Key Takeaways
- Understanding the legal requirements, including obtaining necessary licenses and permits, is crucial when registering a company in Vietnam as a foreigner.
- Cultural considerations, such as building strong relationships with local partners and learning some basic Vietnamese phrases, can be key to success in the Vietnamese market.
- Working with experienced advisors to navigate the investment and taxation landscape in Vietnam is important to ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
Vietnam is rapidly emerging as one of the most dynamic and fastest-growing economies in Southeast Asia, and its government has been actively encouraging foreign investment in the country’s burgeoning business scene.
However, for those who are new to the Vietnamese market, navigating the legal and cultural landscape can be challenging.
As a foreigner, you need to have a clear understanding of the requirements, regulations, and cultural considerations that come with registering a company in Vietnam.
In this article, we’ll explore the top 5 things you need to know before starting the process.
Whether you’re a first-time entrepreneur or an experienced business owner looking to expand into Vietnam, this guide will help you get started on the right foot.
From legal requirements to business structures, investment and taxation, and cultural considerations, we’ve got you covered.
So let’s dive in and explore the top 5 things to know before registering a company in Vietnam as a foreigner.
Before that, can foreigners start a business in Vietnam?
Can Foreigners start a business in Vietnam?
Well, hello there, ambitious entrepreneur.
Are you wondering whether you can start a business in Vietnam as a foreigner?
The answer is a big, fat YES.
You can do it, my friend.
There are two ways to go about it. You can opt for direct foreign investment, where you team up with a Vietnamese partner to form a 100% foreign-owned company or a joint venture company.
Just keep in mind, you’ll need an enterprise license and a bit of legal know-how to make it happen.
Or, if you prefer, you can just do the Employer of Record secret hack to save your hassles in all of this.
If you prefer the indirect route, you can purchase shares of existing companies in Vietnam.
This grants you a stake in the company management, depending on the agreement between you and the Vietnamese company.
But hold your horses, there are a few key considerations to keep in mind.
From navigating the legal procedures to understanding common forms of business investment, we’ve got you covered.
So keep reading to rock your business in Vietnam like a boss!
Before we venture further into this article, we like to share who we are and what we do.
About 9cv9
9cv9 is a business tech startup based in Singapore and Vietnam with a strong presence worldwide.
With over six years of startup and business experience, and being highly involved in connecting with thousands of companies and startups, the 9cv9 team has listed some important learning points in this overview of how to register a company in Vietnam as a foreigner.
If your company needs recruitment and headhunting services down the road after registration, you can use 9cv9 headhunting and recruitment services to hire top talents and candidates in Vietnam. Book a consultation slot here, or send over an email to [email protected].
Top 5 Things to Know Before Registering a Company in Vietnam as a Foreigner
- Legal Requirements
- Business Structure
- Investment and Taxation
- Minimum Capital Requirement
- Cultural Considerations
1. Legal Requirements
Before you can register a company in Vietnam as a foreigner, it’s important to understand the legal requirements and regulations involved.
The Vietnamese government has been actively encouraging foreign investment, but there are still a number of legal hurdles you’ll need to clear in order to get your business up and running.
First and foremost, you’ll need to obtain an Investment Registration Certificate (IRC) from the Department of Planning and Investment in the province where your business will be located.
This certificate is essential for obtaining the necessary licenses and permits to operate legally in Vietnam.
Sounds easy, right?
But hold on, this application has to pass the scrutiny of the almighty Department of Planning and Investment.
The licensing authorities that review your application can vary.
It’s like a game of chance, except instead of winning big, you’re just trying to get your business off the ground.
But don’t worry, with a little patience and perseverance, you’ll be on your way to getting that coveted IRC and fulfilling your entrepreneurial dreams in Vietnam.
For investment projects situated outside of industrial zones, export processing zones, high-tech zones, and economic zone, the right place to do an application is the almighty Department of Planning and Investment.
For those investment projects situated within industrial zones, export processing zones, high-tech zones, and economic zones, then it is the provincial industrial zone management authority or economic zone management authority.
Typically, it takes about 15 days for the Investment Registration Certificate to be approved.
In addition to the IRC, you’ll also need to register your company with the Business Registration Office to obtain an important document called the “Enterprise Registration Certificate” or the ERC.
Read more on our guide to help you get started on the nitty-gritty details of getting the ERC.
This involves submitting a range of documents, including your company’s charter, a list of shareholders, and information about your legal representative in Vietnam.
An ERC application is normally processed in 3 working days or more.
It’s worth noting that the process of registering a company in Vietnam can be quite complex and time-consuming.
It’s important to work with a local lawyer or business consultant, or 9cv9 Corporate Service Team who has experience in this area to ensure that you’re meeting all the necessary requirements and completing the paperwork correctly.
In Vietnam, some investment projects fall under the “conditional” sector, which means you’ll have to jump through a few more hoops to get the green light.
For instance, if you’re interested in making seals, trading securities, or providing accounting/auditing services, you’ll need to apply for further licensing and undergo a rigorous examination by government officials.
And that’s just the tip of the iceberg, folks.
Appendix 4 of the Law on Investment lists several other businesses subject to these conditions, including insurance, security, and project management consultancy services.
But don’t let the red tape get you down.
Once you’ve got the necessary approvals, you’ll need to gather specific documents to complete your business setup in Vietnam.
The type of documents required will depend on the business structure you choose.
Another potential challenge for foreign business owners in Vietnam is the requirement to have a Vietnamese partner or legal representative.
While this requirement has been relaxed somewhat in recent years, it’s still something that you’ll need to consider when setting up your business.
Of course, 9cv9 Corporate Service team has solutions to address and solve this issue for you. Simply, book a consultation slot here, or send over an email to [email protected].
Overall, understanding the legal requirements for registering a company in Vietnam as a foreigner is crucial for ensuring that your business is set up for success.
By working with experienced professionals and ensuring that you’re meeting all the necessary regulations, you can avoid costly mistakes and get your business up and running as quickly as possible.
2. Business Structure
When it comes to registering a company in Vietnam as a foreigner, one of the most important decisions you’ll need to make is choosing the right business structure.
There are several different types of business structures available in Vietnam, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
The most common types of business structures in Vietnam include Limited Liability Companies (LLCs), Joint Stock Companies (JSCs), and Representative Offices (ROs).
LLCs are a popular choice for small and medium-sized businesses as they offer limited liability protection and require a minimum of just one shareholder. For more, read our most comprehensive guide on how to register an LLC in Vietnam.
JSCs, on the other hand, are better suited for larger businesses as they allow for the sale of stocks and the raising of capital from a wide range of investors. For more, read our tantalizing guide to whet your appetite on how to register a JSC in Vietnam.
Representative Offices, on the other hand, are ideal for businesses that are looking to establish a presence in Vietnam but don’t yet have the resources or legal capacity to operate as a fully-fledged company.
They are limited in their scope of activities and cannot generate income, but they allow for market research, product promotion, and other non-commercial activities.
It’s important to carefully consider your business objectives, market positioning, and long-term goals when choosing a business structure in Vietnam.
You’ll also need to consider the tax implications of each structure, as different structures are subject to different tax rates and regulations.
Ultimately, the right business structure for your company will depend on a range of factors, including your industry, business objectives, and financial resources.
By working with experienced legal and business advisors, you can make an informed decision and choose the structure that’s best suited to your needs.
3. Investment and Taxation
When it comes to registering a company in Vietnam as a foreigner, one of the most important factors to consider is investment and taxation.
Understanding the investment climate and taxation system in Vietnam can help you make informed decisions and ensure that you’re maximizing your profits while complying with local regulations.
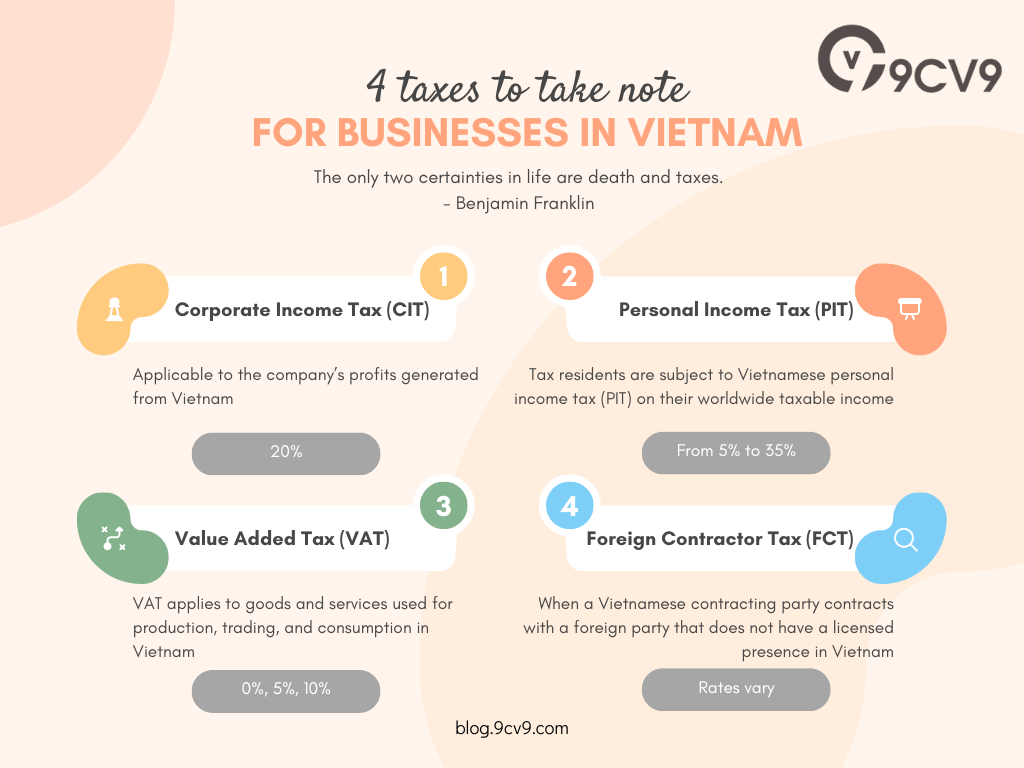
If you’re starting a business in Vietnam, you need to keep an eye out for four common taxes: Value Added Tax (VAT), Corporate Income Tax (CIT), Personal Income Tax (PIT), and Foreign Contractor Tax (FCT).
But don’t freak out just yet.
There are some sweet tax reliefs available to help reduce your tax liabilities.
Here are a few options to consider:
- CIT: You can snag a preferential tax rate and even tax holidays. That’s right, take a vacation from taxes.
- PIT: You can deduct expenses for compulsory insurance contributions, charity purposes, and even family-related expenses. Your tax bill just got a little lighter.
- VAT: Certain businesses can score VAT exemptions. It’s like getting a tax-free pass.
- FCT: If you’re an overseas corporate shareholder, you won’t have to deal with pesky withholding tax on your dividends. Yay for more money in your pocket.
Foreign investors must register with the Department of Tax the tax code number under their company.
If you’re planning to set up a business in Vietnam, you should also take note of the yearly Business License Tax (BLT) imposed on all entities.
The BLT rate is determined by the amount of registered capital of the company, and it varies for different economic entities, households, and individuals.
For instance, if your company’s registered capital is more than 10 billion VND, you’ll be charged a BLT of 3 million VND annually.
If it’s less than 10 billion VND, the charge will be 2 million VND per year.
Meanwhile, branches, representative offices, and business premises will be taxed 1 million VND per year.
That said, the government has decided to waive the first-year Business License Tax (BLT) for freshly incorporated businesses, ROs, branches, and business premises that were established during the exemption period from 25 Feb 2020.
This tax holiday also extends to general education-related entities, households, and individuals starting a business in Vietnam for the first time, as well as small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) who may be eligible for a three-year exemption, but only if they meet certain conditions.
One of the key advantages of investing in Vietnam is its low labor costs and relatively low overheads.
The country also offers a number of tax incentives for foreign investors, including exemptions on corporate income tax and import/export duties for certain industries.
However, it’s important to note that the tax system in Vietnam can be quite complex and regulations are subject to change.
As such, it’s important to work with the 9cv9 Corporate Service team who can help you navigate the system and ensure that you’re complying with all relevant regulations.
Another important consideration when it comes to investment in Vietnam is the country’s Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) laws.
These laws govern the ownership and control of companies in Vietnam by foreign investors and require that a certain percentage of shares be held by Vietnamese individuals or organizations.
In addition to FDI laws, there are also restrictions on foreign ownership in certain industries, such as banking and telecommunications.
It’s important to carefully research these regulations and work with experienced legal advisors to ensure that your investment is compliant and legally protected.
Overall, investing in Vietnam can be a lucrative opportunity for foreign businesses.
However, it’s important to carefully consider investment and taxation factors and work with experienced advisors to ensure that you’re maximizing your profits while complying with all relevant regulations.
4. Minimum Capital Requirement
When it comes to setting up a company in Vietnam, one of the essential aspects to consider is the minimum capital requirement.
While there is no fixed minimum capital requirement, certain conditional business lines have specific capital requirements.
For instance, financial institutions such as commercial banks, branches of foreign banks in Vietnam, or finance companies must have a minimum capital amount ranging between 150 billion VND and 3000 billion VND.
In contrast, investing in higher education institutions or universities in Vietnam requires at least 500 billion VND (21.5 million USD) in capital.
For most other business sectors, having a capital of at least 10,000 USD is a base to consider before investing in Vietnam.
However, the Department of Planning and Investment determines the capital amount required in the field of business for foreign investors.
It is essential to note that having sufficient capital is critical to the success of your business in Vietnam, as it helps to establish your financial stability and credibility in the local market.
In addition to the minimum capital requirement, it’s also important to note that you must have a local bank account in Vietnam to deposit the capital.
This means that you must have a business visa or a work permit, which can take some time to obtain.
It’s important to ensure that you have enough capital to cover your business expenses, such as rent, salaries, and other operational costs.
You should also be aware that the capital requirement may change over time, and it’s essential to keep track of any updates or changes in the law.
In summary, before registering a company in Vietnam as a foreigner, it’s crucial to understand the minimum capital requirement for your business entity type and ensure that you have the necessary funds to cover your expenses.
By doing so, you can avoid any legal issues and ensure a smooth start to your business venture in Vietnam.
5. Cultural Considerations
When it comes to registering a company in Vietnam as a foreigner, it’s important to take cultural considerations into account.
As written in our previous article “10 Characteristics of Workplace Culture in Southeast Asia You Need to Know“, we wrote about some unique behaviors such as:
- Respect and Authority
- Collectivism vs Individualism
- Face-Saving and Conflict Resolution
- Confucian Values
- Emphasis on Relationships
- Work-Life Balance
- Respect for Elders and Experienced Colleagues
- Gift-Giving and Social Obligations
- Continuous Learning and Improvement
- Hierarchical Decision-Making
Vietnam has a unique culture and business environment, and understanding the local customs and practices can help you build strong relationships with customers, partners, and employees.
One of the most important aspects of Vietnamese culture is the emphasis on personal relationships and networking.
Building strong relationships with local partners and stakeholders can be key to the success of your business in Vietnam.
This means investing time and effort into networking events, social gatherings, and other opportunities to connect with local business leaders and influencers.
Another important cultural consideration in Vietnam is the importance of hierarchy and respect for authority.
This can impact business decision-making, negotiation strategies, and overall communication with local partners and employees.
It’s important to understand and respect these cultural norms in order to build strong and effective working relationships.
Language is also an important consideration in Vietnam, as Vietnamese is the official language of business and government.
While many Vietnamese businesspeople speak English, it’s important to learn at least some basic Vietnamese phrases in order to show respect and build rapport with local partners and employees.
Finally, it’s worth noting that Vietnam has a unique work culture, with a strong emphasis on family and work-life balance.
This can impact the way that business is conducted, with a greater focus on personal relationships and flexible working arrangements.
By understanding and respecting these cultural norms, you can build a positive and productive work environment for your employees.
Overall, taking cultural considerations into account is crucial when registering a company in Vietnam as a foreigner.
By investing time and effort into building relationships, understanding cultural norms, and respecting local practices, you can set your business up for success in the Vietnamese market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, registering a company in Vietnam as a foreigner can be a complex and challenging process.
However, by keeping these top five things in mind, you’ll be well on your way to success in the Vietnamese market.
Remember to pay attention to the legal requirements, including obtaining the necessary licenses and permits, and setting up the appropriate business structure.
Make sure you’re aware of the investment and taxation landscape in Vietnam, and work with experienced advisors to ensure that you’re complying with all relevant regulations.
Don’t forget about the cultural considerations, either!
Building strong relationships with local partners, respecting cultural norms, and learning a bit of Vietnamese can go a long way in building a successful business in Vietnam.
And of course, don’t forget to have a sense of humor!
The Vietnamese culture is rich and vibrant, and by embracing the local customs and practices with a light-hearted attitude, you can build strong and lasting relationships with your Vietnamese partners and employees.
So go forth, aspiring entrepreneurs!
With these top five things in mind, you’re ready to take on the Vietnamese market and register your company with confidence. Good luck, and may the phở be with you.
If your company needs HR, hiring, or corporate services, you can use 9cv9 corporate services. Book a consultation slot here, or send over an email to [email protected].
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your corporate friends and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the 9cv9 Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.































![Writing A Good CV [6 Tips To Improve Your CV] 6 Tips To Improve Your CV](https://blog.9cv9.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/2020-06-02-2-100x70.png)


