Key Takeaways
- Secure Anywhere, Work Everywhere: Learn how VPNs empower employees to work securely from any location, ensuring data confidentiality and protecting against cyber threats.
- Encryption: The Digital Fortress: Explore the importance of robust encryption protocols in VPNs, providing a stronghold for sensitive information in the era of remote work.
- Future-Proofing with VPN Technology: Uncover the future trends shaping VPNs, from quantum-resistant encryption to blockchain integration, ensuring your workplace stays ahead in the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape.
In the dynamic landscape of the modern workplace, where the boundaries between office desks and home workstations are increasingly blurred, the significance of robust cybersecurity measures cannot be overstated.
As organizations embrace the flexibility of remote work, the need for secure connectivity becomes paramount, ushering in the era where Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) emerge as unsung heroes safeguarding the integrity of digital interactions.
The Evolution of Remote Work: A Paradigm Shift
The 21st century has witnessed a paradigm shift in how we perceive and engage with work.
Traditional office setups are making way for flexible arrangements, allowing employees to contribute from the comfort of their homes, coffee shops, or co-working spaces.
This transition, while fostering a newfound sense of autonomy, introduces a plethora of cybersecurity challenges that demand innovative solutions.
Unveiling the Power of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
At the heart of this cybersecurity arsenal lies the Virtual Private Network, a technological marvel designed to create a secure and encrypted tunnel over the vast expanse of the internet.
Understanding the importance of VPNs in the modern workplace requires delving into their fundamental functionality, unraveling the layers of protection they provide to both employees and the sensitive data they handle.
Navigating the Perils of Unsecured Networks
As the boundaries of the workplace extend beyond physical office premises, the vulnerabilities associated with unsecured networks come to the forefront.
Coffee shop Wi-Fi, airport lounges, or even the seemingly innocuous home network can be breeding grounds for cyber threats.
Herein lies the crux of the matter — the imperative need to fortify these digital pathways.
Data Privacy in the Digital Age: A Non-negotiable Priority
In an era dominated by digitization and interconnectedness, the stakes of data privacy have never been higher.
The modern workplace, characterized by the seamless flow of information between devices and networks, necessitates a vigilant approach to safeguarding sensitive data.
VPNs emerge as the guardians of privacy, encrypting each piece of information in transit and ensuring that only authorized eyes lay witness to the digital exchange.
Securing Remote Access: Beyond the Conventional Office Walls
The advent of remote work has liberated employees from the confines of the traditional office setting, offering unprecedented flexibility.
Yet, this newfound freedom demands a reevaluation of how organizations secure remote access to critical company resources. VPNs, by establishing secure channels between the user and the company’s network, bridge the geographical gap without compromising on data security.
In the intricate tapestry of the modern workplace, where threads of innovation and connectivity interweave, the importance of VPNs stands out as a foundational element.
This blog will embark on a comprehensive journey, exploring the multifaceted role that VPNs play in securing remote work.
From understanding their core functionality to deciphering the nuanced benefits they bring to HR professionals and employees alike, we delve deep into the world of VPNs, unraveling their significance in the ever-evolving landscape of the modern workplace.
Join us as we navigate the digital realm, unlocking the secrets to a secure and productive remote work experience.
Before we venture further into this article, we like to share who we are and what we do.
About 9cv9
9cv9 is a business tech startup based in Singapore with a strong presence all over the world.
With over six years of startup and business experience, and being highly involved in connecting with thousands of companies and startups, the 9cv9 team has listed some important learning points in this overview of the Importance of VPNs in the Modern Workplace.
If your company needs recruitment and headhunting services, you can use 9cv9 headhunting and recruitment services to hire top talents and candidates. Find out more here, or send over an email to [email protected].
Or just post 1 free job posting here at 9cv9 Hiring Portal in under 10 minutes.
Importance of VPNs in the Modern Workplace: Securing Remote Work
- Understanding VPNs
- Challenges in Remote Work Security
- The Role of VPNs in Remote Work Security
- Benefits of VPNs for Modern Workplaces
- Choosing the Right VPN for Your Workplace
- Best Practices for Implementing VPNs in the Workplace
- Future Trends in VPN Technology
1. Understanding VPNs: Navigating the Digital Fortress
In an era where digital communication transcends geographical boundaries, understanding the intricacies of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) becomes imperative.
This section aims to demystify the functionality of VPNs, exploring how they create a secure conduit in the vast expanse of the internet.
Definition and Core Functionality of VPNs
- VPNs, or Virtual Private Networks, are encrypted tunnels that facilitate secure data transmission over the internet.
- They operate by routing your internet connection through a server and encrypting the data exchanged between your device and the server.

How VPNs Ensure Secure Communication Over the Internet
- Encryption Protocols: VPNs employ robust encryption protocols such as OpenVPN, IKEv2/IPsec, and L2TP/IPsec to encode data packets, rendering them indecipherable to potential attackers.
- Secure Authentication: VPNs utilize authentication methods, ensuring that only authorized users can access the network. This adds an additional layer of protection against unauthorized access.
VPNs as Digital Guardians: A Real-world Analogy
- Imagine a VPN as a secure, private tunnel connecting your device to a destination on the internet. This tunnel ensures that your data travels in a protected environment, shielding it from prying eyes.
- Just as a physical tunnel provides a safe passage through challenging terrain, a VPN creates a digital pathway through the potentially hazardous landscape of the internet.
Navigating the Cybersecurity Landscape with VPNs: A Practical Example
- Public Wi-Fi Risks: Public Wi-Fi networks, often used in coffee shops or airports, are notorious for their susceptibility to cyber threats. Without a VPN, sensitive data transmitted over such networks is at risk of interception.
- Data Breach Statistics: According to a report, 58% of data breach victims in 2020 were small businesses. Implementing VPNs is crucial for businesses of all sizes to mitigate the risks associated with data breaches.

The Role of VPNs in Bypassing Geographical Restrictions
- VPNs are instrumental in circumventing geographical content restrictions, allowing users to access region-specific content by masking their IP address.
- Streaming Services: Users can access a broader range of content on streaming platforms by connecting to a server in a region where that content is available.
VPNs and Corporate Security: A Case Study
- Case Study: IBM’s Remote Work Transition: During the COVID-19 pandemic, IBM successfully transitioned its global workforce to remote work. VPNs played a pivotal role in ensuring the security of sensitive corporate data accessed by employees working from various locations.

Growth in VPN Usage: A Statistical Overview
- Global VPN Market Growth: According to a report, the global VPN market is projected to grow at an expected CAGR of 16.28%, set to reach a staggering USD 47.82 billion by 2028, underscoring the increasing adoption of VPN solutions across industries.
Future Trends in VPN Technology
- VPN technology is evolving rapidly to meet the challenges posed by emerging cyber threats. From the integration of Artificial Intelligence for threat detection to the development of decentralized VPNs, the future promises innovative solutions to enhance digital security.
Understanding VPNs is not just a matter of grasping technical jargon; it’s about recognizing their pivotal role in creating a secure digital environment.
As we delve deeper into the nuances of VPN functionality, we unveil the layers of protection they offer in an ever-evolving landscape of digital communication.
2. Challenges in Remote Work Security: Navigating the Digital Perils
In the era of widespread remote work, organizations grapple with a myriad of cybersecurity challenges that demand strategic solutions.
This section illuminates the significant challenges faced in securing remote work environments, shedding light on real-world examples and statistics that underscore the urgency of robust security measures.
Risks Associated with Unsecured Networks
- Public Wi-Fi Vulnerabilities: Public Wi-Fi networks, ubiquitous in coffee shops and airports, pose a significant threat. Cybercriminals can exploit these networks to intercept sensitive data, potentially leading to data breaches.
- Data Breach Impact: The average cost of a data breach in 2023 was $4.45 million, as reported.
The Human Element: Employee Practices and Awareness
- Phishing Attacks: Remote employees are often targeted through phishing schemes, where malicious actors impersonate legitimate entities to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information.
- Phishing Statistics: According to a Report, 36% of breaches involved phishing attacks.
Endpoint Security Concerns
- Device Security: With employees using a variety of devices for remote work, ensuring consistent endpoint security becomes a challenge. Unsecured devices can become entry points for cyber threats.
- Device Proliferation: The number of connected devices globally is expected to reach 29 billion by 2030, according to Statista.
Balancing Security and Employee Productivity
- Access Controls: Striking a balance between providing employees with the necessary access to perform their tasks and restricting access to sensitive information is a delicate challenge.
Patch Management in a Decentralized Environment
- Software Vulnerabilities: Remote work environments often have varied software configurations. Ensuring that all devices are consistently updated with the latest security patches becomes a logistical challenge.
- Unpatched Software Risks: According to a study, 57% of organizations experienced a data breach due to unpatched vulnerabilities.
Data Privacy and Compliance
- Regulatory Compliance: Remote work brings forth challenges in adhering to data protection regulations. Ensuring that remote practices align with global and industry-specific compliance standards is crucial.
- GDPR Fines: One of the highest GDPR fines to date was €50 million, imposed on Google by the French data protection authority for lack of transparency and consent regarding ad personalization.
The Role of VPNs in Mitigating Remote Work Security Challenges
- VPN Encryption: Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) play a vital role in mitigating many of the challenges associated with remote work. By encrypting data transmission, VPNs safeguard against the risks posed by unsecured networks.
- VPN Adoption Trends: A report indicates a 165% increase in VPN usage worldwide in 2020, underscoring their growing importance in the remote work landscape.
Future Outlook: Adapting to Evolving Cyber Threats
- Emerging Threats: The landscape of cyber threats is continually evolving. Organizations must stay vigilant and adapt security measures to counter new and sophisticated threats.
- Cybersecurity Spending: Global spending on cybersecurity is projected to reach USD 266.2 billion by 2027, as organizations recognize the need to invest in robust security infrastructure.
Navigating the challenges of remote work security demands a multifaceted approach. By understanding the specific risks and leveraging technologies like VPNs, organizations can fortify their defenses against the evolving threat landscape.
3. The Role of VPNs in Remote Work Security: Fortifying the Digital Frontier
In the era of remote work, where digital connectivity is the lifeblood of organizational operations, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) emerge as indispensable guardians of data security.
This section delves into the multifaceted role that VPNs play in fortifying remote work environments, substantiated by real-world examples and statistical insights.
Encrypting Data Transmission: Ensuring Confidentiality
- VPN Encryption Protocols: VPNs employ robust encryption protocols such as AES-256 to encode data, rendering it indecipherable to unauthorized entities.
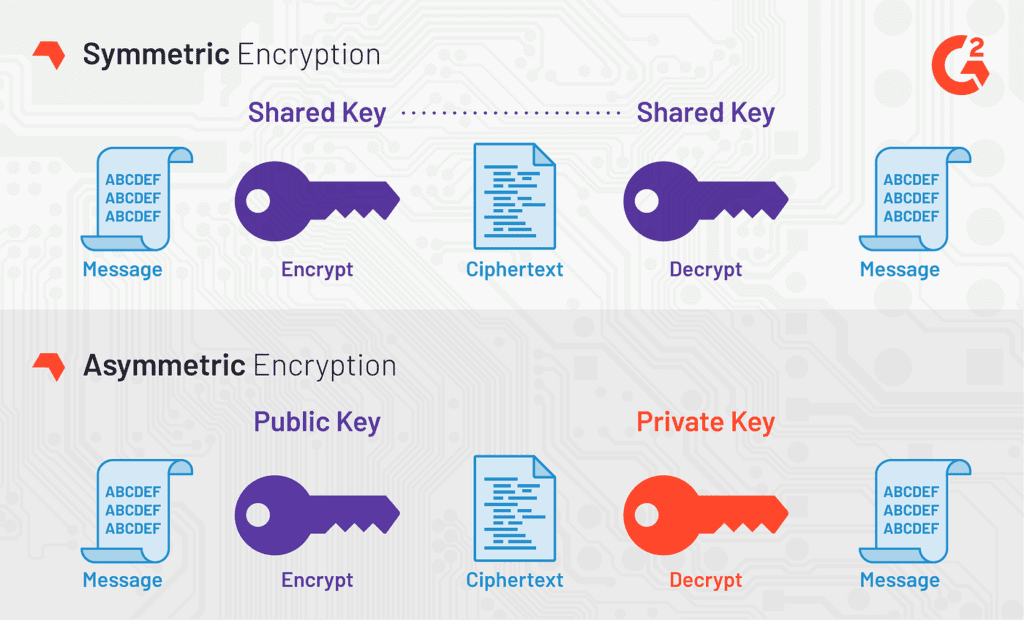
Securing Remote Access to Company Resources
- Establishing Secure Tunnels: VPNs create secure tunnels between remote devices and corporate networks, ensuring that data transmitted between them remains confidential.
- Remote Access Trends: As per a Gartner survey, 82% of company leaders plan to allow remote work post-pandemic, emphasizing the ongoing need for secure remote access solutions.
Mitigating the Risks of Public Wi-Fi Usage
- VPN Shield for Public Networks: When employees connect to public Wi-Fi, a VPN acts as a shield, encrypting data and preventing cybercriminals from intercepting sensitive information.
- Public Wi-Fi Risks: According to a study, more than 60% of users believe their personal information is secure when using public Wi-Fi, highlighting the need for education and VPN adoption.
Enhanced Data Security for HR Professionals
- Protecting Hiring Data: HR professionals deal with sensitive hiring information. VPNs safeguard this data, ensuring that candidate details, resumes, and communication remain confidential.
- HR Data Breach Impact: The global average cost of a data breach in 2023 was USD 4.45 million.
Facilitating Secure Communication Channels
- Encrypted Communication Platforms: VPNs complement secure communication platforms by adding an extra layer of encryption to ensure that internal discussions and collaborations are protected.
- Communication Security Trends: With the rise of remote work, the market for secure communication platforms is projected to grow at a CAGR of 16.7% and reach a valuation of USD 24b during the forecast period of 2031.
Adapting to the Evolving Landscape of Cyber Threats
- VPN Threat Detection: VPNs are evolving to incorporate threat detection mechanisms, identifying and mitigating potential security risks in real-time.
- Cyber Threat Landscape: The number of new malware variants increased by 358%, underscoring the need for adaptive security measures.
Choosing the Right VPN for Your Workplace
- Considerations for HR Managers:
- VPNs vary in features and security levels. HR managers must consider factors such as encryption strength, user authentication, and ease of use.
- VPN Market Overview: The global VPN market size will likely grow from USD 42.80b in 2022 to USD 106.80b by 2025, at a CAGR of 20.2%, indicating a wide array of options for organizations to choose from.
Comparative Analysis of Top VPNs in the Market
- User Reviews and Ratings: Assessing user reviews and ratings provides valuable insights into the user experience and effectiveness of different VPN solutions.
The role of VPNs in remote work security transcends mere encryption; it encapsulates the empowerment of organizations to navigate the digital landscape securely.
As we explore the various dimensions of this role, it becomes evident that VPNs are not just tools; they are integral components of a resilient and secure remote work infrastructure.
4. Benefits of VPNs for Modern Workplaces: Empowering Secure and Flexible Operations
In the contemporary landscape of modern workplaces, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) stand as linchpins of cybersecurity, facilitating secure and flexible operations.
This section unveils the myriad benefits that VPNs bring to the table, supported by real-world examples and substantiated by relevant data.
Enhanced Data Security and Confidentiality
- Encryption Safeguards: VPNs use robust encryption protocols, such as AES-256, to protect data during transmission, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential.
- Data Breach Impact: The average cost of a data breach in 2023 was $4.45 million, emphasizing the financial impact that organizations can avoid by employing VPNs.
Facilitating Seamless Remote Work
- Secure Remote Access: VPNs enable employees to securely access company resources from any location, fostering a seamless and productive remote work environment.
- Remote Work Trends: According to a survey, 83% of companies reported that the adoption of remote work has been successful and has even exceeded expectations.

Overcoming Geographical Content Restrictions
- Access to Global Content: VPNs allow employees to bypass geographical content restrictions, enabling access to region-specific online resources and services.
- Global Content Consumption: As of 2023, global internet users spent an average of 6 hours and 41 minutes online daily, showcasing the importance of seamless content access.
Secure Communication Channels for Collaboration
- Encrypted Collaboration Platforms: VPNs complement secure collaboration platforms, ensuring that internal communications, meetings, and file sharing remain confidential.
- Collaboration Tool Usage: The collaboration software market size exceeded USD 16.1b in 2022 and is projected to observe around 12% CAGR from 2023 to 2032, indicating a growing reliance on digital collaboration.
Protection of Intellectual Property and Sensitive Information
- Guarding Corporate Assets: VPNs play a crucial role in protecting intellectual property and sensitive company information from cyber threats and potential espionage.
Securing Financial Transactions and Customer Data
- E-commerce Security: For organizations engaged in e-commerce, VPNs provide a secure environment for financial transactions, safeguarding customer data and payment information.
- E-commerce Growth: Revenue in the e-commerce Market is projected to reach US$2,928.00bn in 2023.
Regulatory Compliance and Data Protection
- GDPR Compliance: VPNs assist organizations in adhering to data protection regulations like GDPR, ensuring that personal and sensitive data is handled in compliance with legal standards.

Flexibility and Adaptability in the Face of Cyber Threats
- VPN Evolution: VPN technology is evolving to counter emerging cyber threats, providing organizations with adaptable tools to stay ahead of evolving security challenges.
- Cyber Threat Landscape: According to Cybersecurity Ventures, the cost of cybercrime is projected to hit an annual $10.5 trillion by 2025.
Cost-Effective Security Measures
- Reducing Security Costs: Implementing VPNs can be a cost-effective security measure, potentially mitigating the financial impact of data breaches and cyberattacks.
In the modern workplace, where the digital realm is synonymous with operations, the benefits of VPNs extend beyond mere security.
They become catalysts for flexible and efficient work structures, laying the foundation for a resilient and agile organizational ecosystem.
5. Choosing the Right VPN for Your Workplace: Navigating the Landscape of Security Solutions
Selecting the right Virtual Private Network (VPN) for your workplace is a pivotal decision that demands careful consideration.
This section explores the key factors HR managers should weigh when choosing a VPN, offering insights, examples, and data to guide the decision-making process.
Considerations for HR Managers in Selecting VPN Solutions
- User-Friendly Interface: A VPN with an intuitive interface ensures that employees can easily navigate and use the tool without extensive training.
- Employee Productivity: A user-friendly VPN can contribute to employee productivity by reducing the learning curve associated with adopting new technology.
Encryption Strength and Security Features
- Advanced Encryption Protocols: Ensure the VPN employs strong encryption protocols such as AES-256 to safeguard data during transmission.
Server Network and Geographic Coverage
- Global Server Network: A VPN with an extensive server network provides employees with reliable and fast connections, irrespective of their geographical location.
- VPN Market Leaders: Leading VPN providers boast expansive server networks covering various regions.

Speed and Performance
- Bandwidth and Speed: Assess the VPN’s impact on internet speed, ensuring that it does not significantly compromise the performance of critical applications.
Logging Policies and Privacy Standards
- No-Logs Policy: Choose a VPN provider with a strict no-logs policy, ensuring that user activity is not recorded or stored.
- Privacy Concerns: A survey found that majority of consumers are concerned about their online privacy, highlighting the importance of VPNs with robust privacy practices.
Compatibility with Devices and Operating Systems
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Ensure the VPN supports various devices and operating systems, facilitating seamless integration into your organization’s tech ecosystem.
- Device Usage Trends: There are over 15 billion active mobile devices globally, emphasizing the need for VPNs compatible with mobile platforms (Source: Statista).
Reliability and Uptime
- Uptime Statistics: Assess the VPN provider’s historical uptime statistics to ensure consistent and reliable service availability.
Customer Support and Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
- Responsive Customer Support: Choose a VPN provider with responsive customer support to address any issues promptly.
- Downtime Costs: The average cost of IT downtime is estimated to be $5,600 per minute, highlighting the financial impact of service disruptions.
Comparative Analysis of Top VPNs in the Market
- User Reviews and Ratings: Examine user reviews and ratings to gain insights into the practical experiences of organizations using specific VPN solutions.
- VPN Rankings: Platforms regularly publish rankings and reviews of top VPN providers, aiding in informed decision-making.
Cost-Effectiveness and Value for Money
- Transparent Pricing: Evaluate the VPN’s pricing structure to ensure transparency and ascertain the value it brings to your organization.
- ROI of VPN Investment: While costs vary, the return on investment for VPNs is evident in the potential savings from avoiding data breaches and ensuring secure remote work practices.
Security Audits and Certifications
- Third-Party Audits: Choose VPN providers that undergo third-party security audits and hold certifications, demonstrating their commitment to robust security practices.
- Industry Standards: Certifications like ISO/IEC 27001 and SOC 2 signify adherence to globally recognized information security standards.
Making the right choice in VPN selection is paramount for HR managers seeking to fortify their organization’s cybersecurity infrastructure.
By meticulously considering these factors, organizations can ensure a secure and efficient remote work environment that aligns with the unique needs of their workforce.
6. Best Practices for Implementing VPNs in the Workplace: A Strategic Approach to Cybersecurity
Implementing Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) in the workplace is a pivotal step in fortifying cybersecurity.
This section delves into best practices that organizations should consider when integrating VPN solutions, supported by relevant examples and data-driven insights.
Training Employees on VPN Usage
- Educational Workshops: Conduct workshops or training sessions to familiarize employees with VPN usage, emphasizing the importance of secure online practices.
- Employee Awareness Impact: According to a study by CompTIA, organizations with a strong security awareness training program experience 70% fewer security incidents.
Regular Monitoring and Updating of VPN Systems
- Routine System Audits: Implement regular audits of VPN systems to identify vulnerabilities and ensure that security features are up to date.
- Unpatched Vulnerability Risks: The average time to patch a vulnerability is 38 days, emphasizing the need for proactive monitoring and patching.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Implementation
- Enhanced User Authentication: Integrate Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) with VPN access to add an extra layer of identity verification.
- MFA Effectiveness: According to Microsoft, enabling MFA can block 99.9% of automated attacks, significantly enhancing security.
Tailoring Access Controls Based on Job Roles
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Implement RBAC to ensure that employees only have access to the resources necessary for their specific job roles.
- Least Privilege Principle: Adhering to the principle of least privilege reduces the risk of unauthorized access, a key consideration in VPN implementation.
VPN Integration with Endpoint Security Solutions
- Comprehensive Endpoint Protection: Integrate VPNs with endpoint security solutions to provide a holistic approach to cybersecurity.
Incident Response Planning and Drills
- Simulated Cybersecurity Drills: Conduct drills to simulate cybersecurity incidents, ensuring that the organization is well-prepared to respond effectively.
VPN Usage Policies and Acceptable Use Guidelines
- Clear Usage Policies: Develop and communicate clear VPN usage policies and acceptable use guidelines to establish expectations for employees.
Integration with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems
- Real-time Monitoring: Integrate VPNs with SIEM systems for real-time monitoring of network activity and rapid detection of security incidents.
- SIEM Adoption Trends: The global SIEM market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9.8% from 2022 to 2030, showcasing the increasing adoption of SIEM solutions.
Regular Security Awareness Campaigns
- Continuous Employee Education: Implement ongoing security awareness campaigns to keep employees informed about emerging threats and best practices.
- Impact of Security Awareness: A study found that security awareness training can reduce the risk of a security incident by 70%.
Vendor Security Assessment and Due Diligence
- Thorough Vendor Evaluations: Before selecting a VPN provider, conduct a comprehensive security assessment and due diligence to ensure their reliability.
- Third-Party Security Risks: A survey indicates that 53% of organizations experienced a third-party breach, emphasizing the importance of vendor security evaluations.
Periodic Security Risk Assessments
- Identifying Vulnerabilities: Conduct regular security risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities in the VPN infrastructure.
Collaboration with IT and Security Teams
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Foster collaboration between IT, security, and HR teams to ensure a cohesive approach to VPN implementation and cybersecurity.
By adopting these best practices, organizations can create a robust and resilient cybersecurity posture, leveraging VPNs as integral components of their defense strategy.
This strategic approach ensures not only the security of remote work environments but also the overall integrity of the organizational infrastructure.
7. Future Trends in VPN Technology: Navigating the Evolving Landscape of Cybersecurity
The world of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) is continuously evolving to meet the challenges of an ever-changing cybersecurity landscape.
This section explores the future trends in VPN technology, offering insights into the innovations and advancements that will shape the next generation of secure digital communication.
Anticipated Developments in VPNs for Remote Work
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA):
- Definition: ZTNA is an approach that ensures no user or device is trusted by default, even if they are inside the corporate network.
- Implementation in VPNs: Future VPNs are likely to integrate ZTNA principles, providing a more dynamic and secure access control model.
- Cloud-Native VPNs:
- Shift to Cloud Environments: With the increasing adoption of cloud services, VPNs are expected to become more cloud-native, providing seamless integration with cloud infrastructures.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud-native VPNs offer scalability and flexibility, adapting to the dynamic resource demands of modern organizations.
Advanced Encryption and Quantum-Resistant Algorithms
- Post-Quantum Encryption:
- Quantum Computing Impact: With the rise of quantum computing, VPNs will likely adopt post-quantum encryption algorithms to secure communications against quantum threats.
- NIST Post-Quantum Cryptography Standardization: The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is actively standardizing post-quantum cryptographic algorithms.
- Homomorphic Encryption:
- Preserving Data Privacy: Homomorphic encryption allows computations on encrypted data without decrypting it, enhancing data privacy.
- Use Cases: Future VPNs may leverage homomorphic encryption to perform computations on encrypted data, maintaining confidentiality.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in VPN Security
- Threat Detection and Prevention:
- AI Algorithms: AI algorithms will play a crucial role in real-time threat detection, identifying and mitigating potential security risks.
- Adaptive Security: VPNs equipped with AI can adapt to evolving cyber threats, enhancing their ability to counter sophisticated attacks.
- User Behavior Analytics (UBA):
- Behavioral Patterns: AI-driven UBA in VPNs can analyze user behavior patterns to identify deviations that may indicate potential security breaches.
- Predictive Security Measures: By understanding normal behavior, AI can predict and prevent security incidents before they occur.
Decentralized VPNs and Blockchain Integration
- Decentralized VPNs:
- Peer-to-Peer Networks: Decentralized VPNs leverage peer-to-peer networks, reducing reliance on central servers.
- Enhanced Privacy: Users’ traffic is distributed across multiple nodes, enhancing privacy and reducing the risk of single points of failure.
- Blockchain for Security Assurance:
- Immutable Security Records: Blockchain integration in VPNs can create immutable records of security events, enhancing transparency and accountability.
- Smart Contracts: VPNs may utilize smart contracts on blockchain to automate security protocols and ensure contractual adherence.
Focus on Usability and User Experience
- Seamless Integration with Applications:
- API Integration: Future VPNs may seamlessly integrate with various applications and services through APIs, ensuring a user-friendly experience.
- User Adoption: Improved usability can contribute to increased user adoption of VPNs, enhancing overall cybersecurity.
- Intuitive User Interfaces:
- Graphical Representations: VPNs may incorporate more intuitive graphical representations of security status and settings for users.
- Reducing Human Error: User-friendly interfaces contribute to reducing the risk of human errors in VPN configuration and usage.
IPv6 Adoption and Address Space Expansion
- Transition to IPv6:
- Depletion of IPv4 Addresses: The depletion of IPv4 addresses necessitates the transition to IPv6, offering an expanded address space.
- IPv6 Support in VPNs: Future VPNs are likely to fully support IPv6, ensuring compatibility with the evolving internet infrastructure.
- Enhanced Security Features:
- Built-in IPsec Support: IPv6 often integrates with IPsec for improved security, and VPNs may offer built-in support for IPv6 and IPsec combinations.
- Network Layer Security: IPv6 enhances network layer security, aligning with the overarching goals of VPNs in securing digital communication.
Shift towards Edge Computing and VPNs
- Edge VPNs:
- Decentralized Processing: Edge VPNs may evolve to support the needs of edge computing, providing secure connections closer to the edge devices.
- Reduced Latency: Edge VPNs contribute to reduced latency by processing data closer to the source, improving overall performance.
- 5G Integration:
- Bandwidth Demands: With the rollout of 5G networks, VPNs will need to adapt to the increased bandwidth demands and connectivity options.
- Edge Computing in 5G Networks: VPNs can play a vital role in securing communications in edge computing environments powered by 5G networks.
Regulatory Compliance and Privacy Enhancements
- Global Data Protection Regulations:
- Adherence to GDPR and Similar Regulations: Future VPNs will likely focus on ensuring compliance with global data protection regulations, such as GDPR.
- Data Privacy as a Priority: VPNs will continue to prioritize user data privacy to align with evolving legal frameworks.
- Privacy-Centric VPN Services:
- No-Logs Policies: VPN providers emphasizing no-logs policies will gain prominence, assuring users of the protection of their sensitive data.
- Transparency Reports: Providers may issue transparency reports detailing government requests for user data, enhancing trust among users.
The future of VPN technology is poised to be dynamic and transformative, embracing innovations to address emerging cybersecurity challenges.
Organizations adopting these trends will position themselves at the forefront of secure and efficient digital communication in the years to come.
Conclusion
In the dynamic landscape of the modern workplace, the pivotal role of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) in securing remote work has never been more apparent.
As organizations increasingly embrace flexible work arrangements, the importance of VPNs transcends mere cybersecurity measures; they emerge as the bedrock of a secure, interconnected digital infrastructure.
Elevating Security to Unprecedented Heights
The contemporary workplace is not confined to the traditional office space; it extends to coffee shops, home offices, and public spaces.
VPNs, through robust encryption protocols and secure access controls, elevate the security of data transmission to unprecedented heights.
As remote work becomes the norm rather than the exception, the ability to navigate the digital landscape securely is paramount.
Mitigating Risks on Uncharted Digital Terrains
The risks associated with remote work, from the vulnerabilities of public Wi-Fi networks to the challenges of endpoint security, are effectively mitigated by the implementation of VPNs.
By creating secure tunnels and encrypting data, VPNs act as digital shields, safeguarding against cyber threats and ensuring the integrity of sensitive information.
Empowering Productivity without Compromising Security
The delicate balance between productivity and security is a challenge that organizations grapple with daily.
VPNs, with their ability to provide secure access to company resources from any location, empower employees to work efficiently without compromising on the stringent security measures demanded by the modern digital landscape.
Championing Data Privacy in an Interconnected World
In an era where data is a currency, VPNs emerge as champions of data privacy.
With the integration of encryption and zero-trust network access principles, VPNs ensure that sensitive information remains confidential, protecting both organizational assets and individual privacy.
As global data protection regulations evolve, the role of VPNs in ensuring compliance becomes increasingly crucial.
The Role of VPNs in Navigating Cybersecurity Challenges
The challenges posed by the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape require adaptive solutions.
VPNs, equipped with artificial intelligence for threat detection and integration with advanced encryption algorithms, stand as stalwarts in the face of emerging cyber threats.
Their role in identifying and mitigating risks in real-time ensures that organizations are not merely reacting to threats but proactively fortifying their digital perimeters.
Looking Ahead: VPNs in the Future Workplace
As we look ahead, the future of VPN technology holds exciting possibilities.
From the integration of post-quantum encryption to the adoption of blockchain for security assurance, VPNs are poised to evolve alongside emerging technologies.
Cloud-native architectures, artificial intelligence-driven security protocols, and seamless integration with edge computing are set to redefine the landscape of secure digital communication.
In conclusion, the importance of VPNs in the modern workplace extends beyond the conventional understanding of cybersecurity tools.
They are catalysts for transformation, enablers of flexible work structures, and guardians of data integrity.
As organizations chart their course in an interconnected digital future, the role of VPNs in securing remote work not only remains pivotal but continues to expand, ensuring that the future of work is not just remote but resilient, efficient, and, above all, secure.
If your company needs HR, hiring, or corporate services, you can use 9cv9 hiring and recruitment services. Book a consultation slot here, or send over an email to [email protected].
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your hiring manager and C-level suite friends and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the 9cv9 Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.
To get access to top-quality guides, click over to 9cv9 Blog.
People Also Ask
What are the benefits of VPN in the workplace?
VPNs in the workplace enhance data security by encrypting transmissions, provide secure remote access to company resources, overcome content restrictions, safeguard intellectual property, ensure compliance with data protection regulations, and offer cost-effective solutions for secure online transactions.
What is the importance of a VPN to a company?
VPNs are vital for companies as they secure data transmission, enable secure remote access, protect intellectual property, ensure regulatory compliance, and offer a cost-effective solution for safeguarding sensitive information, fostering a resilient and secure digital infrastructure.
What is the importance of a VPN?
VPNs are crucial for online security, encrypting data to protect against cyber threats. They ensure private and secure communication, facilitate remote work by providing secure access to company resources, and maintain anonymity online. VPNs are indispensable for safeguarding sensitive information in the digital age.





























![Writing A Good CV [6 Tips To Improve Your CV] 6 Tips To Improve Your CV](https://blog.9cv9.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/2020-06-02-2-100x70.png)


