Key Takeaways
- 2026 marks the shift of robotaxis from testing to full commercial scale, with leading companies achieving rider-only operations, improved safety metrics, and falling cost per mile.
- The top robotaxi companies succeed through different strategies, including mass-market affordability, premium autonomous mobility, and deep regulatory integration across global cities.
- Safety data, fleet economics, and regulatory readiness have become the core competitive advantages determining which robotaxi operators will dominate urban transportation beyond 2026.
The global transportation industry is undergoing one of the most profound transformations in its history, and at the center of this shift is the rapid rise of robotaxis. By 2026, autonomous ride-hailing has moved decisively beyond experimental pilots and limited demonstrations, emerging instead as a commercially viable, data-driven, and increasingly essential component of modern urban mobility. Cities across North America, China, the Middle East, and parts of Europe are now witnessing daily rider-only robotaxi operations, signaling a fundamental change in how people move within dense urban environments.

For years, autonomous vehicles were framed as a long-term vision constrained by technical complexity, regulatory uncertainty, and public skepticism. That narrative has changed dramatically. Advances in artificial intelligence, sensor fusion, high-performance computing, and real-time fleet orchestration have converged with clearer regulatory pathways to unlock real-world deployment at scale. In 2026, robotaxis are no longer defined by safety drivers and restricted test routes, but by fully driverless services operating in busy city centers, on highways, and during peak demand hours.
Summary of the 2026 Market Leaders
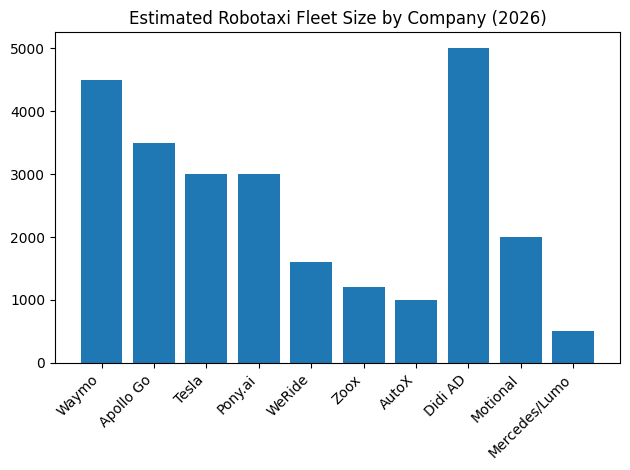
The following table summarizes the strategic positioning of the top 10 companies as of mid-2026.
| Company | Core Market | 2026 Strategy | Tech Philosophy |
| Waymo | USA | Rapid city-by-city scale; freeway operations 12 | High-fidelity LiDAR/Radar fusion |
| Apollo Go | China | Mass-produced RT6; UK/Middle East trials 18 | Low-cost LiDAR/Vision fusion |
| Tesla | Global | “Cybercab” volume production; Unsupervised FSD 29 | Vision-only neural networks |
| Pony.ai | China/Global | Gen-7 high-compute hardware; IPO scaling 3 | 1000+ TOPS high-redundancy |
| WeRide | Global | Diversified AV fleet; 8-country licensing 39 | Multi-product L4 integration |
| Zoox | USA | Purpose-built design; bi-directional urban pods 43 | Vertical integration/Pod design |
| AutoX | China | “Urban Village” navigation; 2200 TOPS compute 47 | Extreme urban sensor-fusion |
| Didi | China | Hybrid network backbone; GAC mass production 52 | Platform-integrated L4 |
| Motional | USA/Global | Assembly-line integrated IONIQ 5; Uber/Lyft deals 58 | Automotive-grade mass scale |
| Mercedes/Lumo | Middle East | S-Class luxury robotaxi; premium business mobility 65 | Premium “Service-as-Luxury” |
This evolution has significant implications not only for transportation providers, but also for consumers, city planners, regulators, and the global economy. Robotaxis are beginning to challenge the cost structure of private car ownership and traditional ride-hailing services by offering lower per-mile costs, predictable pricing, and consistently improving safety performance. As wait times decrease and service coverage expands, autonomous ride-hailing is increasingly viewed as a practical alternative to owning a car, particularly in cities struggling with congestion, parking shortages, and emissions targets.
The year 2026 represents a critical inflection point for the robotaxi industry. Leading companies have accumulated tens of millions of autonomous miles, refined their operating models, and demonstrated statistically meaningful safety advantages over human-driven vehicles in urban settings. At the same time, hardware costs for sensors and onboard computing have fallen sharply, while vehicle utilization rates have improved through station-based operations, centralized charging, and AI-driven fleet optimization. These developments have pushed robotaxi economics closer to breakeven and, in some markets, into early profitability.
Importantly, the robotaxi landscape in 2026 is not defined by a single dominant approach. Different companies have emerged as leaders through distinct strategies shaped by geography, regulation, and market demand. Some focus on rapid city-by-city expansion backed by deep safety data and regulatory trust. Others prioritize mass-market affordability through low-cost vehicle platforms and government-supported deployment. A smaller but influential segment targets premium and luxury autonomous mobility, where the value proposition centers on comfort, privacy, and in-cabin productivity rather than price alone. Together, these strategies illustrate the flexibility of robotaxis as a mobility layer capable of serving multiple use cases and income segments.
Another defining feature of 2026 is the growing concentration of market power. A relatively small group of global leaders now accounts for the majority of robotaxi activity worldwide. These companies benefit from scale advantages that compound over time: larger fleets generate more data, which improves software performance, reduces disengagements, and accelerates regulatory approvals. This feedback loop is widening the gap between established leaders and smaller players still confined to limited pilot programs.
Regulation remains the final and most complex variable shaping the pace of robotaxi adoption. While technology readiness is no longer the primary constraint, differences in national and regional policy frameworks continue to influence where and how quickly robotaxis can scale. Jurisdictions with clear autonomous vehicle regulations are attracting investment and deployment, while fragmented or restrictive environments risk falling behind. As a result, the companies leading the robotaxi market in 2026 are not only technological innovators, but also skilled navigators of regulatory, legal, and public trust challenges.
This comprehensive guide to the Top 10 Leading Robotaxi Companies in 2026 examines the organizations that are defining this new era of transportation. It explores how each company approaches autonomy, fleet operations, safety, pricing, and market expansion, while highlighting the broader trends reshaping the industry. Whether viewed through the lens of technology, economics, or urban planning, robotaxis are no longer a speculative future concept. In 2026, they are becoming a foundational layer of global mobility, setting the stage for how cities and societies will move in the decades ahead.
Before we venture further into this article, we would like to share who we are and what we do.
About 9cv9
9cv9 is a business tech startup based in Singapore and Asia, with a strong presence all over the world.
With over nine years of startup and business experience, and being highly involved in connecting with thousands of companies and startups, the 9cv9 team has listed some important learning points in this overview of the Top 10 Leading Robotaxi Companies in 2026.
If you like to get your company listed in our top B2B software reviews, check out our world-class 9cv9 Media and PR service and pricing plans here.
Top 10 Leading Robotaxi Companies in 2026
- Waymo
- Apollo Go (Baidu)
- Tesla
- Pony.ai
- WeRide
- Zoox
- AutoX
- Didi Autonomous Driving
- Motional
- Mercedes-Benz / Momenta / Lumo
1. Waymo
Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., enters 2026 as the most operationally advanced robotaxi company in the world. After more than a decade of real-world testing and commercial pilots, Waymo has moved beyond experimentation and into repeatable, city-level scaling. Its long-term deployments in Phoenix and San Francisco have become the foundation for a disciplined, city-by-city expansion model that few global competitors have been able to replicate.
By early 2026, Waymo One is no longer limited to a handful of showcase locations. The service has expanded into more than ten major U.S. cities, including Atlanta, Austin, Miami, and Los Angeles. This expansion signals a shift from proof-of-concept operations to a standardized commercial rollout strategy, supported by mature software, proven safety data, and increasingly optimized fleet economics.
Fleet Strategy and Platform Evolution
Waymo’s ability to scale in 2026 is closely tied to its transition away from experimental vehicle platforms toward purpose-built autonomous vehicles. Earlier Jaguar I-PACE models played a critical role in validation and safety testing, but they were not optimized for high-volume ride-hailing. The newer Hyundai IONIQ 5 and Zeekr RT platforms mark a decisive improvement in cost efficiency, passenger comfort, and operational flexibility.
The Zeekr RT, in particular, is designed specifically for autonomous ride-hailing use cases. It features low-step entry, a wider cabin, and modular interiors that reduce vehicle downtime during cleaning and maintenance. In several early-stage 2026 markets, steering wheels are still retained to meet regulatory requirements during initial software validation, but Waymo’s long-term roadmap continues to point toward fully driverless, steering-wheel-free configurations where regulations permit.
Operational Performance and Utilization Metrics
Waymo’s operational metrics show steady and measurable improvements year over year, reflecting both software maturity and better fleet orchestration.
Waymo operational performance overview
| Waymo Performance Indicators | 2024 Actuals | 2025 Actuals | 2026 Projected |
| Active Fleet Size (Vehicles) | ~700 | ~2,500 | 3,500 – 4,500 |
| Weekly Paid Rides | 100,000 | 250,000 | 450,000+ |
| Total Rider-Only Miles | 25M | 96M | 150M+ |
| Passenger Wait Time (Avg) | 5.8 Minutes | 5.2 Minutes | 4.7 Minutes |
The reduction in average wait time to approximately 4.7 minutes is especially significant. This threshold places Waymo’s service around 20 percent faster than traditional human-driven ride-hailing services in dense urban environments, removing one of the key psychological barriers to adoption.
Equally important is fleet efficiency. Waymo’s idle-mile rate has dropped to roughly 8 percent, compared to approximately 15 percent for human-driven ride-hailing platforms. Lower idle mileage directly improves unit economics by increasing revenue-generating miles per vehicle, accelerating the path toward sustainable margins.
Revenue Outlook and Commercial Expansion
While Waymo’s early years were defined by heavy investment, the financial profile entering 2026 shows clear signs of improvement. Analysts estimate 2024 revenue in the range of USD 50–75 million, accompanied by substantial losses driven by R&D, sensor development, and geographic expansion. These losses are increasingly viewed as front-loaded infrastructure investments rather than structural weaknesses.
The 2026 outlook improves materially as Waymo expands paid freeway rides in large metropolitan markets such as Los Angeles and Phoenix. Freeway access significantly increases average trip length, broadens use cases beyond short urban hops, and raises overall revenue per ride. This shift transforms Waymo from a city-center convenience service into a more comprehensive urban mobility solution.
Safety Performance and Regulatory Advantage
Safety remains Waymo’s strongest competitive moat in 2026. Across more than 71 million rider-only miles recorded by early 2025, Waymo has demonstrated a 96 percent reduction in intersection crashes and an 88 percent reduction in injury-causing crashes when compared with human-driven benchmarks. These results are based on real-world driving data rather than simulations, giving regulators a high level of confidence in the platform.
Notably, there have been no fatalities recorded across more than 10 million paid rides. This safety record plays a decisive role in regulatory approvals, particularly with bodies such as the California Public Utilities Commission and other state-level transport authorities. Smaller competitors often struggle to match this depth of statistically significant safety evidence, slowing their expansion timelines.
Strategic Positioning for 2026
By 2026, Waymo is no longer competing primarily on technology alone. Its advantage lies in operational maturity, regulatory trust, and scalable economics. The company has successfully transitioned from a research-driven autonomous vehicle project into a commercially viable mobility platform.
Waymo’s position at the top of the global robotaxi landscape is defined not by ambition, but by execution. Its combination of fleet efficiency, safety leadership, and disciplined expansion makes it the benchmark against which all other robotaxi companies are measured heading into 2026.
2. Apollo Go (Baidu)
Apollo Go, developed by Baidu Inc., stands out in 2026 as the largest robotaxi operation in the Eastern hemisphere by scale and ride volume. Its rapid growth is strongly supported by China’s national push for Intelligent Connected Vehicles, where local governments actively enable large-scale autonomous driving pilots and commercial deployments.
By 2026, Apollo Go is operating in 16 major Chinese cities, including Beijing, Wuhan, Shenzhen, and Shanghai. Its total fleet size has exceeded 1,000 autonomous vehicles, and weekly ride volumes often match or surpass those of leading Western competitors. This scale places Apollo Go at the center of China’s autonomous mobility ecosystem and positions it as a global benchmark for volume-driven robotaxi operations.
Mass Deployment and Cost Leadership
The defining feature of Apollo Go’s success in 2026 is the large-scale rollout of the Apollo RT6, Baidu’s sixth-generation purpose-built robotaxi. Unlike earlier retrofitted vehicles used by many Western companies, the RT6 is designed from the ground up for autonomous ride-hailing. It features a modular interior, removable steering wheel options, and simplified hardware architecture focused on cost efficiency.
One of the most disruptive aspects of the RT6 is its manufacturing cost. At approximately RMB 250,000 per vehicle, the RT6 costs nearly 70 percent less than many Western robotaxi platforms that rely on modified premium electric vehicles. This cost advantage allows Baidu to deploy vehicles at city-level density much faster than competitors, dramatically improving ride availability and reducing passenger wait times.
Apollo Go operational performance overview
| Apollo Go Performance Metrics | Q4 2021 | Q2 2025 | 2026 Projection |
| Quarterly Rides | 213,000 18 | 2,200,000 18 | 3,500,000+ |
| Weekly Rides (Avg) | 16,380 | 170,000 18 | 250,000+ 19 |
| Total Driverless Miles | N/A | 120,000,000 18 | 200,000,000+ |
| Operating Cities | 10 18 | 16 18 | 25+ |
The sharp rise in ride volume reflects a transition from pilot programs to city-wide commercial services. By mid-2025, Apollo Go reported year-over-year ride growth of more than 140 percent, driven by aggressive fleet deployment and improved routing algorithms.
The Wuhan Density Model
A major driver behind Apollo Go’s scale is what industry observers refer to as the “Wuhan Model.” In this approach, Baidu deploys hundreds of robotaxis within a single city rather than spreading vehicles thinly across multiple regions. In Wuhan alone, more than 500 autonomous vehicles operate simultaneously, creating a service density comparable to traditional taxi fleets.
This high-density strategy reduces average wait times, increases vehicle utilization, and builds public trust through frequent exposure to autonomous vehicles. The model has since been replicated in other Chinese cities and is widely viewed as one of the most effective methods for accelerating robotaxi adoption.
Global Expansion and Strategic Partnerships
By 2026, Apollo Go is no longer focused solely on domestic growth. Baidu has begun testing international expansion through strategic partnerships that extend its reach beyond China. Collaborations with Uber and Lyft have enabled pilot trials of Apollo Go vehicles in London, marking one of the first instances of Chinese autonomous driving technology entering a major European capital.
In parallel, Baidu has signed agreements with the Dubai Roads and Transport Authority to deploy up to 1,000 autonomous vehicles in the region. This move highlights the Middle East as a strategic growth market, where regulatory openness and premium urban mobility demand create strong conditions for robotaxi profitability.
Strategic Position in the Global Robotaxi Market
In 2026, Apollo Go’s competitive advantage lies in scale, cost efficiency, and regulatory alignment. While many robotaxi companies continue to focus on incremental rollouts, Baidu has demonstrated that mass deployment is achievable when vehicle costs, software maturity, and government support align.
Apollo Go is widely regarded as the volume leader of the global robotaxi industry. Its ability to operate hundreds of vehicles in single cities, deliver millions of rides annually, and expand beyond China positions it as one of the most influential players shaping the future of autonomous urban transportation.
3. Tesla
Tesla is widely viewed as the most aggressive cost disruptor in the global robotaxi race heading into 2026. Unlike most competitors that rely on purpose-built fleets and centralized operations, Tesla’s strategy is built around software-driven autonomy deployed across a massive base of consumer-owned vehicles. This approach has the potential to reshape urban mobility economics, but it also faces higher regulatory and safety scrutiny than traditional robotaxi models.
| Tesla Robotaxi Forecast (Morgan Stanley) | 2025 (Pilot) | 2026 (Launch) | 2035 (Scale) |
| Fleet Size on Road | 50 – 150 | 1,000 | 1,000,000 |
| FSD Supervised Safety | 1 Crash / 5.39M Miles | 1 Crash / 7M+ Miles | N/A |
| US Baseline Safety | 1 Crash / 0.67M Miles | 1 Crash / 0.70M Miles | N/A |
| Target Cost per Mile | N/A | $0.30 – $0.40 | $0.20 – $0.25 |
Cost Strategy and Economic Positioning
Tesla’s robotaxi vision for 2026 centers on extreme cost reduction. The company has publicly targeted an operating cost of approximately USD 0.30 to USD 0.40 per mile for autonomous ride services. This pricing strategy is designed to dramatically undercut existing transportation options.
Cost comparison overview
Transport mode | Average cost per mile
Traditional ride-hailing | ~USD 2.00
Personal car ownership | ~USD 0.70
Tesla robotaxi target (2026) | USD 0.30–0.40
If achieved at scale, Tesla’s pricing would not only disrupt ride-hailing platforms but also challenge the long-term economics of private car ownership in urban and suburban markets. This cost advantage is driven by the absence of lidar hardware, reliance on camera-based vision, vertically integrated software development, and the use of existing Tesla vehicles rather than dedicated robotaxi fleets.
Safety Metrics and Early Performance Indicators
Tesla’s autonomy performance data shows mixed signals when compared with other leading robotaxi operators. Internal and publicly cited figures suggest crash rates ranging from one crash per approximately 670,000 to 700,000 miles in supervised or semi-supervised Full Self-Driving use cases. However, these figures are not directly comparable to fully driverless robotaxi benchmarks, as most Tesla deployments still require human supervision.
Autonomy performance snapshot
Metric | Observed range
Crash frequency | 1 crash per ~0.67–0.70 million miles
Fully driverless operations | Not yet broadly deployed
Human supervision requirement | Present in most scenarios
The lack of large-scale, unsupervised commercial operations remains the biggest gap between Tesla and established robotaxi leaders. While Tesla emphasizes rapid software iteration through over-the-air updates, regulators continue to evaluate whether this approach delivers consistent safety outcomes across diverse driving conditions.
Regulatory Scrutiny and Deployment Constraints
Tesla’s transition to unsupervised robotaxi services in 2026 remains under close review by safety authorities. In 2025, investigations by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration highlighted concerns related to Full Self-Driving performance in low-visibility conditions and inconsistent responses to emergency vehicles.
As a result, early robotaxi deployments in 2026 are expected to be geographically limited. Favorable climates with predictable weather, wide road networks, and simpler traffic patterns, such as parts of Texas and Nevada, are considered the most likely initial markets. These regions reduce the frequency of edge cases involving snow, heavy fog, or complex urban intersections.
Strategic Position in the 2026 Robotaxi Landscape
Tesla’s robotaxi strategy differs fundamentally from fleet-based competitors. Instead of building a controlled operating environment first, Tesla is attempting to scale autonomy through consumer vehicles and software intelligence. This approach carries higher short-term regulatory risk but offers unmatched long-term scalability if fully approved.
In the context of the top robotaxi companies worldwide in 2026, Tesla is positioned as the most ambitious cost-focused challenger. While it may trail leaders in fully driverless commercial miles, its pricing targets and software-driven model make it one of the most closely watched players shaping the future economics of autonomous mobility.
4. Pony.ai
Pony.ai has emerged as one of the most advanced independent robotaxi companies globally as the industry moves toward 2026. With dual headquarters in Guangzhou and Fremont, the company operates at the intersection of China’s large-scale urban mobility market and Silicon Valley’s autonomous driving research ecosystem. Unlike platforms backed by consumer internet giants or car manufacturers, Pony.ai has built its strategy around technical efficiency, regulatory readiness, and cost-optimized hardware built specifically for dense city environments.
By late 2025, Pony.ai signaled its readiness for full commercial expansion with the unveiling of its seventh-generation robotaxi at the Hong Kong Auto Expo. This launch marked a critical milestone, positioning the company for broad Level 4 autonomous deployment across selected Chinese cities in 2026.
| Pony.ai Strategic Metrics | 2025 Actual | 2026 Projection | 2035 Forecast |
| Estimated Valuation | $10 Billion | $12.6 Billion | N/A |
| Fleet Size | 250 – 500 | 3,000 | N/A |
| Hardware Cost Reduction | N/A | 70% | N/A |
| Vehicle Lifespan | 600,000 KM | 600,000 KM | N/A |
Technology-First Design Philosophy
Pony.ai’s competitive advantage in 2026 is rooted in its hardware-software co-design approach. The seventh-generation robotaxi reflects years of iteration focused on reducing cost while increasing computational reliability. Instead of relying on experimental components, Pony.ai prioritizes automotive-grade systems that can operate continuously over long service lifecycles.
At the core of the Gen-7 platform is a high-redundancy compute system powered by NVIDIA DRIVE Orin processors. The vehicle uses four Orin chips, delivering more than 1,000 TOPS of AI computing power. This level of redundancy allows the system to process complex urban driving scenarios in real time while maintaining fail-safe performance.
The sensor architecture is equally robust. Each vehicle integrates 34 sensors, including high-resolution cameras, multiple LiDAR units, and radar systems. This multi-modal perception stack enables consistent performance in dense traffic, complex intersections, and mixed pedestrian environments.
Cost Optimization and Hardware Efficiency
One of the most significant breakthroughs for Pony.ai heading into 2026 is its ability to reduce hardware costs without compromising safety. The company has cut the cost of its Autonomous Driving Kit by approximately 70 percent compared to earlier generations. As a result, Pony.ai’s sensor suite is priced 20 to 30 percent lower than leading Western competitors, improving unit economics at scale.
Hardware efficiency overview
Metric | Performance outcome
Autonomous driving hardware cost | Reduced by ~70 percent
Sensor suite pricing | 20–30 percent lower than premium competitors
AI compute capacity | 1,016 TOPS with full redundancy
Vehicle service lifespan | Up to 600,000 kilometers
This aggressive cost control allows Pony.ai to deploy vehicles more rapidly while maintaining a long operational lifespan of around ten years per robotaxi. Lower depreciation per mile strengthens the company’s path toward profitability in high-density markets.
Operational Scale and Strategic Metrics
Pony.ai’s operational roadmap reflects steady, controlled expansion rather than aggressive overreach. The company focuses on markets where regulatory approvals are clear and urban density supports high utilization rates.
Pony.ai strategic outlook
Metric | 2025 Actual | 2026 Projection | Long-term outlook
Estimated valuation | USD 10 billion | USD 12.6 billion | Continued growth
Active fleet size | 250–500 vehicles | ~3,000 vehicles | Large-scale expansion
Vehicle lifespan | 600,000 km | 600,000 km | Automotive-grade standard
Industry analysts highlight Pony.ai’s disciplined scaling model as a key strength. Rather than prioritizing headline ride numbers, the company emphasizes regulatory trust, operational uptime, and cost efficiency, which are critical for long-term sustainability.
Regulatory Strength and Long-Term Vision
Pony.ai has secured one of the strongest regulatory positions among independent robotaxi operators in China. Its close collaboration with local authorities has enabled driverless testing and commercial operations in multiple cities ahead of many rivals. This regulatory momentum provides a foundation for broader expansion as national autonomous driving frameworks mature.
Looking beyond 2026, Pony.ai has set an ambitious long-term objective of capturing a significant share of China’s ride-hailing demand by 2035. Analysts view this target as achievable due to the company’s early regulatory approvals, scalable hardware design, and focus on mass-manufactured components with long service lives.
Position in the Global Robotaxi Rankings for 2026
Within the global top robotaxi companies for 2026, Pony.ai occupies a unique position as a high-efficiency independent player. It combines advanced AI computing, cost-optimized hardware, and strong regulatory execution without relying on a consumer super-app ecosystem or legacy automaker backing.
As the robotaxi market shifts from experimentation to industrial scale, Pony.ai is increasingly seen as a model for how independent autonomous driving companies can compete with much larger corporate rivals through precision engineering, disciplined deployment, and long-term operational focus.
5. WeRide
WeRide has built a distinctive position among the world’s top robotaxi companies by pursuing a diversified and highly international expansion strategy. Instead of focusing only on robotaxis, WeRide operates a broad portfolio of autonomous products, including robobuses and autonomous urban sanitation vehicles. This multi-product approach allows the company to generate revenue across different use cases while strengthening relationships with governments and city authorities worldwide.
| WeRide Operational Summary (Q3 2025) | Value (RMB) | Value (USD) | Growth (YoY) |
| Total Revenue | 171 Million | 24 Million | 144.3% |
| Robotaxi Revenue | 35.3 Million | 5.0 Million | 761.0% |
| Gross Profit | 56.3 Million | 7.9 Million | 1,123.9% |
| Cash & Investments | 5.4 Billion | 764 Million | N/A |
| Total AV Fleet | 1,600+ Vehicles | 1,600+ | N/A |
By late 2025, WeRide had achieved a milestone unmatched by most competitors. It became the only autonomous driving company to hold official permits across eight different countries. Its operations span key markets in China, the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Switzerland, and other regions that are actively investing in smart city infrastructure. This wide regulatory footprint positions WeRide as one of the most globally diversified autonomous mobility providers heading into 2026.
Multi-Product Deployment and Global Footprint
WeRide’s strategy focuses on adapting autonomous technology to multiple urban scenarios rather than limiting deployment to passenger transport alone. Robotaxis serve dense urban centers, robobuses address fixed-route public transportation, and autonomous sweepers support municipal services. This diversification reduces dependency on a single revenue stream and improves resilience during regulatory or market shifts.
The company’s presence across Asia, the Middle East, and Europe demonstrates its ability to tailor autonomous solutions to different traffic laws, road conditions, and cultural expectations. This adaptability is increasingly valuable as governments prefer proven, flexible partners when issuing autonomous driving permits.
Revenue Acceleration and Financial Momentum
As WeRide approaches 2026, its financial performance shows a clear transition from research-driven operations to commercial scale. In the third quarter of 2025, the company reported strong year-over-year revenue growth, driven primarily by rapid expansion in its robotaxi business.
WeRide financial and operational snapshot (Q3 2025)
Metric | Value (RMB) | Value (USD) | Year-over-year growth
Total revenue | 171 million | ~24 million | 144.3%
Robotaxi revenue | 35.3 million | ~5.0 million | 761.0%
Gross profit | 56.3 million | ~7.9 million | 1,123.9%
Cash and investments | 5.4 billion | ~764 million | Not applicable
Total autonomous fleet | 1,600+ vehicles | 1,600+ vehicles | Not applicable
One of the most notable trends is the rapid rise of robotaxi revenue. In just one year, this segment grew from less than 6 percent of total revenue to more than 20 percent, highlighting accelerating commercial adoption. At the same time, WeRide’s gross margin expanded to approximately 32.9 percent in 2025 and early 2026, up sharply from 6.5 percent in 2024. This improvement signals stronger cost control, higher vehicle utilization, and increasing operational efficiency.
Path to Sustainable Commercial Operations
WeRide’s improving margins indicate that the company is successfully moving beyond heavy research and development spending into a more balanced commercial phase. Higher fleet utilization, standardized vehicle platforms, and long-term government contracts contribute to more predictable revenue and profitability.
The company’s strong cash position further supports its expansion plans. With substantial reserves in cash and investments, WeRide is well-positioned to fund international rollouts, localize operations, and absorb the upfront costs associated with entering new regulated markets.
International Expansion Plans for 2026
Looking ahead to 2026, WeRide is expected to deepen its role as a global exporter of autonomous driving technology. Planned launches of fully driverless public passenger services in Singapore and Zurich represent a significant step forward. These markets are known for strict safety standards and advanced urban infrastructure, making them important validation points for WeRide’s technology.
By securing approvals in such regions, WeRide strengthens its credibility not only with regulators but also with potential enterprise and government partners worldwide.
Strategic Position Among the Top Robotaxi Companies in 2026
Within the global robotaxi landscape for 2026, WeRide stands out for its geographic reach, diversified product portfolio, and accelerating commercial traction. While some competitors focus narrowly on single-city robotaxi deployments, WeRide has built a scalable, multi-market model that balances innovation with regulatory compliance.
This combination of international permits, fast-growing robotaxi revenue, and expanding margins positions WeRide as one of the most versatile and globally relevant autonomous mobility companies shaping the next phase of robotaxi adoption.
6. Zoox
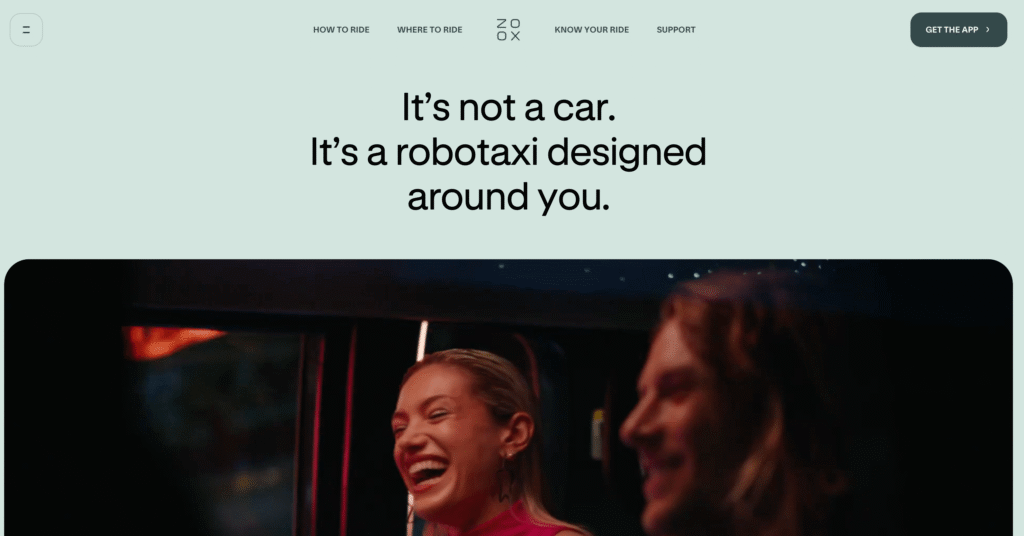
Zoox, owned by Amazon, represents one of the most unconventional and forward-looking approaches in the global robotaxi industry as it enters 2026. Instead of adapting existing electric vehicles, Zoox has designed a fully autonomous vehicle from the ground up, with every element optimized for dense urban mobility, passenger comfort, and long-term scalability.
| Zoox Technical Profile | Feature / Value |
| Operational Design | Bidirectional (No U-turns needed) |
| Max Speed | 45 MPH |
| Sensor Suite | Cameras, Radars, LiDARs |
| Manufacturing Plant | Hayward, CA (10,000 units/year capacity) |
| Waitlist Status | Active in SF, Vegas, Seattle, Austin |
By 2026, Zoox is moving beyond its early-stage roboshuttle operations in Las Vegas and transitioning into broader public ride-hailing services. Planned and ongoing expansions include major U.S. cities such as San Francisco, Miami, and Washington D.C., signaling Zoox’s shift from controlled pilot environments to complex, real-world urban deployments.
Purpose-Built Vehicle Architecture
Zoox’s defining characteristic is its fully custom vehicle design. Unlike most robotaxis that resemble traditional cars, the Zoox vehicle is fully symmetrical and capable of bidirectional movement. This means it can drive forward or backward without needing to turn around, an advantage in crowded city streets where U-turns and three-point turns increase risk and delay.
The absence of a steering wheel, pedals, or driver seat reflects Zoox’s commitment to full autonomy. Every component, from the chassis to the cabin layout, is engineered specifically for autonomous operation rather than retrofitted from human-driven designs.
Zoox vehicle design highlights
Feature | Description
Driving orientation | Fully bidirectional, no front or rear
Traditional controls | None
Urban maneuverability | Optimized for tight streets and curbside stops
Primary use case | Dense city ride-hailing
This architecture allows Zoox to reduce mechanical complexity while improving traffic flow efficiency in high-density areas.
Sensor Redundancy and Safety Systems
Safety and redundancy are central to Zoox’s technical strategy. Each vehicle uses a comprehensive sensor suite that provides continuous 360-degree coverage with overlapping fields of view. Objects can be detected at distances exceeding 150 meters in all directions, ensuring high awareness even in fast-changing urban conditions.
Zoox relies on a combination of cameras, radar, and LiDAR systems, all designed with redundancy so that the vehicle can continue operating safely even if one sensor type is degraded. This approach aligns with strict safety expectations in cities like San Francisco and Washington D.C., where pedestrian density and mixed traffic are constant challenges.
Zoox technical profile overview
Specification | Value
Maximum operating speed | 45 miles per hour
Sensor configuration | Cameras, radar, LiDAR
Detection range | 150+ meters in all directions
Vehicle layout | Symmetrical pod design
Manufacturing capacity | Up to 10,000 units per year
Passenger-Centric Experience Design
Inside the vehicle, Zoox has focused heavily on passenger comfort and safety. Seating is arranged in a face-to-face configuration, similar to a subway car or lounge, which encourages social interaction and improves space efficiency. Doors slide open rather than swinging outward, reducing the risk of opening into traffic or cyclists during pickups and drop-offs.
The cabin environment is designed to feel more like a shared urban space than a traditional car interior. Large windows, balanced lighting, and smooth acceleration profiles are intended to reduce motion discomfort and increase trust among first-time riders.
Controlled Scaling and Data-Driven Rollout
Zoox’s rollout strategy for 2026 prioritizes experience quality over immediate monetization. Through programs such as Zoox Explorers, the company offers free rides in select cities to gather detailed feedback on rider behavior, comfort preferences, and interface usability. This data-driven approach allows Zoox to refine its service before transitioning fully to paid ride-hailing.
Zoox expansion readiness snapshot
Area | Status
Active test cities | San Francisco, Las Vegas
Upcoming expansions | Miami, Washington D.C.
Ride access model | Invitation and waitlist-based
Pricing approach | Free rides during testing phase
Manufacturing and Vertical Integration
Zoox’s manufacturing operations are based in Hayward, California, where a converted bus factory now serves as its primary production facility. This site is capable of producing up to 10,000 vehicles annually and plays a crucial role in Zoox’s tight integration between hardware and software development.
By controlling its own manufacturing pipeline, Zoox can rapidly test design changes, deploy software updates, and iterate on vehicle components without relying on third-party automakers. This vertical integration mirrors Amazon’s broader operational philosophy of owning critical infrastructure to improve speed and reliability.
Strategic Role in the Global Robotaxi Market for 2026
Within the global top robotaxi companies for 2026, Zoox stands apart as the most radical rethinking of what an autonomous vehicle should be. While many competitors focus on scaling modified electric cars, Zoox is betting on long-term advantages from a fully purpose-built platform.
Backed by Amazon’s financial resources, cloud infrastructure, and operational discipline, Zoox is positioned as a long-term contender rather than a short-term volume leader. Its emphasis on safety, passenger experience, and urban efficiency makes it one of the most closely watched robotaxi companies shaping the next generation of autonomous transportation worldwide.
7. AutoX

AutoX has built its global reputation by focusing on some of the most difficult driving environments anywhere in the world. Backed by Alibaba Group, AutoX concentrates on ultra-dense urban areas in China where narrow roads, informal traffic behavior, and heavy pedestrian movement create extreme challenges for autonomous systems. These environments, often described as urban villages, serve as real-world stress tests that few robotaxi platforms can handle reliably.
| AutoX Gen-5 Sensor Suite | Specification |
| Total Sensors | 50 |
| Cameras | 28 (360-degree, 220M pixels/sec) |
| LiDAR Modules | 6 (15 million points/sec) |
| Radar Units | 4D Radar (0.9-degree resolution) |
| AI Compute | 2,200 TOPS (NVIDIA Ampere GPUs) |
By 2026, AutoX operates one of the largest Level 4 robotaxi fleets in China, with more than 1,000 fully autonomous vehicles active across major cities such as Shenzhen, Guangzhou, and Shanghai. Its ability to function safely in these environments places AutoX among the top robotaxi companies globally as the industry moves toward mass adoption.
Urban Complexity as a Core Strategy
AutoX’s approach differs from many competitors that begin in simpler suburban or grid-based cities. Instead, the company deliberately targets locations with unpredictable pedestrian flows, delivery scooters emerging from blind spots, and tightly packed residential streets. These conditions require faster perception, deeper prediction models, and higher computing redundancy.
Operating successfully in such environments allows AutoX to build software that scales downward in difficulty when deployed in more structured cities. Regulators in China view this as a strong indicator of safety maturity, particularly for megacities where traditional traffic rules are often loosely followed.
High-Performance Gen-5 Autonomous Platform
The technical foundation of AutoX’s leadership in 2026 is its fifth-generation autonomous driving platform. Although first unveiled earlier in the decade, the Gen-5 system reaches full commercial maturity by 2026 and remains one of the most powerful autonomous stacks in production use.
At the center of the platform is an exceptionally high level of AI computing power. With approximately 2,200 TOPS, AutoX’s system delivers nearly double the compute capacity of many other Level 4 robotaxi platforms. This processing power is essential for analyzing dense, fast-changing scenes where dozens of objects may appear or disappear within seconds.
AutoX Gen-5 sensor and compute overview
Component | Specification
Total sensor count | 50
Cameras | 28 automotive-grade cameras with full 360-degree coverage
Camera data throughput | ~220 million pixels per second
LiDAR units | 6 high-resolution modules
LiDAR data rate | ~15 million points per second
Radar system | Advanced 4D radar with fine angular resolution
AI computing power | ~2,200 TOPS using NVIDIA Ampere GPUs
This dense sensor configuration allows AutoX vehicles to detect partially hidden objects, such as scooters or pedestrians emerging from behind parked vehicles, at long distances. Such capabilities are especially valuable in cities with heavy last-mile delivery traffic.
Safety Performance and Regulatory Trust
AutoX’s strong performance in complex urban areas has made it a preferred partner for safety-focused regulators. The system’s ability to identify occluded objects and predict unconventional traffic behavior improves reaction time and reduces collision risk in crowded neighborhoods.
Regulatory authorities increasingly see AutoX’s deployments as evidence that high-density autonomy is achievable without sacrificing safety. This trust has enabled the company to scale its fleet faster than many peers in China’s largest cities.
Partnership-Driven Expansion Model
Looking toward 2026 and beyond, AutoX positions itself as a technology provider as much as an operator. The company is actively working with global automotive partners such as Stellantis and Honda to integrate its Gen-5 autonomous system into multiple vehicle platforms.
This partner-centric strategy supports AutoX’s long-term goal of making autonomous driving accessible across different vehicle types and price points. Rather than limiting autonomy to a single robotaxi model, AutoX aims to embed its software stack into mass-market vehicles, accelerating adoption across regions.
Strategic Position Among the Top Robotaxi Companies in 2026
Within the global robotaxi landscape for 2026, AutoX stands out as the specialist in extreme urban navigation. Its combination of high compute density, expansive sensor coverage, and real-world testing in some of the toughest traffic environments gives it a strong technical and regulatory advantage.
As cities worldwide look to deploy robotaxis in dense downtown areas rather than controlled pilot zones, AutoX’s experience in complex urban villages positions it as one of the most relevant and battle-tested robotaxi companies shaping the future of autonomous mobility.
8. Didi Autonomous Driving

Didi has taken a distinctive path in the global robotaxi race by building its autonomous driving strategy on top of one of the world’s largest ride-hailing networks. Instead of treating robotaxis as a standalone service, Didi focuses on deep integration between human-driven vehicles and autonomous fleets. This hybrid approach allows the company to scale autonomy while maintaining service reliability, coverage, and passenger convenience.
By 2026, Didi Autonomous Driving is transitioning from testing and pilots to real commercial deployment. The company is rolling out its first mass-production Level 4 robotaxi, developed jointly with GAC Aion under the joint venture Andi Technology. This marks a major milestone, positioning Didi among the top robotaxi companies worldwide entering large-scale operations.
| Didi Strategic Milestones | 2023 | 2025 | 2026 Projected |
| Cumulative Test Mileage | 30M KM | 80M KM | 120M+ KM |
| Active Test Fleet | 1,000 AVs | 3,000 AVs | 5,000+ AVs |
| Manufacturing Partner | GAC Group | GAC Aion | International OEMs |
| Funding Rounds | 6 | 7 | N/A |
Data-Driven Foundation and Hybrid Model
Didi’s strongest advantage comes from its massive pool of real-world ride-hailing data. Billions of trips completed by human drivers have given the company deep insight into traffic patterns, passenger behavior, pricing sensitivity, and city-level demand fluctuations. This data is used to train autonomous systems that are optimized not just for driving, but for real commercial operations.
Rather than replacing human drivers overnight, Didi integrates robotaxis into its existing network. Passengers may be matched with either a human-driven car or a robotaxi, depending on availability, location, and traffic conditions. This “mixed-trip” model improves fleet utilization and ensures consistent service levels, especially during peak hours or in complex urban zones.
Mass-Production Robotaxi Platform
The core of Didi’s 2026 deployment strategy is its AE3.0 autonomous platform. This platform is built on a purpose-designed electric vehicle developed with GAC Aion and engineered specifically for robotaxi use. The vehicle emphasizes safety redundancy, sensor coverage, and long operational life.
AE3.0 platform technology overview
Component | Specification
Vehicle type | Electric special-purpose robotaxi
Total sensors | 33
LiDAR units | 10
Radar system | Advanced 4D millimeter-wave radar
Primary focus | Urban Level 4 autonomy at scale
This sensor-heavy design allows the vehicle to operate reliably in dense city environments while meeting regulatory expectations for redundancy and fault tolerance.
Strategic Funding and Capital Strength
Didi Autonomous Driving has been heavily funded to support long-term scaling. In October 2025, the unit closed a major Series D funding round worth approximately RMB 2 billion, bringing total investment in the autonomous driving program to more than RMB 13 billion. This capital is directed toward vehicle manufacturing, software development, and multi-city expansion.
The scale of funding reflects investor confidence in Didi’s hybrid strategy, which reduces risk by monetizing autonomy within an already profitable ride-hailing ecosystem rather than relying solely on standalone robotaxi economics.
Testing Progress and Operational Growth
Didi’s autonomous program shows steady growth in both mileage and fleet size, reflecting a disciplined expansion model focused on safety validation before mass deployment.
Didi autonomous driving milestones
Metric | 2023 | 2025 | 2026 Projected
Cumulative test mileage | 30 million km | 80 million km | 120 million+ km
Active autonomous fleet | ~1,000 vehicles | ~3,000 vehicles | 5,000+ vehicles
Primary manufacturing partner | GAC Group | GAC Aion | Expanded OEM partnerships
This progression highlights Didi’s transition from testing to commercial readiness, supported by increasing vehicle counts and broader geographic coverage.
Digital Backbone Strategy for Mobility
Looking ahead to 2026, Didi positions itself as the digital backbone of urban mobility rather than just a robotaxi operator. The company plans to manage autonomous fleets on behalf of multiple vehicle owners, handling routing, pricing, dispatch, and demand forecasting through its AI-driven generalization engine.
This platform-centric approach allows Didi to scale robotaxi services across 11 major cities while maintaining consistent passenger experiences. By coordinating human-driven and autonomous vehicles within a single system, Didi can reduce wait times, smooth demand spikes, and optimize vehicle availability across the network.
Position Among the Top Robotaxi Companies in 2026
Within the global robotaxi landscape for 2026, Didi Autonomous Driving stands out for its integration-first strategy. While many competitors focus on isolated robotaxi fleets, Didi leverages its existing ride-hailing dominance to deploy autonomy faster and more efficiently.
Its combination of large-scale funding, mass-production vehicles, deep data assets, and hybrid network integration makes Didi one of the most strategically positioned robotaxi players worldwide. As autonomous mobility moves toward real-world scale, Didi’s model offers a practical blueprint for blending innovation with operational stability.
9. Motional
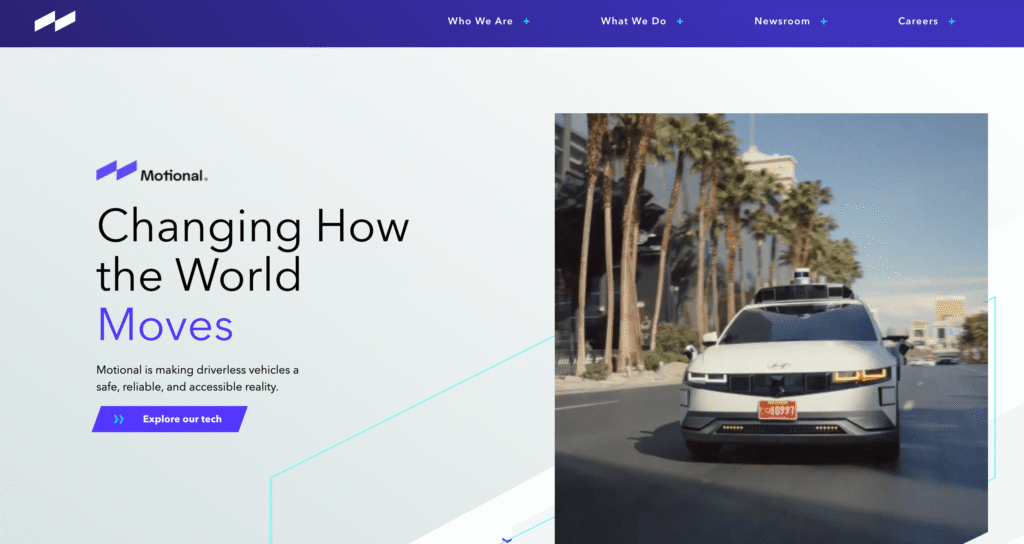
Motional is positioned as one of the most manufacturing-focused robotaxi companies entering 2026. Formed as a joint venture between Hyundai Motor Group and Aptiv, Motional brings together decades of large-scale vehicle production expertise with advanced autonomous driving software. Headquartered in Boston, the company has deliberately aligned its robotaxi strategy with automotive-grade reliability, safety validation, and repeatable mass production.
In 2026, Motional is moving into full commercial deployment with a driverless service built around the all-electric Hyundai IONIQ 5 robotaxi. This launch represents a shift from pilot programs to standardized operations designed for long-term city-scale rollouts.
| ONIQ 5 Robotaxi Technical Details | Specification |
| Autonomy Level | SAE Level 4 |
| Sensor Modalities | Cameras, Radar, LiDAR, Microphones |
| Operational Support | Remote Vehicle Assistance (RVA) |
| Night Operations | Fully Supported in Las Vegas |
| Partnership Reach | Uber, Lyft, Via |
Manufacturing-First Autonomous Design
Motional’s key differentiation lies in how its robotaxis are built. Rather than retrofitting sensors onto consumer vehicles after production, Motional integrates the entire autonomous sensor suite directly into the vehicle during manufacturing. This process takes place at the Hyundai Motor Group Innovation Center in Singapore, ensuring consistency, quality control, and automotive-grade durability from the first unit onward.
This assembly-line integration reduces long-term maintenance complexity and improves reliability, as sensors, wiring, and compute systems are designed to meet strict automotive safety and lifespan standards. For regulators and city partners, this approach signals a lower operational risk compared to experimental or heavily modified platforms.
Sensor Redundancy and Safety Architecture
The Hyundai IONIQ 5 robotaxi used by Motional is equipped with a comprehensive and redundant sensor stack. More than 30 sensors are embedded into the vehicle, providing overlapping perception and fault tolerance across all driving scenarios. The platform is designed specifically for Level 4 autonomy, meaning it can operate without a human driver within defined environments.
IONIQ 5 robotaxi technical overview
Specification | Details
Autonomy level | SAE Level 4
Sensor types | Cameras, radar, LiDAR, microphones
Sensor count | 30+ integrated units
Primary vehicle platform | Hyundai IONIQ 5 (electric)
Manufacturing approach | Factory-integrated autonomous systems
This multi-modal sensing approach allows the vehicle to maintain safe operation even if individual sensors are impaired, an essential requirement for night driving, poor weather, and dense urban traffic.
Operational Support and Remote Assistance
A defining feature of Motional’s deployment model in 2026 is its Remote Vehicle Assistance system. Instead of handing control to a remote driver, this system allows trained human operators to provide high-level guidance in rare and complex situations. These may include unexpected construction barriers, temporary road closures, or irregular roadside activity that falls outside standard autonomous decision-making.
Remote Vehicle Assistance enables vehicles to resolve edge cases without shutting down or blocking traffic. This capability significantly improves fleet uptime and reduces the risk of service interruptions caused by unpredictable local infrastructure issues.
Operational capability snapshot
Capability | Status
Night-time driving | Fully supported in Las Vegas
Edge-case handling | Assisted via Remote Vehicle Assistance
Human driver presence | Not required during normal operations
Fleet reliability focus | Continuous service continuity
Strategic Partnerships and Market Reach
Motional’s commercial strategy is reinforced by strong partnerships with leading mobility platforms. The company maintains long-term collaborations with Uber, Lyft, and Via. A notable component of this strategy is a multi-year agreement with Uber, under which Motional plans to offer driverless ride-hailing and delivery services across several U.S. cities starting in 2026.
These partnerships allow Motional to focus on vehicle safety, autonomy, and manufacturing excellence while leveraging established platforms for demand generation, routing, and customer access.
Position in the Global Robotaxi Landscape for 2026
Among the top robotaxi companies in the world for 2026, Motional stands out as the automotive-grade benchmark. Its emphasis on factory-built autonomous vehicles, strict safety redundancy, and structured operational support reflects a mindset closer to traditional car manufacturing than experimental mobility startups.
By combining Hyundai’s global production capabilities with Aptiv’s autonomous software expertise, Motional offers a model for how robotaxis can scale responsibly and reliably. As cities increasingly demand proven safety, consistency, and regulatory compliance, Motional’s manufacturing-led approach positions it as one of the most trusted and deployment-ready robotaxi operators worldwide.
10. Mercedes-Benz / Momenta / Lumo

Mercedes-Benz, Momenta, and Lumo have jointly created a new premium category within the global robotaxi market as it enters 2026. This three-way partnership represents the emergence of a luxury-focused robotaxi model, where autonomous mobility is positioned not as a low-cost alternative, but as a high-end service tailored to comfort, privacy, and productivity.
| Luxury Robotaxi Specifications | Feature / Value |
| Base Vehicle | Mercedes-Benz S-Class |
| Tech Provider | Momenta |
| Operator | Lumo (UAE) |
| Deployment Year | 2026 |
| Expansion Target | Global Luxury Markets |
This collaboration has been launched in the Middle East, with Abu Dhabi serving as the flagship market. The region’s advanced infrastructure, supportive regulatory environment, and strong demand for premium transport services make it an ideal testing ground for luxury autonomous mobility.
Premium Urban Mobility in Abu Dhabi
The robotaxi service operates using the Mercedes-Benz S-Class, a vehicle long associated with executive travel and top-tier comfort. Instead of targeting mass ridership, the service is designed for business travelers, government officials, and high-net-worth individuals who prioritize reliability, discretion, and in-cabin experience.
In Abu Dhabi, the service focuses on high-value urban routes such as financial districts, luxury hotels, airports, and government zones. The emphasis is not on volume, but on delivering a refined and consistent experience that aligns with the expectations of premium passengers.
Autonomous Technology and Data-Driven Intelligence
Momenta provides the autonomous driving technology powering this luxury robotaxi fleet. Its approach is built around a data-driven “flywheel” model, where large volumes of driving data from mass-produced vehicles are continuously used to train and improve Level 4 autonomous systems. This method allows the software to mature rapidly while remaining adaptable to different driving environments.
By integrating Momenta’s autonomous stack into a luxury vehicle platform, the partnership demonstrates that advanced autonomy is no longer limited to experimental shuttles or utilitarian robotaxis. Instead, it can be seamlessly embedded into high-end vehicles without compromising ride quality or brand standards.
Operational Model and Fleet Responsibilities
Lumo acts as the local operator, managing fleet operations, regulatory coordination, and customer service within the UAE. This division of responsibilities allows each partner to focus on its core strength: Mercedes-Benz on vehicle engineering and luxury design, Momenta on autonomous software, and Lumo on day-to-day mobility operations.
Luxury robotaxi deployment overview
Attribute | Details
Base vehicle | Mercedes-Benz S-Class
Autonomous technology provider | Momenta
Local operator | Lumo
Initial deployment location | Abu Dhabi
Commercial launch year | 2026
Expansion focus | Global luxury urban markets
This structure creates a scalable model that can be replicated in other cities with strong demand for premium mobility services.
Interior Experience and Luxury-as-a-Service
A defining feature of this robotaxi offering is its interior configuration. The S-Class cabins are customized to support both productivity and relaxation. Passengers can conduct private meetings, work uninterrupted, or unwind in a quiet, climate-controlled environment while the vehicle handles navigation autonomously.
High-quality seating, advanced noise insulation, ambient lighting, and seamless connectivity transform travel time into usable or restorative time. This shift reflects a broader 2026 trend toward “Luxury-as-a-Service,” where transportation is evaluated not only by speed and safety, but by the quality of the experience inside the vehicle.
Strategic Significance in the Global Robotaxi Market
Within the global top robotaxi companies for 2026, the Mercedes-Benz, Momenta, and Lumo partnership represents the emergence of a distinct luxury tier. While many robotaxi operators compete on cost efficiency and fleet scale, this model focuses on value per ride rather than total ride volume.
By combining a globally recognized luxury brand, a rapidly advancing autonomous technology provider, and a regionally strong mobility operator, this partnership sets a blueprint for premium autonomous transport in major international cities. As demand grows for differentiated robotaxi experiences, this luxury-focused approach is expected to expand beyond the Middle East into other high-income urban markets worldwide.
The 2026 Inflection Point: Transitioning from Pilot Programs to Mass Market Integration
The year 2026 represents a decisive turning point for the robotaxi industry worldwide. After more than a decade of heavy investment, long pilot phases, and technology validation, autonomous ride-hailing is moving out of controlled trials and into real-world, large-scale commercial integration. What was once dominated by research programs and safety-driver experiments is now evolving into a functioning transportation layer that directly competes with private car ownership and human-driven ride-hailing services.
By mid-2026, robotaxi operations in multiple regions have reached a level of maturity where rider-only services are no longer an exception. Improvements in onboard computing power, sensor fusion accuracy, and real-time decision-making have reduced the need for human oversight. At the same time, regulatory frameworks in key markets have matured, providing clearer pathways for permits, liability structures, and commercial licensing. Together, these factors mark the industry’s shift from experimentation to mass-market readiness.
From Research Projects to Scalable Urban Infrastructure
Earlier robotaxi programs were defined by limited geofenced routes, safety drivers, and high per-mile operating costs. In contrast, the 2026 generation of robotaxi fleets is designed for scalability. Purpose-built vehicles, automotive-grade hardware, and centralized fleet orchestration systems are now enabling consistent service across entire cities rather than small test zones.
A major breakthrough has been the improvement in unit economics. Leading robotaxi operators are approaching or achieving breakeven at the fleet level. This progress is driven by several structural changes, including sharp declines in hardware costs, higher vehicle utilization rates, and longer vehicle lifespans. As a result, robotaxi services are beginning to challenge both the cost of owning a personal car and the pricing models of traditional ride-hailing platforms.
Rapid Market Expansion and Long-Term Growth Outlook
The financial trajectory of the global robotaxi market highlights how quickly the sector is maturing. In 2024, the market was still relatively small, valued at around USD 2.6 billion. By 2025, it had already expanded to approximately USD 4.8 billion. Projections for the coming years show exponential growth, with estimates ranging into the hundreds of billions of dollars by the early to mid-2030s.
This rapid expansion is supported by an exceptionally high compound annual growth rate, driven by large-scale deployments in urban centers, improved consumer trust, and increasing pressure on cities to reduce congestion and emissions. While different forecasts vary widely, the underlying trend is consistent: robotaxis are expected to capture a meaningful share of global passenger transportation spending.
Global robotaxi market valuation overview
Market segment | 2024 valuation (USD million) | 2025 valuation (USD million) | 2026 projected (USD million) | Long-term forecast (USD million)
Global robotaxi market | 789.30 | 1,433.40 | 4,840.00 | 416,627.20
North America | 319.35 | 589.98 | 1,400.00 | 45,400.00
Asia-Pacific | 276.25 | 523.19 | 1,300.00 | 48,500.00
Europe | 157.86 | 286.68 | 1,200.00 | 42,100.00
Level 4 autonomy segment | 631.44 | 1,146.72 | 3,872.00 | 13,301.76
These figures show how quickly Level 4 autonomy is becoming the dominant technical standard for robotaxi services, particularly in dense urban environments where full driverless operation delivers the greatest economic advantage.
Understanding the Wide Range of Market Estimates
The significant variation in long-term market projections, ranging from tens of billions to nearly USD 700 billion, is largely due to differences in how analysts define the robotaxi market. Lower estimates focus strictly on direct robotaxi service revenue. Higher estimates incorporate the total addressable market of passenger transportation that robotaxis are expected to replace, including private car usage, taxis, and ride-hailing services.
In this broader view, robotaxis are not just a new mobility product but a replacement layer for much of urban passenger transport. This explains why some projections expand so dramatically as adoption accelerates and operational costs continue to decline.
Transportation as the Core Adoption Driver
In 2026, passenger transportation accounts for more than 93 percent of the total autonomous vehicle market value. This dominance highlights that robotaxis, rather than autonomous freight or industrial vehicles, remain the primary engine of commercial adoption. The daily, repeat-use nature of urban passenger travel creates the strongest demand signals and the fastest path to scale.
As robotaxi fleets grow denser and wait times fall below those of human-driven alternatives, consumer behavior is beginning to shift. For many urban residents, autonomous ride-hailing is becoming a practical alternative to owning a car, especially in cities with high parking costs and traffic congestion.
Strategic Implications for the Top Robotaxi Companies in 2026
For the leading robotaxi companies in the world, 2026 is not just another year of growth. It is the moment when long-term strategies are tested under real market conditions. Companies that can combine regulatory trust, cost-efficient hardware, high fleet utilization, and consistent rider experience are moving ahead rapidly. Those unable to scale beyond pilots risk falling behind as cities and consumers increasingly expect fully operational services.
The 2026 inflection point confirms that robotaxis are no longer a future concept. They are becoming a core component of modern urban mobility, setting the stage for widespread global integration in the years that follow.
The Economics of the Robotaxi Ride: Costs, Process, and User Experience
By 2026, robotaxi services have become familiar to urban passengers across major global cities. While the experience of booking and riding an autonomous vehicle now feels similar to traditional ride-hailing, the economic structure behind each trip has changed dramatically. Lower operating costs, higher vehicle utilization, and automation-driven efficiencies are reshaping how riders evaluate value, convenience, and price.
From a user perspective, the robotaxi journey can be understood through three connected stages: onboarding and booking, the in-ride experience, and the final cost-versus-utility decision.
Onboarding and Booking Experience
Robotaxi onboarding in 2026 is designed to be fast, intuitive, and nearly frictionless. Most users access autonomous rides through dedicated robotaxi applications or through hybrid ride-hailing platforms that combine human-driven and autonomous vehicles.
Passengers typically book robotaxis through platforms such as Waymo One, Apollo Go, or integrated marketplaces like Uber and Lyft. In selected U.S. markets, riders using Uber can actively choose an autonomous option, including vehicles powered by Nuro autonomy systems operating on Lucid Motors platforms. This integration allows robotaxis to scale rapidly without requiring users to adopt entirely new mobility habits.
For first-time riders, safety reassurance remains an essential part of onboarding. Apps usually provide short in-app walkthroughs explaining emergency stop functions, customer support access, and remote assistance features. These brief tutorials help build trust and reduce anxiety, especially for passengers new to driverless travel.
Personalization has also become a competitive differentiator. Premium robotaxi services, including those operated by Motional and Zoox, allow riders to preset cabin temperature, airflow, and seating preferences before the vehicle arrives. Once the robotaxi reaches the pickup point, doors unlock directly through the app. Purpose-built vehicles with sliding doors and no driver’s seat create a noticeably open and spacious cabin, reinforcing the sense that the experience is fundamentally different from a traditional taxi.
Ride Experience and Perceived Value
During the ride, passengers increasingly judge robotaxi services on comfort, smoothness, and reliability rather than novelty. Quiet electric drivetrains, predictable driving behavior, and consistent routing contribute to a calm experience that many users describe as more relaxing than human-driven rides.
The absence of a driver also changes social dynamics. For many riders, the appeal lies in privacy and uninterrupted time. Business travelers use robotaxis for calls and work, while others value the quiet, distraction-free environment. This “no small talk” factor has become a subtle but powerful value proposition in premium robotaxi markets.
Comparative Ride Economics Across Markets
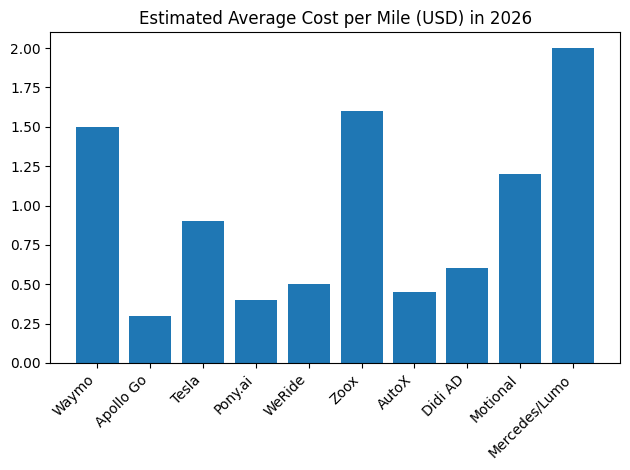
Pricing is where robotaxis most clearly differentiate themselves in 2026. Cost per mile varies widely depending on geography, regulatory support, and fleet economics. Government subsidies and lower vehicle manufacturing costs have enabled especially aggressive pricing in China, while U.S. and European markets reflect higher labor, compliance, and infrastructure costs.
Robotaxi pricing comparison in 2026
| City / Service | 2026 Avg Fare (USD) | Comparative UberX (USD) | Cost per Mile (USD) |
| Waymo (San Francisco) | $20.43 | $15.00 | $1.40 – $1.60 |
| Tesla (Austin – Pilot) | $4.20 (Flat) | $12.00 | $0.80 – $1.00 |
| Apollo Go (Wuhan) | $0.55 (4 Yuan) | $2.50 | $0.25 – $0.35 |
| Pony.ai (Guangzhou) | $0.75 | $2.60 | $0.30 – $0.45 |
The stark contrast between regions reflects structural differences. In China, robotaxi operators benefit from lower vehicle costs and public-sector support, enabling prices that undercut both private cars and human-driven ride-hailing. In the United States, Waymo continues to position its service as a premium offering, often pricing rides several dollars above comparable Uber trips. This premium is justified by consistency, comfort, and perceived safety advantages.
Emerging Price Pressure and Long-Term Trends
Tesla’s entry into robotaxi pilots, particularly with flat-rate pricing in cities like Austin, has introduced downward pressure on fares in North America. Although still limited in scope, these pilots have intensified competition and prompted analysts to anticipate a long-term price convergence.
Industry projections suggest that as hardware costs fall further and autonomous fleets reach higher utilization rates, average robotaxi pricing could move closer to USD 0.50 per mile by the end of the decade. This shift would place robotaxis well below the cost of owning a personal vehicle and significantly cheaper than today’s ride-hailing services.
Cost, Convenience, and the User Decision
By 2026, the decision to choose a robotaxi is no longer driven by curiosity alone. Riders increasingly weigh reliability, comfort, wait time, and total trip cost. In dense urban centers, robotaxis are becoming a rational alternative to car ownership, especially where parking is expensive and traffic congestion is high.
For the top robotaxi companies in the world, these economics define competitive advantage. Operators that can balance low per-mile costs with consistent user experience are best positioned to scale. As pricing continues to decline and services become more widely available, robotaxis are steadily shifting from a novelty into a default urban mobility option.
Safety Metrics: The Statistical Case for Autonomy
By 2026, safety performance has become the most decisive factor in evaluating the world’s top robotaxi companies. The discussion has moved beyond isolated test incidents to large-scale statistical comparisons between human-driven vehicles and fully autonomous fleets. With millions of real-world miles now recorded, regulators, cities, and passengers are increasingly relying on data rather than perception to judge whether autonomous driving is safer than conventional transport.
This safety narrative is shaped by extensive datasets collected from national traffic authorities, state motor vehicle agencies, and operator-reported rider-only statistics. Together, these data sources provide a clearer picture of how machine-driven systems perform under real urban conditions.
Human Drivers Versus Autonomous Systems
When comparing human drivers to robotaxis, it is important to distinguish between all reported incidents and those that result in injuries or serious outcomes. Human drivers are prone to fatigue, distraction, impairment, and inconsistent reaction times. Autonomous systems, while not perfect, operate with constant attention and predictable behavior.
Comparative accident and safety outcomes
| Metric | Human (Conventional) | Robotaxi (Avg Driverless) | Waymo (Rider-Only) |
| Crashes Per 1M Miles | 4.2 | 9.1 | ~0.8 – 1.2 |
| Any-Injury Reduction | Baseline | N/A | 88% Fewer |
| Fatalities per 10M Trips | 9.4 | 0.1 (Est) | 0.0 |
| Serious Injury Reduction | Baseline | N/A | 79% Fewer |
At first glance, robotaxis appear to have a higher number of crashes per million miles. However, this figure is misleading without context. Many reported robotaxi “crashes” involve low-speed contact, emergency stops, or situations where the vehicle safely halts and is lightly impacted by another road user. These incidents are logged conservatively by autonomous operators, whereas similar minor events often go unreported in human driving.
When the data is filtered to focus only on injury-causing accidents or airbag-deploying collisions, leading robotaxi fleets show a clear safety advantage over human drivers. This performance gap is primarily driven by the absence of fatigue, distraction, or impairment, which account for nearly 70 percent of serious human ride-hailing accidents.
Performance of Leading Robotaxi Fleets
Among global robotaxi operators, fleets operated by Waymo and Apollo Go are often cited as benchmarks for rider-only safety. Their vehicles have accumulated tens of millions of autonomous miles without a single fatality in paid service.
Waymo’s rider-only data, in particular, has become a reference point for regulators. Across more than 70 million autonomous miles, the fleet has demonstrated dramatic reductions in both injury-causing and serious crashes compared to human-driven benchmarks. This level of statistical confidence is one of the main reasons Waymo continues to receive expanded operating approvals in dense U.S. cities.
Understanding Disengagements and System Reliability
Beyond crash statistics, engineering teams closely track disengagements. A disengagement occurs when an autonomous system hands control to a human operator or requires intervention due to uncertainty or an edge-case scenario. While disengagements do not necessarily indicate unsafe behavior, they are a key measure of system maturity and reliability.
Disengagement performance snapshots
Operator | Disengagement insights
Cruise | Reported around 16 disengagements per million miles prior to its 2024–2025 operational pause
Waymo | Internal data shows disengagement rates falling by roughly 50% year over year
Tesla | Supervised Full Self-Driving shows one accident per ~6.36 million miles
Waymo’s declining disengagement rate reflects steady software improvements in complex scenarios such as unprotected left turns, temporary construction layouts, and dense pedestrian crossings. These are situations that historically challenge both human drivers and autonomous systems.
Tesla’s performance, while still based on supervised autonomy, is notable for a different reason. Despite relying primarily on camera-based perception rather than LiDAR, Tesla reports accident rates significantly better than the U.S. national human driving average. This highlights how even partial automation can reduce risk when properly monitored, although it remains distinct from fully driverless robotaxi operations.
Why Autonomous Safety Improves at Scale
One of the defining advantages of robotaxi systems is that safety improvements scale globally. When a human driver learns from a mistake, that knowledge stays with one person. When an autonomous fleet encounters a rare edge case, the solution can be deployed across thousands of vehicles almost instantly.
This collective learning effect means that every mile driven improves the entire fleet, not just an individual vehicle. Over time, this leads to consistent reductions in both disengagements and serious incidents, reinforcing the statistical case for autonomy.
Safety as a Competitive Advantage in 2026
For the top robotaxi companies in the world in 2026, safety performance is no longer just a regulatory requirement. It is a core competitive advantage. Operators with strong injury-reduction data gain faster approvals, broader city access, and higher passenger trust.
As autonomous fleets continue to accumulate millions of rider-only miles, the safety debate is increasingly moving from “whether robotaxis are safe” to “how quickly they outperform human driving at scale.” In this context, safety metrics are not only validating the technology, but also accelerating the global rollout of robotaxi services across major urban markets.
Strategic Implications and Future Forecast (2026-2035)
As the robotaxi industry advances through 2026, competitive momentum is concentrating around a small group of global leaders. Waymo, Baidu, Tesla, Pony.ai, and WeRide together account for more than 70 percent of global robotaxi activity. This concentration is shaping how technology, operations, and policy evolve over the next decade, with ripple effects extending far beyond transportation.
Market Concentration and Competitive Dynamics
By 2026, scale has become the decisive advantage. The leading operators benefit from vast datasets, mature safety records, and capital-intensive infrastructure that smaller entrants struggle to replicate. As fleets grow denser and software improves through shared learning, the gap between the leaders and the rest of the market widens. This dynamic points to continued consolidation through partnerships, acquisitions, and regional exclusivity agreements through the early 2030s.
Big Five market positioning snapshot
Operator | Core strength | Primary regions | Strategic edge
Waymo | Safety data and regulatory trust | United States | Deep rider-only mileage
Baidu (Apollo Go) | Low-cost mass deployment | China | Vehicle cost leadership
Tesla | Software-led scale | United States | Cost disruption potential
Pony.ai | Hardware efficiency | China | Automotive-grade longevity
WeRide | Global diversification | China, Middle East, Europe | Multi-product expansion
Operational Shift From On-Demand to Station-Based Fleets
Early robotaxi deployments mirrored traditional ride-hailing, with vehicles roaming freely and returning to service immediately after trips. In 2026, leading operators are increasingly adopting station-based models. These hubs centralize charging, cleaning, diagnostics, and routine maintenance, improving fleet uptime and reducing per-mile costs.
For electric robotaxi fleets, station-based operations are especially critical. Coordinated charging schedules prevent service gaps during peak demand, while centralized maintenance ensures consistent performance and safety standards. This operational shift supports higher utilization rates and accelerates progress toward sustainable unit economics.
Operational model comparison
Model type | Key features | Cost impact | Scalability
On-demand roaming | Flexible routing | Higher operating cost | Limited at scale
Station-based hubs | Centralized charging and service | Lower cost per mile | High scalability
Secondary Economic Effects Beyond Transportation
Robotaxis are generating economic effects that extend well beyond mobility. Analysts at Barclays have identified a potential surge in consumer spending linked to safer nightlife transportation. With autonomous rides reducing the risks associated with drunk driving, increased social activity could contribute an estimated USD 42 billion uplift to alcohol-related spending in the United States over time.
Equally significant is the productivity impact. As commuting time shifts from driving to working, resting, or planning, efficiency gains accumulate across the economy. Global estimates suggest that by 2030, productivity improvements enabled by autonomous mobility could contribute up to USD 26 trillion to global GDP through better logistics coordination, reduced congestion, and optimized personal time use.
Macro-economic impact outlook
Impact area | Estimated value | Time horizon
Nightlife and leisure spending | USD 42 billion (US) | Late 2020s
Productivity gains | USD 26 trillion (global) | By 2030
Logistics efficiency | Multi-sector uplift | Ongoing
Regulation as the Primary Constraint
By 2026, technological readiness is no longer the main barrier to robotaxi expansion. Regulation has become the limiting factor. Jurisdictions with clear autonomous vehicle frameworks are advancing quickly, while others lag despite proven safety data.
In the United Kingdom, national self-driving initiatives have opened the door to pilot services involving international operators such as Baidu and Uber. In contrast, parts of the United States remain cautious, with some states maintaining restrictive policies that delay commercial deployments. This uneven landscape creates fragmented growth and raises operating costs for global fleets.
Long-term success will depend on the standardization of automated vehicle frameworks that enable permit reciprocity across states and borders. Harmonized rules for safety reporting, liability, and remote assistance would allow operators to scale more efficiently and accelerate international expansion through the late 2020s.
Regulatory readiness comparison
Region | Policy stance | Impact on deployment
United Kingdom | Proactive national framework | Faster trials and scaling
United States (mixed states) | Fragmented regulation | Uneven rollout
China | Central and local alignment | Rapid city-level expansion
Strategic Outlook Through 2035
Looking ahead, the robotaxi industry is entering a phase defined by operational excellence, regulatory navigation, and ecosystem integration. The leading companies are evolving from mobility providers into infrastructure operators that influence urban planning, energy management, and digital services.
Between 2026 and 2035, the winners will be those that combine safety leadership, cost-efficient station-based operations, and strong government relationships. As autonomous permits become more standardized and fleets scale internationally, robotaxis are positioned to become a foundational layer of urban life, reshaping how people move, work, and spend time across major global cities.
Summary of the 2026 Market Leaders
By mid-2026, the robotaxi industry has clearly moved beyond experimentation and pilot programs. What once appeared to be a long-term research challenge has now become a functioning, revenue-generating transportation sector. The leading robotaxi companies are operating large fleets, expanding across cities and countries, and proving that autonomous mobility can outperform human-driven transport on both cost and safety.
The global market is now shaped by a small group of dominant players, each following a distinct strategy based on geography, technology philosophy, and commercial focus. Together, these companies define the competitive landscape for autonomous ride-hailing in 2026.
Strategic Positioning of the Top Robotaxi Companies
The table below provides a consolidated view of how the top robotaxi companies are positioned in 2026, highlighting their core markets, strategic priorities, and underlying technology approaches.
Company | Core market focus | Primary 2026 strategy | Technology philosophy
Waymo | United States | Rapid city-by-city expansion with freeway-enabled operations | High-precision LiDAR and radar fusion
Apollo Go | China | Mass deployment of the RT6 vehicle and international trials | Low-cost LiDAR and vision fusion
Tesla | Global | High-volume Cybercab production and push toward unsupervised Full Self-Driving | Vision-only neural networks
Pony.ai | China and global markets | Gen-7 hardware rollout and IPO-driven scaling | High-redundancy compute exceeding 1,000 TOPS
WeRide | Global | Diversified autonomous fleet with licensing across multiple countries | Multi-product Level 4 integration
Zoox | United States | Purpose-built, bi-directional urban robotaxi deployment | Vertical integration with pod-style design
AutoX | China | Extreme urban navigation in dense city environments | High-density sensor fusion with ultra-high compute
Didi | China | Hybrid human and autonomous network with mass production | Platform-integrated Level 4 autonomy
Motional | United States and global | Factory-integrated robotaxis with large platform partnerships | Automotive-grade mass-scale autonomy
Mercedes-Benz and partners | Middle East | Premium S-Class robotaxi for executive and business travel | Luxury-focused autonomous service model
Key Themes Defining Market Leadership in 2026
Several clear patterns emerge when comparing these market leaders. First, hardware costs have fallen sharply, enabling mass deployment rather than limited trials. Second, ride volumes are rising quickly as wait times drop and service reliability improves. Third, statistical safety performance now favors autonomous fleets over human drivers in urban settings, especially when injury-related incidents are measured.
Another defining factor is strategic focus. Some companies prioritize low-cost, high-volume transportation for dense cities, while others concentrate on premium experiences, logistics integration, or global licensing reach. This diversity shows that robotaxis are not a single product category, but a flexible mobility layer that can serve multiple market segments.
The Robotaxi Industry’s New Reality
In 2026, the robotaxi is no longer viewed as a futuristic concept or a scientific experiment. It has become a multi-billion-dollar infrastructure asset that cities, regulators, and consumers are actively integrating into daily life. Autonomous vehicles are now competing directly with private car ownership and traditional ride-hailing on cost, convenience, and safety.
Looking forward, the companies that will dominate the next phase of global transportation are those that successfully manage three critical challenges at once: navigating complex regulatory environments, maintaining strong safety performance at scale, and mastering the unit economics of the autonomous mile. Those that succeed are not just building robotaxi fleets, but laying the foundation for the next century of urban mobility worldwide.
Conclusion
The year 2026 stands as a defining milestone in the evolution of autonomous transportation. What was once viewed as a high-risk experimental sector has now matured into a commercially viable, data-driven, and increasingly essential layer of urban mobility. The top 10 leading robotaxi companies in 2026 are no longer testing whether autonomy works. They are proving how it works at scale, how it integrates into real cities, and how it competes directly with private car ownership and human-driven ride-hailing.
Across the United States, China, the Middle East, and select European markets, robotaxis have moved decisively from pilot programs into daily operations. Millions of rider-only miles, expanding service areas, falling wait times, and improving safety metrics confirm that autonomous ride-hailing is not a future concept but a present reality. The industry has crossed the threshold where performance, cost efficiency, and reliability matter more than novelty.
Clear Market Leaders and Distinct Strategic Paths
One of the most striking takeaways from 2026 is that there is no single blueprint for robotaxi success. Instead, the market leaders have emerged through sharply different strategies. Some companies prioritize deep regulatory trust and safety data, others focus on extreme cost reduction and mass deployment, while a smaller group targets premium and luxury mobility experiences. Together, these approaches demonstrate the flexibility of the robotaxi model and its ability to serve multiple segments of the transportation market.
Despite these differences, all leading robotaxi companies share common foundations. They operate purpose-built or heavily optimized vehicles, rely on advanced AI and sensor fusion systems, and manage fleets with centralized software platforms that continuously learn from every mile driven. These shared capabilities are what separate industry leaders from companies still confined to limited testing zones.
Safety, Economics, and Scale as the Core Competitive Advantages
By 2026, safety is no longer argued through theory or simulation. It is demonstrated through large-scale, real-world data. Leading robotaxi fleets show clear reductions in injury-causing and serious accidents compared to human-driven benchmarks, particularly in dense urban environments. This statistical advantage is becoming one of the strongest drivers of regulatory approvals and public acceptance.
At the same time, economics have shifted decisively. Declining hardware costs, longer vehicle lifespans, and higher fleet utilization rates are pushing robotaxi services closer to, and in some regions below, the cost of private car ownership. In markets with supportive regulation and high urban density, autonomous rides are already cheaper than traditional ride-hailing. This economic inflection point is critical, as cost competitiveness is what enables mass adoption rather than niche usage.
Scale amplifies both safety and economics. Every additional vehicle and every additional mile strengthens the data advantage of leading operators, allowing faster software improvement and better fleet optimization. This creates a widening gap between market leaders and smaller competitors, reinforcing consolidation around a handful of dominant global players.
Regulation as the Final Gatekeeper
While technology and economics have largely aligned, regulation remains the most significant variable shaping the future of robotaxis beyond 2026. Regions with clear, standardized autonomous vehicle frameworks are accelerating deployment, while fragmented or restrictive policies continue to slow progress in other areas. The companies best positioned for long-term success are those that combine technical excellence with deep regulatory engagement and compliance.
Looking ahead, the standardization of autonomous driving rules across cities, states, and countries will be the key catalyst for global scale. As regulatory reciprocity improves, robotaxi networks will expand more rapidly across borders, transforming autonomous mobility into a truly international service.
From Transportation Product to Urban Infrastructure
Perhaps the most important shift revealed in 2026 is the changing role of robotaxis in society. They are no longer just a transportation product competing for rides. They are becoming urban infrastructure. Robotaxi fleets influence city planning, parking demand, energy usage, and even how people allocate time during daily commutes. Travel time is increasingly transformed into productive or restorative time, reshaping work patterns and lifestyle choices.
For cities facing congestion, emissions targets, and rising mobility costs, robotaxis offer a scalable alternative that aligns with long-term urban sustainability goals. For consumers, they represent a practical and increasingly attractive option that reduces the need to own a personal vehicle.
The Road Ahead Beyond 2026
As this analysis of the top 10 leading robotaxi companies in 2026 shows, the industry has entered a phase of execution rather than experimentation. The winners of the next decade will be those that master three interconnected challenges: maintaining superior safety performance at scale, achieving sustainable unit economics, and navigating complex regulatory landscapes across multiple regions.
Robotaxis are no longer a question of if, but of how fast and how widely they will reshape global transportation. The companies leading the market in 2026 are not just building autonomous vehicles. They are laying the foundation for a new mobility system that will define how cities move, work, and grow for decades to come.
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your hiring manager and C-level suite friends and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the 9cv9 Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.
To get access to top-quality guides, click over to 9cv9 Blog.
To hire top talents using our modern AI-powered recruitment agency, find out more at 9cv9 Modern AI-Powered Recruitment Agency.
People Also Ask
What is a robotaxi and how does it work in 2026
A robotaxi is a fully autonomous vehicle that provides ride-hailing services without a human driver, using AI, sensors, and real-time navigation to transport passengers safely in defined areas.
Which are the top robotaxi companies in 2026
The leading robotaxi companies in 2026 include global players from the US, China, and the Middle East that operate large-scale driverless fleets with proven safety and commercial deployment.
Are robotaxis commercially available in 2026
Yes, robotaxis are commercially available in several major cities worldwide in 2026, offering rider-only trips without safety drivers in approved urban zones.
How safe are robotaxis compared to human drivers
Data from large fleets shows robotaxis have significantly fewer injury-related accidents than human drivers, especially in urban areas, due to constant attention and predictable driving behavior.
Do robotaxis cost less than Uber or taxis in 2026
In many cities, robotaxis are already cheaper than traditional ride-hailing, particularly in China, while some premium services still charge slightly more for comfort and reliability.
Can robotaxis operate without a human inside the vehicle
Yes, leading robotaxi companies in 2026 operate fully driverless vehicles, with remote support available only for rare edge-case situations.
Which countries allow robotaxi services in 2026
Robotaxi services are active in the United States, China, the UAE, parts of Europe, and select Asian markets with supportive autonomous vehicle regulations.
What technology powers robotaxis in 2026
Robotaxis rely on AI software, sensor fusion using cameras, radar, and LiDAR, high-performance computing, and real-time mapping to navigate complex urban environments.
Are robotaxis electric vehicles
Most robotaxis in 2026 are fully electric, as EV platforms reduce operating costs, support sustainability goals, and integrate well with autonomous driving systems.
How do robotaxis handle emergencies or road closures
Robotaxis use advanced AI to reroute automatically and can request remote human assistance when encountering unusual road conditions or unexpected obstacles.
Do robotaxis work at night and in bad weather
Yes, many robotaxi fleets operate 24/7, including nighttime driving, though extreme weather conditions may still limit service in certain regions.
Can robotaxis replace private car ownership
In dense cities, robotaxis are becoming a practical alternative to owning a car by eliminating parking, maintenance, and insurance costs for daily travel.
What is Level 4 autonomy in robotaxis
Level 4 autonomy means the vehicle can drive itself without human input within specific areas and conditions, which is the standard for most robotaxis in 2026.
How do passengers book a robotaxi
Passengers typically book robotaxis through mobile apps, either dedicated robotaxi apps or integrated platforms that also offer human-driven rides.
Are robotaxis available for airport transfers
Yes, many robotaxi services in 2026 include airport routes, especially in cities where regulations allow freeway and long-distance autonomous driving.
Do robotaxis have steering wheels
Some robotaxis still include steering wheels for regulatory reasons, while purpose-built models operate without any traditional driving controls.
How do robotaxi companies make money
Robotaxi companies generate revenue through per-ride fares, fleet partnerships, data-driven mobility services, and in some cases premium or enterprise transport offerings.
What is the biggest challenge for robotaxis in 2026
The main challenge is regulatory approval across regions, as laws and safety requirements differ widely between countries and even individual states or cities.
Can robotaxis operate internationally
Some leading robotaxi companies are expanding internationally, but large-scale global operations depend on regulatory harmonization between countries.
Are robotaxis environmentally friendly
Robotaxis reduce emissions by using electric vehicles and optimizing routes, while also lowering the total number of cars needed in busy cities.
Do robotaxis reduce traffic congestion
When deployed at scale, robotaxis can reduce congestion by increasing vehicle utilization, lowering idle time, and decreasing private car ownership.
How fast is the robotaxi market growing
The robotaxi market is growing rapidly, with strong year-over-year increases in ride volume and long-term forecasts reaching hundreds of billions in market value.
Are robotaxis used for business travel
Yes, many professionals use robotaxis for business travel due to privacy, reliability, and the ability to work during the ride.
What is remote vehicle assistance
Remote vehicle assistance allows trained operators to guide robotaxis through rare or complex situations without taking direct control of the vehicle.
Can robotaxis be used by elderly or disabled passengers
Many robotaxi services support accessibility features such as step-free entry, spacious cabins, and app-based assistance for elderly or disabled users.
How do robotaxis learn and improve over time
Robotaxis improve through fleet learning, where data from millions of miles is used to update software across all vehicles simultaneously.
Are robotaxis allowed on highways
In approved markets, robotaxis can operate on highways, which increases trip range and improves overall service usefulness.
Will robotaxis replace human drivers completely
Robotaxis will reduce demand for human drivers in urban transport, but human-operated vehicles are expected to remain in certain roles and regions.
What makes a robotaxi company a market leader
Market leaders combine strong safety data, low operating costs, regulatory trust, scalable fleets, and consistent passenger experience across cities.
What does the future look like for robotaxis after 2026
Beyond 2026, robotaxis are expected to expand globally, become cheaper, integrate with city infrastructure, and play a major role in daily urban mobility.
Sources
Grand View Research
Market.us
Netguru
Zapier
Crunchbase News
DataCamp
AT Labs AI
GM Insights
Medium
Vast AI
CometAPI
AIxploria
Jotform
TMCnet
Synthesia
PCMag
Skywork AI
Sima Labs AI
AI Tools SME
Pixazo AI
Imagine Art
AIMultiple
Aloa
InVideo AI
Luma AI
Tracxn
Max Productive AI
HeyGen
Hyperstack
Kling AI
Eesel AI
WPP
Future Party
TheWrap
PetaPixel
U.S. Copyright Office
McDermott Will & Schulte
Finnegan
Crescendo AI
AI Funding Tracker































![Writing A Good CV [6 Tips To Improve Your CV] 6 Tips To Improve Your CV](https://blog.9cv9.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/2020-06-02-2-100x70.png)


