmented legacy data | Low | AI remains experimental
Centralised but rigid data | Medium | Limited scalability
Data mesh and fabric | High | Full agentic deployment
Modern data foundations turn AI from a promise into a repeatable capability.
Strategic Pillar Two: Operationalise Trust as a Competitive Advantage
Trust has become the defining currency of retail banking in 2026. Customers no longer judge banks only by convenience or pricing, but by how safe, transparent, and reliable they feel. This shift is driven by the rise of deepfake fraud, agent impersonation, and AI-enabled financial crime.
Winning banks operationalise trust by unifying fraud detection, decisioning, and case management across all channels. AI is used not only to detect threats in real time, but also to explain decisions clearly to customers, regulators, and internal teams.
Trust Enablement Framework Table
Trust Capability | Low Maturity State | High Maturity State
Fraud detection | Reactive and siloed | Real-time and unified
Decision transparency | Limited | Explainable and auditable
Customer protection | After-the-fact response | Preventive intelligence
Regulatory posture | Defensive | Confidence-driven
Institutions that can prove their intelligence and protect customers from evolving threats secure long-term loyalty and relevance.
Strategic Pillar Three: Drive Intelligent Growth Through Embedded AI
The third strategic priority for 2026 is a shift from efficiency-driven AI to intelligent growth. This means embedding AI into every decision and customer interaction to increase the lifetime value of relationships, not just to reduce costs.
Leading banks are using hyper-personalised insights, proactive financial guidance, and invisible payments to move beyond transactional banking. AI anticipates customer needs, automates routine actions in the background, and supports better financial outcomes without constant user intervention.
Growth Strategy Evolution Table
Banking Model | Value Delivered | Customer Perception
Utility banking | Transactions only | Replaceable
Digital banking | Convenience and speed | Competitive
Intelligent banking | Personalised, proactive support | Trusted partner
This evolution allows banks to become part of customers’ daily lives rather than occasional service providers.
Illustrative Strategic Impact Chart (Text-Based)
Relative importance of strategic priorities in 2026:
Data modernisation impact: █████████████████████████
Trust and security advantage: ███████████████████████
Intelligent growth enablement: █████████████████████
This visual highlights that data and trust are prerequisites for sustainable growth.
The Shift from Promise to Proof in Banking Strategy
By 2026, the era of AI promises has ended. Regulators, customers, and shareholders now expect proof: measurable outcomes, explainable decisions, and consistent performance. Banks that fail to demonstrate real value from AI investments risk losing both market share and credibility.
Agentic AI represents the next frontier of this proof-driven era. When implemented correctly, it reduces operational burden, improves decision quality, and allows human teams to focus on empathy, judgement, and relationship-building.
The Future Belongs to the Intelligent Enterprise
The structural transformation of retail banking in 2026 makes one conclusion unavoidable. The future belongs to institutions that combine industrialised AI, trusted data foundations, and customer-centric intelligence into a single operating model.
Banks that follow these strategic recommendations do not merely adopt new technology. They redefine how banking works. In an environment shaped by agentic intelligence, the winners are those that move decisively from experimentation to execution and from promise to proof, becoming truly intelligent enterprises built for long-term relevance.
Conclusion
As the retail banking industry moves deeper into 2026, it is increasingly clear that artificial intelligence is no longer an emerging capability or a competitive add-on. It has become the structural foundation on which modern banking operates. The top AI tools shaping retail banking today are not simply improving efficiency at the margins; they are redefining how banks engage customers, manage risk, deliver products, and sustain trust in an environment of constant technological and economic change.
What distinguishes the leading AI platforms in retail banking is their shift from isolated automation toward fully integrated, agentic intelligence. These systems go beyond dashboards, chatbots, or basic analytics. They orchestrate workflows, make governed decisions, and act in real time across lending, payments, fraud prevention, compliance, and customer engagement. This transition marks a decisive break from the digital transformation efforts of the past decade and signals the arrival of the autonomous, intelligence-driven bank.
A central theme across the best AI tools for retail banking in 2026 is scale with control. Banks are no longer choosing between speed and governance. The most successful platforms embed explainability, auditability, and regulatory readiness directly into their AI architectures. This allows institutions to deploy advanced intelligence at enterprise scale while maintaining accountability, customer trust, and compliance with evolving global regulations. In a world of deepfakes, agent impersonation, and AI-enabled financial crime, trust has become a measurable outcome, and AI is now the primary mechanism for delivering it.
Another defining insight from the 2026 landscape is the growing importance of data foundations. Even the most advanced AI tools cannot deliver sustained value without clean, well-structured, and well-governed data. Leading banks are pairing AI adoption with modern data architectures that treat data as a product and enable real-time access across the organisation. This combination allows AI systems to move from experimental pilots to mission-critical operations that support millions of customers simultaneously.
The best AI tools in retail banking are also driving a fundamental shift in growth strategy. Rather than focusing solely on cost reduction, banks are using AI to increase the lifetime value of customer relationships. Hyper-personalised insights, proactive financial guidance, intelligent lending decisions, and invisible payments are transforming banks from transactional utilities into trusted financial partners embedded in customers’ daily lives. This evolution is especially important as customer expectations continue to rise and competition extends beyond traditional financial institutions to technology-driven ecosystems.
From an operational perspective, AI is reshaping the future of work inside banks. Development cycles are shorter, decision-making is faster, and human teams are increasingly focused on judgement, empathy, and complex problem-solving rather than repetitive tasks. Agentic AI systems handle the operational burden, while people provide the oversight and human connection that remain essential in financial services. This balance between automation and human leadership defines the modern banking organisation.
Looking ahead, the significance of choosing the right AI platforms in 2026 cannot be overstated. The top AI tools discussed in this landscape are not interchangeable solutions; they represent long-term strategic commitments. Banks that align themselves with platforms capable of agentic orchestration, real-time analytics, and enterprise-grade governance position themselves to adapt as technology, regulation, and customer behaviour continue to evolve.
Ultimately, the story of retail banking in 2026 is the story of moving from promise to proof. Artificial intelligence is no longer judged by vision statements or pilot results, but by measurable outcomes: safer transactions, faster decisions, stronger customer relationships, and resilient operations. The banks that succeed are those that treat AI as core infrastructure, invest in the right platforms, and embed intelligence into every layer of their organisation.
In this environment, the top AI tools for retail banking are not just enabling transformation; they are defining what modern banking is. Institutions that embrace this reality will lead the next era of financial services, while those that hesitate risk falling behind in an industry where intelligence, trust, and speed have become the ultimate competitive advantages.
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your hiring manager and C-level suite friends and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the 9cv9 Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.
To get access to top-quality guides, click over to 9cv9 Blog.
To hire top talents using our modern AI-powered recruitment agency, find out more at 9cv9 Modern AI-Powered Recruitment Agency.
People Also Ask
What are AI tools in retail banking?
AI tools in retail banking are software platforms that use machine learning and automation to improve lending, fraud detection, customer service, compliance, and decision-making at scale.
Why are AI tools critical for retail banking in 2026?
In 2026, AI is essential because banks face rising fraud risks, higher customer expectations, and pressure to reduce costs while delivering faster, more personalised services.
What makes an AI tool suitable for retail banking?
A strong retail banking AI tool must be secure, explainable, scalable, and compliant, while delivering real-time insights across customer, risk, and operational workflows.
How do AI tools improve customer experience in banking?
AI tools personalise interactions, provide proactive financial guidance, automate routine tasks, and deliver faster service, making banking more relevant and convenient for customers.
What is agentic AI in retail banking?
Agentic AI refers to semi-autonomous systems that can plan, decide, and act across workflows, handling tasks like approvals, monitoring, and customer support with human oversight.
How do AI tools help with fraud detection?
AI tools analyse behaviour, transactions, and patterns in real time to detect fraud early, reduce false positives, and stop complex attacks such as deepfake and agent impersonation fraud.
Are AI tools replacing human bankers?
AI tools do not replace human bankers; they handle repetitive and data-heavy work so humans can focus on judgement, relationships, and complex decision-making.
What role does data play in AI banking tools?
High-quality, well-governed data is essential, as AI tools rely on accurate, real-time data to deliver reliable insights, predictions, and automated decisions.
What is the difference between traditional automation and AI tools?
Traditional automation follows fixed rules, while AI tools learn from data, adapt to new patterns, and support intelligent decision-making across dynamic banking processes.
How do AI tools support lending and credit decisions?
AI tools assess risk faster, analyse more data points, reduce bias, and speed up approvals, improving both customer experience and portfolio performance.
What are the risks of using AI tools in banking?
Risks include data quality issues, bias, explainability gaps, and security concerns, which is why governance and responsible AI frameworks are critical.
How do AI tools help banks reduce operational costs?
They automate manual processes, reduce errors, improve productivity, and enable straight-through processing across servicing, compliance, and back-office operations.
What is hyper-personalisation in retail banking AI?
Hyper-personalisation uses AI to deliver tailored insights, offers, and guidance based on individual customer behaviour, preferences, and financial context.
Are AI tools compliant with banking regulations?
Leading AI tools are built with compliance in mind, offering explainability, audit trails, and governance features that support regulatory requirements.
How do AI tools improve compliance and AML operations?
They monitor transactions in real time, detect complex patterns, reduce manual reviews, and provide explainable insights for regulatory reporting.
What is the importance of explainable AI in banking?
Explainable AI helps banks understand and justify decisions, build customer trust, and meet regulatory expectations for transparency.
How do banks measure ROI from AI tools?
Banks measure ROI through cost savings, faster processing times, reduced fraud losses, higher customer retention, and increased product adoption.
What are multiagent systems in retail banking?
Multiagent systems use multiple specialised AI agents that work together to handle complex processes, improving scalability and resilience.
How do AI tools support digital transformation in banks?
AI tools modernise legacy systems, enable real-time intelligence, and support new digital products and services without full system replacement.
Can small and mid-sized banks benefit from AI tools?
Yes, AI tools allow smaller banks to deliver advanced personalisation, fraud protection, and automation that was once only available to large institutions.
What is the role of cloud in AI banking tools?
Cloud infrastructure provides scalability, speed, and flexibility, enabling AI tools to operate in real time and handle large data volumes.
How do AI tools handle deepfake and identity fraud?
They use behavioural analysis, biometrics, and continuous verification to detect synthetic identities and impersonation attempts.
What trends define AI in retail banking for 2026?
Key trends include agentic AI, real-time fraud prevention, hyper-personalisation, responsible AI, and enterprise-wide automation.
How do AI tools improve decision-making in banks?
They provide predictive insights, scenario analysis, and real-time recommendations, helping banks make faster and more accurate decisions.
What is responsible AI in retail banking?
Responsible AI ensures fairness, transparency, security, and accountability in AI systems, reducing risk and increasing trust.
How long does it take to implement AI tools in banks?
Implementation time varies, but modern AI platforms allow phased deployment, with early benefits often seen within months.
Do AI tools increase customer trust in banks?
Yes, when implemented correctly, AI tools improve security, transparency, and service quality, making customers feel safer.
What skills do banks need to use AI tools effectively?
Banks need data literacy, AI governance expertise, and cross-functional collaboration between technology and business teams.
How will AI tools shape the future of retail banking?
AI tools will enable autonomous operations, deeper customer relationships, stronger risk control, and more resilient, intelligent banks.
Sources
Backbase
PR Newswire
SS&C Blue Prism
CIO Dive
Gartner
Deutsche Bank
Barclays Investment Bank
The Economic Times
Morningstar
Kore.ai
Forrester
CFOtech India
Matrix BCG
nCino
WilmingtonBiz
Tracxn
SDK.finance
Apps Run The World
IBS Intelligence
GetGenerative
Grazitti Interactive
Salesforce
ZenML
Integrate
SiliconANGLE
The SaaS News
Feedzai
G2
Eesel AI
Personetics
Microsoft
Deloitte
Citizens Bank
Manila Bulletin
Business Research Insights































![Writing A Good CV [6 Tips To Improve Your CV] 6 Tips To Improve Your CV](https://blog.9cv9.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/2020-06-02-2-100x70.png)


