Key Takeaways
- The top 10 Desktop as a Service (DaaS) software in 2026 compete on security, AI-driven management, pricing flexibility, and multi-cloud performance.
- Modern DaaS platforms reduce Total Cost of Ownership by up to 20% through automation, usage-based pricing, and cloud-native scalability.
- Choosing the right DaaS solution in 2026 depends on workforce size, compliance requirements, GPU needs, and long-term digital transformation strategy.
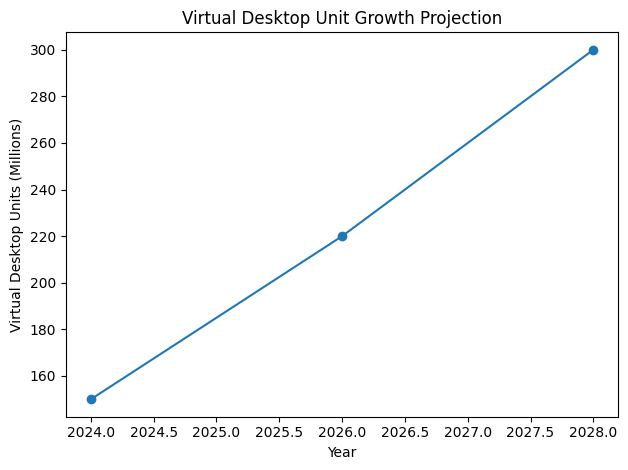
In 2026, Desktop as a Service (DaaS) is no longer a niche virtualization strategy reserved for remote access scenarios. It has evolved into the backbone of modern enterprise IT, redefining how organizations deploy, secure, and scale digital workspaces. As businesses navigate hybrid work models, rising cybersecurity threats, global talent distribution, and increasing cost pressures, cloud-based virtual desktops have become a strategic necessity rather than an optional enhancement.

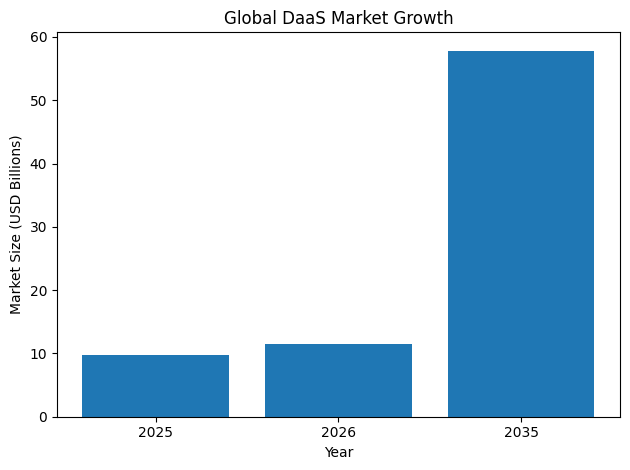
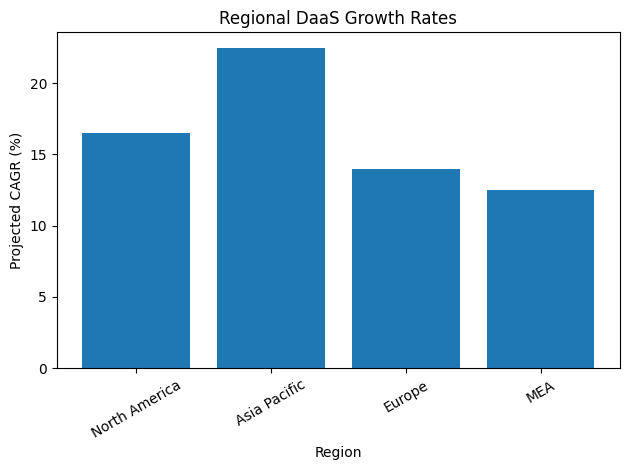
The global Desktop as a Service market has matured into a multi-billion-dollar industry, driven by demand for secure cloud desktops, AI-powered management tools, and flexible pricing models that align with dynamic workforce structures. Enterprises are moving beyond traditional endpoint-heavy infrastructure and adopting centralized, cloud-delivered computing environments that decouple user experience from physical hardware. This transformation allows employees to securely access their corporate desktop from any device, anywhere in the world, without compromising performance or compliance.
The top 10 Desktop as a Service software platforms in 2026 represent the most advanced and widely adopted solutions shaping this digital workspace revolution. These platforms differ in architecture, pricing strategy, performance optimization, security frameworks, and ecosystem integration. Some emphasize deep multi-cloud compatibility across Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud. Others focus on GPU-powered virtual workstations for engineering and creative workloads. Still others redefine efficiency through container streaming or browser-native environments that eliminate traditional virtual machine overhead.
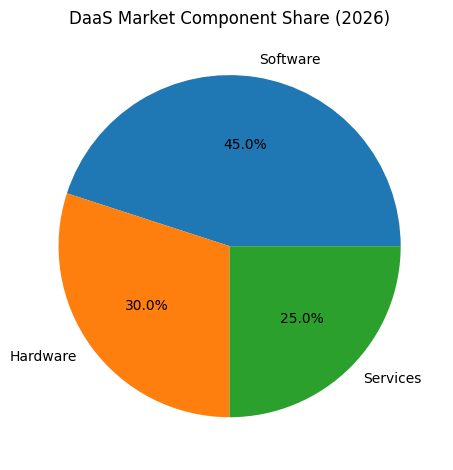
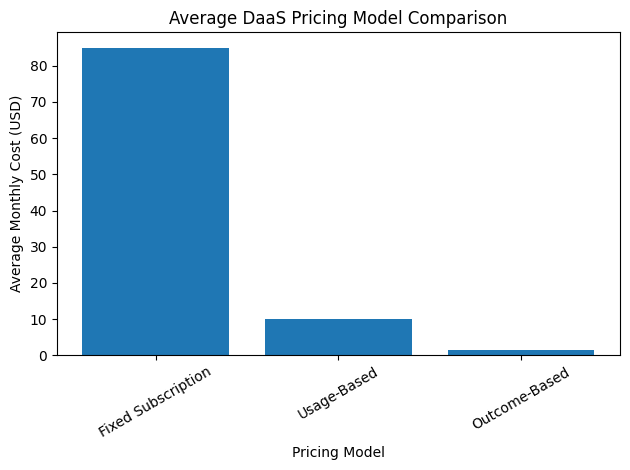
Choosing the right DaaS software in 2026 requires more than comparing feature lists. IT leaders must evaluate Total Cost of Ownership, bandwidth requirements, Zero Trust security models, compliance certifications, AI-driven automation capabilities, and long-term scalability. Pricing structures have also diversified significantly, ranging from fixed per-user subscriptions to usage-based and hybrid billing models that support contractors, seasonal workers, and globally distributed teams. As SaaS pricing continues to evolve, organizations must align their digital workspace strategy with workforce dynamics and financial forecasting models.
Security remains a primary catalyst behind DaaS adoption. With ransomware attacks and data exfiltration incidents increasing in sophistication, businesses are prioritizing cloud-hosted desktops that isolate corporate data within secure environments. Modern DaaS platforms incorporate Zero Trust Network Access, granular Data Loss Prevention controls, continuous compliance monitoring, and AI-driven anomaly detection to protect sensitive information across remote endpoints. For regulated industries such as finance, healthcare, and government, these capabilities are not optional; they are mandatory.
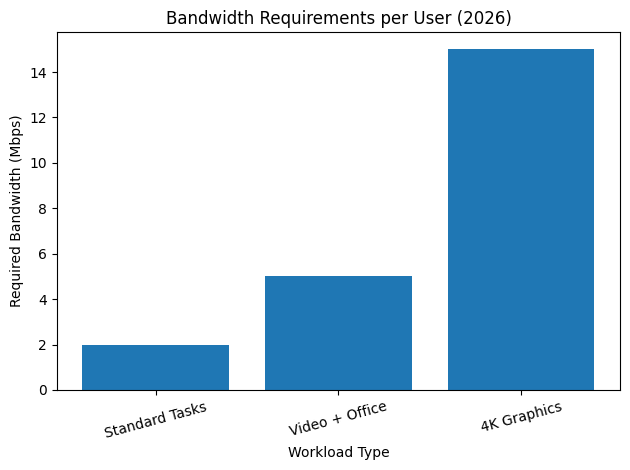
Performance has also undergone dramatic improvements. Advances in remoting protocols, GPU virtualization, adaptive compression, and edge computing have reduced bandwidth requirements while enabling high-resolution, low-latency experiences. In 2026, many DaaS providers can deliver 4K, 60fps desktop performance with significantly lower bandwidth consumption than previous generations, making cloud desktops viable even for graphics-intensive workloads.
The rise of AI integration is another defining trend. Leading Desktop as a Service platforms now embed intelligent orchestration engines capable of predictive scaling, automated patch management, behavioral authentication, and real-time optimization. This shift from manual administration to AI-driven infrastructure management significantly reduces operational overhead and enhances service reliability.
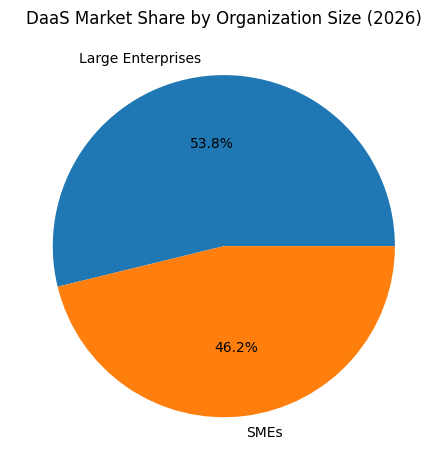
As organizations plan their digital transformation roadmap, understanding the strengths and differentiators of the top 10 Desktop as a Service software platforms in 2026 is critical. Each solution addresses a specific market segment, whether small and medium enterprises seeking cost efficiency, large enterprises requiring global compliance controls, development teams needing cloud-native workstations, or creative industries demanding GPU acceleration.
This comprehensive guide examines the leading DaaS providers in 2026, analyzing their pricing models, security architecture, management capabilities, protocol efficiency, and ideal use cases. By evaluating the strategic advantages and limitations of each platform, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals, workforce structure, and long-term innovation strategy.
In a world where work is no longer defined by location or hardware, Desktop as a Service has become the standard definition of enterprise computing. The organizations that embrace this shift strategically will gain competitive advantages in agility, security, cost optimization, and workforce empowerment.
Before we venture further into this article, we would like to share who we are and what we do.
About 9cv9
9cv9 is a business tech startup based in Singapore and Asia, with a strong presence all over the world.
With over nine years of startup and business experience, and being highly involved in connecting with thousands of companies and startups, the 9cv9 team has listed some important learning points in this overview of the Top 10 Desktop as a Service (DaaS) Software in 2026.
If you like to get your company listed in our top B2B software reviews, check out our world-class 9cv9 Media and PR service and pricing plans here.
Top 10 Desktop as a Service (DaaS) Software in 2026
- Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD)
- Amazon WorkSpaces
- Windows 365 (Microsoft Cloud PC)
- Citrix DaaS
- Omnissa Horizon Cloud (formerly VMware)
- Parallels RAS (Remote Application Server)
- Nutanix Frame
- Kasm Workspaces
- Workspot
- Google Cloud Workstations
1. Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD)
Desktop as a Service (DaaS) has evolved significantly by 2026, driven by hybrid work models, cybersecurity requirements, global workforce mobility, and cost optimization strategies. Among the top 10 Desktop as a Service software platforms worldwide, Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop consistently stands out as a market leader due to its architectural flexibility, enterprise-grade security, and deep ecosystem integration.
Positioned at the intersection of cloud infrastructure and digital workspace management, Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD) is widely regarded as a strategic platform for enterprises seeking scalable, secure, and centrally managed desktop virtualization.
Overview of Microsoft Azure Virtual Desktop in 2026
Azure Virtual Desktop remains one of the most influential DaaS platforms globally. It is particularly dominant among enterprises operating within the Microsoft ecosystem, offering seamless integration with Microsoft 365, Azure services, and Windows Enterprise licensing models.
Its most differentiated feature in 2026 continues to be the exclusive Windows 11 and Windows 10 Enterprise multi-session capability. This architecture allows multiple users to share a single virtual machine while maintaining isolated user environments, significantly optimizing infrastructure utilization.
By reducing one-to-one virtual desktop allocations, organizations are able to lower compute costs, reduce operating system overhead, and improve overall cloud efficiency.
Core Platform Capabilities
Azure Virtual Desktop provides a comprehensive set of technical capabilities designed for enterprise-grade deployment:
Product Architecture and OS Support
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Supported Operating Systems | Windows 11 Enterprise, Windows 10 Enterprise, Windows Server |
| Deployment Models | Public Azure, Azure Local (Hybrid On-Premises), Multi-Region |
| Virtualization Type | Multi-session and Single-session |
| Application Delivery | MSIX App Attach for dynamic app streaming |
| User Profile Management | FSLogix container-based profile management |
| Infrastructure Management | Azure Resource Manager-based orchestration |
The integration with Azure Local allows organizations to host workloads partially on-premises while maintaining centralized management from Azure. This hybrid flexibility has become increasingly important for industries with regulatory data residency requirements.
Multi-Session Efficiency Model
| Deployment Model | VM Allocation Method | Cost Impact Level | Use Case Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional 1:1 VDI | 1 user per VM | High infrastructure | High-security isolation |
| AVD Multi-Session | Multiple users per VM | Optimized cloud spend | Task workers, knowledge workers |
| Hybrid Pooling | Dynamic user allocation | Variable | Seasonal workloads |
The multi-session capability remains the primary cost optimization driver, particularly for large-scale rollouts across distributed teams.
Security Architecture and Compliance Framework
Security is a defining pillar of Azure Virtual Desktop’s global adoption in 2026. The platform integrates deeply with Microsoft’s identity, compliance, and threat detection stack.
Security and Identity Controls
| Security Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Reverse Connect Technology | Eliminates need for inbound open ports |
| Identity Management | Entra ID integration with granular RBAC |
| Conditional Access | Policy-based device and user validation |
| Endpoint Security Integration | Native integration with Microsoft Defender |
| Data Encryption | Encryption at rest and in transit |
Reverse connection technology ensures that no inbound ports are required, reducing exposure to external attack vectors. Role-based access control through Entra ID enables fine-grained administrative permissions, making it suitable for complex enterprise environments.
Compliance Readiness
Azure Virtual Desktop aligns with major global regulatory frameworks through Microsoft Azure’s compliance portfolio. Industries such as finance, healthcare, and public sector leverage this compliance foundation to meet audit and governance standards.
Pricing and Cost Structure in 2026
Unlike traditional subscription-based DaaS platforms, Azure Virtual Desktop operates under a consumption-based pricing model.
Cost Components Overview
| Cost Element | Billing Model |
|---|---|
| Compute Resources | Pay-as-you-go per VM usage |
| Storage | Based on Azure storage consumption |
| Networking | Data egress and bandwidth pricing |
| Licensing | Eligible Microsoft 365 or Windows license |
| Autoscale Management | Reduces off-hours compute spend |
Organizations manage costs directly through their Azure subscription. The Autoscale capability dynamically adjusts infrastructure capacity based on user demand, which is critical for reducing after-hours or seasonal operational expenses.
Enterprise IT teams typically achieve cost savings when implementing optimized multi-session host pools and right-sizing virtual machines.
Strengths and Considerations
Strengths Matrix
| Strength Category | Evaluation |
|---|---|
| Ecosystem Integration | Deep integration with Microsoft 365 and Azure |
| Multi-Session Optimization | Unique enterprise advantage |
| Hybrid Deployment | Strong hybrid cloud support |
| Security Model | Enterprise-grade, zero inbound exposure |
| Global Infrastructure | Extensive Azure data center footprint |
Challenges and Considerations
| Consideration Area | Impact Level | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Architecture Design | High | Requires detailed planning and expertise |
| Networking Configuration | Moderate | Complex Azure networking knowledge required |
| FSLogix Optimization | Moderate | Profile container configuration learning curve |
| Skill Requirements | High | IT staff must understand Azure ecosystem deeply |
Organizations frequently report that deployment success is highly dependent on initial architecture design. Without proper planning around networking, storage, and profile management, performance issues may arise.
Real-World User Experience in 2026
Enterprise user feedback in 2026 reflects a consistent theme: Azure Virtual Desktop performs exceptionally well once properly configured.
Many organizations highlight that the platform requires a significant learning period, particularly in understanding Azure networking architecture and FSLogix profile containers. However, after customization and optimization, the solution delivers stable performance and measurable cost reductions.
The multi-session capability is often cited as the decisive factor in long-term adoption. Compared to traditional one-to-one VDI deployments, organizations report noticeable reductions in monthly cloud expenditures when user density is optimized.
Strategic Position Within the Top 10 DaaS Platforms Globally
Within the competitive landscape of Desktop as a Service software in 2026, Azure Virtual Desktop is typically positioned as:
| Category | Market Position |
|---|---|
| Enterprise Scalability | Market Leader |
| Microsoft Ecosystem Integration | Dominant |
| Hybrid Cloud Capability | Advanced |
| Cost Efficiency (Optimized Setup) | High |
| Ease of Initial Deployment | Moderate to Complex |
While other DaaS vendors may offer simpler out-of-the-box experiences, Azure Virtual Desktop excels in enterprise customization, global scalability, and long-term cost optimization for organizations already invested in Microsoft infrastructure.
Conclusion
As organizations worldwide continue to refine their hybrid work strategies, Azure Virtual Desktop remains a cornerstone solution within the top 10 Desktop as a Service platforms in 2026. Its exclusive multi-session Windows capability, enterprise-grade security architecture, and consumption-based cost model position it as a powerful yet technically demanding solution.
For enterprises with strong Azure expertise and strategic cloud governance, Azure Virtual Desktop represents one of the most scalable and cost-effective DaaS solutions available in the global market.
2. Amazon WorkSpaces
As Desktop as a Service adoption accelerates globally in 2026, enterprises are increasingly evaluating platforms based on performance stability, ecosystem compatibility, cost transparency, and remote workforce scalability. Among the top 10 Desktop as a Service (DaaS) software platforms worldwide, Amazon WorkSpaces continues to maintain a strong position, particularly among organizations deeply invested in Amazon Web Services infrastructure.
Amazon WorkSpaces is widely recognized for delivering a fully managed, persistent virtual desktop environment that emphasizes reliability, operational consistency, and seamless integration with AWS-native services.
Platform Overview and Market Position
Amazon WorkSpaces is designed as a cloud-native desktop virtualization service that removes the complexity of managing traditional VDI infrastructure. In 2026, the platform has matured significantly, especially in hardware flexibility and performance tiers.
One of its major enhancements is the expansion of high-performance hardware bundles, including the GraphicsPro instance class. These bundles target media professionals, 3D designers, architects, and engineering teams requiring GPU-accelerated rendering capabilities.
Within the broader DaaS landscape, Amazon WorkSpaces is typically positioned as a dependable, enterprise-ready solution for organizations that prioritize:
• Persistent desktops
• Predictable configuration management
• AWS ecosystem integration
• Flexible billing models
Technical Specifications and Architecture
Amazon WorkSpaces supports both Windows and Linux operating systems, making it suitable for mixed IT environments.
Core Technical Capabilities
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Supported Operating Systems | Windows, Linux |
| Desktop Type | Persistent (user retains same desktop environment) |
| Protocol Technology | WorkSpaces Streaming Protocol (WSP) |
| Storage Architecture | Persistent storage backed up to Amazon S3 |
| GPU Options | Graphics and GraphicsPro bundles |
| Directory Integration | AWS Directory Service, Active Directory |
The WorkSpaces Streaming Protocol (WSP) has become a defining technical component. It is engineered to improve responsiveness in environments with higher network latency, which is particularly important for globally distributed teams.
Persistent Desktop Model
Unlike non-persistent pooled desktop models common in some DaaS platforms, Amazon WorkSpaces primarily operates as a persistent desktop solution.
| Desktop Model | Configuration Persistence | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Persistent Desktop | Full user state retained | Knowledge workers, developers |
| GPU-Accelerated | High graphics retention | Designers, media professionals |
| Standard Bundles | Office and admin tasks | General workforce |
User data and system state remain intact between sessions, reducing onboarding friction and minimizing user disruption.
Pricing Structure in 2026
Amazon WorkSpaces offers one of the more flexible pricing models in the global DaaS market. Organizations can choose between predictable monthly billing or variable hourly consumption.
Pricing Model Comparison
| Pricing Option | Structure Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly Subscription | Flat monthly rate for unlimited usage | Full-time employees |
| Hourly (Pay-as-You-Go) | Base monthly infrastructure fee plus hourly usage | Contractors, seasonal staff |
Example Cost Breakdown (Illustrative)
| Cost Component | Approximate Structure |
|---|---|
| Base Infrastructure Fee | Approximately 7 USD per month |
| Hourly Usage Fee | Approximately 0.20 USD per hour |
| Storage & Data Transfer | Based on AWS S3 and network usage |
The hourly pricing model includes a small fixed monthly fee combined with variable hourly charges. While flexible, this model requires careful monitoring to prevent unexpected cost escalation, especially in environments with unpredictable user activity.
Operational Integration Within AWS Ecosystem
Amazon WorkSpaces is particularly advantageous for organizations already operating core workloads within AWS.
Infrastructure Adjacency Benefits
| AWS Service | Integration Advantage |
|---|---|
| Amazon RDS | Low-latency database access |
| Amazon S3 | Native persistent storage and backups |
| AWS IAM | Identity and access management integration |
| Amazon EC2 | Backend application proximity |
| AWS CloudWatch | Monitoring and usage analytics |
Desktops can be deployed within the same virtual private cloud (VPC) as backend databases, file systems, and applications. This architecture significantly reduces latency between user desktops and enterprise applications.
For AWS-native enterprises, this proximity simplifies network design and improves overall application responsiveness.
Performance and User Experience in 2026
Real-world enterprise feedback in 2026 highlights several consistent themes regarding Amazon WorkSpaces.
Strengths Observed
| Performance Area | Assessment |
|---|---|
| Onboarding Speed | Rapid provisioning of new desktops |
| Infrastructure Reliability | Stable and dependable daily operation |
| AWS Compatibility | Seamless ecosystem integration |
| Persistent Configuration | Minimal user disruption between sessions |
Common Challenges Identified
| Operational Concern | Impact Level | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Network Sensitivity | Moderate to High | Performance varies by internet quality |
| User Interface Simplicity | Moderate | Some workflows favor technical users |
| Cost Monitoring | High | Requires active usage oversight |
Performance is highly dependent on end-user network quality. While WSP improves stability over high-latency connections, remote users with inconsistent internet access may experience variability in responsiveness.
Additionally, organizations frequently note that cost governance is critical. Without usage monitoring, the hourly model can lead to unexpected billing fluctuations.
Strategic Comparison Within the Global DaaS Landscape
In the broader comparison of top Desktop as a Service providers in 2026, Amazon WorkSpaces is typically evaluated across the following dimensions:
| Evaluation Criteria | Market Position |
|---|---|
| AWS Ecosystem Integration | Market Leader |
| Persistent Desktop Experience | Strong |
| GPU-Enhanced Performance | Advanced |
| Hybrid Multi-Cloud Flexibility | Moderate |
| Ease of Enterprise Governance | Requires Active Oversight |
Compared to other DaaS platforms that may emphasize pooled multi-session optimization, Amazon WorkSpaces focuses on predictable, individualized persistent desktop environments.
Enterprise User Perspective in 2026
Organizations report that Amazon WorkSpaces has significantly improved standardization across distributed teams, particularly in remote-first business models. The ability to provision desktops quickly and maintain consistent configurations simplifies onboarding and compliance management.
However, the platform is not entirely frictionless. User experience can feel more technically oriented, especially during initial setup or troubleshooting. Additionally, leadership teams emphasize the importance of implementing monitoring policies to avoid unanticipated cost increases.
Conclusion
In 2026, Amazon WorkSpaces remains one of the most dependable and infrastructure-aligned Desktop as a Service platforms in the world. Its strength lies in persistent desktop reliability, GPU-enhanced hardware bundles, and deep integration with AWS services.
For enterprises already operating within Amazon Web Services, WorkSpaces offers a logical extension of cloud strategy into virtual desktop infrastructure. While it requires proactive cost monitoring and network performance management, it continues to meet core enterprise requirements for scalability, stability, and operational continuity in the modern hybrid workforce environment.
3. Windows 365 (Microsoft Cloud PC)

As Desktop as a Service adoption matures globally in 2026, enterprises are increasingly divided between highly customizable virtual desktop infrastructures and simplified, fully managed cloud PC solutions. Windows 365, widely known as Microsoft Cloud PC, represents Microsoft’s strategic response to organizations seeking virtualization benefits without the architectural complexity associated with traditional VDI environments.
Within the top 10 Desktop as a Service (DaaS) software platforms worldwide, Windows 365 is recognized for its streamlined provisioning model, predictable pricing, and seamless endpoint management through Microsoft Intune. It is particularly attractive to small and medium-sized enterprises, distributed teams, and bring-your-own-device (BYOD) environments.
Platform Overview and Strategic Position
Windows 365 operates on a Cloud PC model. Unlike infrastructure-heavy desktop virtualization platforms that require host pools, networking configuration, and scaling optimization, Windows 365 delivers dedicated, persistent cloud-based desktops assigned to individual users.
Each user receives a fixed virtual machine with consistent compute resources. The service is provisioned, secured, and managed entirely via Microsoft Intune, enabling IT departments to administer cloud desktops using the same policies applied to physical endpoints.
In 2026, this simplified model has strengthened Windows 365’s reputation as a turnkey DaaS solution that minimizes infrastructure management overhead.
Core Architectural Characteristics
Dedicated Cloud PC Model
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Desktop Type | Dedicated, persistent per user |
| Resource Allocation | Fixed vCPU, RAM, and storage per subscription tier |
| Management Console | Microsoft Intune |
| Identity Integration | Entra ID integration |
| Deployment Model | Fully cloud-hosted via Microsoft infrastructure |
Unlike pooled or multi-session models, Windows 365 assigns a single virtual machine to each user. This ensures predictable performance and avoids resource contention.
Operating System and Experience
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Supported OS | Windows 10 and Windows 11 |
| Security Baselines | Pre-configured Microsoft security policies |
| App Integration | Integration with Microsoft App |
| User Experience Model | Seamless local-to-cloud desktop transition |
| Boot-to-Cloud Capability | Direct sign-in to Cloud PC from device startup |
The integration with Microsoft App enhances continuity between local devices and cloud environments. The Boot-to-Cloud feature allows devices to bypass local operating systems entirely and launch directly into the Cloud PC, which is particularly useful in shared-device environments.
Pricing Model and Subscription Structure
One of the most distinguishing features of Windows 365 is its fixed monthly subscription pricing. Unlike consumption-based or variable billing models, Windows 365 provides predictable costs per user.
Subscription Tier Comparison
| Tier Category | vCPU Allocation | RAM Allocation | Storage Allocation | Intended Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Tier | Low | Entry Level | Standard | Office productivity, email, web apps |
| Standard Tier | Moderate | Mid-Level | Increased | Business applications, multitasking |
| High-Performance Tier | High | Advanced | Expanded | Development, analytics, advanced workloads |
Each tier is billed on a per-user, per-month basis. There are no variable hourly charges, reducing the risk of unexpected cloud spending.
Cost Predictability Matrix
| Pricing Attribute | Windows 365 Evaluation |
|---|---|
| Billing Model | Fixed monthly subscription |
| Resource Scaling | Tier upgrade required |
| Budget Forecasting Ease | High |
| Infrastructure Management | Fully managed by Microsoft |
This fixed-cost structure has been particularly appealing to financial controllers and IT managers seeking budget certainty.
Management and Administrative Simplicity
Windows 365 is deeply integrated into the Microsoft endpoint management ecosystem. IT administrators manage Cloud PCs similarly to physical PCs.
Management Capability Overview
| Administrative Function | Execution Method |
|---|---|
| Device Policy Enforcement | Microsoft Intune |
| Security Compliance Monitoring | Intune and Entra ID |
| Software Deployment | Standard endpoint application policies |
| User Provisioning | Automated via Microsoft 365 environment |
The alignment between cloud desktops and endpoint management tools reduces the need for specialized VDI expertise.
Market Adoption and Use Case Scenarios in 2026
Windows 365 has gained strong traction in several organizational segments:
Primary Adoption Segments
| Organization Type | Adoption Strength |
|---|---|
| Small and Medium Enterprises | Very High |
| Education Institutions | High |
| BYOD Workforces | High |
| Large Enterprises | Moderate (Selective Use Cases) |
For small and medium enterprises, Windows 365 eliminates the need to architect and manage complex Azure environments. For BYOD scenarios, it ensures data remains in the cloud while providing users with a familiar Windows experience.
Comparative Position Within Global DaaS Landscape
| Evaluation Criteria | Windows 365 Position |
|---|---|
| Ease of Deployment | Market Leader |
| Infrastructure Complexity | Minimal |
| Cost Predictability | Very High |
| Advanced Customization | Limited compared to traditional VDI |
| Enterprise Scalability | Strong but structured by tiers |
While Azure Virtual Desktop is often chosen for highly customized enterprise deployments, Windows 365 appeals to organizations prioritizing simplicity and rapid rollout.
Enterprise User Experience in 2026
User feedback consistently highlights accessibility and ease of use. Educators, remote professionals, and hybrid employees emphasize the ability to access a consistent Windows environment across multiple devices.
Key User Experience Insights
| Experience Area | Observed Feedback |
|---|---|
| Cross-Device Access | Seamless and reliable |
| Hardware Independence | Strong benefit for low-end devices |
| IT Support Simplicity | Reduced compared to previous VDI setups |
| Learning Curve | Minimal for end users |
In education and specialized professional settings, the ability to maintain a personalized desktop environment regardless of local hardware has been described as transformative.
Strengths and Considerations
Strengths Matrix
| Strength Category | Assessment |
|---|---|
| Deployment Simplicity | Excellent |
| Endpoint Integration | Deep Microsoft ecosystem alignment |
| Budget Predictability | High |
| User Experience Consistency | Strong |
| BYOD Compatibility | Highly effective |
Considerations
| Operational Factor | Impact Level | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Custom Infrastructure Tuning | Limited | Less flexible than full VDI platforms |
| Resource Scaling Flexibility | Tier-based only | Requires subscription upgrade |
| High-Performance Customization | Moderate | Less granular than Azure-based solutions |
Organizations requiring highly specialized networking architectures or multi-session optimization may prefer more customizable VDI platforms. However, for standardized deployments, Windows 365 excels in operational simplicity.
Conclusion
In 2026, Windows 365 has solidified its position among the top Desktop as a Service platforms globally by redefining virtualization as a straightforward Cloud PC subscription model. Its fully managed infrastructure, fixed pricing tiers, and deep integration with Microsoft Intune have made it especially popular among SMEs, educational institutions, and BYOD-focused organizations.
By removing the complexity traditionally associated with virtual desktop infrastructure, Windows 365 delivers a predictable, accessible, and scalable cloud desktop experience aligned with modern hybrid work demands.
4. Citrix DaaS
In the global Desktop as a Service market in 2026, Citrix DaaS remains one of the most established enterprise virtualization platforms. Known for its high-definition user experience (HDX) protocol and mature remote application delivery architecture, Citrix continues to serve organizations that require advanced graphics performance, hybrid-cloud portability, and centralized control across diverse infrastructure environments.
Among the top 10 Desktop as a Service software providers worldwide, Citrix DaaS distinguishes itself through protocol efficiency, multi-cloud brokering capabilities, and enterprise-grade monitoring tools. However, the platform also faces increasing competition from modern cloud-native and zero-trust-first alternatives.
Market Position and Strategic Direction
Citrix has historically led the virtual desktop infrastructure segment, and in 2026 it maintains its relevance by evolving into a unified DaaS control plane. Rather than restricting customers to a single cloud ecosystem, Citrix DaaS allows desktops and applications to be brokered across multiple environments, including:
• Microsoft Azure
• Amazon Web Services
• Google Cloud Platform
• On-premises hypervisors
This hybrid and multi-cloud versatility appeals to large enterprises with distributed infrastructure strategies or regulatory constraints that require workload flexibility.
Unified Management Architecture
| Infrastructure Component | Capability |
|---|---|
| Cloud Integration | Azure, AWS, Google Cloud |
| On-Premises Support | Hypervisors and private data centers |
| Control Plane | Centralized cloud-based management console |
| Desktop Brokering | Cross-environment workload distribution |
| Application Delivery | Virtual apps and full desktop publishing |
The unified management plane allows IT administrators to monitor and manage sessions, applications, and user policies across hybrid infrastructures from a single console.
Technical Capabilities and Performance
At the core of Citrix DaaS remains the HDX protocol, which continues to be one of the most technically advanced remoting protocols available in 2026.
HDX Protocol Performance Profile
| Performance Factor | HDX Evaluation |
|---|---|
| High-Latency Network Optimization | Strong |
| 3D Graphics Rendering | Advanced |
| Video Compression Efficiency | Optimized for enterprise workloads |
| Bandwidth Adaptability | Dynamic adjustment capabilities |
HDX is particularly valued in industries such as architecture, engineering, media production, and manufacturing, where large CAD files, 3D models, and high-resolution video editing demand low-latency responsiveness.
Advanced Monitoring and Analytics
Citrix DaaS includes enterprise monitoring and management capabilities designed to provide visibility into user sessions and performance metrics.
| Monitoring Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Session Recording | Full recording for compliance and auditing |
| Performance Analytics | Real-time performance monitoring |
| User Experience Monitoring | Session-level diagnostics |
| Security Event Tracking | Activity visibility and alerts |
These capabilities are particularly useful in regulated industries requiring audit trails or in environments with strict internal governance policies.
Pricing Structure in 2026
Citrix DaaS has shifted toward simplified subscription tiers, replacing many legacy on-premises licensing models.
Subscription Tier Comparison
| Plan Name | Price (USD per user/month) | Key Inclusions |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Plus | 13 | Core DaaS capabilities and management |
| Premium | 20 | Advanced management tools and enhanced monitoring |
| Premium Plus | 23 | Security analytics and performance optimization tools |
The tiered model allows organizations to align functionality with budget priorities. Higher-tier plans emphasize analytics, security insights, and advanced performance monitoring.
Pricing Evaluation Matrix
| Cost Consideration | Citrix DaaS Assessment |
|---|---|
| Entry-Level Affordability | Competitive |
| Advanced Feature Access | Tier-dependent |
| Infrastructure Flexibility | High |
| Predictability of Licensing | Structured subscription model |
While the base subscription appears competitively priced, total cost of ownership may vary depending on infrastructure complexity and deployment scale.
Protocol Efficiency and Graphics Workloads
Citrix HDX continues to be widely regarded as a preferred protocol for graphics-intensive and latency-sensitive workloads.
Use Case Performance Comparison
| Workload Type | Citrix HDX Suitability |
|---|---|
| General Office Productivity | Strong |
| CAD and 3D Modeling | Excellent |
| Video Editing | Excellent |
| Engineering Simulations | High Performance |
| High-Latency Remote Sites | Optimized |
For engineering teams and creative professionals operating from remote sites, HDX often provides smoother performance compared to standard remote display protocols.
Enterprise User Experience in 2026
Real-world enterprise feedback presents a balanced view of Citrix DaaS performance.
Strengths Frequently Reported
| User Experience Factor | Observed Outcome |
|---|---|
| Session Responsiveness | Generally fast and stable |
| Graphics Performance | Superior for CAD and modeling tasks |
| Hybrid Infrastructure Support | Flexible deployment options |
| Centralized Administration | Robust management controls |
Common Challenges Identified
| Operational Concern | Impact Level | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| User Session Controls | Moderate | Limited user-level customization in some cases |
| Session Timeouts | Reported Issues | Occasional disconnects |
| Security Modernization | Perceived Gap | Compared to newer zero-trust-native platforms |
| Administrative Complexity | High | Requires experienced virtualization teams |
Some organizations note that while performance remains strong, the platform can feel operationally complex. Security perception also varies, with certain enterprises comparing Citrix to more cloud-native, zero-trust-focused DaaS providers.
Competitive Position in the 2026 DaaS Landscape
| Evaluation Criteria | Citrix DaaS Position |
|---|---|
| Hybrid-Cloud Versatility | Market Leader |
| Graphics Performance | Best-in-Class |
| Enterprise Governance | Strong |
| Ease of Deployment | Moderate to Complex |
| Zero-Trust Native Architecture | Evolving |
Citrix DaaS remains highly competitive in environments that demand superior graphics rendering and hybrid infrastructure portability. However, it may require greater operational oversight than simpler, cloud-native DaaS alternatives.
Conclusion
In 2026, Citrix DaaS continues to serve as a high-performance, enterprise-grade Desktop as a Service platform with a strong focus on HDX-driven user experience and hybrid-cloud versatility. Its ability to broker desktops across multiple cloud providers and on-premises environments makes it attractive for large, complex organizations.
While some enterprises report administrative challenges and evolving security expectations, Citrix remains a preferred solution for engineering, design, and graphics-intensive workloads where remote performance cannot be compromised.
5. Omnissa Horizon Cloud (formerly VMware)
In the rapidly evolving Desktop as a Service landscape of 2026, Omnissa Horizon Cloud has emerged as a refined, cloud-first virtualization platform following its separation from VMware. The restructured company has repositioned Horizon as a next-generation, cloud-native desktop delivery solution designed to compete directly with the world’s top 10 DaaS software providers.
Omnissa’s strategy centers on simplifying control-plane management, strengthening Microsoft Azure alignment, and enhancing performance for both Windows and Linux virtual desktop infrastructure workloads.
Strategic Transformation and Market Repositioning
Following its divestiture from VMware, Omnissa undertook a structural redesign of Horizon Cloud to modernize its architecture. Rather than relying heavily on on-premises infrastructure components, the next-generation platform shifts critical management services into the cloud.
This architectural change has resulted in:
• Reduced local infrastructure dependencies
• Improved control-plane scalability
• Simplified lifecycle management
• Enhanced platform resilience
In 2026, Omnissa Horizon Cloud is positioned as a high-performance, multi-cloud DaaS solution optimized for enterprise-grade deployments, with a strong emphasis on Microsoft Azure environments.
Unified Cloud Control Plane
| Management Component | Capability |
|---|---|
| Centralized Control Plane | Cloud-hosted management services |
| Multi-Cloud Deployment | Azure, other supported cloud platforms |
| On-Prem Integration | Supported for hybrid environments |
| Policy Administration | Centralized configuration and monitoring |
| Lifecycle Management | Automated updates and maintenance |
The streamlined control plane reduces administrative complexity compared to legacy on-premises VDI deployments.
Technical Capabilities and Architecture
Omnissa Horizon Cloud retains many of the advanced virtualization technologies that made Horizon popular in enterprise environments, while modernizing their deployment model.
Protocol and Performance
| Protocol Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| Blast Extreme | Adaptive protocol optimized for graphics and multimedia |
| Bandwidth Optimization | Dynamic network adjustment |
| High-Latency Handling | Strong performance across distributed sites |
Blast Extreme continues to be a core differentiator. It delivers efficient compression, adaptive display encoding, and consistent performance across variable network conditions. In graphics-intensive workflows, Blast competes effectively with other leading virtualization protocols.
Instant Clone Technology
One of the most impactful features remains Instant Clone technology.
| Feature | Operational Benefit |
|---|---|
| Instant Clone Provisioning | Near-instant desktop deployment |
| Resource Optimization | Reduced storage and compute overhead |
| Rapid Scaling | Fast response to workforce changes |
Instant Clones allow IT teams to provision desktops in seconds rather than minutes, supporting dynamic workforce scaling.
Application and User Environment Management
| Component | Functionality |
|---|---|
| App Volumes | Dynamic application layering and delivery |
| Dynamic Environment Manager (DEM) | User personalization and profile configuration |
| Policy Enforcement | Granular desktop configuration control |
App Volumes enables real-time application assignment without rebuilding base images, while DEM ensures user-specific settings persist across sessions.
Operational Stability and Cloud-Native Benefits
The transition to a cloud-first architecture has improved overall system stability. By relocating more management components to cloud infrastructure, Omnissa reduces dependency on local connection servers and management appliances.
Operational Stability Matrix
| Stability Factor | Next-Gen Architecture Impact |
|---|---|
| Local Infrastructure Footprint | Reduced |
| Control Plane Resilience | Increased |
| Update and Patch Management | Centralized and simplified |
| Scalability | Improved across regions |
This architectural shift has resulted in fewer points of failure and improved service continuity for global deployments.
Integration with Microsoft Azure
In 2026, Omnissa Horizon Cloud shows particularly strong alignment with Microsoft Azure. Many enterprises deploy Horizon on Azure infrastructure while leveraging Azure-specific cost optimizations.
Azure-Focused Deployment Benefits
| Azure Integration Element | Enterprise Advantage |
|---|---|
| Azure Infrastructure Hosting | Global region availability |
| Azure Multi-Session Compatibility | Cost optimization for shared desktops |
| Native Networking Integration | Simplified virtual network management |
| Identity Integration | Azure-based authentication support |
Organizations running hybrid or multi-cloud strategies can combine Horizon’s management capabilities with Azure’s infrastructure efficiency.
Market Niche and Competitive Position
Omnissa Horizon Cloud occupies a specialized niche in the 2026 DaaS market.
| Evaluation Category | Horizon Cloud Position |
|---|---|
| Multi-Cloud Flexibility | Strong |
| High-Performance Graphics | Competitive |
| Linux VDI Support | Strong |
| Cloud-Native Management | Improved over legacy versions |
| Ease of Migration from Legacy VDI | Moderate |
The platform is particularly well-suited for enterprises requiring both Windows and Linux VDI delivery at scale.
Enterprise User Experience in 2026
User feedback following the transition period indicates notable improvements in responsiveness and administrative usability.
Strengths Frequently Reported
| Experience Factor | Observed Outcome |
|---|---|
| Desktop Provisioning Speed | Near-instant via Instant Clones |
| Graphics Handling | Strong performance under Blast protocol |
| Azure Cost Efficiency | Effective integration with Azure multi-session |
| Management Console Usability | More intuitive than prior on-prem version |
Challenges During Transition
| Operational Area | Reported Issue |
|---|---|
| Post-Divestiture Adjustment | Initial instability during transition period |
| Learning Curve | Moderate for teams migrating from legacy systems |
While the separation from VMware initially introduced operational uncertainty, by 2026 the platform appears stabilized and more cloud-aligned.
Competitive Comparison in the 2026 DaaS Landscape
| Platform Dimension | Horizon Cloud Assessment |
|---|---|
| Cloud-Native Evolution | Significantly Improved |
| Graphics and Multimedia Support | Strong |
| Multi-Cloud Deployment | Flexible |
| Cost Optimization on Azure | High Potential |
| Administrative Complexity | Moderate |
Compared to simpler subscription-based DaaS models, Horizon Cloud requires deeper virtualization knowledge. However, it offers significantly more control and performance flexibility for enterprise deployments.
Conclusion
In 2026, Omnissa Horizon Cloud represents a modernized evolution of enterprise virtual desktop infrastructure. By shifting to a cloud-native control plane and strengthening Azure integration, the platform has regained stability and competitiveness within the global Desktop as a Service market.
For organizations requiring high-performance multi-cloud desktop delivery, support for both Windows and Linux workloads, and advanced provisioning technologies such as Instant Clones and App Volumes, Omnissa Horizon Cloud remains a compelling enterprise-grade DaaS solution.
6. Parallels RAS (Remote Application Server)
In the competitive global Desktop as a Service market in 2026, Parallels RAS has carved out a distinct identity as a value-focused, enterprise-ready solution. While other vendors emphasize complex feature tiers and advanced customization, Parallels RAS prioritizes simplicity, affordability, and operational efficiency.
Among the top 10 Desktop as a Service software platforms worldwide, Parallels RAS is frequently described as the practical choice for mid-sized organizations and enterprises that require reliable remote application and desktop delivery without maintaining a large, specialized virtualization team.
Market Position and Strategic Identity
Parallels RAS has positioned itself as a value leader in the DaaS and remote access sector. Its differentiation strategy centers on offering a unified licensing model that includes core enterprise features often sold as premium add-ons by competitors.
This streamlined approach appeals to organizations that want predictable costs and minimal configuration complexity.
Strategic Differentiation Overview
| Market Dimension | Parallels RAS Position |
|---|---|
| Licensing Simplicity | Strong competitive advantage |
| Feature Bundling | Comprehensive standard inclusion |
| Enterprise Accessibility | Designed for mid-market and growing enterprises |
| Administrative Complexity | Lower than traditional VDI platforms |
Unlike more complex virtualization ecosystems, Parallels RAS aims to reduce the administrative burden while maintaining enterprise-grade functionality.
Technical Capabilities and Architecture
Parallels RAS supports both virtual desktop delivery and application publishing across diverse environments. It integrates with common Windows infrastructure and supports both on-premises and cloud-hosted deployments.
Core Technical Specifications
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Client Access Options | Native client and HTML5 browser-based access |
| Load Balancing | Built-in, automated |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Included natively |
| Image Management | Automated image lifecycle management |
| Application Delivery | Integrated publishing capabilities |
| Profile and App Integration | Supports FSLogix and MSIX App Attach |
The inclusion of HTML5 client support allows users to connect directly through a web browser without requiring full client installation, which simplifies remote workforce enablement.
Built-In Enterprise Features
One of Parallels RAS’s primary advantages lies in bundling critical infrastructure features within its base licensing model.
Feature Inclusion Matrix
| Capability | Included by Default |
|---|---|
| Load Balancing | Yes |
| Multi-Factor Authentication | Yes |
| Centralized Reporting | Yes |
| Image Automation | Yes |
| Role-Based Access Control | Yes |
By integrating these capabilities into a single administrative console, Parallels reduces the need for third-party extensions or costly add-on modules.
Pricing Structure in 2026
Parallels RAS is widely regarded as one of the most cost-effective enterprise-grade DaaS solutions available in 2026.
Pricing Characteristics
| Pricing Attribute | Parallels RAS Evaluation |
|---|---|
| Subscription Model | Simple per-user subscription |
| Tiered Licensing | Minimal or eliminated |
| Add-On Costs | Limited compared to competitors |
| Budget Predictability | High |
The absence of complex tiered licensing structures simplifies procurement and long-term financial planning. Organizations typically pay a straightforward per-user subscription, avoiding the layered cost escalation common with some legacy virtualization providers.
Operational Simplicity and Deployment Experience
Parallels RAS emphasizes ease of deployment and management, which contributes significantly to its adoption among mid-sized organizations.
Operational Simplicity Overview
| Operational Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Deployment Time | Typically fast and streamlined |
| Configuration Complexity | Moderate to low |
| IT Team Requirements | Smaller virtualization team sufficient |
| Ongoing Maintenance | Centralized management reduces workload |
The centralized console consolidates authentication, load balancing, reporting, and policy management, enabling administrators to control the environment without navigating multiple management layers.
Best-Fit Organizational Profile
Parallels RAS is particularly well suited for:
| Organization Type | Suitability Level |
|---|---|
| Mid-Sized Enterprises | Very High |
| Distributed Offices | High |
| Resource-Constrained IT Teams | Very High |
| Highly Specialized VDI Environments | Moderate |
For enterprises requiring extremely advanced customization or specialized high-definition graphics workloads, other platforms may offer more granular tuning. However, for the majority of business users, Parallels RAS delivers stable and reliable performance.
Enterprise User Experience in 2026
User feedback in 2026 frequently highlights the smooth migration process and responsive vendor support.
Strengths Reported
| Experience Category | Observed Feedback |
|---|---|
| Transition Process | Smooth and well-supported |
| Feature Consolidation | No hidden add-on costs |
| Reliability for Daily Use | Strong for majority of users |
| Administrative Efficiency | Centralized and intuitive console |
Limitations Identified
| Consideration Area | Impact Level |
|---|---|
| Advanced Customization Depth | Moderate compared to Citrix |
| Ultra-High-End Graphics Support | Not primary focus |
While it may not offer the same depth of advanced performance tuning as higher-end virtualization platforms, Parallels RAS meets the needs of most office-based and line-of-business application scenarios.
Competitive Position in the 2026 DaaS Landscape
| Evaluation Dimension | Parallels RAS Position |
|---|---|
| Cost Efficiency | Market Leader in value segment |
| Ease of Deployment | Strong |
| Feature Consolidation | Comprehensive |
| Enterprise Scalability | Moderate to Strong |
| Specialized Graphics Workloads | Limited focus |
Parallels RAS competes not by offering the most complex feature set, but by delivering practical enterprise functionality in a cost-effective and simplified package.
Conclusion
In 2026, Parallels RAS stands out as a streamlined and cost-efficient Desktop as a Service solution tailored for organizations seeking reliability without excessive infrastructure complexity. Its unified licensing model, built-in enterprise features, and simplified administration make it an attractive alternative to more expensive and technically demanding virtualization platforms.
For mid-sized enterprises and organizations operating with lean IT teams, Parallels RAS provides a balanced combination of performance, predictability, and operational clarity within the global DaaS market.
7. Nutanix Frame

In the 2026 global Desktop as a Service market, Nutanix Frame has solidified its reputation as a browser-first, infrastructure-flexible DaaS platform. Designed to operate seamlessly across public clouds and on-premises environments powered by Nutanix hyper-converged infrastructure, Frame distinguishes itself through architectural simplicity, intelligent automation, and high-performance storage capabilities.
Among the top 10 Desktop as a Service software platforms worldwide, Nutanix Frame is frequently selected by enterprises pursuing hybrid multi-cloud strategies while aiming to minimize client-side complexity.
Market Position and Architectural Identity
Nutanix Frame is uniquely positioned as a browser-based DaaS solution that eliminates the need for local client software. Users access virtual desktops directly through a secure web browser, reducing endpoint management overhead and accelerating workforce onboarding.
Its architectural flexibility enables desktop deployment across:
• Public cloud providers
• Private cloud environments
• On-premises Nutanix AHV infrastructure
This deployment versatility is particularly valuable for organizations operating under data sovereignty regulations or requiring localized compute resources.
Deployment Flexibility Matrix
| Infrastructure Option | Supported by Frame |
|---|---|
| Public Cloud Providers | Yes |
| Nutanix AHV On-Premises | Yes |
| Hybrid Multi-Cloud | Yes |
| Browser-Based Access | Native capability |
By abstracting desktop delivery from specific cloud dependencies, Frame enables organizations to maintain strategic control over workload placement.
Technical Capabilities and Management Architecture
Nutanix Frame integrates deeply with Nutanix management and automation tools, particularly Prism Central and Nutanix Cloud Manager (NCM).
Core Technical Specifications
| Component | Capability |
|---|---|
| Management Interface | Prism Central |
| Cloud Operations Platform | Nutanix Cloud Manager (NCM) |
| VM Deployment | Automated and policy-driven |
| Infrastructure Foundation | Hyper-Converged Infrastructure (HCI) |
| Performance Profile | High IOPS and low latency |
The hyper-converged infrastructure roots of Nutanix provide optimized storage and compute performance. High input/output operations per second (IOPS) and low latency contribute to smooth desktop responsiveness, even under demanding workloads.
Intelligent Capacity Planning and Automation
Nutanix Cloud Manager enhances Frame’s operational efficiency through predictive capacity planning and automated provisioning.
Automation Capabilities Overview
| Feature | Operational Impact |
|---|---|
| Intelligent Capacity Forecasting | Predicts infrastructure needs |
| Automated VM Provisioning | Deploys desktops based on approval workflows |
| Resource Optimization | Balances workloads dynamically |
| Lifecycle Orchestration | Centralized infrastructure updates |
This automation reduces manual intervention and accelerates desktop rollout, particularly beneficial in rapidly scaling organizations.
Security Framework in 2026
Security is integrated into Nutanix Frame’s core architecture. The platform leverages infrastructure-level protections alongside DaaS-specific controls.
Security Capability Matrix
| Security Feature | Implementation |
|---|---|
| Role-Based Access Control | Granular administrative permissions |
| Automated Patching (LCM) | Managed via Life Cycle Management |
| Micro-Segmentation | Built-in network isolation |
| Infrastructure-Level Isolation | HCI-based security controls |
Micro-segmentation limits lateral movement within the environment, enhancing protection against internal threats. Automated patching through Life Cycle Management ensures consistent system updates without extensive downtime.
Performance Characteristics and Infrastructure Advantage
Because Frame operates on Nutanix hyper-converged infrastructure, it benefits from tightly integrated compute and storage resources.
Performance Evaluation
| Performance Dimension | Frame Assessment |
|---|---|
| Storage IOPS | High |
| Latency | Low |
| Resource Scalability | Dynamic |
| Desktop Responsiveness | Strong |
Organizations migrating from legacy hardware environments often report significant performance improvements, particularly in storage-intensive use cases.
Licensing and Competitive Position
In 2026, Nutanix Frame’s licensing model is widely viewed as flexible and straightforward compared to certain traditional virtualization platforms.
Licensing Evaluation Matrix
| Licensing Factor | Nutanix Frame Assessment |
|---|---|
| Complexity | Low to Moderate |
| Tier Transparency | Clear and manageable |
| Add-On Requirements | Limited |
| Cost Predictability | High |
The simplified licensing approach reduces administrative overhead and enhances procurement transparency.
Best-Fit Organizational Profiles
Nutanix Frame is especially suitable for organizations that:
| Organization Type | Suitability Level |
|---|---|
| Hybrid Cloud Enterprises | Very High |
| On-Prem HCI Environments | Very High |
| Cloud-Agnostic Infrastructure Teams | High |
| Browser-Centric Workforces | High |
Enterprises already invested in Nutanix HCI benefit from seamless integration and centralized infrastructure management.
Enterprise User Experience in 2026
Real-world feedback in 2026 emphasizes ease of use and performance gains following deployment.
Commonly Reported Strengths
| Experience Category | Observed Outcome |
|---|---|
| Management Simplicity | Intuitive NCM interface |
| Automated Deployment | Reduced manual VM provisioning |
| Storage Performance | Improved IOPS compared to legacy systems |
| Licensing Clarity | Easier than many competitors |
Reported Considerations
| Operational Area | Impact Level |
|---|---|
| Dependency on Nutanix Ecosystem | High for on-prem optimization |
| Advanced Custom Graphics Workloads | Moderate compared to specialized VDI tools |
Organizations utilizing Citrix or other application delivery layers on top of Nutanix infrastructure often report improved performance due to the optimized HCI backend.
Competitive Standing in the 2026 DaaS Landscape
| Evaluation Dimension | Nutanix Frame Position |
|---|---|
| Browser-Based Access | Market Differentiator |
| Hybrid Multi-Cloud Flexibility | Strong |
| Infrastructure Automation | Advanced |
| Performance on HCI | Excellent |
| Licensing Simplicity | Competitive Advantage |
While not always positioned as the default choice for ultra-large global enterprises seeking ultra-customized VDI frameworks, Nutanix Frame excels in environments prioritizing hybrid flexibility, infrastructure automation, and browser-native access.
Conclusion
In 2026, Nutanix Frame stands out within the global Desktop as a Service market as a browser-first, hybrid-capable solution rooted in hyper-converged infrastructure performance. Its integration with Prism Central and Nutanix Cloud Manager delivers intelligent automation, high IOPS storage performance, and streamlined VM lifecycle management.
For organizations seeking flexible deployment across cloud and on-premises environments without client-side software complexity, Nutanix Frame offers a compelling, performance-oriented DaaS platform aligned with modern hybrid IT strategies.
8. Kasm Workspaces
In 2026, as Desktop as a Service platforms continue to evolve beyond traditional virtual desktop infrastructure models, Kasm Workspaces has emerged as a disruptive force within the global DaaS landscape. Rather than allocating full virtual machines per user, Kasm introduces a container streaming architecture that emphasizes security isolation, operational efficiency, and browser-native access.
Among the top 10 Desktop as a Service software platforms worldwide, Kasm Workspaces stands out for redefining how desktops and applications are delivered. Its lightweight, containerized approach significantly reduces infrastructure overhead while enhancing session security.
Architectural Innovation: Container Streaming Model
Traditional DaaS platforms rely on full operating system virtualization. Kasm Workspaces, by contrast, streams containerized environments directly to the user’s browser.
Container-Based Delivery Model
| Architecture Component | Kasm Workspaces Approach |
|---|---|
| Desktop Delivery Mechanism | Container streaming |
| Operating System Virtualization | Not required per user session |
| Access Method | 100 percent browser-based |
| Client Installation | Not required |
| Infrastructure Footprint | Lightweight and scalable |
Because containers share underlying system resources while remaining isolated, Kasm achieves higher density per host compared to traditional VM-based DaaS solutions.
Disposable Session Technology
A defining feature of Kasm Workspaces is its disposable session capability. Each session can be configured to terminate and completely destroy its environment upon user logout.
Session Lifecycle Model
| Session Feature | Operational Benefit |
|---|---|
| Disposable Environments | Eliminates persistence of threats |
| Automatic Session Destruction | Reduces risk of data retention |
| On-Demand Launch | Rapid session provisioning |
| Stateless Architecture | Enhanced security isolation |
This stateless model is particularly valuable in cybersecurity testing, browser isolation, and sensitive data access scenarios.
Technical Specifications and Developer Capabilities
Kasm Workspaces integrates advanced automation and security tooling, making it attractive for technical teams.
Core Technical Capabilities
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Platform Access | Browser-based only |
| Developer API | Robust RESTful API support |
| Data Loss Prevention Controls | Built-in DLP configuration |
| Container Orchestration | Scalable deployment |
| Secure Browser Isolation | Native functionality |
The developer API allows organizations to integrate Kasm into CI/CD pipelines, automated lab environments, and custom security workflows.
Security and Compliance Advantages
Kasm Workspaces is frequently adopted in environments where security posture is a top priority.
Security Capability Matrix
| Security Control | Implementation |
|---|---|
| Session Isolation | Container-level isolation |
| Data Loss Prevention | Policy-driven restrictions |
| No Local Data Storage | Browser-based streaming |
| Network Segmentation | Container network isolation |
| Disposable Session Cleanup | Automated upon logout |
Because no persistent data resides on the endpoint, the risk of data exfiltration is significantly reduced. This makes Kasm particularly suitable for regulated industries and cybersecurity operations.
Pricing Structure in 2026
Kasm Workspaces offers one of the most competitively priced licensing models within the DaaS market.
Subscription Tier Comparison
| Edition Name | Monthly Price (USD per user) | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|
| Community Edition | 0 | Testing and small-scale deployments |
| Professional/Personal | 5 | Individual developers and small teams |
| Enterprise Edition | 10 | Organizations requiring advanced controls |
The availability of a free Community Edition lowers the barrier to entry and encourages experimentation. The Professional and Enterprise tiers remain competitively priced compared to traditional VM-based DaaS platforms.
Cost Efficiency Evaluation
| Pricing Attribute | Kasm Assessment |
|---|---|
| Entry-Level Accessibility | Very High |
| Resource Efficiency | High due to container density |
| Licensing Simplicity | Straightforward |
| Infrastructure Cost Overhead | Reduced compared to VM-based DaaS |
Because container sessions consume fewer resources than full virtual machines, infrastructure cost efficiency is often improved.
Primary Use Cases in 2026
Kasm Workspaces has found strong adoption in specialized environments.
Use Case Suitability Matrix
| Use Case Category | Suitability Level |
|---|---|
| Cybersecurity Labs | Excellent |
| Development and Testing | Excellent |
| Secure Browser Isolation | Excellent |
| Education and Training Labs | High |
| Traditional Office Workloads | Moderate |
For developers and cybersecurity professionals, the ability to launch isolated environments instantly and destroy them after use provides unmatched operational security.
Enterprise User Experience in 2026
Feedback from engineers and cybersecurity professionals highlights performance efficiency and secure workflow enablement.
Commonly Reported Strengths
| Experience Factor | Observed Outcome |
|---|---|
| Browser-Based Access | Seamless, no client installation |
| Chromebook Compatibility | Strong support for lightweight devices |
| Session Security | Highly trusted disposable model |
| Resource Efficiency | Fast and responsive container sessions |
Reported Limitations
| Consideration Area | Impact Level |
|---|---|
| Included Usage Hours | Tier-dependent limitations |
| Traditional Desktop Features | Limited compared to full OS virtualization |
Lower subscription tiers may include usage limits that restrict session hours, which can affect heavy users. However, many organizations consider the pricing-to-performance ratio highly favorable.
Competitive Position in the 2026 DaaS Landscape
| Evaluation Dimension | Kasm Workspaces Position |
|---|---|
| Container-Based Innovation | Market Differentiator |
| Security Isolation | Industry-Leading for Stateless Sessions |
| Cost Competitiveness | Very High |
| Traditional Enterprise VDI | Not primary focus |
| Developer Integration | Strong API ecosystem |
Unlike conventional DaaS platforms focused on full Windows desktop virtualization, Kasm specializes in secure, task-specific environments delivered through container technology.
Conclusion
In 2026, Kasm Workspaces represents a forward-looking evolution in Desktop as a Service delivery. By replacing full virtual machine virtualization with container streaming, the platform achieves high security isolation, resource efficiency, and browser-native accessibility.
For cybersecurity teams, developers, and organizations prioritizing disposable environments and secure browser isolation, Kasm Workspaces offers a uniquely efficient and competitively priced DaaS solution that challenges traditional virtualization models.
9. Workspot
In the 2026 global Desktop as a Service market, Workspot has established itself as a turnkey SaaS provider focused on simplicity, predictable pricing, and high-performance cloud workstations. Unlike platforms that require organizations to architect and manage their own cloud infrastructure, Workspot delivers a fully bundled Cloud PC and GPU workstation experience designed for enterprises seeking operational clarity and global scalability.
Among the top 10 Desktop as a Service software platforms worldwide, Workspot is frequently recognized for its flat-rate pricing model, integrated cloud compute costs, and ability to deliver graphics-intensive virtual workstations with low latency.
Market Position and Value Proposition
Workspot’s differentiation lies in its SaaS-first approach. Rather than acting solely as a virtualization layer on top of public cloud infrastructure, Workspot packages cloud compute, storage, management, monitoring, support, and maintenance into a unified service.
Strategic Differentiation Overview
| Market Dimension | Workspot Position |
|---|---|
| Cloud Infrastructure Management | Fully managed SaaS model |
| Pricing Transparency | Bundled cloud costs |
| GPU Workstation Delivery | Core specialization |
| Enterprise Scalability | Global deployment capability |
| Operational Complexity | Reduced compared to self-managed VDI |
By absorbing the complexity of cloud resource management, Workspot enables IT teams to focus on user experience rather than infrastructure orchestration.
Technical Architecture and Cloud Delivery
Workspot delivers desktops and workstations primarily from Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud environments, allowing customers to leverage hyperscale cloud availability without managing it directly.
Core Technical Specifications
| Component | Capability |
|---|---|
| Cloud Providers Supported | Azure and Google Cloud |
| Desktop Types | Cloud PCs and GPU-enabled workstations |
| Observability Platform | Workspot Watch |
| Performance Monitoring | Real-time analytics and user session insights |
| Global Region Coverage | Multi-region deployment support |
The platform is designed to provide consistent performance across distributed geographic regions, supporting global enterprises with remote teams.
Workspot Watch and Observability
A key component of the platform is Workspot Watch, a real-time observability tool that provides actionable insights into desktop performance and user experience.
Observability Capability Matrix
| Monitoring Feature | Operational Benefit |
|---|---|
| Real-Time User Performance Data | Immediate troubleshooting insights |
| Latency Tracking | Identification of network bottlenecks |
| Resource Utilization Monitoring | Optimization of GPU and CPU allocation |
| Automated Alerts | Proactive issue detection |
This level of visibility helps IT teams maintain service reliability and quickly address performance anomalies.
Pricing Model and Cost Structure
Workspot’s pricing structure is one of its strongest differentiators in 2026. The company offers a flat-rate model that typically includes the cost of underlying cloud infrastructure.
Pricing Overview
| Pricing Attribute | Workspot Evaluation |
|---|---|
| Starting Price | From 15 USD per user per month |
| Billing Model | Subscription-based or usage-based |
| Cloud Compute Costs | Included in bundled pricing |
| Support and Maintenance | Included |
| Predictability | High compared to consumption-only models |
Unlike platforms that require customers to manage separate Azure or Google Cloud bills, Workspot consolidates costs into a unified subscription, simplifying budgeting and financial planning.
Performance and GPU Workstation Capabilities
Workspot is particularly renowned for delivering GPU-enabled virtual workstations optimized for graphics-intensive applications.
Performance Profile
| Workload Type | Suitability Level |
|---|---|
| Architecture, Engineering, Construction (AEC) | Excellent |
| Manufacturing and CAD | Excellent |
| 3D Modeling | High Performance |
| General Office Productivity | Strong |
| Remote High-Latency Environments | Optimized for low latency |
The platform’s ability to deliver low-latency GPU desktops makes it a preferred choice for industries requiring high graphical fidelity and computational power.
Operational Stability and Deployment Experience
Enterprise feedback in 2026 indicates that while initial deployments may require careful planning, ongoing operations are stable and efficient.
Operational Experience Matrix
| Operational Factor | Observed Outcome |
|---|---|
| Initial Deployment | Learning curve during setup |
| Ongoing Stability | High reliability post-deployment |
| Management Simplicity | Centralized SaaS console |
| Vendor Support | Strong enterprise support reputation |
Organizations often report that once fully implemented, the platform provides consistent speed and reliability for demanding workloads.
Competitive Position in the 2026 DaaS Landscape
| Evaluation Dimension | Workspot Position |
|---|---|
| Turnkey SaaS Delivery | Market Differentiator |
| GPU Workstation Performance | Industry-Leading |
| Pricing Transparency | Strong advantage |
| Infrastructure Customization | Limited compared to DIY VDI |
| Enterprise Scalability | Global-ready |
Compared to self-managed DaaS platforms, Workspot reduces architectural burden but may offer less granular customization. However, for enterprises prioritizing performance and predictable cost structures, it presents a compelling alternative.
Best-Fit Organizational Profiles
Workspot is particularly well suited for:
| Organization Type | Suitability Level |
|---|---|
| AEC and Manufacturing Enterprises | Very High |
| Global Engineering Teams | Very High |
| Organizations Seeking GPU Desktops | High |
| IT Teams Seeking SaaS Simplicity | High |
Its bundled pricing and global deployment capabilities make it attractive to enterprises seeking consistent performance without maintaining complex multi-cloud configurations.
Conclusion
In 2026, Workspot stands out within the global Desktop as a Service market as a turnkey SaaS platform delivering Cloud PCs and high-performance GPU workstations at scale. By bundling cloud compute, management, monitoring, and support into a unified subscription model, it simplifies cost management and operational oversight.
For industries requiring low-latency graphics performance and predictable budgeting, Workspot offers a reliable, scalable, and performance-driven DaaS solution aligned with modern enterprise cloud strategies.
10. Google Cloud Workstations

In 2026, Google Cloud Workstations has evolved into a specialized Desktop as a Service solution purpose-built for software development teams and security-sensitive enterprises. Rather than targeting traditional office productivity or full Windows desktop virtualization, this platform focuses on managed development environments that are tightly integrated with Google Cloud Platform services and artificial intelligence tooling.
Among the top Desktop as a Service platforms globally, Google Cloud Workstations occupies a distinct niche centered on developer productivity, cloud-native workflows, and AI-assisted coding environments.
Strategic Position in the Global DaaS Market
Google Cloud Workstations is not positioned as a general-purpose virtual desktop replacement. Instead, it is optimized for engineering teams building cloud-native applications, data platforms, and AI-driven systems.
Its value proposition revolves around:
• Fully managed development workstations
• Native integration with Google AI services
• Secure browser and SSH access
• Tight alignment with Google Cloud infrastructure
This focused positioning makes it especially attractive to organizations already embedded within the Google Cloud ecosystem.
Core Technical Architecture
Google Cloud Workstations provides high-performance, managed virtual machines designed specifically for development workflows.
Technical Capability Overview
| Component | Specification |
|---|---|
| Access Methods | Browser-based IDE, SSH access |
| VM Performance | High-performance, predictable uptime |
| AI Integration | Native Gemini code assistance |
| IDE Compatibility | Web-based VS Code and other tools |
| Infrastructure Backbone | Google Cloud Platform |
The integration with Gemini, formerly known as Duet AI, provides intelligent code assistance directly within development environments. This includes contextual suggestions, debugging insights, and automated code generation capabilities.
AI-Enhanced Developer Workflow
| AI Capability | Operational Impact |
|---|---|
| Code Completion | Accelerated development cycles |
| Debugging Assistance | Faster issue resolution |
| Contextual Code Recommendations | Improved productivity |
| AI-Driven Documentation Support | Reduced manual documentation effort |
This AI-native integration distinguishes Google Cloud Workstations from more generic DaaS platforms.
Access Flexibility and Device Independence
One of the most compelling aspects of the platform is its accessibility from virtually any device capable of running a modern web browser.
Access Model Comparison
| Access Method | Use Case Suitability |
|---|---|
| Web Browser IDE | Remote-first distributed teams |
| SSH Access | Advanced development workflows |
| Lightweight Devices | Chromebooks and low-end laptops |
Developers can access full development environments without relying on high-performance local hardware. This reduces endpoint costs and simplifies hardware lifecycle management.
Performance and Infrastructure Reliability
Because the platform is built directly on Google Cloud infrastructure, it benefits from predictable uptime and scalable compute resources.
Performance Evaluation Matrix
| Performance Factor | Google Cloud Workstations Assessment |
|---|---|
| VM Uptime Reliability | High |
| Latency (Global Access) | Low in major regions |
| Resource Scalability | Dynamic allocation |
| AI Tool Responsiveness | Integrated and optimized |
This reliability is particularly valuable for globally distributed engineering teams operating across time zones.
Pricing Model in 2026
Google Cloud Workstations follows a consumption-based billing structure, consistent with broader Google Cloud Platform pricing models.
Pricing Structure Overview
| Pricing Element | Details |
|---|---|
| Billing Model | Consumption-based |
| Free Credit for New Users | 300 USD introductory credit |
| Support Tiers | Basic (free) to Premium (15,000 USD per month) |
| Enterprise Scalability | High for mission-critical environments |
Support tiers vary significantly based on operational criticality. Enterprises running large-scale production workloads may opt for Premium support packages designed for mission-critical systems.
Cost Consideration Matrix
| Pricing Attribute | Assessment |
|---|---|
| Entry Barrier | Low with free credits |
| Budget Predictability | Variable based on usage |
| Enterprise Support Scalability | Extensive but premium-priced |
| Infrastructure Cost Transparency | Clear but consumption-driven |
While consumption-based pricing offers flexibility, it requires careful resource monitoring to prevent cost escalation.
Integration within the Google Cloud Ecosystem
Google Cloud Workstations is deeply embedded within the broader GCP environment, which strengthens its appeal to data-driven organizations.
Ecosystem Integration Matrix
| GCP Service | Integration Benefit |
|---|---|
| BigQuery | Direct data querying within dev workflows |
| Vertex AI | Seamless machine learning experimentation |
| Google Kubernetes Engine | Cloud-native application development |
| Identity and Access Management | Centralized security governance |
For teams leveraging BigQuery analytics or Vertex AI for model training, the tight integration shortens development cycles and reduces data transfer complexity.
Enterprise Use Cases in 2026
Google Cloud Workstations is particularly well suited for:
| Organization Type | Suitability Level |
|---|---|
| Cloud-Native Development Teams | Excellent |
| AI and Data Science Teams | Excellent |
| Distributed Global Engineering Groups | Very High |
| Traditional Office Productivity | Limited focus |
The platform is optimized for development and AI workloads rather than general business desktop virtualization.
Enterprise User Experience
User feedback in 2026 highlights flexibility and performance improvements for distributed teams.
Commonly Reported Strengths
| Experience Category | Observed Outcome |
|---|---|
| Remote Accessibility | Strong global availability |
| Device Independence | Reduced reliance on powerful laptops |
| AI Integration | Noticeable productivity gains |
| Data Tool Integration | Accelerated decision-making |
Reported Considerations
| Operational Factor | Impact Level |
|---|---|
| Cost Monitoring | Important in consumption model |
| Non-Developer Use Cases | Not primary target audience |
| Advanced Support Cost | High at premium tier |
While not intended to replace traditional enterprise desktops, Google Cloud Workstations excels in development-centric workflows.
Competitive Position in the 2026 DaaS Landscape
| Evaluation Dimension | Google Cloud Workstations Position |
|---|---|
| Developer-Focused Optimization | Market Leader in niche |
| AI-Native Integration | Strong differentiator |
| General Enterprise Desktop | Limited |
| Ecosystem Alignment | Deep GCP integration |
| Hardware Independence | High flexibility |
Compared to traditional VDI platforms, Google Cloud Workstations focuses narrowly on engineering productivity and AI-enhanced workflows rather than broad workforce virtualization.
Conclusion
In 2026, Google Cloud Workstations stands as a specialized Desktop as a Service solution tailored to development teams and security-conscious enterprises operating within the Google Cloud ecosystem. Its integration with Gemini for AI-assisted coding, seamless browser access, and alignment with BigQuery, Vertex AI, and Kubernetes make it a powerful tool for modern engineering organizations.
For distributed global development teams seeking scalable, secure, and AI-enhanced work environments, Google Cloud Workstations represents a forward-looking and strategically aligned DaaS platform within the evolving cloud productivity landscape.
The 2026 Global Desktop as a Service (DaaS) Market: Strategic Analysis of Leadership, Economics, and Technological Evolution
By 2026, Desktop as a Service (DaaS) has transitioned from an auxiliary IT solution into a foundational pillar of enterprise digital infrastructure. What was once deployed primarily for remote access and contingency planning has become the dominant operating model for workforce computing. Organizations are no longer evaluating DaaS as an alternative to physical desktops; they are restructuring entire IT strategies around cloud-delivered work environments.
Market data indicates that the global DaaS market reached approximately USD 11.53 billion in 2026, up from USD 9.82 billion in 2025. This year-over-year expansion reflects not merely seat growth but a systemic shift in enterprise IT architecture. By 2026, an estimated 80 percent of all virtual desktops are delivered through DaaS platforms, compared to only 30 percent in 2021. This represents one of the most significant structural transitions in enterprise computing in the past decade.
Technological Catalysts Driving Structural Transformation
The acceleration of DaaS adoption in 2026 is directly linked to the convergence of several technological enablers:
• Widespread deployment of 5G connectivity
• Maturation of edge computing architectures
• AI-driven orchestration of compute and storage resources
• Automated lifecycle management of virtual environments
Historically, adoption was hindered by latency issues, bandwidth limitations, and operational complexity. These constraints have been materially reduced. High-speed wireless networks and geographically distributed cloud regions now enable low-latency desktop delivery even in remote and emerging markets. At the same time, AI-based capacity planning systems dynamically allocate compute resources, minimizing waste while maintaining performance consistency.
An additional macroeconomic driver is the enterprise hardware refresh cycle. Devices deployed during the 2020–2021 remote work surge are reaching end-of-life in 2025–2026. Rather than reinvesting in traditional endpoint-heavy architectures, organizations are increasingly opting for virtualized cloud environments that decouple performance from physical hardware limitations.
Global Market Size and Growth Projections
The economic scale of the DaaS sector in 2026 reflects both adoption maturity and long-term structural confidence.
Global DaaS Market Projections and Economic Indices
| Metric | 2025 (Base Year) | 2026 (Estimate) | 2034/2035 (Forecast) | CAGR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global DaaS Market Size (USD) | 9.82 Billion | 11.53 Billion | 57.83 Billion | 19.4% |
| Conservative Growth Model (USD) | 4.84 Billion | 5.49 Billion | 14.95 Billion | 13.35% |
| DaaS Provider-Specific Revenue (USD) | 5.03 Billion | 5.71 Billion | 23.80 Billion | 17.7% |
| Device-as-a-Service Bundle Size (USD) | 43.81 Billion | 55.75 Billion | 262.10 Billion | 21.3% |
The variation in compound annual growth rate (CAGR), ranging from 13.35 percent to 19.4 percent, reflects differing methodologies regarding whether managed services, bundled infrastructure, and endpoint subscriptions are included.
The projection of USD 57.83 billion by 2035 illustrates sustained confidence in the DaaS delivery model. This trajectory indicates that cloud-based desktops are not a temporary trend but a structural redefinition of enterprise computing.
Virtual Desktop Volume Expansion
The expansion of DaaS is equally evident in unit deployment metrics.
Virtual Desktop Unit Growth
| Year | Estimated Units (Millions) |
|---|---|
| 2024 | 150 |
| 2026 | Approximately 210–230 |
| 2028 | 300 |
Between 2024 and 2028, the total volume of virtual desktops is projected to double, reaching 300 million units globally. This growth demonstrates increasing trust in virtualized environments as the primary computing platform rather than as a backup or niche solution.
Component Market Share Distribution
The value composition of the DaaS ecosystem has shifted from hardware-centric to software-driven economics.
Market Component Share Distribution (2026)
| Component | Market Share |
|---|---|
| Software | 45% |
| Hardware | 30% |
| Services | 25% |
The dominance of software reflects the rising importance of orchestration engines, security layers, analytics platforms, and AI-driven automation. The hardware layer, while still relevant, no longer commands primary value in the ecosystem.
Regional Market Dynamics and Growth Patterns
DaaS adoption patterns vary significantly by geography, with clear regional leaders and emerging accelerators.
Regional Market Share and Growth Trajectories
| Region | 2026 Market Status | Key Drivers | Projected CAGR |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | Largest Revenue Share | Remote work maturity, IT outsourcing, 5G penetration | 15–18% |
| Asia Pacific | Fastest Growth Region | SME digitization, IoT investments, government initiatives | 22.44% |
| Europe | High Compliance Demand | GDPR, data sovereignty, sustainable IT mandates | 11–17% |
| Middle East & Africa | Emerging Expansion | Infrastructure modernization, 5G rollout | 10–15% |
North America maintains the largest revenue base due to enterprise maturity and high cloud penetration. However, Asia Pacific demonstrates the strongest growth momentum, driven by large-scale digital transformation programs in China, India, and Indonesia.
National-Level Economic Impact
Specific national markets illustrate the economic concentration of DaaS services:
| Country | 2026 Estimated Service Value (USD) |
|---|---|
| United States | 10.83 Billion |
| China | 5.16 Billion |
| United Kingdom | 4.00 Billion |
These figures highlight the strategic importance of DaaS infrastructure in globally competitive labor markets. Countries investing heavily in cloud-delivered workspaces are enhancing workforce mobility, cybersecurity resilience, and operational agility.
Macroeconomic Implications
The 2026 DaaS market expansion reflects broader macroeconomic trends:
• Hybrid and remote work normalization
• Enterprise cost rationalization pressures
• Increased cybersecurity risk mitigation
• Global talent sourcing without geographic constraints
Organizations increasingly view DaaS as a financial optimization strategy. Capital expenditure on endpoint hardware is being replaced with operational expenditure models aligned to subscription-based cloud economics. This transition improves cash flow predictability and aligns IT spending with workforce scale.
Strategic Outlook Through 2035
If current growth rates sustain, DaaS will become the default desktop delivery model by the early 2030s. The following structural shifts are expected:
Strategic Evolution Matrix
| Trend | Expected Impact by 2035 |
|---|---|
| AI-Orchestrated Workloads | Automated performance tuning at scale |
| Edge-Integrated DaaS Nodes | Ultra-low latency regional deployment |
| Zero-Trust Native Architectures | Security embedded into session layers |
| Device Abstraction | Minimal reliance on endpoint specifications |
The evolution of DaaS is no longer tied solely to remote work enablement. It is becoming central to enterprise digital transformation, AI adoption, and global workforce distribution.
Conclusion
In 2026, the global Desktop as a Service market represents a fundamental reconfiguration of enterprise IT strategy. With a valuation exceeding USD 11.53 billion and projections approaching USD 57.83 billion by 2035, the sector demonstrates strong economic resilience and long-term structural relevance.
The convergence of high-speed connectivity, AI-driven management, and lifecycle-driven hardware refresh cycles has eliminated many historical adoption barriers. Regional expansion, particularly in Asia Pacific, further reinforces the global momentum.
DaaS is no longer a tactical solution; it is the architectural foundation of the modern digital enterprise.
SME vs. Large Enterprise Adoption Dynamics in the 2026 Desktop as a Service Market
Strategic Divergence by Organization Size
In 2026, Desktop as a Service adoption is no longer uniform across the enterprise landscape. The strategic intent behind implementation differs markedly between small and medium enterprises (SMEs) and large enterprises. While both segments contribute substantially to global market growth, their motivations, risk tolerances, and operational priorities diverge in measurable ways.
SMEs predominantly view DaaS as a financial optimization mechanism, whereas large enterprises treat it as a security, compliance, and resilience platform embedded within broader digital transformation strategies.
SME Adoption Model: Financial Agility and Operational Scalability
For small and mid-sized organizations, DaaS functions as a capital preservation tool. Historically, deploying virtual desktop infrastructure required significant upfront investment in server hardware, storage arrays, networking equipment, and specialized engineering expertise. In contrast, DaaS enables SMEs to transition from capital expenditure (CapEx) to operational expenditure (OpEx), replacing infrastructure ownership with subscription-based cloud consumption.
This shift produces several measurable advantages:
• Elimination of large upfront hardware procurement
• Reduced dependency on specialized VDI architects
• Faster provisioning cycles
• Simplified IT lifecycle management
An SME can scale desktop capacity from 10 users to 100 users within hours through automated cloud provisioning, compared to traditional multi-month hardware deployment cycles. This elasticity is especially valuable for seasonal businesses, startups experiencing rapid growth, and organizations operating with lean IT teams.
SME Value Proposition Matrix
| Primary Objective | DaaS Benefit for SMEs |
|---|---|
| Cost Minimization | Predictable subscription pricing |
| Rapid Scalability | On-demand provisioning |
| Operational Flexibility | Remote workforce enablement |
| Reduced IT Overhead | Managed infrastructure services |
In addition, SMEs benefit from standardized cloud security frameworks that would otherwise be expensive to implement independently.
Large Enterprise Strategy: Security, Compliance, and Resilience
Large enterprises approach DaaS from a fundamentally different perspective. For multinational corporations and heavily regulated industries, the primary drivers are risk mitigation and compliance management rather than cost avoidance alone.
As ransomware attacks and data exfiltration threats increase in frequency and sophistication, enterprises require centralized data isolation. DaaS enables corporate data to remain within secure cloud environments, ensuring that sensitive information never resides permanently on endpoint devices.
Key enterprise-level drivers include:
• Centralized data control within secure cloud perimeters
• Enhanced ransomware containment
• Integrated identity and access governance
• Advanced disaster recovery capabilities
The ability to rapidly restore virtual desktops after cyber incidents significantly reduces downtime and financial exposure. In high-risk industries such as finance, healthcare, and government, this resilience is mission-critical.
Onshore DaaS and Data Sovereignty
A notable development in 2026 is the growing adoption of onshore DaaS deployments. In response to stricter data sovereignty regulations, enterprises increasingly require that virtual desktops be hosted within national borders.
This segment is expanding at an annual growth rate between 9 percent and 15 percent. Onshore deployments address compliance mandates related to:
• National data residency laws
• Sector-specific regulatory frameworks
• Cross-border data transfer restrictions
By localizing cloud infrastructure, enterprises reduce regulatory risk while maintaining global operational continuity.
Comparative Market Share and Growth Dynamics
The distribution of market share between large enterprises and SMEs in 2026 reflects a balanced ecosystem.
User Segment Market Distribution
| User Segment | Market Share (2026) | Primary Value Driver | Growth Forecast |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large Enterprises | Approximately 53.81% | Compliance, Security, Disaster Recovery | 10–16% |
| SMEs / MSMEs | Approximately 46.19% | Cost Minimization, Scalability, Flexibility | 11–17% |
Large enterprises maintain a slightly larger share of market revenue due to higher per-user spending, broader geographic deployment, and compliance-driven investments. However, SMEs are contributing disproportionately to unit growth, reflecting widespread adoption across smaller organizations.
Economic Implications of Segment Differences
The dichotomy between SME and enterprise adoption models illustrates two complementary growth engines within the DaaS market:
• SMEs drive volume expansion through scalability and cost efficiency
• Large enterprises drive revenue concentration through premium security and compliance services
While SMEs emphasize operational flexibility and simplified management, enterprises invest in advanced features such as zero-trust architectures, granular role-based access control, and integrated disaster recovery frameworks.
Strategic Outlook
Looking beyond 2026, both segments are expected to expand steadily. SME growth will continue to be fueled by cloud-first startup ecosystems and the normalization of remote work. Large enterprises, meanwhile, will deepen investment in onshore hosting, advanced analytics, and AI-driven threat detection embedded within DaaS platforms.
Ultimately, the SME versus large enterprise dichotomy does not represent a division in market direction but rather a diversification of strategic use cases. Desktop as a Service in 2026 serves as both a financial equalizer for smaller firms and a security fortress for global enterprises, reinforcing its role as a foundational pillar of the modern digital workspace economy.
The Economics of Desktop as a Service in 2026: Pricing Innovation and Total Cost of Ownership Optimization
Structural Shift in DaaS Pricing Philosophy
By 2026, the economic framework governing Desktop as a Service has evolved significantly beyond the traditional per-seat licensing model. Enterprises increasingly demand cost alignment with actual usage patterns, performance intensity, and workforce variability. Analysts project that approximately 70 percent of businesses now prefer usage-based pricing models over fixed per-seat subscriptions, reflecting a broader trend toward fiscal transparency and consumption-aligned IT spending.
This evolution is not merely cosmetic. It represents a recalibration of enterprise financial planning, where CIOs and CFOs seek to eliminate unpredictable cost overruns—often referred to as “bill shock”—in environments characterized by fluctuating contractor headcounts, seasonal workloads, and project-based teams.
Comparative Cost Metrics and TCO Benchmarks
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) has become the dominant financial metric guiding DaaS procurement decisions in 2026. Organizations no longer evaluate only monthly subscription fees; they analyze lifecycle costs over three to five years, including infrastructure, administration, energy consumption, and security overhead.
Comparative Annual TCO Analysis
| Workstation Model | Estimated Annual TCO (USD) | Cost Differential |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Laptop Deployment | 2,440 | Baseline |
| Virtual Desktop + Thin Client + AI Automation | 1,936 | ~21% Savings |
The nearly 21 percent cost reduction is attributed to several structural efficiencies:
• Lower endpoint hardware refresh expenses
• Reduced energy consumption through thin clients
• Decreased helpdesk workload via AI-driven remediation
• Centralized patching and compliance automation
In addition, organizations benefit from longer hardware lifecycles for thin clients compared to traditional laptops.
2026 DaaS Pricing Models and Market Applications
The pricing ecosystem in 2026 has diversified into multiple models designed to accommodate distinct operational scenarios.
Comparative Pricing Model Framework
| Pricing Model | Description | Estimated Monthly Cost (USD) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Subscription | Predictable flat fee per user | 20 – 150 | Stable, full-time workforce |
| Usage-Based | Pay only for active usage hours | 5 – 15 + Compute | Contractors, seasonal teams |
| Outcome-Based | Charged per task or resolution | 0.99 – 2.00 per event | AI agents, automated workflows |
| Hybrid Model | Base subscription plus metered consumption | Variable | Power users, mixed workloads |
The shift toward usage-based pricing is especially pronounced in industries with fluctuating staffing patterns, such as retail, construction, and consulting. Meanwhile, outcome-based pricing models are emerging in environments where AI agents or automated workflows replace traditional user sessions.
AI-Premium Tiers and SaaS Inflation
In 2026, many DaaS vendors have introduced AI-enhanced subscription tiers. These packages incorporate:
• Predictive performance tuning
• Automated threat detection
• Self-healing infrastructure diagnostics
• AI-driven capacity optimization
Organizations budgeting for AI-enabled desktop stacks typically allocate 25 to 35 percent additional spend compared to standard subscription tiers.
At the same time, SaaS price inflation has accelerated. Average annual increases now range between 8 and 12 percent, with certain providers implementing hikes of 15 to 25 percent when bundling enhanced security, analytics, and compliance modules into base offerings.
SaaS Pricing Pressure Matrix
| Pricing Factor | 2026 Impact |
|---|---|
| AI Feature Integration | +25–35% premium tier uplift |
| Security Bundling | Drives higher base subscription costs |
| Annual SaaS Inflation | 8–12% average increase |
| Aggressive Vendor Increases | Up to 15–25% in select markets |
This environment has increased the importance of detailed cost modeling and long-term contract negotiation.
Three-Year Total Cost of Ownership Model
In 2026, financial evaluation models for DaaS typically extend across a 36-month horizon. A simplified three-year TCO formula is expressed as:
TCO_3 = I_setup + Σ (S_monthly + C_compute + M_admin)
Where:
I_setup represents initial migration, onboarding, and training costs.
S_monthly represents recurring subscription fees.
C_compute represents variable cloud resource costs, including vCPU, RAM, and data egress.
M_admin represents administrative labor costs.
Administrative labor has historically been one of the largest hidden expenses in virtual desktop infrastructure. However, AI-driven orchestration and self-healing tools have dramatically reduced this component.
Administrative Cost Reduction Impact
| Cost Element | 2019 Environment | 2026 Environment |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Intervention | High | Significantly Reduced |
| Patch Management Effort | Intensive | Automated |
| Troubleshooting Workload | Reactive | Predictive and Automated |
| Admin Labor Cost (M_admin) | Major TCO Driver | Reduced by AI Tools |
Industry analysts forecast that by 2027, virtual desktops will be cost-effective for approximately 95 percent of workers, compared to just 40 percent in 2019. The principal factor driving this change is the sharp reduction in M_admin through automation and predictive remediation technologies.
Strategic Financial Implications for IT Leadership
In 2026, DaaS procurement decisions are increasingly integrated into broader financial strategy discussions. Key considerations include:
• OpEx predictability versus CapEx depreciation
• Workforce elasticity requirements
• AI integration value versus cost premium
• Long-term SaaS inflation exposure
For stable enterprises with predictable headcounts, fixed subscription models may provide budget certainty. Conversely, organizations with dynamic workforce structures often derive greater financial efficiency from usage-based or hybrid pricing.
Conclusion
The economics of Desktop as a Service in 2026 are defined by flexibility, transparency, and automation-driven efficiency. With annual TCO savings approaching 21 percent compared to traditional endpoint models, DaaS has evolved into a financially compelling alternative for most enterprise workloads.
As pricing models shift toward consumption-based frameworks and AI-enhanced tiers introduce new cost considerations, IT leaders must evaluate deployments through a multi-year TCO lens. The combination of automation-driven administrative reduction and cloud elasticity positions DaaS not only as a technical innovation but as a structurally advantageous economic model for modern enterprises.
Security Architecture and Compliance in the 2026 Desktop as a Service Landscape
Security as the Primary Migration Catalyst
By 2026, security has become the dominant driver behind Desktop as a Service adoption. While cost efficiency and scalability remain important, most enterprise migrations are justified by risk mitigation, regulatory compliance, and cyber-resilience priorities. DaaS platforms are now architected around a layered security stack designed to minimize attack surfaces and enforce continuous governance.
The modern DaaS security framework in 2026 is built upon three foundational pillars:
• Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
• Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
• Continuous Compliance Monitoring
Together, these elements redefine how enterprises protect sensitive data in a distributed, device-agnostic workforce.
The Three Pillars of the 2026 DaaS Security Stack
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
ZTNA replaces legacy perimeter-based security models with identity-centric access controls. Instead of relying on VPN tunnels and open inbound ports, DaaS platforms enforce session-level authentication through reverse proxy architectures.
Core Characteristics of ZTNA in 2026
| Security Control | Operational Function |
|---|---|
| Identity-Based Access | User and device posture verification |
| Reverse Proxy Connectivity | Eliminates open inbound ports |
| Micro-Segmentation | Limits lateral movement |
| Least Privilege Enforcement | Granular access per session |
Zero Trust architectures assume no implicit trust—every session, device, and action is continuously validated.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Data Loss Prevention mechanisms have evolved significantly. Instead of merely encrypting endpoints, modern DaaS platforms enforce enclave isolation and granular data control policies.
Advanced DLP Capabilities
| DLP Feature | 2026 Implementation |
|---|---|
| Clipboard Restrictions | Session-level enforcement |
| File Transfer Controls | Policy-driven approvals |
| Watermarking and Screen Capture | Controlled or blocked |
| Granular Data Tagging | Sensitivity-based restrictions |
This ensures that corporate data remains within controlled environments, even when accessed from unmanaged or BYOD devices.
Continuous Compliance Monitoring
Compliance is no longer an annual exercise. In 2026, policy enforcement operates in real time.
Compliance Evolution Matrix
| Compliance Model (Legacy) | Compliance Model (2026 DaaS) |
|---|---|
| Annual Audit | Continuous Monitoring |
| Manual Documentation | Policy-as-Code |
| Periodic Risk Reviews | Real-Time Telemetry |
| Reactive Reporting | Automated Governance Dashboards |
Policy-as-Code frameworks allow organizations to embed regulatory rules directly into infrastructure templates, ensuring that any deviation triggers automated remediation.
Security Certifications and Enterprise Procurement
Enterprises evaluating DaaS providers in 2026 prioritize rigorous security certifications as a proxy for operational maturity. Certifications are assessed at both the vendor and internal IT team level.
Key Certifications for DaaS Governance
| Certification | Strategic Importance |
|---|---|
| CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) | Leadership-level security governance standard |
| Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator Associate (AZ-104) | Essential for Azure-based DaaS management |
| AWS Certified Solutions Architect – Professional | Critical for securing AWS WorkSpaces architectures |
| CompTIA Security+ | Foundational credential for security analysts |
These certifications signal technical capability in identity governance, cloud infrastructure security, and compliance enforcement.
Comparative Security Architecture: Standard vs. Advanced ZTNA DaaS
The security maturity gap between legacy DaaS implementations and advanced Zero Trust deployments is measurable.
Security Capability Comparison
| Security Domain | Standard DaaS Security | Advanced 2026 ZTNA DaaS |
|---|---|---|
| Access Control | VPN / Open Inbound Ports | Reverse Proxy / Zero Trust |
| Data Protection | Local Encryption | Enclave Isolation / Granular DLP |
| Identity Management | Basic Multi-Factor Authentication | Continuous Behavioral Authentication |
| Compliance Model | Annual Audit | Policy-as-Code / Real-Time Audit |
Continuous behavioral authentication leverages AI to analyze user behavior patterns. Deviations—such as unusual login times or abnormal data access—trigger adaptive security controls.
DaaS Alternatives: The Emergence of Local Isolation Models
Although DaaS dominates the market in 2026, a complementary category of solutions has gained traction for specific use cases. These “local isolation” platforms take a different architectural approach.
Instead of hosting the entire desktop in the cloud, these solutions create a secure enclave directly on the user’s local hardware. Business applications and data operate within this isolated container, protected by enterprise-grade controls, while still running natively on the device.
Local Isolation vs. Cloud-Hosted DaaS
| Architectural Model | Cloud-Hosted DaaS | Local Secure Enclave Model |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Environment | Remote cloud infrastructure | Local hardware container |
| Latency | Dependent on network conditions | Minimal (local execution) |
| Data Residency | Cloud-controlled | Locally isolated within policy boundaries |
| BYOD Suitability | Strong | Very strong in unstable networks |
Advantages of Local Isolation
• Eliminates remote display protocol latency
• Maintains high performance for resource-intensive local applications
• Preserves corporate firewall enforcement within the enclave
• Ideal for environments with inconsistent network reliability
This model is particularly attractive in regions with variable internet infrastructure or for teams requiring uninterrupted access to high-performance local applications.
Strategic Implications for 2026 and Beyond
Security architecture in 2026 reflects a broader shift from perimeter defense to session-level governance. Organizations now evaluate DaaS platforms based on:
• Zero Trust enforcement maturity
• Real-time compliance visibility
• AI-driven anomaly detection
• Flexible deployment models (cloud vs. local isolation)
While cloud-hosted DaaS remains dominant due to centralized control and global scalability, local isolation solutions provide a targeted alternative for BYOD-heavy and network-sensitive environments.
Conclusion
In 2026, security architecture is the central determinant of DaaS adoption decisions. Zero Trust Network Access, advanced Data Loss Prevention, and continuous compliance monitoring form the foundation of modern deployments. Certifications and governance expertise further reinforce enterprise trust.
At the same time, emerging local isolation models demonstrate that the future of secure digital workspaces may not be exclusively cloud-hosted. Instead, the ecosystem is diversifying to accommodate varied performance, regulatory, and infrastructure requirements—while maintaining the same core objective: secure, resilient, and compliant access to enterprise computing resources.
Technical Synthesis: Remoting Protocols, Bandwidth Economics, and Network Constraints in 2026
The Central Role of Remoting Protocols
In 2026, the practical effectiveness of Desktop as a Service deployments is determined less by raw compute power and more by the efficiency of remoting protocols. The so-called “Protocol Wars” over the past five years have driven measurable innovation, with modern protocols delivering 4K resolution at 60 frames per second while consuming 30 to 50 percent less bandwidth than comparable 2021 implementations.
This improvement has been achieved through:
• Advanced video codec integration (H.264, H.265, AV1 in some cases)
• Adaptive bitrate streaming
• GPU offloading for encoding and decoding
• Intelligent frame deduplication and compression
As DaaS platforms increasingly support graphics-intensive workloads, protocol optimization has become a competitive differentiator rather than a background technical detail.
Comparative Protocol Landscape in 2026
The leading remoting protocols in 2026 reflect distinct architectural philosophies aligned with their respective platform ecosystems.
Remoting Protocol Comparison Matrix
| Protocol | Developer | Primary Advantage | Bandwidth Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDX | Citrix | High-latency resilience, advanced 3D optimization | Very High |
| Blast Extreme | Omnissa | Low CPU overhead, H.264/H.265 hardware offload | High |
| WSP | Amazon Web Services | Cloud-native design, secure streaming | High |
| RDP / FRP | Microsoft / Nutanix | Deep OS integration, simplicity and compatibility | Moderate to High |
Each protocol addresses specific performance scenarios.
HDX remains highly optimized for engineering, 3D modeling, and CAD workloads, especially in high-latency global deployments.
Blast Extreme emphasizes encoding efficiency and reduced CPU utilization through hardware-assisted video processing.
WSP (WorkSpaces Streaming Protocol) is optimized for cloud-native elasticity and security-focused remote access.
RDP and related frame remoting protocols prioritize deep operating system integration and administrative simplicity.
Bandwidth Efficiency Gains
Between 2021 and 2026, protocol optimization has resulted in measurable reductions in bandwidth consumption for comparable workloads.
| Resolution and Performance | Estimated Bandwidth (2021) | Estimated Bandwidth (2026) |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Office Work (1080p) | 2–3 Mbps | 1–2 Mbps |
| 4K, 60fps Multimedia Workload | 20–25 Mbps | 10–15 Mbps |
These improvements are driven by adaptive compression algorithms and smarter transport-layer tuning. However, even with enhanced efficiency, network performance remains the single most critical dependency in DaaS architecture.
The Network Bottleneck Constraint
Despite global 5G expansion and fiber rollout in developed markets, network bandwidth remains a limiting factor for DaaS scalability.
Bandwidth Requirements by Use Case
| User Workload Type | Recommended Bandwidth per User |
|---|---|
| Basic Productivity Tasks | 1–2 Mbps |
| Video Conferencing + Office | 3–5 Mbps |
| Graphics-Intensive 4K Work | Up to 15 Mbps |
For organizations deploying hundreds or thousands of virtual desktops, aggregate bandwidth requirements can escalate rapidly.
Example:
1,000 knowledge workers at 2 Mbps each require approximately 2 Gbps of sustained network throughput.
100 high-performance graphics users at 15 Mbps each require 1.5 Gbps independently.
In regions with limited broadband infrastructure, this requirement can significantly constrain adoption.
Impact on Total Cost of Ownership
While DaaS reduces endpoint hardware costs and administrative overhead, insufficient network capacity can introduce hidden expenses.
Network Cost Impact Matrix
| Cost Element | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Bandwidth Upgrades | Increased ISP contracts or MPLS expansion |
| Redundant Connectivity | Required for business continuity |
| Edge Optimization Appliances | Additional capital investment |
| Latency Mitigation Services | Premium routing or SD-WAN solutions |
For organizations operating in underserved or rural markets, network upgrades may offset some of the projected TCO savings associated with DaaS migration.
5G and Edge Computing Mitigation
The expansion of 5G and edge computing infrastructure has partially alleviated these constraints. Edge nodes reduce physical distance between users and compute resources, minimizing round-trip latency.
Network Evolution Factors in 2026
| Technology Trend | Effect on DaaS Performance |
|---|---|
| 5G Deployment | Improved mobile and remote performance |
| Edge Compute Regions | Lower latency in distributed geographies |
| SD-WAN Optimization | Dynamic traffic prioritization |
| AI Traffic Shaping | Automated bandwidth allocation |
However, these technologies are unevenly distributed globally. In emerging markets, inconsistent connectivity remains a primary adoption barrier.
Strategic Considerations for IT Architects
When modeling DaaS deployments in 2026, IT leaders must incorporate network capacity into financial and architectural planning.
Critical Evaluation Areas
• Per-user bandwidth modeling under peak load
• Geographic distribution of workforce
• Redundancy requirements for mission-critical users
• SD-WAN or traffic prioritization investments
Ignoring network limitations can undermine user experience, leading to session lag, input latency, and degraded multimedia performance.
Conclusion
In 2026, remoting protocols represent the technological backbone of Desktop as a Service effectiveness. Advances in compression, hardware acceleration, and adaptive streaming have significantly improved bandwidth efficiency, enabling high-resolution, high-frame-rate experiences with 30 to 50 percent lower data consumption than earlier generations.
Nevertheless, network capacity remains the primary constraint on DaaS scalability. While cloud infrastructure and AI-driven orchestration continue to mature, sustained bandwidth availability—typically 1 to 2 Mbps for standard users and up to 15 Mbps for graphics-intensive workloads—remains a fundamental prerequisite.
As a result, protocol efficiency and network architecture planning are no longer secondary considerations. They are central determinants of DaaS performance, cost predictability, and long-term viability in the global digital workspace ecosystem.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026 CIOs: Navigating the Mature DaaS Ecosystem
Executive Context
By 2026, the Desktop as a Service market has evolved into a sophisticated, multi-layered ecosystem offering extensive architectural flexibility, pricing diversity, and security maturity. With global market projections approaching USD 57.83 billion by 2035, DaaS is no longer positioned as an alternative delivery model. It is becoming the default enterprise desktop paradigm.
For CIOs and digital transformation leaders, the central challenge is no longer whether to adopt DaaS, but how to implement it strategically to maximize financial efficiency, security resilience, and operational agility.
Three foundational priorities define successful DaaS strategies in 2026.
Prioritize the Management Plane Over the Hypervisor
In earlier virtualization eras, infrastructure selection—hypervisors, storage arrays, and compute clusters—was the primary technical focus. In 2026, the competitive advantage lies in the intelligence of the management plane.
The core question is not where the virtual machine resides, but how effectively it is orchestrated.
Management-Centric Evaluation Framework
| Strategic Layer | 2026 Priority Focus |
|---|---|
| Compute Infrastructure | Commodity, cloud-abstracted |
| Hypervisor Selection | Secondary to automation layer |
| Management Plane | Primary differentiator |
| AI-Orchestrated Automation | Critical for cost optimization |
Modern DaaS success depends on:
• Automated lifecycle management
• Predictive performance optimization
• AI-driven remediation
• Policy-as-code compliance enforcement
Platforms with advanced management layers enable lower administrative overhead, reduced Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR), and optimized resource allocation. CIOs should evaluate DaaS vendors based on orchestration intelligence rather than raw infrastructure specifications.
Align Pricing Models with Workforce Dynamics
The 2026 DaaS pricing landscape is highly diversified. Organizations that apply a single pricing strategy across all workforce segments often overpay or underutilize resources.
CIOs should segment pricing models based on employee type and usage variability.
Workforce Segmentation Strategy
| Workforce Segment | Recommended Pricing Model | Strategic Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Core Permanent Staff | Fixed Subscription | Budget predictability and stability |
| Contractors / Freelancers | Usage-Based Billing | Avoid idle resource costs |
| Seasonal Employees | Consumption or Hybrid Model | Elastic scaling capability |
| Power Users / Developers | Hybrid with Performance Scaling | High compute variability |
Fixed subscription models provide financial stability for permanent staff with consistent usage patterns. Conversely, usage-based models reduce wasted capacity in fluctuating or project-driven environments.
This alignment ensures pricing elasticity mirrors workforce elasticity, optimizing Return on Investment (ROI).
Invest in Skills, Not Just Software
DaaS platforms in 2026 are powerful but complex. Advanced configurations, particularly within large-scale Azure or multi-cloud deployments, require specialized knowledge.
Software selection alone does not determine deployment success. Organizational capability is equally critical.
Skill Investment Matrix
| Competency Area | Strategic Importance |
|---|---|
| Cloud Infrastructure (AWS, Azure) | Essential for secure, scalable deployment |
| Security Governance | Critical for Zero Trust enforcement |
| Network Architecture | Required for performance optimization |
| Automation and Scripting | Enables cost and efficiency gains |
Certifications such as AWS architecture credentials, Azure administration credentials, and foundational security certifications are not optional enhancements. They are structural enablers of long-term operational stability.
Without internal expertise, organizations risk:
• Misconfigured networking
• Escalating compute costs
• Security policy gaps
• Underutilized automation features
CIOs must treat workforce upskilling as a parallel investment alongside DaaS licensing.
Embed DaaS Within a Broader Innovation Strategy
Forward-looking organizations are not deploying DaaS solely for remote access enablement. They are leveraging it as a platform for:
• AI-driven workplace automation
• Rapid workforce onboarding
• Global talent distribution
• Resilient disaster recovery
Strategic Impact Outlook
| Strategic Dimension | DaaS Contribution by 2035 |
|---|---|
| Operational Resilience | High, centralized recovery capabilities |
| Innovation Enablement | AI-integrated digital workspaces |
| Workforce Flexibility | Location-independent productivity |
| Cost Optimization | Automated resource scaling |
As DaaS matures, it will increasingly serve as the foundation for integrated AI agents, workflow automation, and predictive IT operations.
Long-Term Strategic Outlook
With the market projected to exceed USD 57.83 billion by 2035, DaaS is transitioning from an emerging cloud service to the standardized definition of enterprise desktop computing.
Organizations that will outperform in this environment share three characteristics:
• They optimize management intelligence rather than infrastructure specifications.
• They align financial models with workforce variability.
• They build internal expertise to fully leverage platform capabilities.
Conclusion
For CIOs in 2026, Desktop as a Service is not a tactical response to hybrid work trends. It is a structural decision that shapes security posture, financial modeling, workforce strategy, and innovation capacity for the next decade.
The enterprises that thrive will be those that treat DaaS as a strategic operating platform—one that integrates automation, security, and scalability into the very core of digital operations.
Conclusion
The global Desktop as a Service (DaaS) market in 2026 represents a decisive turning point in enterprise computing. What began as a remote access solution has matured into a strategic digital workspace platform that underpins modern hybrid work, cybersecurity resilience, AI-driven automation, and global workforce scalability. The top 10 Desktop as a Service software solutions in 2026 are no longer competing solely on virtual desktop delivery. They are competing on ecosystem integration, management intelligence, pricing flexibility, security architecture, and performance optimization.
As organizations reassess their IT operating models, DaaS has become the architectural foundation of cloud-first strategies. The ability to decouple the desktop experience from physical hardware enables enterprises to operate more securely, more flexibly, and more efficiently. From small and medium enterprises seeking cost predictability to global corporations requiring zero-trust security enforcement, Desktop as a Service platforms now address a wide spectrum of operational needs.
Why Desktop as a Service Is the Standard in 2026
By 2026, DaaS adoption is no longer experimental. It is mainstream. Enterprises across industries including finance, healthcare, manufacturing, education, retail, and government have adopted cloud desktops as their default workspace model. Several macro trends have accelerated this shift:
• Hybrid and remote workforce normalization
• Rising cybersecurity threats and ransomware risks
• Hardware lifecycle refresh cycles
• AI-driven infrastructure automation
• Global talent sourcing beyond geographic boundaries
Desktop as a Service software in 2026 offers more than remote desktop access. It provides secure, compliant, scalable, and AI-enhanced digital workspaces that are accessible from any device, anywhere in the world.
Key Differentiators Among the Top 10 DaaS Providers in 2026
The top Desktop as a Service platforms globally distinguish themselves across several critical dimensions:
Security Architecture
Zero Trust Network Access, granular Data Loss Prevention, and real-time compliance monitoring have become baseline requirements. Advanced providers integrate behavioral analytics, micro-segmentation, and policy-as-code frameworks to reduce risk exposure and ensure regulatory alignment.
Pricing Models and Cost Transparency
The DaaS pricing landscape has evolved beyond simple per-user subscriptions. In 2026, organizations can choose from:
• Fixed monthly subscription models
• Usage-based pricing
• Hybrid billing structures
• Outcome-based models for AI-driven workflows
This flexibility allows businesses to align Desktop as a Service costs with workforce dynamics, reducing unnecessary overhead while maintaining performance standards.
Performance and Remoting Protocol Innovation
Modern DaaS protocols deliver high-resolution, low-latency experiences while consuming significantly less bandwidth than previous generations. Whether supporting knowledge workers or graphics-intensive engineering teams, performance optimization has become a major competitive differentiator.
Management Intelligence and Automation
The real strategic advantage in 2026 lies in the management plane. AI-driven orchestration, predictive scaling, automated patching, and self-healing systems dramatically reduce administrative labor costs and improve operational uptime. The most successful DaaS software platforms emphasize intelligent automation over raw infrastructure complexity.
The Strategic Value of Choosing the Right DaaS Software
Selecting from the top 10 Desktop as a Service software platforms in 2026 is not simply a technical procurement decision. It is a long-term strategic investment that impacts:
• Total Cost of Ownership over multiple years
• Security posture and data governance
• Workforce productivity and flexibility
• Disaster recovery readiness
• AI and digital transformation integration
Organizations that evaluate DaaS platforms solely on price risk overlooking hidden variables such as bandwidth requirements, compliance capabilities, administrative complexity, and ecosystem compatibility. A comprehensive evaluation must consider management tooling, scalability, vendor support quality, and alignment with cloud infrastructure strategies.
DaaS for SMEs vs. Large Enterprises
One of the defining characteristics of the 2026 Desktop as a Service market is its adaptability across organizational sizes.
Small and medium enterprises benefit from:
• Reduced capital expenditure
• Rapid scalability
• Simplified IT operations
• Predictable operational costs
Large enterprises leverage DaaS for:
• Advanced zero-trust security models
• Onshore deployments for data sovereignty
• Integrated compliance frameworks
• Large-scale disaster recovery strategies
The top 10 DaaS providers offer tailored value propositions across both segments, ensuring that organizations of all sizes can modernize their digital workspaces effectively.
The Future Outlook of Desktop as a Service
Market projections suggest continued expansion toward multi-billion-dollar valuations by the mid-2030s. As AI becomes more deeply embedded into workplace systems, DaaS platforms will increasingly serve as the delivery layer for intelligent automation, digital assistants, and advanced analytics tools.
Emerging trends shaping the future of DaaS include:
• AI-native virtual desktops
• Edge-integrated cloud delivery
• Advanced GPU virtualization for high-performance workloads
• Increased adoption of browser-based and containerized environments
• Deeper integration with identity and access management frameworks
In this evolving ecosystem, Desktop as a Service will no longer be described as a cloud alternative to traditional desktops. It will be considered the default architecture for secure enterprise computing.
Final Perspective
The top 10 Desktop as a Service software platforms in the world in 2026 represent the culmination of years of innovation in virtualization, cloud infrastructure, networking, and cybersecurity. Each provider brings a unique combination of strengths, whether in cost efficiency, graphics performance, AI integration, multi-cloud flexibility, or management simplicity.
For organizations developing their digital workspace strategy, the priority is not simply to adopt DaaS, but to select the platform that aligns with long-term operational goals. The right Desktop as a Service solution enables financial optimization, reduces security risk, supports global workforce expansion, and lays the groundwork for continuous innovation.
In 2026 and beyond, Desktop as a Service is not just reshaping IT infrastructure. It is redefining how work itself is delivered, secured, and optimized across the global enterprise landscape.
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your hiring manager and C-level suite friends and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the 9cv9 Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.
To get access to top-quality guides, click over to 9cv9 Blog.
To hire top talents using our modern AI-powered recruitment agency, find out more at 9cv9 Modern AI-Powered Recruitment Agency.
People Also Ask
What is Desktop as a Service (DaaS) in 2026?
Desktop as a Service in 2026 is a cloud-based solution that delivers virtual desktops to users over the internet, enabling secure remote access, centralized management, and scalable computing without relying on local hardware.
Which are the top 10 Desktop as a Service software platforms in 2026?
The leading DaaS platforms in 2026 include major cloud providers and virtualization specialists offering secure, scalable, and AI-enhanced cloud desktops for enterprises and SMEs worldwide.
How does DaaS differ from traditional VDI?
DaaS is fully managed and cloud-hosted by a provider, while traditional VDI requires on-prem infrastructure and in-house management, increasing complexity and capital expenditure.
Why are businesses adopting DaaS in 2026?
Organizations adopt DaaS for improved security, lower Total Cost of Ownership, hybrid workforce enablement, AI-driven automation, and easier scalability across global teams.
Is Desktop as a Service secure for enterprise use?
Yes, modern DaaS platforms use Zero Trust security, data loss prevention, encryption, and continuous monitoring to protect corporate data from ransomware and breaches.
What is the average cost of DaaS in 2026?
DaaS pricing typically ranges from USD 5 to USD 150 per user per month, depending on performance tier, GPU requirements, and usage-based or subscription models.
Does DaaS reduce Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)?
Yes, DaaS can reduce TCO by up to 20% compared to traditional laptops by lowering hardware refresh costs, energy consumption, and administrative overhead.
Which DaaS software is best for small businesses?
SMEs often prefer simple, fixed-cost DaaS platforms that require minimal IT expertise and offer predictable pricing with strong security controls.
What is the best DaaS platform for large enterprises?
Large enterprises typically choose DaaS solutions with advanced security, compliance certifications, multi-cloud flexibility, and disaster recovery capabilities.
Can DaaS support high-performance GPU workloads?
Yes, many top DaaS providers in 2026 offer GPU-enabled virtual desktops for 3D modeling, engineering, video editing, and AI development tasks.
How much bandwidth does DaaS require?
Standard office tasks require 1–2 Mbps per user, while 4K graphics-intensive workloads may require up to 15 Mbps for optimal performance.
What is usage-based pricing in DaaS?
Usage-based pricing charges organizations based on active user hours or compute consumption, making it ideal for contractors or seasonal staff.
Is DaaS suitable for remote and hybrid work?
Yes, DaaS is designed for hybrid work, allowing employees to securely access corporate desktops from any device and location.
How does DaaS improve cybersecurity?
DaaS isolates corporate data in the cloud, prevents local data storage, and uses continuous authentication and monitoring to reduce cyber risks.
What industries benefit most from DaaS in 2026?
Finance, healthcare, manufacturing, education, and technology sectors benefit from DaaS due to strict compliance needs and distributed teams.
What certifications matter for managing DaaS environments?
Certifications such as CISSP, Azure Administrator, AWS Solutions Architect, and CompTIA Security+ are important for secure DaaS governance.
Can DaaS run on low-end devices or Chromebooks?
Yes, DaaS enables high-performance virtual desktops to run on low-spec devices, as processing occurs in the cloud.
What is Zero Trust in DaaS security?
Zero Trust ensures every user and device is continuously verified before accessing resources, eliminating implicit trust within networks.
Does DaaS support multi-cloud deployment?
Many top DaaS platforms in 2026 support multi-cloud and hybrid environments, allowing deployment across Azure, AWS, Google Cloud, or on-premises.
What is the future of Desktop as a Service beyond 2026?
DaaS is expected to become the default enterprise desktop model, with deeper AI integration and edge computing enhancements.
How quickly can businesses deploy DaaS?
Most DaaS platforms allow deployment within hours or days, depending on configuration complexity and migration requirements.
Is DaaS better than buying new laptops?
For many organizations, DaaS offers better scalability, lower long-term costs, centralized security, and reduced hardware dependency.
What is a Cloud PC?
A Cloud PC is a dedicated virtual desktop hosted in the cloud and assigned to a specific user with fixed compute resources.
How does DaaS handle compliance requirements?
DaaS platforms support policy-based compliance monitoring, data residency controls, and real-time auditing for regulatory alignment.
Can DaaS integrate with Microsoft 365 and other SaaS apps?
Yes, leading DaaS providers offer seamless integration with Microsoft 365, collaboration tools, and enterprise SaaS applications.
What are AI-powered DaaS features?
AI features include automated scaling, predictive performance tuning, behavioral authentication, and self-healing infrastructure.
Is DaaS suitable for BYOD environments?
Yes, DaaS is ideal for Bring Your Own Device scenarios because data remains secure in the cloud rather than on personal hardware.
What network challenges affect DaaS performance?
Limited bandwidth, high latency, and unstable internet connections can impact DaaS performance, especially for graphics-heavy tasks.
How do organizations calculate DaaS ROI?
ROI is calculated by comparing subscription costs against savings from reduced hardware, energy, maintenance, and administrative labor.
Will DaaS replace traditional desktops completely?
By the early 2030s, DaaS is expected to become the dominant enterprise desktop model, though niche local computing use cases may remain.
Sources
Research Nester
Fortune Business Insights
Computerworld
Business Research Insights
Global Insight Services
Mordor Intelligence
Research and Markets
Market Research Future
Inuvika
Microsoft Learn
Gartner
Medium
Campus Technology
Graphon
Omnissa
Venn
Capterra
Nutanix
AWS Marketplace
TrustRadius
Software Advice
SourceForge
GetApp
G2
DigitalOcean
GRSEE Consulting
Bilginç IT Academy
Bright Data































![Writing A Good CV [6 Tips To Improve Your CV] 6 Tips To Improve Your CV](https://blog.9cv9.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/2020-06-02-2-100x70.png)


