Key Takeaways
- Follow the required steps: To register a company in Vietnam, it’s important to follow the required steps and provide the necessary documentation within the specified timeframe. The dossier for registration must include essential details such as the application form for business registration, company charter, list of members or stakeholders, legal documents of the organization and authorized representatives, and the Investment registration certificate for foreign investors as per the Law on Investment.
- Pay attention to tax obligations: To avoid penalties, it’s crucial to pay attention to the tax obligations for your business in Vietnam. Companies must obtain an electronic signature to access the online tax system and submit their tax declarations and reports through it. Additionally, the business license certificate number doubles as the company’s tax number.
- Adhere to the timeline: Once you receive the Business Registration Certificate, you have 90 days to make the capital contribution. It’s important to adhere to this timeline to avoid any fines or penalties. Additionally, after being granted the certificate, businesses must make a public announcement on the National Business Registration Portal within 30 days.
If you are planning to start a business in Vietnam, one of the first steps you will need to take is registering your company.
Vietnam is a country with a thriving economy and a rapidly growing business landscape, which makes it an attractive destination for entrepreneurs and investors looking to tap into Southeast Asia’s market.
However, starting a business in Vietnam can be a complex process, with various legal and administrative requirements that need to be met.
In this article, we will guide you through the process of registering a company in Vietnam.
From understanding the different types of businesses and legal structures available to obtaining the necessary licenses and permits, we will provide you with a comprehensive guide to help you navigate the registration process.
Whether you are planning to start a small business or a large corporation, this guide will give you the knowledge and tools you need to register your company successfully.
We will begin by discussing the importance of registering a company in Vietnam and provide an overview of the country’s business landscape.
We will then move on to the preparations you need to make before registering your company, such as choosing the right legal structure, understanding the necessary documents, and deciding on a business name.
We will also explain the licensing requirements you need to meet to start your business.
Next, we will provide a step-by-step guide to registering a company in Vietnam.
This will include registering your business name, obtaining an investment certificate, registering for a tax code, opening a bank account, and obtaining other necessary licenses.
We will also discuss the post-registration requirements, such as complying with Vietnamese laws and regulations, maintaining proper accounting and bookkeeping records, and hiring employees.
Finally, we will conclude by summarising the registration process and highlighting the benefits of registering a company in Vietnam.
We will also provide you with key takeaways and recommendations to help you navigate the business landscape successfully.
Whether you are a local or foreign investor, this article will provide you with the knowledge and resources you need to register your company in Vietnam.
Before we venture further into this article, we like to share who we are and what we do.
About 9cv9
9cv9 is a business tech startup based in Singapore and Vietnam with a strong presence all over the world.
With over six years of startup and business experience, and being highly involved in connecting with thousands of companies and startups, the 9cv9 team has listed some important learning points in this overview of how to register a company in Vietnam.
If your company needs recruitment and headhunting services down the road after registration, you can use 9cv9 headhunting and recruitment services to hire top talents and candidates in Vietnam. Book a consultation slot here, or send over an email to [email protected].
Why Vietnam?
Vietnam has become an attractive destination for entrepreneurs and investors due to its growing economy, favorable business environment, and strategic location in Southeast Asia.
The country has experienced impressive economic growth in recent years, with a Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth rate of 7.08% in 2018 and 2.91% in 2020 despite the COVID-19 pandemic.
In 2022, Vietnam’s economy grew by 8.02%, the fastest annual pace since 1997. In comparison, Singapore’s economy grew by only 3.6%, and Indonesia grew by 5.2% in 2022.
Vietnam’s economy is expected to continue to grow at a steady pace in the coming years, making it an excellent place to invest, register a company, and build your business empire.
Vietnam ranked 70 among 190 economies in this year’s Doing Business 2020 report released by the World Bank, illustrating the somewhat difficulties in registering a business and hence the motivation to write this article.
As of December 2022, the Foreign Direct Investment (“FDI”) reached about USD 27.72b, showing the keen interest of many foreign investors with respect to Vietnam.
There are many reasons why investors choose to look toward Vietnam.
Firstly, Vietnam’s ability to maintain socio-political stability and Vietnam is known to be one of the most dynamic economies.
The GDP growth between 2000 and 2020 averaged 6.38% each year and despite many difficulties in 2020, Vietnam’s GDP advanced by 4.48% year-on-year in the fourth quarter of 2020.
Secondly, Vietnam is now in a period of golden population structure – 60% of its population is working age.
The government is very welcoming towards FDI, they’re committed to creating a fair and attractive business environment for foreign investors, and constantly improving its legal framework and institutions related to business and investment.
Vietnam views the success of FDI enterprises as its own success.
With such a positive atmosphere, Vietnam offers promising opportunities to open a business.
Vietnam’s strategic location in Southeast Asia is also a key factor in its appeal.
It borders China to the north and Laos and Cambodia to the west, making it an excellent gateway to the rest of the region.
Vietnam has a large and growing consumer market, which makes it an attractive destination for businesses looking to expand their reach in the region.
If you’re interested to establish a foreign-owned company in Vietnam, here is a guideline for you to understand the requirements and process.
Can Foreigners Set up a Business in Vietnam?
As a foreigner, it is possible to start a business in Vietnam through direct or indirect foreign investments.
Direct foreign investment involves working with a Vietnamese partner to establish either a wholly foreign-owned company or a joint venture company.
To obtain a direct investment in Vietnam, you must obtain an enterprise license and go through legal procedures according to local laws.
We will explain how to do it in the below sections.
A wholly foreign-owned company is a type of business structure where foreign investors own 100% of the company’s shares.
This structure allows for full control and decision-making power over the business.
A joint venture company, on the other hand, is a partnership between foreign investors and local Vietnamese partners, sharing ownership and control over the company.
Indirect foreign investment, on the other hand, refers to the purchase of shares of existing companies in Vietnam.
This type of investment grants you a position in company management, depending on the agreement between you and the Vietnamese company.
For the purpose of this article, we will be delving and focusing on the direct investment and involvement of foreigners in setting up the company in Vietnam.
However, if you are looking to set up operations without needing to set up a legal entity, then an “Employer of Record” will be the right strategy for you.
When starting a business in Vietnam as a foreigner, it is important to consider key factors such as the legal and regulatory environment, market conditions, and cultural differences.
Restricted Business Activities for Foreigners to Set Up a Business in Vietnam
Foreigners who are interested in establishing a business in Vietnam should be aware that there are certain restrictions on the types of activities that they can engage in.
The Law on Investment (LOI) 2020, outlines the activities that are restricted for foreigners.
One of the major restrictions is related to business activities that involve narcotic substances, which are stipulated in Appendix 1 of the LOI.
This means that foreigners are not allowed to engage in any business activities related to drugs or any illegal substances.
Similarly, toxic chemicals, precursors, and minerals that are listed in Appendix 2 of the LOI are also prohibited for foreigners to carry out any business activities.
This restriction aims to protect the environment and ensure that the use of chemicals and minerals is regulated.
Another restriction for foreigners is related to natural specimens of endangered, rare, and precious wild fauna and flora species.
This is stipulated in Appendix I of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) and Appendix 3 of the LOI.
This restriction is put in place to preserve biodiversity and prevent the exploitation of endangered species.
Business activities related to prostitution, human trafficking, or cloning of human-related businesses are strictly prohibited for foreigners.
This is to ensure that such illegal activities are not promoted in Vietnam and to protect the human rights of the Vietnamese people.
Moreover, foreigners are also restricted from engaging in firecracker-related businesses, as well as debt collection activities.
These restrictions are put in place to maintain public safety and prevent any illegal activities that can harm society.
Foreigners who are interested in starting a business in Vietnam should be aware of the restrictions outlined in the LOI.
These restrictions aim to protect the environment, preserve biodiversity, prevent illegal activities, and ensure public safety.
Now, onto the main steps of how to register a company in Vietnam in 2023.
How to Register a Company in Vietnam (Updated in 2023)
- Understanding the Different Types of Businesses in Vietnam
- Knowing How to Choose the Right Structure for your Business in Vietnam
- Understanding the Necessary Documents
- Deciding on a Business Name
- Being Aware of Licensing Requirements
- Executing the Steps to Register a Company in Vietnam
- Compiling with the Post-Registration Requirements
1. Understanding the Different Types of Businesses in Vietnam
In Vietnam, there are several types of businesses that you can choose to register depending on your goals and objectives.
Typically, the Limited Liability Company (LLC) and Joint Stock Company (JSC) are the most popular legal entity choices for foreign investors who want to register a company in Vietnam.
Since most industries in Vietnam allow foreign investors to own up to 100% of shares, a Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise (WFOE) is a common business structure in Vietnam.
For example, under the new Law on Insurance Business No. 08/2022/QH15, foreign investors can now own 100% of the shares of an insurance company.
Foreign investors can also incorporate with a local partner to form a Joint Venture Company with local-foreign ownership.
The most common types of businesses in Vietnam are the following:
- Sole Proprietorship
- Partnership
- Limited Liability Company (LLC)
- Joint-Stock Company (JSC)
- Representative Office
- Branch Office
A) Sole Proprietorship
This is a business structure where an individual owns and operates the business.
The owner is personally responsible for all debts and liabilities of the business.
In Vietnam, a sole proprietorship is referred to as an individual business household.
It is a business structure where a single individual owns and operates the business.
This type of business structure is relatively easy and inexpensive to set up, making it a popular choice for small businesses and startups.
Here are some key points to note about sole proprietorships in Vietnam:
- Registration: To register as an individual business household, the owner must submit a business registration application to the local Department of Planning and Investment (DPI) or Business Registration Office. The registration process usually takes around 3-5 working days.
- Liability: The owner of an individual business household is personally responsible for all debts and liabilities incurred by the business. This means that the owner’s personal assets may be used to pay off business debts in case of bankruptcy.
- Taxation: Sole proprietors are required to pay personal income tax on their business income, and they are not subject to corporate income tax. The tax rate varies depending on the amount of income earned.
- Reporting requirements: Sole proprietors are required to keep accounting records and submit monthly and annual tax returns. Failure to comply with these requirements may result in penalties or fines.
- Limitations: Individual business households are limited in their ability to raise capital, and they cannot issue shares or bring in external investors.
While sole proprietorships are relatively easy to set up and operate, they do have some limitations, and the owner’s personal liability can be a significant risk.
B) Partnership
A partnership is a business structure where two or more individuals or entities share ownership of the business. Partnerships can be either limited or general partnerships.
In Vietnam, partnerships are a popular legal structure for businesses involving two or more owners who want to share the profits and losses of the business.
There are two types of partnerships in Vietnam: general partnerships and limited partnerships.
Here are some key points to note about partnerships in Vietnam:
- General Partnership: A general partnership is a business structure where two or more partners manage and operate the business. Each partner has unlimited liability for the debts and obligations of the business. This means that the personal assets of the partners may be used to pay off business debts in case of bankruptcy.
- Limited Partnership: A limited partnership is a business structure where there are both general partners and limited partners. General partners have unlimited liability for the debts and obligations of the business, while limited partners have limited liability, meaning their personal assets are not at risk beyond their investment in the business.
- Registration: To register a partnership in Vietnam, the partners must submit a business registration application to the local Department of Planning and Investment (DPI) or the Business Registration Office. The registration process usually takes around 3-5 working days.
- Taxation: Partnerships are not subject to corporate income tax in Vietnam. Instead, partners are required to pay personal income tax on their share of the partnership profits. The tax rate varies depending on the amount of income earned.
- Reporting requirements: Partnerships are required to keep accounting records and submit monthly and annual tax returns. Failure to comply with these requirements may result in penalties or fines.
Partnerships in Vietnam offer several benefits, such as shared management and resources and the ability to pool capital and share risks.
It’s essential to consider the risks involved, particularly for general partners who have unlimited liability.
C) Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC is a popular business structure in Vietnam that offers limited liability protection to its owners.
This means that the owners are not personally responsible for the debts and liabilities of the business.
An LLC can be owned by individuals or other legal entities.
An LLC is the most common legal entity type in Vietnam.
This business entity only requires at least one founder.
Because of its simple corporate structure, this company type is suitable for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and startups.
Moreover, it is also perfect for entrepreneurs who intend to protect their personal assets, since the liability of the shareholders is limited to their shares only.
It is also faster to establish an LLC compared to other entity types in Vietnam because of the lean registration process and less paperwork needed.
However, LLC is not allowed to issue public shares and be publicly listed on the Vietnamese stock exchange.
Here are some key points to note about LLCs in Vietnam:
- Registration: To register an LLC in Vietnam, the owners must submit a business registration application to the local Department of Planning and Investment (DPI) or the Business Registration Office. The registration process usually takes around 3-5 working days.
- Liability: The owners of an LLC have limited liability for the debts and obligations of the company. This means that their personal assets are protected in case the business incurs any debts or legal issues.
- Management: LLCs are managed by a board of members or a managing director. The board of members can be elected by the members of the LLC or appointed by the managing director.
- Taxation: LLCs are subject to corporate income tax in Vietnam, and the tax rate is currently 20%. Additionally, the owners are required to pay personal income tax on their share of the company’s profits.
- Reporting requirements: LLCs are required to keep accounting records and submit monthly and annual tax returns. Failure to comply with these requirements may result in penalties or fines.
LLCs in Vietnam offer several benefits, such as limited liability, flexible management structure, and the ability to attract external investment.
However, it’s essential to consider the costs involved, such as corporate income tax and accounting fees, before deciding on this legal structure for your business.
D) Joint-Stock Company (JSC)
A JSC is a business structure where ownership is divided into shares, which can be publicly traded.
A JSC is typically used for large businesses with multiple shareholders.
A Joint-Stock Company (JSC) is recommended for medium and large-sized businesses because of its complicated corporate structure and the requirement to have at least three founders.
The ownership of JSC can be either 100% owned by foreign investors (WFOE) or partly owned by foreign investors and local investors (Joint Venture Company).
It is compulsory for a JSC to have a corporate structure that consists:
- A Management Board that is supervised by an annual general meeting and an inspection committee
- A Chairman of the Management Board
- A Director who will play the role of the company’s Legal Representative
The registration process often takes a long time due to more demanding requirements.
However, unlike LLC, this business entity is allowed to issue shares and be publicly listed on the Vietnamese stock exchange.
Therefore, this entity is preferred by the majority of large companies despite its demanding requirements.
Here are some key points to note about JSCs in Vietnam:
- Registration: To register a JSC in Vietnam, the owners must submit a business registration application to the local Department of Planning and Investment (DPI) or Business Registration Office. The registration process usually takes around 3-5 working days.
- Capital: JSCs in Vietnam must have a minimum charter capital of VND 10 billion (approximately USD 440,000) for public companies and VND 3 billion (approximately USD 130,000) for private companies. The capital is divided into shares, and the shareholders have limited liability for the debts and obligations of the company.
- Management: JSCs are managed by a board of directors, which is elected by the shareholders. The board of directors is responsible for making strategic decisions and overseeing the day-to-day operations of the company.
- Shares: JSCs can issue two types of shares: common shares and preferred shares. Common shares represent ownership in the company and typically carry voting rights. Preferred shares, on the other hand, do not carry voting rights but may offer higher dividends or other benefits.
- Reporting requirements: JSCs are required to keep accounting records and submit monthly and annual tax returns. Additionally, public JSCs must comply with stricter reporting requirements and disclose information to the public, including financial statements and information on the company’s management and ownership.
JSCs in Vietnam offer several advantages, such as the ability to raise capital through public offerings of stock, limited liability for shareholders, and a clear management structure.
However, the process of setting up a JSC can be more complex and costly compared to other legal structures, and public JSCs must comply with stricter reporting requirements.
E) Representative Office
A representative office is a type of legal structure in Vietnam that allows foreign companies to establish a presence in the country without incorporating a separate legal entity.
Representative offices can be set up for a variety of reasons, such as market research, marketing, and liaison activities.
Here are some key points to note about representative offices in Vietnam:
- Registration: To set up a representative office in Vietnam, the foreign company must submit an application to the Ministry of Industry and Trade or the Department of Industry and Trade. The registration process can take up to 20 working days.
- Activities: Representative offices are not allowed to engage in any commercial or profit-generating activities in Vietnam. They are limited to conducting market research, promoting the parent company’s products or services, and other non-commercial activities.
- Legal status: Representative offices in Vietnam do not have a separate legal personality and cannot enter into contracts or engage in any legal proceedings. The parent company is liable for any obligations or liabilities incurred by the representative office.
- Taxation: Representative offices in Vietnam are not subject to corporate income tax as they do not generate any income. However, they are required to pay annual business license fees and other taxes related to their operations.
- Reporting requirements: Representative offices in Vietnam are required to submit annual reports to the licensing authority, detailing their activities in Vietnam.
Representative offices in Vietnam offer foreign companies a way to establish a presence in the country without incurring the costs and legal obligations of incorporating a separate legal entity.
However, they are limited in their activities and do not have a separate legal personality.
F) Branch Office
A branch office is a type of legal structure in Vietnam that allows foreign companies to establish a full-fledged presence in the country with a separate legal entity.
Branch offices can engage in a wide range of commercial activities and have the same legal rights and obligations as local companies.
Here are some key points to note about branch offices in Vietnam:
- Registration: To set up a branch office in Vietnam, the foreign company must submit an application to the Department of Planning and Investment. The registration process can take up to 45 working days.
- Activities: Branch offices can engage in a wide range of commercial activities in Vietnam, subject to the relevant licensing requirements and regulations.
- Legal status: Branch offices in Vietnam have a separate legal personality from the parent company and can enter into contracts and engage in legal proceedings in their own name. The parent company is liable for any obligations or liabilities incurred by the branch office.
- Taxation: Branch offices in Vietnam are subject to corporate income tax on their profits generated in Vietnam. They are also required to comply with all relevant tax laws and regulations.
- Reporting requirements: Branch offices in Vietnam are required to submit annual financial statements and tax returns to the relevant authorities.
Setting up a branch office in Vietnam can be a good option for foreign companies that want to establish a full-fledged presence in the country and engage in commercial activities.
However, it comes with additional costs and legal obligations compared to a representative office or other legal structures.
Seeking professional advice and carefully considering the purpose and objectives of establishing a branch office in Vietnam can help ensure compliance with all legal requirements and regulations.
When choosing a business structure, it is important to consider factors such as liability protection, ownership structure, and taxation.
If you need help in deciding the best corporate structure to optimize your operations in Vietnam, book a slot here.
2. Knowing How to Choose the Right Structure for your Business in Vietnam
Choosing the right legal structure for your business is an important decision as it can impact your business’s taxation, ownership, and liability.
Here are some factors to consider when choosing the right legal structure for your business in Vietnam:
- Liability: Consider the level of protection you need for personal assets. If you want to limit your personal liability, you may consider registering a limited liability company (LLC) or a joint-stock company (JSC). These are the two most popular company structures that most business owners and startup founders will be looking to set up. In the early stage, it will most likely be an LLC and when the company has grown big enough to be a public company, then a JSC will be set up.
- Ownership: Consider the ownership structure you want for your business. For instance, if you want to keep the business under your sole ownership, you may register a sole proprietorship or a one-member limited liability company.
- Taxation: Consider the tax implications of each legal structure. For instance, if you want to minimize your tax liability, you may consider registering a limited liability company, as it is subject to a lower corporate income tax rate than a joint-stock company.
- Cost: Consider the cost of registration and ongoing compliance requirements of each legal structure. Some structures may require more extensive documentation and administrative work than others.
- Future growth: Consider the potential for future growth and expansion of your business. If you plan to raise capital from investors or list your company on the stock exchange, you may want to register a joint-stock company.
It is important to consult with a qualified professional, such as a lawyer or accountant, to help you choose the most suitable legal structure for your business in Vietnam.
Getting in touch with the 9cv9 corporate service team here will be helpful in making the best and optimal choice for your organization.
They can provide you with advice and guidance on the registration process and the legal and regulatory requirements that need to be met.
3. Understanding the Necessary Documents
When registering a company in Vietnam, there are several necessary documents that need to be prepared and submitted.
These documents may vary depending on the type of legal structure chosen, but some common documents include:
Business registration application form: This is the application form used to register the business and contains information such as the company name, business address, business activities, and ownership structure.
Business plan: A detailed business plan outlining the objectives, strategies, and financial projections of the business may be required to demonstrate the viability of the company.
Articles of Association (AoA): The AoA outlines the internal management and governance structure of the company, including the roles and responsibilities of shareholders, board members, and managers.
Certificate of incorporation: This is the official document that confirms the legal existence of the company and includes the company name, registration number, and other essential details.
Lease agreement: A lease agreement for the business premises is required, which should be registered with the local authorities.
Identification documents: Identification documents such as passports or identity cards are required for the owners, managers, and legal representatives of the company.
Tax registration: A tax registration certificate is required to enable the company to conduct business activities and comply with tax obligations.
Labor registration: Labor registration with the local labor authority is required if the company plans to employ local workers.
It is important to note that the documents required for company registration in Vietnam may vary depending on the legal structure and industry in which the company operates.
It is recommended to seek professional advice from a lawyer or accountant to ensure that all necessary documents are prepared and submitted accurately and on time.
4. Deciding on a Business Name
Choosing the right business name is an important step in registering a company in Vietnam. Here are some tips to help you decide on a business name:
- Make it memorable: Choose a name that is easy to remember and unique. Avoid using generic or common names that may be difficult to differentiate from other businesses.
- Reflect your business: Your business name should reflect your business activities, values, and objectives. Consider using keywords related to your industry or services to make your business more searchable.
- Check for availability: Ensure that the business name you choose is available and not already registered by another company. You can check for name availability through the National Business Registration Portal or with the Department of Planning and Investment in your local province.
- Avoid prohibited words: There are certain words that are prohibited for use in business names, such as words that are offensive, obscene, or suggest illegal activities.
- Consider cultural factors: Consider the cultural context of Vietnam when choosing a business name. Avoid names that may be offensive or culturally inappropriate.
- Register your domain: Consider registering a domain name that matches your business name to establish a strong online presence.
It is important to note that the business name you choose will be a significant part of your company’s identity and branding.
It is recommended to seek professional advice from a branding or marketing expert to ensure that your business name is effective and aligns with your overall business strategy.
5. Being Aware of Licensing Requirements
In Vietnam, businesses are required to obtain various licenses and permits to operate legally.
The licensing requirements may vary depending on the type of business activities, location, and industry.
Here are some common licenses and permits required for businesses in Vietnam:
- Business registration certificate: This is the first license required to establish a legal business entity in Vietnam.
- Investment certificate: Foreign investors are required to obtain an investment certificate to operate in Vietnam.
- Trading license: A trading license is required for businesses engaged in import/export activities, wholesale and retail trading, and distribution.
- Construction permit: A construction permit is required for businesses engaged in construction activities.
- Environmental permit: A permit is required for businesses that may cause environmental impacts.
- Food hygiene and safety certificate: A certificate is required for businesses engaged in food production and processing.
- Fire prevention and fighting certificate: A certificate is required for businesses that use flammable or explosive materials.
- Health service operation permit: A permit is required for businesses providing healthcare services.
- Transport operation license: A license is required for businesses engaged in transport activities, such as passenger transportation or cargo transportation.
- Intellectual property registration: A registration for trademarks, patents, and copyrights may be required to protect intellectual property rights.
It is important to note that the licensing requirements and procedures may change frequently in Vietnam.
It is recommended to seek professional advice from a qualified lawyer or consultant to ensure compliance with the current regulations and requirements for licensing.
6. Executing the Steps to Register a Company in Vietnam
The steps to register a company in Vietnam can be tedious, complicated and expensive.
It’s best to hire a professional corporate service team such as 9cv9 or to find your own corporate service provider in Vietnam that will execute the registration steps for you.
- Determine the legal structure: Decide on the type of legal structure for your company, such as a limited liability company, joint-stock company, or partnership.
- Choose a business name: Choose a unique business name that is not already registered by another company.
- Prepare necessary documents: Prepare all the necessary documents, such as the business registration application form, business plan, Articles of Association, lease agreement, and identification documents.
- Open a bank account: Open a bank account in Vietnam to deposit the minimum required capital for your chosen legal structure.
- Register the business: Submit the application for business registration to the Department of Planning and Investment in your local province.
- Obtain licenses and permits: Obtain all necessary licenses and permits required for your business activities and industry.
- Register for tax: Register for tax at the local tax office to comply with tax obligations.
- Register for labor: Register with the local labor authority if you plan to employ local workers.
- Post-registration procedures: After registering the company, complete post-registration procedures such as obtaining a seal, registering for social insurance and health insurance, and registering with the Ministry of Labor, Invalids, and Social Affairs.
Requirements for registering an LLC as a company
- A registered business address: this can be a physical or a virtual address.
- Business Certificate (Certificate of Establishment) or an equivalent paper
- Charter Capital: the amount must be enough to cover the company’s expenses for at least the next six months. In general, for a simple LLC, the recommended amount is between USD 10,000 – 25,000.
- Financial documents: for instance, bank statements with the same or bigger amount of the charter capital and legalized at the Vietnamese Embassy in the country of the bank statement and then translated and notarized in Vietnam.
- Legal Representative: should be in a management role or higher, living in Vietnam full time, and can be a foreigner.
- Official identity: notarized copies of the Investor and Legal Representative(s)’s official ID.
Requirements for registering an LLC as an individual
- A registered business address: this can be a physical or a virtual address.
- Charter Capital: the amount must be enough to cover the company’s expenses for at least the next six months. In general, for a simple LLC, the recommended amount is between USD 10,000 – 25,000.
- Legalised Bank Statement: bank statement with the same or bigger amount of the charter capital and legalized at the Vietnamese Embassy in the country of the bank statement and then translated and notarized in Vietnam.
- Legal Representative: should be in a management role or higher, living in Vietnam full time, and can be a foreigner.
Official identity: notarized copies of the Investor and Legal Representative(s)’s official ID.
Requirements for registering a JSC
- A bank certificate as proof of funds
- Proposal for the investment project
- Documents required for an Investment Registration Certificate (IRC) application
- Personal details of every shareholder and their respective amount of shares
- Legal status certificate for all founding shareholders
- A capital bank account
- Proposal for land use
- A Foreign Investment Certificate
- Financial statements that have been audited
- Submission of annual return
Procedures for establishing an LLC
Step 1) Investment Registration Certificate (IRC) application
In Vietnam, the issuance of an Investment Registration Certificate (IRC) is required for all foreign investors who intend to establish a new investment project or expand an existing one.
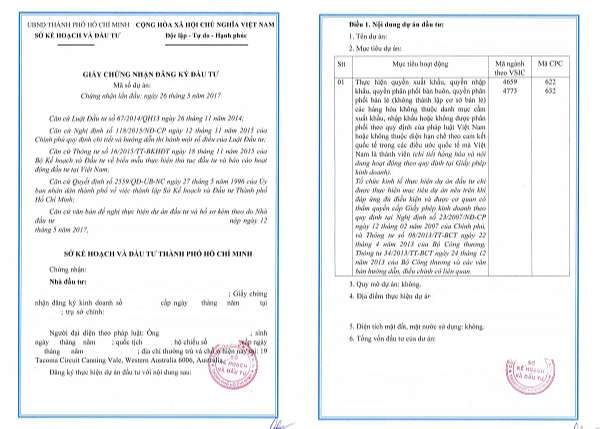
The IRC confirms the legal status of the investment project and provides the investor with permission to conduct business in the country.
The following information provides an overview of the authority to issue the IRC, as well as the documents required to apply for it.
Authority to Issue the Investment Registration Certificate:
The Management Boards of Industrial Parks, Export-Processing Zones, Hi-Tech Zones, and Economic Zones are responsible for receiving, issuing, adjusting, and revoking the IRC of investment projects located within their respective areas.
The Services of Planning and Investment shall receive, issue, adjust, and revoke the IRC of investment projects outside these zones, with the exception of cases where the investment project spans multiple provinces or is executed both inside and outside the designated zones.
In such cases, the Service of Planning and Investment of the province where the investor intends to establish the head office or operating office shall receive, issue, adjust, and revoke the IRC.
Documents Required to Apply for the Investment Registration Certificate:
To apply for an IRC, investors must prepare a dossier that includes the following documents:
- A written request for permission to execute the investment project;
- Copy of ID card or passport (if the investor is an individual) or copy of Certificate of Establishment or equivalent paper certifying the legal status of the investor (if the investor is an organization);
- Investment proposal that specifies investor(s) in the project, investment objectives, investment scale, investment capital, method of capital raising, location and duration of investment, labor demand, requests for investment incentives, and assessment of socio-economic effects of the project;
- Copies of any of the following documents: financial statements of the last two years of the investor, the commitment of the parent company to provide financial support, the commitment of financial institutions to provide financial support, guarantee for the investor’s financial capacity or description of the investor’s financial capacity;
- Office lease agreement and documents proving the lessor’s right;
- Demand for land use;
- A explanation for the application of technologies to the project mentioned in the List of technologies restricted from transfer under the law on technology transfer;
- Business cooperation contract (if the project is executed under a business cooperation contract).
How to Register the Investment Registration Certificate:
Investors must first register by declaring online information about their investment projects on the National Foreign Investment Information System.
Within 15 days from the date of online filing, the investor must submit the application file for the IRC to the Investment Registration Authority.
Once the application is received, the investor will be provided with an online account to access the National Foreign Investment Information System to track the processing and results of the application.
In the event of a successful IRC registration, the investment registration agency will issue a code through this account to the investment project.
If the application is rejected, the agency must notify the investor in writing and provide an explanation for the rejection.
Step 2) Enterprise Registration Certificate (ERC) application

To register a company in Vietnam, the requirements and procedures are the same for both Vietnamese and foreign-owned companies.
The company registration dossier must include the following documents:
- An application form for business registration
- The company’s charter
- A list of members (for limited companies) or stakeholders (for joint-stock companies)
- Certified copies of identification papers of the members, including ID cards or other ID papers of individuals and a decision on Establishment, Business Registration Certificate, or an equivalent document of the organization and the letter of authorization for the authorized representatives of the member organizations. If a member is a foreign organization, a copy of the Certificate of Business registration or an equivalent document must be consular legalized.
- The Investment Registration Certificate of the foreign investors as prescribed by the Law on Investment
- Legal service provision contract (Authorization contract) to authorize a law firm to perform the business establishment service
The application dossier must be submitted to the Business Registration Authority through the National Business Registration Portal within 03 – 05 days.
After the agency receives the application dossier, they will issue a business registration certificate, and you must make a public announcement on the National Business Registration Portal within 30 days from the date of publication.
It is important to note that the business registration certificate is just one step in the process of setting up a company in Vietnam.
The investor must also obtain other necessary licenses and permits depending on the nature of the business.
For example, a trading company must obtain a trading license, while a manufacturing company must obtain a manufacturing license.
Additionally, it is recommended to work with a reputable law firm or business consulting service to navigate the complex legal and bureaucratic process of setting up a company in Vietnam.
They can help ensure that all necessary documentation is prepared correctly and submitted on time, as well as provide guidance on the various licenses and permits required for the business to operate legally in Vietnam.
Step 3) Tax registration and payment of the business license tax
The business license certificate number serves as the unique identification number for a company in Vietnam and also doubles as its tax number. Therefore, it is crucial for companies to obtain this certificate before they can start conducting any business activities in the country.
Moreover, the Vietnamese government has made it mandatory for all companies to pay taxes through an online system. This online tax payment system is known as the National Public Service Portal, and it was introduced to make the process of tax payment and submission more convenient and efficient for businesses. To access this system, companies must first obtain an electronic signature, which serves as a digital authentication tool to verify the identity of the user and their authorization to perform specific actions in the system.
In addition to tax payment and submission, the National Public Service Portal also offers other useful services for businesses, such as online business registration, online application for investment certificates, and electronic submission of customs declarations, among others. Therefore, companies that plan to operate in Vietnam are advised to familiarize themselves with the National Public Service Portal and the various services it offers to streamline their business operations and comply with the country’s regulations.
Step 4) Capital contribution
Capital contribution is an essential step in establishing a company in many countries, including Vietnam. Once a Business Registration Certificate (BRC) is issued, the company’s founders must make their capital contribution within 90 days. In Vietnam, this requirement is mandated by the Law on Enterprises.
The capital contribution is the amount of money, property, or assets that the founders of a company invest in it. This capital is used to cover the initial expenses of the business, including purchasing equipment, renting space, and paying salaries. The amount of capital required varies depending on the type of company and the industry it operates in.
If the founders fail to make their capital contribution within the 90-day period, they may be subject to fines. In Vietnam, the penalty for late capital contribution is specified in the Law on Enterprises and varies depending on the amount of capital and the duration of the delay.
It is important to note that capital contributions can be made in different forms, including cash, property, and other assets. The founders must ensure that their capital contribution complies with the laws and regulations of Vietnam, as well as the requirements specified in the company’s charter.
Step 5) Required licenses or certificates and sub-licenses (if any) application
Some business sectors need to apply for additional licenses or sub-licenses. The application process can take around two weeks to several months.
The whole LLC registration process takes approximately two months. However, it may vary depending on the business sector.
It is important to note that the procedures and requirements for registering a company may vary depending on the legal structure and industry in which the company operates.
It is recommended to seek professional advice from a lawyer or accountant to ensure compliance with all legal requirements and procedures.
7. Compiling with the Post-Registration Requirements
After registering a company in Vietnam, there are several post-registration requirements that businesses must comply with. Here are some of the common post-registration requirements:
- Obtaining a seal: Companies are required to obtain a company seal for official use, such as signing contracts, opening bank accounts, and registering for taxes.
- Registering for social insurance and health insurance: Companies must register for social insurance and health insurance for their employees within 30 days of starting work.
- Registering with the Ministry of Labor, Invalids, and Social Affairs: Companies with 10 or more employees must register with the Ministry of Labor, Invalids, and Social Affairs within 30 days of starting work.
- Reporting changes: Companies must report any changes to their business registration, such as changes in ownership, legal representative, or address, to the Department of Planning and Investment within 10 days.
- Filing taxes: Companies must file taxes on a monthly, quarterly, and annual basis depending on their business activities and size.
- Conducting annual meetings: Companies are required to hold annual shareholder meetings and submit annual reports to the relevant authorities.
- Renewing licenses and permits: Licenses and permits obtained during the registration process must be renewed periodically to remain valid.
It is important to note that failure to comply with post-registration requirements can result in penalties or even the revocation of the company’s business registration certificate.
Therefore, it is recommended to seek professional advice from a qualified lawyer or accountant to ensure compliance with all post-registration requirements or get in touch with the 9cv9 corporate service team by booking a free consultation slot here, which can help you streamline your corporate needs in Vietnam.
Conclusion
Registering a company in Vietnam is a relatively straightforward process that requires careful planning and preparation.
Vietnam is a rapidly growing market with a young and dynamic workforce, making it an attractive destination for foreign investors and entrepreneurs looking to expand their businesses in the Southeast Asian region.
Choosing the right legal structure, understanding the necessary documents, deciding on a business name, and understanding the licensing requirements are some of the key steps involved in registering a company in Vietnam.
It is important to seek professional advice and assistance from a qualified lawyer or accountant to ensure compliance with all legal requirements and regulations.
Or get in touch with the 9cv9 corporate service team by booking a free consultation slot here, which can help you streamline your corporate needs in Vietnam.
Once the company is registered, there are several post-registration requirements that businesses must comply with, such as obtaining a seal, registering for social insurance and health insurance, filing taxes, conducting annual meetings, and renewing licenses and permits.
Overall, registering a company in Vietnam requires careful planning, attention to detail, and adherence to legal requirements and regulations.
With the right guidance and support, entrepreneurs and investors can successfully establish and operate a business in Vietnam and take advantage of the many opportunities available in this vibrant and growing market.
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your business and startup friends and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the 9cv9 Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.
People Also Ask
How much does it cost to register a company in Vietnam?
The cost of registering a company in Vietnam depends on various factors such as the type of company, the location, and the services of a lawyer or a service provider. Generally, the cost ranges from $500 to $1,000, including government fees and legal fees. However, the cost may increase if additional services are required, such as obtaining work permits, obtaining investment registration certificates, and others. It is recommended to consult with a local service provider such as the 9cv9 Corporate Service Team, or a lawyer to get an accurate estimate of the cost of registering a company in Vietnam.
Can foreigners register a company in Vietnam?
Yes, foreigners can register a company in Vietnam. In fact, Vietnam encourages foreign investment in the country, and there are no restrictions on foreign ownership in most industries. However, there are some industries that have foreign ownership restrictions or require special permits for foreign investment. Foreigners can register a company in Vietnam as either a limited liability company or a joint-stock company, depending on their preferences and the requirements of the specific industry.































![Writing A Good CV [6 Tips To Improve Your CV] 6 Tips To Improve Your CV](https://blog.9cv9.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/2020-06-02-2-100x70.png)


