Key Takeaways
- The top 10 DevOps software in the world in 2026 prioritize unified platforms, AI-driven automation, and integrated DevSecOps for faster, more reliable software delivery.
- Enterprise DevOps tools focus on governance, scalability, and compliance, while startups benefit from serverless CI/CD, high concurrency, and cost-efficient pricing models.
- Future-ready DevOps platforms combine agentic AI, FinOps cost control, and GreenOps sustainability metrics to deliver resilient, scalable, and economically optimized systems.
The global software economy in 2026 is defined by velocity, resilience, and intelligent automation. Organizations no longer compete solely on product features; they compete on how quickly, securely, and reliably they can deliver software. At the center of this transformation lies DevOps software. What began as a cultural movement bridging development and operations has evolved into a multi-billion-dollar strategic technology category that underpins digital transformation across every major industry.

The top 10 DevOps software platforms in the world in 2026 represent more than popular tools. They function as integrated delivery ecosystems that unify source control, continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD), security scanning, artifact management, infrastructure automation, cost governance, and AI-driven observability. These platforms enable enterprises and startups alike to deploy multiple times per day, maintain near-zero downtime, enforce compliance standards, and optimize cloud spending in real time.
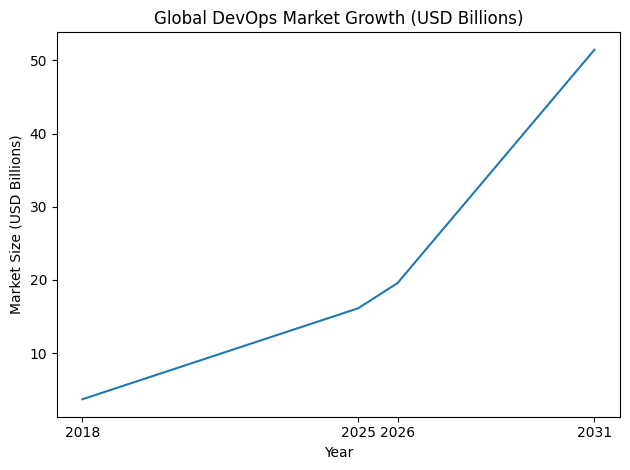
In today’s market, DevOps is no longer optional. It is a foundational operating model for modern organizations. Global public cloud spending continues to surge, hybrid and multi-cloud architectures are the norm, and artificial intelligence workloads demand elastic scalability. This complexity has forced a consolidation of fragmented toolchains into unified DevOps platforms that prioritize developer experience, governance, and automation intelligence.
The Evolution of DevOps Software in 2026
By 2026, DevOps software has matured into a fully integrated lifecycle management layer. The early 2020s were marked by tool sprawl, where teams stitched together multiple vendors for version control, build automation, deployment orchestration, and security testing. While functional, this approach introduced operational friction, integration overhead, and governance blind spots.
Today’s leading DevOps platforms focus on consolidation and platform engineering. Internal developer platforms, golden deployment paths, and policy-as-code frameworks are standard features. Rather than relying on manual configuration, organizations implement repeatable, standardized workflows that accelerate onboarding and reduce operational toil.
Artificial intelligence has further reshaped the competitive landscape. In 2026, DevOps software integrates agentic AI capabilities capable of detecting deployment anomalies, predicting infrastructure exhaustion, triggering automated rollbacks, and optimizing cloud resource allocation. This shift from rule-based automation to autonomous remediation represents one of the most significant technological advances in the industry.
Why the Top 10 DevOps Software Platforms Matter
Choosing among the top DevOps software tools in 2026 is no longer a matter of comparing feature checklists. It is a strategic decision that influences engineering productivity, regulatory compliance, cost control, and long-term scalability. The right DevOps platform can:
Increase deployment frequency by enabling continuous delivery pipelines
Reduce mean time to recovery through predictive monitoring
Automate security and compliance enforcement
Lower infrastructure costs through intelligent resource optimization
Support hybrid and multi-cloud orchestration
Enhance developer experience with integrated workflows
For large enterprises, governance and scalability are paramount. Financial institutions, healthcare organizations, and global corporations require robust audit trails, role-based access controls, and policy enforcement across thousands of projects. For startups and SMEs, speed, simplicity, and cost transparency take precedence. Serverless CI/CD, high-concurrency builds, and consumption-based pricing models empower lean teams to innovate rapidly without heavy infrastructure overhead.
The Rise of AI-Driven and Autonomous DevOps
One of the defining characteristics of DevOps software in 2026 is the transition from AI-assisted systems to AI-autonomous operations. Earlier generations of DevOps tools provided dashboards and alerts. Modern platforms now proactively fix security vulnerabilities, rebalance cloud workloads, and optimize pipelines in real time.
This agentic AI layer significantly reduces manual intervention. Engineers shift from troubleshooting infrastructure to designing governance policies and architectural standards. As autonomy increases, DevOps becomes less about maintaining pipelines and more about orchestrating intelligent delivery ecosystems.
Market Forces Shaping DevOps in 2026
Several macro trends are influencing the top DevOps software platforms in 2026:
The expansion of Kubernetes and cloud-native architectures
The growth of serverless DevOps and NoOps models
The integration of FinOps for cost governance
The emergence of GreenOps and carbon-aware compute
The standardization of DORA metrics as performance benchmarks
The rapid adoption of internal developer platforms
These trends highlight that DevOps software is no longer isolated within engineering teams. It intersects directly with financial governance, sustainability reporting, and executive-level strategic planning.
Defining Excellence in DevOps Software
Elite DevOps organizations in 2026 deploy multiple times per day while maintaining recovery times under one hour. They integrate security into every stage of development and monitor costs continuously. Their platforms support scalability without sacrificing compliance or performance.
The top 10 DevOps software tools in the world in 2026 embody these characteristics. They deliver unified platform experiences, AI-driven automation, scalable CI/CD pipelines, and economic efficiency. They support both enterprise governance and startup agility, reflecting the diverse demands of a global software-driven economy.
What This Guide Will Cover
This comprehensive guide explores the leading DevOps platforms shaping the industry in 2026. It analyzes their features, pricing models, AI capabilities, scalability, governance frameworks, and suitability for different organizational sizes. Whether you are an enterprise architect evaluating multi-cloud compliance tools or a startup founder seeking a fast and cost-effective CI/CD solution, understanding the competitive landscape of DevOps software is essential.
In an era where software delivery velocity directly impacts market resilience and revenue growth, selecting the right DevOps platform is one of the most consequential technology decisions an organization can make. The platforms highlighted in this analysis represent the cutting edge of modern software delivery and define the standards that will shape the future of DevOps through the remainder of the decade.
Before we venture further into this article, we would like to share who we are and what we do.
About 9cv9
9cv9 is a business tech startup based in Singapore and Asia, with a strong presence all over the world.
With over nine years of startup and business experience, and being highly involved in connecting with thousands of companies and startups, the 9cv9 team has listed some important learning points in this overview of the Top 10 Best DevOps Software in 2026.
If you like to get your company listed in our top B2B software reviews, check out our world-class 9cv9 Media and PR service and pricing plans here.
Top 10 Best DevOps Software in 2026
- GitLab
- GitHub Enterprise
- Azure DevOps
- Atlassian Platform (Jira and Bitbucket)
- Harness
- AWS CodeCatalyst
- CircleCI
- Google Cloud DevOps (Cloud Build and Cloud Deploy)
- CloudBees (Enterprise Jenkins)
- Octopus Deploy
1. GitLab

In the rapidly evolving DevOps software landscape of 2026, GitLab stands as one of the most influential unified DevSecOps platforms globally. Recognized consistently in leading industry analyst evaluations, GitLab has strengthened its reputation as a comprehensive, single-application solution designed to streamline planning, development, security, and operations within one integrated ecosystem.
By 2026, the DevOps market has become increasingly defined by automation, artificial intelligence, cloud-native architectures, and security-first development practices. GitLab’s AI-native architecture and fully integrated workflows have positioned it at the forefront of enterprise DevSecOps transformation. Its long-standing emphasis on consolidating toolchains into one platform continues to resonate with organizations seeking efficiency, visibility, and governance across the software development lifecycle.
Strategic Context: The DevOps Software Landscape in 2026
The global DevOps software industry in 2026 is characterized by several dominant trends:
AI-Embedded Workflows
Organizations now expect intelligent automation across coding, testing, security, and deployment processes. AI assistants are no longer experimental; they are foundational.
Platform Consolidation
Enterprises are reducing tool sprawl. Unified platforms offering version control, CI/CD, security scanning, compliance, and monitoring in one environment are preferred over fragmented toolchains.
Shift-Left Security
Security is integrated early in the development cycle, reducing vulnerabilities before production deployment.
Cloud-Native and Platform Engineering Adoption
Kubernetes, microservices, and internal developer platforms have become standard practices in large-scale software operations.
Within this environment, GitLab’s architecture directly addresses these demands.
Unified DevSecOps Architecture and AI-Native Capabilities
GitLab differentiates itself through a single data store architecture that supports all DevSecOps phases. Unlike multi-tool ecosystems requiring complex integrations, GitLab’s unified system reduces latency, integration overhead, and cross-tool inconsistencies.
A defining feature in 2026 is GitLab Duo, the platform’s AI-powered suite that embeds intelligent assistance across the software lifecycle. Rather than functioning as an add-on, AI capabilities are integrated into planning boards, code reviews, vulnerability scanning, merge requests, and observability dashboards.
Core AI-Driven Capabilities in 2026
| Capability Area | AI-Enabled Functionality | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Planning and Issue Management | AI-assisted backlog refinement and sprint planning | Faster prioritization and reduced planning overhead |
| Code Development | Intelligent code suggestions and automated reviews | Improved developer productivity and code quality |
| Security and Compliance | Automated vulnerability detection and risk scoring | Reduced security exposure before production |
| CI/CD Pipelines | AI-optimized pipeline configuration | Shorter build times and fewer deployment failures |
| Monitoring and Observability | Anomaly detection and automated remediation suggestions | Improved reliability and faster incident resolution |
Security-at-the-Source Philosophy
GitLab’s Security-at-the-Source model embeds security scanning, dependency checks, and compliance validations directly into daily development workflows. In regulated industries such as finance, healthcare, and government, this approach reduces audit risk and improves traceability.
By integrating static and dynamic testing, container scanning, and supply chain risk assessment into merge requests, GitLab ensures that vulnerabilities are identified before reaching production environments.
Enterprise Use Case Leadership
Between 2025 and 2026, GitLab ranked highly across multiple enterprise use cases within analyst evaluations. Its strongest areas of performance included:
| Enterprise Use Case | GitLab Strengths in 2026 |
|---|---|
| Agile Software Delivery | End-to-end workflow automation and sprint transparency |
| Cloud-Native Application Delivery | Kubernetes-native integration and container security |
| Platform Engineering | Support for internal developer platforms and governance |
| Regulated Industry Delivery | Built-in compliance dashboards and audit-ready reporting |
This broad coverage across use cases reinforces GitLab’s positioning as a single-platform DevSecOps solution capable of supporting startups, mid-sized enterprises, and large global corporations alike.
Financial and Licensing Structure in 2026
GitLab’s tiered pricing model supports scalability from individual developers to multinational enterprises. Pricing remains structured around annual billing and feature access levels.
| Tier Name | Annual Pricing Structure | Included CI/CD Minutes | Key Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free | $0 | 400 per month | Source control, basic CI/CD, issue tracking |
| Premium | $29 per user per month (annual) | 10,000 per month | Advanced CI/CD, disaster recovery, code review workflows |
| Ultimate | Custom enterprise pricing | Enterprise-based | Compliance dashboards, vulnerability management, value stream analytics |
The Ultimate tier is particularly attractive to regulated industries due to its advanced governance controls and detailed audit reporting capabilities.
Competitive Positioning Matrix in the 2026 DevOps Market
The following matrix illustrates GitLab’s comparative strengths against general DevOps platform characteristics in 2026.
| Evaluation Criteria | GitLab Positioning in 2026 | Market Average Positioning |
|---|---|---|
| Unified Toolchain | Very High | Moderate |
| AI Integration Depth | High and Embedded | Partial or Add-On |
| Security Integration | Fully Integrated | Often Separate Tools |
| Compliance Reporting | Enterprise-Grade | Basic to Moderate |
| Integration Overhead | Minimal | High |
| Scalability Across Teams | Enterprise-Level | Variable |
Customer Experience and Market Feedback
Enterprise users in 2025–2026 consistently highlight GitLab’s completeness and stability as major strengths. Organizations transitioning from fragmented DevOps ecosystems frequently cite reduced operational complexity and improved governance visibility.
Customer observations frequently include:
Platform Stability
Users report reliable release governance and strong access control management.
Open-Source Supply Chain Management
Organizations managing complex dependency chains value GitLab’s proactive scanning and vulnerability detection.
AI Workflow Acceleration
Integrated AI capabilities contribute to faster feature releases and improved development efficiency.
Learning Curve Considerations
While comprehensive, some enterprises report that mastering advanced security modules requires structured onboarding and training.
Overall Industry Impact
As of 2026, GitLab represents a defining example of the consolidated DevSecOps platform model. Its unified data architecture, AI-powered workflows, and deeply embedded security capabilities align directly with the demands of modern software engineering environments.
In a market increasingly shaped by artificial intelligence, compliance requirements, and cloud-native transformation, GitLab’s strategic positioning reinforces its status among the top DevOps software platforms globally. Organizations seeking scalability, governance, automation, and security within a single application continue to view GitLab as a benchmark solution in the enterprise DevOps ecosystem.
2. GitHub Enterprise
By 2026, GitHub Enterprise continues to hold a dominant position in the global DevOps software market, widely recognized as the industry standard for developer ecosystems. Measured by total developer headcount and active repositories, GitHub remains the most adopted platform worldwide. Its influence extends beyond source control into CI/CD automation, AI-assisted coding, and large-scale collaborative software engineering.
GitHub’s sustained leadership is rooted in three core strengths: a best-in-class developer experience, a vast marketplace of automation templates, and a mature cloud-native CI/CD engine known as GitHub Actions. Together, these components form one of the most scalable and extensible developer platforms available in the DevOps software ecosystem in 2026.
The 2026 DevOps Environment and GitHub’s Strategic Position
The DevOps landscape in 2026 is defined by automation maturity, cost transparency, AI integration, and ecosystem extensibility. Organizations expect CI/CD systems that scale globally, integrate seamlessly with cloud platforms, and provide measurable cost efficiency.
GitHub Enterprise aligns with these priorities through:
Deep CI/CD Standardization
GitHub Actions has effectively become the de facto standard for CI/CD workflows across startups, mid-market firms, and enterprise organizations.
Marketplace-Driven Workflow Customization
A large and active marketplace enables rapid deployment of reusable CI/CD templates and integrations.
AI-Embedded Development Experience
Through Copilot Business and Copilot Enterprise, GitHub integrates AI-driven code generation and repository-aware conversational assistance directly into workflows.
Cloud-Native Scalability
Hosted runners and cloud-based automation reduce infrastructure complexity while maintaining performance reliability.
GitHub Actions: The CI/CD Standard in 2026
GitHub Actions has solidified its reputation as a default automation engine for modern development teams. By 2026, it supports billions of automation minutes monthly, particularly benefiting open-source communities through free public repository allocations.
The marketplace of pre-built Actions templates allows teams to deploy testing pipelines, security scans, container builds, and multi-cloud deployments with minimal configuration overhead.
GitHub Actions Ecosystem Overview
| Feature Category | Capability Description | Operational Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Workflow Templates | Pre-configured CI/CD templates from marketplace contributors | Accelerated pipeline deployment |
| Hosted Runners | Managed execution environments | Reduced infrastructure management burden |
| Self-Hosted Runners | On-premises or custom cloud execution | Greater security and regulatory control |
| Matrix Builds | Parallel testing across environments | Faster validation cycles |
| Native Repository Integration | Direct merge request automation | Seamless DevOps workflow alignment |
Pricing and Cost Model Adjustments in 2026
In January 2026, GitHub introduced a significant pricing update designed to better align usage-based billing with infrastructure consumption. Hosted runner pricing was reduced by up to 39 percent, while a new $0.002 per-minute cloud platform charge was introduced. This model reflects a broader industry shift toward granular cost accountability in DevOps operations.
Despite these adjustments, GitHub continues to provide more than 11.5 billion free GitHub Actions minutes for public repositories, reinforcing its support for open-source innovation.
GitHub Enterprise Performance and Pricing Structure (2026)
| GitHub Component | Price (2026) | CI/CD Minutes Included | Storage Included | Key Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GitHub Team | $4 per user per month | 3,000 per month | 2 GB | Core collaboration, basic CI/CD, code review |
| GitHub Enterprise | $21 per user per month | 50,000 per month | 50 GB | Advanced security, governance controls, enterprise support |
| Copilot Business | $19 per user per month | N/A | N/A | AI code completion, contextual suggestions |
| Copilot Enterprise | $39 per user per month | N/A | N/A | Repository-aware AI chat, cross-project contextual insight |
AI Integration: Copilot’s Expanding Role
Artificial intelligence has become central to GitHub’s enterprise offering. Copilot Business provides intelligent code completion and security-aware recommendations within development environments. Copilot Enterprise expands on this by enabling context-aware AI chat across all repositories, allowing developers to query large codebases conversationally.
AI Capabilities Comparison
| AI Feature | Copilot Business | Copilot Enterprise | Market Standard in 2026 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inline Code Suggestions | Yes | Yes | Common |
| Security-Aware Recommendations | Standard | Advanced | Partial |
| Repository-Wide Context | Limited | Full | Rare |
| Conversational Codebase Chat | No | Yes | Emerging |
Governance and Enterprise Controls
While GitHub’s developer experience remains a leading advantage, governance and compliance features are largely concentrated within higher-tier plans. Enterprise-level customers benefit from advanced audit logs, policy enforcement, and access management tools.
Governance Feature Distribution
| Governance Capability | Team Plan | Enterprise Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Role-Based Access Control | Basic | Advanced |
| Audit Logs | Limited | Full |
| SAML/SSO Integration | No | Yes |
| Compliance Reporting | Limited | Enterprise-Grade |
Customer Experience and Industry Feedback
Enterprise users consistently cite GitHub’s ecosystem strength and community-driven innovation as major advantages. The smooth onboarding experience and integration of GitHub Actions significantly reduce time-to-deployment compared to fragmented toolchains.
Commonly Reported Strengths
Platform Reliability
GitHub maintains high availability and performance consistency across global teams.
Community and Marketplace Depth
A mature ecosystem of contributors accelerates workflow customization.
Developer-Centric Design
The interface and collaboration features are optimized for productivity.
Commonly Reported Challenges
Governance Cost Distribution
Advanced compliance and policy controls are limited to higher pricing tiers, impacting cost planning for large organizations.
Support Response Times
While generally effective, complex workflow issues may occasionally experience slower support turnaround times.
Competitive Positioning Matrix in 2026 DevOps Market
| Evaluation Criteria | GitHub Enterprise Position | Market Average Position |
|---|---|---|
| Developer Adoption Scale | Very High | Moderate |
| CI/CD Ecosystem Maturity | High | Moderate |
| Marketplace Integration | Extensive | Limited |
| AI Integration Depth | Advanced | Emerging |
| Governance Flexibility | Tier-Dependent | Variable |
| Cost Transparency | Improved in 2026 | Inconsistent |
Strategic Role Among the Top DevOps Software Platforms in 2026
Within the global ranking of top DevOps software platforms in 2026, GitHub Enterprise occupies a unique position as the most widely adopted developer-centric ecosystem. Its strength lies not only in technology but also in community scale, marketplace extensibility, and continuous innovation in AI-assisted development.
Organizations prioritizing developer productivity, scalable CI/CD automation, and open-source collaboration consistently regard GitHub Enterprise as a foundational component of their DevOps strategy. While governance and enterprise cost management considerations remain relevant factors, the platform’s ecosystem maturity and reliability continue to reinforce its standing as a global industry benchmark in modern software delivery.
3. Azure DevOps

In 2026, Azure DevOps continues to serve as a foundational DevOps platform for organizations deeply embedded in the Microsoft technology ecosystem. As enterprises increasingly standardize on Microsoft cloud services, Azure DevOps remains strategically positioned as a tightly integrated solution that connects planning, development, testing, and deployment within a unified environment.
Unlike fragmented DevOps toolchains that rely on multiple third-party integrations, Azure DevOps provides a structured, end-to-end lifecycle management system. Its integration across Azure Boards, Azure Repos, Azure Pipelines, and Azure Test Plans enables a centralized operational framework often described as a single source of truth for engineering teams.
Strategic Context: Azure DevOps in a Cloud-First Microsoft Strategy
The DevOps software market in 2026 is heavily influenced by cloud adoption and enterprise platform consolidation. Microsoft’s broader cloud-first strategy significantly shapes Azure DevOps pricing, licensing, and feature evolution.
Key strategic drivers influencing Azure DevOps in 2026 include:
Deep Integration with Microsoft Cloud
Azure DevOps aligns closely with Microsoft Azure infrastructure, Microsoft 365 services, and enterprise identity management systems.
Enterprise Traceability Requirements
Organizations increasingly require full traceability from backlog item to production deployment.
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Support
While optimized for Azure, Azure DevOps supports deployments across AWS, Google Cloud, and on-premises infrastructure.
Licensing Modernization
The New Commerce Experience model introduces incremental pricing adjustments and subscription-based flexibility.
Unified Platform Architecture and Core Components
Azure DevOps is structured around five primary service pillars:
Azure Boards
Agile project management, backlog tracking, sprint planning, and work item traceability.
Azure Repos
Git-based version control with enterprise-grade access management.
Azure Pipelines
CI/CD automation supporting both cloud-hosted and self-hosted agents.
Azure Test Plans
Manual and automated testing workflows integrated into development pipelines.
Azure Artifacts
Package management and artifact storage for controlled software distribution.
Azure DevOps Core Services Overview
| Service Component | Primary Function | Enterprise Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Azure Boards | Agile planning and backlog management | End-to-end work item traceability |
| Azure Repos | Version control and branch management | Secure, centralized code management |
| Azure Pipelines | CI/CD automation | Streamlined multi-environment deployments |
| Azure Test Plans | Test case management and reporting | Integrated quality assurance visibility |
| Azure Artifacts | Package and dependency management | Controlled artifact distribution and governance |
Pricing Structure and Licensing Updates in 2026
Azure DevOps pricing in 2026 reflects Microsoft’s ongoing transition toward subscription-based, cloud-aligned licensing models. The first five users remain free under the Basic plan, supporting small teams and pilot projects. Additional users incur a $6 per user per month fee.
For organizations requiring comprehensive test management capabilities, the Basic + Test Plans license is priced at $52 per user per month.
In early 2026, Microsoft implemented a 5 percent pricing increase for subscriptions under the New Commerce Experience framework, impacting certain enterprise agreements.
Azure DevOps Service Costs in 2026
| Service | Price (2026) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Plan | $6 per user per month | First 5 users free; core Boards, Repos, Pipelines |
| Basic + Test Plans | $52 per user per month | Advanced test case management and reporting |
| Microsoft-Hosted Job | $40 per month | 1 parallel job, unlimited minutes |
| Self-Hosted Job | $15 per month | 1 parallel job, unlimited minutes |
| Artifact Storage | $2 per GiB | First 2 GiB free; scalable storage expansion |
Parallel Job Cost Comparison Matrix
| Job Type | Monthly Cost | Infrastructure Control | Scalability | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft-Hosted Job | $40 | Managed by Microsoft | High | Cloud-native CI/CD environments |
| Self-Hosted Job | $15 | Customer-managed | Variable | On-premises or regulated systems |
Enterprise Strengths in 2026
Traceability and Governance
One of Azure DevOps’ strongest differentiators remains its end-to-end traceability. Work items in Azure Boards can be directly linked to commits in Azure Repos, builds in Azure Pipelines, and results in Azure Test Plans. This integrated data chain supports auditability and regulatory compliance in sectors such as finance, healthcare, and government.
Microsoft Identity and Security Alignment
Integration with Azure Active Directory enables centralized identity management and enterprise-grade access controls. This alignment reduces security configuration complexity compared to multi-vendor toolchains.
Integrated Testing Visibility
Automation testers benefit from real-time test execution reporting directly connected to builds and backlog items. This reduces manual reporting overhead and improves release quality transparency.
Operational Experience and User Feedback
Organizations frequently report that consolidating planning, version control, CI/CD, and testing into Azure DevOps significantly improves workflow coherence. Teams managing large development programs highlight the advantage of centralized version control and automated traceability.
Commonly Cited Benefits
Unified Workflow Visibility
The seamless connection between Boards, Repos, and Pipelines enhances cross-team coordination.
Real-Time Test Integration
Build triggers automatically update test suites and reporting dashboards.
Enterprise Stability
The platform provides reliable performance within Microsoft-centric environments.
Commonly Noted Challenges
Interface Complexity
The extensive feature set can result in a dense user interface, particularly for new users.
Performance Lag in Large Backlogs
Large-scale project boards may occasionally experience slower load times.
Comparative Positioning in the 2026 DevOps Market
| Evaluation Criteria | Azure DevOps Position | Market Average Position |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Ecosystem Integration | Very High | Limited |
| End-to-End Traceability | High | Moderate |
| Cloud-Native Optimization | Strong (Azure-Focused) | Variable |
| Governance and Compliance | Enterprise-Grade | Inconsistent |
| Developer Experience Simplicity | Moderate | Moderate |
| Cross-Platform Flexibility | Moderate | High |
Strategic Role Among the Top DevOps Software Platforms in 2026
Within the broader ranking of top DevOps software platforms in 2026, Azure DevOps maintains a distinctive role as the preferred solution for enterprises standardized on Microsoft technologies. Its value proposition lies not in marketplace extensibility or community scale alone, but in structured integration and enterprise governance alignment.
Organizations prioritizing centralized control, audit traceability, and seamless Microsoft Azure integration consistently regard Azure DevOps as a strategic cornerstone of their DevOps architecture. While complexity and incremental licensing adjustments remain considerations, the platform’s unified planning, development, and testing capabilities continue to solidify its reputation as a powerhouse within the enterprise DevOps software ecosystem.
4. Atlassian Platform (Jira and Bitbucket)
In 2026, the Atlassian platform has firmly established itself as a leading Agile AI-native DevOps ecosystem. Originally known for its modular collaboration and issue-tracking tools, Atlassian has strategically unified Jira Software, Bitbucket, Confluence, and related services into a cohesive DevOps platform capable of supporting end-to-end software delivery.
Recognized by major industry analysts as a market leader in 2025, Atlassian’s 2026 positioning is defined by the integration of artificial intelligence across planning, development, and collaboration workflows. At the center of this transformation is Rovo, an agentic AI assistant embedded across Atlassian’s cloud ecosystem.
Strategic Context: Agile-Centric DevOps in 2026
The DevOps software landscape in 2026 increasingly favors platforms that tightly connect Agile planning, CI/CD automation, and AI-assisted development. Organizations demand:
Alignment Between Planning and Code
Backlog items, user stories, and epics must map directly to source control activity and deployment pipelines.
AI-Driven Workflow Acceleration
Automation should assist not only coding but also story refinement, documentation, and team alignment.
Cloud-First Modular Scalability
Teams require flexible pricing models that scale with consumption of compute minutes and AI credits.
Atlassian’s ecosystem is uniquely positioned in this environment due to its deep penetration in Agile project management through Jira and its growing DevOps capabilities through Bitbucket and Rovo.
Platform Architecture and Integrated Workflow
The Atlassian DevOps platform in 2026 connects the following core components:
Jira Software
Agile planning, backlog management, sprint tracking, and epic structuring.
Bitbucket
Git-based source control and CI/CD pipelines.
Rovo Dev
AI-powered assistant operating across Jira, Bitbucket, and Confluence.
Confluence
Documentation and knowledge management integration.
Atlassian DevOps Core Service Matrix
| Platform Component | Primary Function | DevOps Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Jira Software | Agile backlog and sprint management | Strong planning-to-development alignment |
| Bitbucket | Version control and CI/CD pipelines | Integrated source-to-build workflow |
| Rovo Dev | AI code review and story enhancement | Automated task refinement and productivity |
| Confluence | Documentation and collaboration | Context-aware project visibility |
Rovo: Agentic AI Embedded in Agile Workflows
Rovo represents Atlassian’s major innovation in 2026. Unlike standalone AI code assistants, Rovo operates across the Atlassian ecosystem, drawing contextual insights from Jira tasks, sprint goals, and repository data.
Rovo Dev credits are priced at $20 per user per month for 2,000 credits. These credits enable AI-driven code reviews, automated recommendations, task breakdown generation, and content enhancement.
Rovo AI Capabilities Overview
| AI Capability | Description | Business Value |
|---|---|---|
| Improve Description | Enhances Jira work item clarity | Faster backlog refinement |
| Automatic Child Work Item Creation | Generates subtasks from Epics | Improved team alignment |
| AI Code Review | Context-aware recommendations in Bitbucket | Higher code quality |
| Task-Based Code Suggestions | Links Jira descriptions to implementation hints | Reduced development friction |
| Documentation Assistance | Summarization and drafting support | Accelerated knowledge management |
While adoption has grown rapidly, user feedback suggests that Rovo’s contextual awareness across large documentation directories can be inconsistent. Nevertheless, its automation potential for repetitive tasks remains highly promising.
Bitbucket Pricing and AI-Encouraged Adoption Model
Bitbucket’s 2026 pricing structure reflects a deliberate strategy to encourage AI integration and pipeline usage. The Premium tier includes expanded build minutes and enhanced security controls tailored for enterprise-grade deployments.
Atlassian DevOps Pricing and Consumption (2026)
| Product or Tier | Price (2026) | Compute or AI Allowance |
|---|---|---|
| Bitbucket Standard | $3.65 per user per month | 2,500 build minutes per month |
| Bitbucket Premium | $7.25 per user per month | 3,500 build minutes per month |
| Rovo Dev | $20 per user per month | 2,000 AI credits per user per month |
| Extra Build Minutes | $10 per 1,000 minutes | Applicable to Standard and Premium |
Security Feature Comparison: Bitbucket Standard vs Premium
| Feature Category | Standard Plan | Premium Plan |
|---|---|---|
| CI/CD Build Minutes | 2,500 | 3,500 |
| IP Allowlisting | No | Yes |
| Deployment Permissions | Basic | Advanced |
| Branch Permissions | Yes | Yes |
| Advanced Security Controls | Limited | Expanded |
Enterprise Strengths in 2026
Agile-First DevOps Integration
Atlassian’s major competitive advantage lies in its deep Agile roots. Jira remains one of the most widely adopted Agile project management platforms globally, giving Atlassian a natural planning-first DevOps alignment.
AI-Augmented Planning
Rovo’s ability to transform rough backlog entries into polished user stories significantly improves team efficiency. Automated epic decomposition enhances sprint readiness and cross-functional clarity.
Modular Scalability
Organizations can adopt Bitbucket independently or as part of a broader Atlassian ecosystem. This modular flexibility appeals to companies seeking incremental DevOps transformation rather than wholesale migration.
User Experience and Market Feedback
Teams leveraging Atlassian in 2026 frequently highlight the value of AI-assisted backlog management and automatic subtask generation. The ability to refine descriptions and align epics with implementation tasks reduces manual effort and improves communication clarity.
Commonly Cited Strengths
Enhanced Team Alignment
Automatic generation of child work items ensures consistent sprint breakdowns.
Agile-Centric Development Flow
Direct mapping between Jira issues and Bitbucket commits enhances traceability.
Accessible Pricing for Smaller Teams
Competitive entry-level pricing supports startup and mid-market adoption.
Commonly Observed Limitations
Inconsistent Cross-Document AI Awareness
Rovo may occasionally miss contextual data within large Confluence directories.
Credit-Based AI Consumption
Organizations must actively manage Rovo credit usage to optimize value.
Comparative Positioning in the 2026 DevOps Market
| Evaluation Criteria | Atlassian Platform Position | Market Average Position |
|---|---|---|
| Agile Planning Integration | Very High | Moderate |
| AI in Backlog Management | Advanced | Emerging |
| CI/CD Maturity | Strong | Moderate |
| Marketplace and Integrations | Extensive | Variable |
| Security Controls | Tier-Based | Inconsistent |
| AI Consumption Transparency | Structured Credit Model | Mixed Approaches |
Strategic Role Among the Top DevOps Software Platforms in 2026
Within the ranking of top DevOps software platforms in 2026, the Atlassian platform distinguishes itself as the Agile AI-native leader. Its integration of planning, code management, and AI assistance delivers a workflow-centric DevOps model rather than a purely infrastructure-focused one.
Organizations prioritizing Agile alignment, team collaboration, and AI-enhanced backlog refinement increasingly view Atlassian as a strategic DevOps foundation. While AI maturity continues to evolve and credit consumption models require monitoring, the platform’s cohesive ecosystem and strong Agile heritage solidify its position as one of the most influential DevOps solutions globally in 2026.
5. Harness
By 2026, Harness has emerged as one of the most innovative DevOps software platforms, redefining how organizations approach modern software delivery. Unlike traditional CI/CD vendors that focus primarily on pipeline automation, Harness positions itself as a comprehensive modern software delivery platform powered by artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Harness is widely recognized for embedding AI directly into deployment workflows, enabling automated verification, anomaly detection, and intelligent rollback mechanisms. Its emphasis on reliability engineering and data-driven performance measurement has placed it among the top DevOps software platforms globally.
Strategic Context: Modern Software Delivery in 2026
The DevOps ecosystem in 2026 is increasingly focused on measurable outcomes rather than pipeline execution alone. Organizations prioritize:
Deployment Reliability
Reducing failed releases and minimizing production incidents.
Performance Benchmarking
Tracking DORA metrics such as deployment frequency, lead time for changes, mean time to recovery, and change failure rate.
Automated Risk Mitigation
Using machine learning to identify anomalies before they impact users.
Modular Scalability
Adopting DevOps capabilities incrementally across CI/CD, feature flags, cloud cost management, and security testing.
Harness aligns with these priorities by combining automation, observability, and analytics into an integrated software delivery lifecycle.
AI-Driven Deployment Verification
Harness differentiates itself through its machine learning-based deployment verification engine. During deployments, the platform continuously analyzes application performance data, log metrics, and infrastructure signals. If anomalies are detected beyond defined thresholds, the system can automatically trigger rollbacks without manual intervention.
AI Deployment Verification Capabilities
| Capability Area | Functionality Description | Operational Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Verification | Monitors performance metrics during deployment | Early anomaly detection |
| Automated Rollbacks | Reverts deployments upon threshold breach | Reduced change failure rate |
| Risk-Based Deployment Decisions | Uses ML models to evaluate release health | Improved production stability |
| Canary Deployment Automation | Validates limited rollouts before full release | Lower release risk |
| Integrated Observability | Correlates logs, metrics, and traces | Holistic performance assessment |
This AI-first deployment strategy has positioned Harness as a reliability-focused DevOps platform rather than a traditional build-and-deploy tool.
Harness Software Engineering Insights (SEI)
Harness Software Engineering Insights (SEI) has become a widely adopted solution for tracking DORA metrics in 2026. By integrating data from version control systems, CI/CD pipelines, and issue trackers, SEI provides executive-level visibility into engineering productivity and operational maturity.
DORA Metrics Tracking via Harness SEI
| DORA Metric | Measurement Capability in SEI | Strategic Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment Frequency | Tracks production releases over time | Identifies release velocity trends |
| Lead Time for Changes | Measures commit-to-deployment duration | Evaluates engineering efficiency |
| Change Failure Rate | Monitors failed or rolled-back deployments | Assesses release stability |
| Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR) | Calculates time to restore service | Measures operational resilience |
By benchmarking these metrics against industry standards, organizations can quantify DevOps maturity and identify performance gaps.
Modular Platform Architecture
Harness operates on a modular pricing model, allowing enterprises to adopt specific capabilities such as CI/CD, feature management, cloud cost optimization, chaos engineering, and security testing independently.
Core Harness Modules in 2026
| Module Category | Primary Function | Target Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Integration | Build and test automation | Development teams |
| Continuous Delivery | Deployment automation and verification | Release engineering |
| Feature Flags | Progressive feature rollout | Product teams |
| Cloud Cost Management | Infrastructure cost visibility | FinOps teams |
| Security Testing Orchestration | Integrated vulnerability scanning | Security teams |
| Software Engineering Insights (SEI) | DORA metric tracking and benchmarking | Engineering leadership |
This modular design supports scalable adoption but introduces complexity in cost forecasting due to usage-based pricing.
Harness Performance and ROI Metrics
Harness reports measurable operational performance indicators that influence enterprise adoption decisions.
Harness Modular Pricing and ROI Metrics
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Time to Implement | 3 months |
| Return on Investment | 10 months |
| Average Discount | 11 percent |
| Capability Rating | 4.6 out of 5 stars |
The relatively short implementation window combined with rapid ROI realization makes Harness attractive to medium and large organizations seeking quantifiable DevOps improvements.
Enterprise Strengths in 2026
AI-Centric Reliability Engineering
Harness’ automated rollback capabilities significantly reduce production risk.
Data-Driven Engineering Management
SEI provides objective performance metrics aligned with industry benchmarks.
Deployment Intelligence
Machine learning models continuously refine deployment evaluation criteria.
Scalable Modular Adoption
Organizations can introduce capabilities incrementally without full platform replacement.
Commonly Reported Challenges
Pricing Complexity
Each module is priced independently and often tied to usage, which can make long-term cost forecasting challenging.
Cost Scalability Concerns
As organizations expand pipeline usage and feature rollouts, costs may increase unpredictably without careful monitoring.
User Experience and Industry Feedback
Enterprise users consistently highlight the value of AI-driven deployment verification as a core differentiator. Automated anomaly detection and rollback features reduce release failures at scale, particularly for high-availability systems.
Commonly Reported Benefits
Improved Deployment Reliability
Automated rollbacks enhance production stability.
Actionable Performance Insights
SEI dashboards enable benchmarking against DORA standards.
Scalable CI/CD Operations
Supports medium to large enterprise deployment environments.
Commonly Noted Limitations
Modular Cost Transparency
Understanding cumulative costs across modules requires careful financial planning.
Comparative Positioning in the 2026 DevOps Software Market
| Evaluation Criteria | Harness Position in 2026 | Market Average Position |
|---|---|---|
| AI Deployment Verification | Advanced | Limited |
| DORA Metrics Benchmarking | Comprehensive | Partial |
| Automated Rollback Capability | Native and Integrated | Rare |
| Modular Pricing Flexibility | High | Moderate |
| Cost Predictability | Variable | Moderate |
| Enterprise Deployment Reliability | Very High | Moderate |
Strategic Role Among the Top DevOps Software Platforms in 2026
Within the competitive ranking of top DevOps software platforms in 2026, Harness distinguishes itself as the pioneer of AI-driven software delivery reliability. Its emphasis on machine learning-based deployment validation, automated rollback mechanisms, and data-backed engineering insights aligns with the evolving priorities of enterprise DevOps teams.
Organizations seeking to minimize change failure rates, benchmark engineering performance, and scale delivery reliability increasingly view Harness as a strategic platform for modern software delivery. While pricing complexity remains a consideration, the measurable improvements in deployment stability and engineering visibility reinforce Harness’ position as a leading innovator in the global DevOps ecosystem.
6. AWS CodeCatalyst

In 2026, AWS CodeCatalyst has established itself as a purpose-built DevOps platform tailored specifically for organizations operating within the Amazon Web Services ecosystem. Rather than competing as a general-purpose DevOps solution, CodeCatalyst is positioned as an AWS-native, opinionated platform that integrates source control, CI/CD pipelines, and project management within a single, cloud-aligned environment.
As enterprises continue migrating workloads to AWS, the demand for tightly integrated development experiences has increased. CodeCatalyst addresses this need by simplifying infrastructure configuration, automating pipeline creation, and embedding project management capabilities directly into the AWS cloud development lifecycle.
Strategic Context: Cloud-Native DevOps in the AWS Era
The DevOps software landscape in 2026 emphasizes consolidation, automation, and environment standardization. Organizations increasingly seek platforms that:
Reduce Toolchain Fragmentation
Minimize reliance on third-party integrations and custom connectors.
Accelerate Environment Provisioning
Enable rapid setup of development environments without manual configuration.
Align Directly with Cloud Infrastructure
Provide built-in integration with cloud services, identity management, and resource provisioning.
Offer Predictable Resource Allocation
Structure pricing around compute minutes and development environment hours.
AWS CodeCatalyst aligns directly with these trends by offering a unified development experience optimized for AWS services.
Unified Platform Architecture
AWS CodeCatalyst integrates multiple DevOps components into a single interface, reducing the need for external configuration.
Core Capabilities of AWS CodeCatalyst
| Platform Component | Primary Function | AWS-Native Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Source Repositories | Managed code hosting | Direct IAM integration and AWS security alignment |
| CI/CD Workflows | Pipeline automation and build execution | Native connection to AWS deployment services |
| Dev Environments | Cloud-based development workspaces | Pre-configured AWS resource access |
| Project Management | Task tracking and collaboration | Built-in planning without external tools |
| Identity and Access | AWS Identity and Access Management integration | Centralized security governance |
This unified model simplifies DevOps onboarding for teams already operating within AWS infrastructure.
Resource Allocation and Pricing Model in 2026
AWS CodeCatalyst follows a tiered pricing structure that allocates compute minutes and Dev Environment hours per user. The Enterprise tier, priced at $20 per user per month in 2026, includes 1,500 compute minutes and 160 development environment hours per user.
CodeCatalyst Resource Allocation and Costs (2026)
| Tier | Price Per User | Included Compute Minutes | Included Dev Environment Hours |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free | $0 | 2,000 minutes | 60 hours |
| Standard | $4 | 3,000 minutes | 200 hours |
| Enterprise | $20 | 1,500 minutes | 160 hours |
This resource-based model allows organizations to estimate usage more directly, particularly for teams that rely heavily on cloud-based development workspaces.
Compute and Dev Environment Comparison Matrix
| Evaluation Criteria | Free Tier | Standard Tier | Enterprise Tier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target Team Size | Small Teams | Growing Teams | Enterprise Units |
| Monthly Compute Allocation | Moderate | High | Focused |
| Dev Environment Hours | Limited | Extensive | Balanced |
| Advanced Governance | Basic | Moderate | Full Enterprise |
| AWS Integration Depth | Full | Full | Full |
Enterprise Strengths in 2026
Deep AWS Integration
CodeCatalyst offers seamless integration with AWS services such as AWS Lambda, Amazon EC2, Amazon S3, and AWS CloudFormation. Deployment pipelines can directly target AWS environments without complex third-party configuration.
Opinionated DevOps Design
The platform provides predefined workflows and best-practice templates. This structured design reduces setup time and ensures architectural consistency across teams.
Simplified Development Environment Setup
Cloud-based Dev Environments enable developers to start coding without manual dependency installation or infrastructure provisioning.
Centralized Project Visibility
Built-in task management eliminates the need for separate Agile planning tools, offering traceability within a single AWS-centric dashboard.
User Experience and Industry Feedback
Organizations heavily invested in AWS frequently describe CodeCatalyst as a cohesive and efficient DevOps solution. The integration of code repositories, CI/CD workflows, and project tracking enhances organizational clarity.
Commonly Reported Benefits
Tight AWS Service Alignment
Direct connections to AWS infrastructure reduce deployment friction.
Reduced Toolchain Complexity
Combining code, pipelines, and project management simplifies operations.
Structured Development Experience
Opinionated workflows provide clear guidance for teams adopting DevOps practices.
Commonly Reported Limitations
Limited Customization for Non-Standard Use Cases
Advanced or highly customized DevOps architectures may feel constrained by predefined workflows.
Steeper Learning Curve for Non-AWS Teams
Organizations unfamiliar with AWS identity, networking, or service structures may require additional onboarding time.
Comparative Positioning in the 2026 DevOps Market
| Evaluation Criteria | AWS CodeCatalyst Position | Market Average Position |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud-Native Integration | Very High (AWS-Focused) | Moderate |
| Unified Toolchain Experience | High | Variable |
| Customization Flexibility | Moderate | High |
| Multi-Cloud Support | Limited | Expanding |
| Dev Environment Automation | Strong | Emerging |
| Cost Predictability | Structured Allocation | Mixed Models |
Strategic Role Among the Top DevOps Software Platforms in 2026
Within the global ranking of top DevOps software platforms in 2026, AWS CodeCatalyst occupies a specialized yet strategically significant position. It is not designed to be a universal DevOps solution across multi-cloud ecosystems; instead, it excels as a unified AWS-native development platform.
Organizations prioritizing deep integration with Amazon Web Services, streamlined environment provisioning, and consolidated development workflows increasingly consider CodeCatalyst a practical and efficient choice. While its opinionated structure may limit flexibility for highly customized workflows, its alignment with AWS infrastructure and simplified DevOps orchestration make it a compelling option for cloud-centric enterprises in 2026.
7. CircleCI

In 2026, CircleCI continues to distinguish itself as one of the fastest and most scalable CI/CD platforms in the global DevOps software market. Known for its performance-first architecture, CircleCI is particularly favored by engineering teams that operate complex, parallelized workflows requiring high concurrency and reproducibility.
While many DevOps platforms emphasize full lifecycle management, CircleCI focuses intensely on continuous integration and continuous delivery performance. Its credit-based pricing model and customizable resource classes allow teams to scale compute capacity dynamically, making it especially attractive to organizations with large codebases, microservices architectures, and infrastructure-as-code deployments.
Strategic Context: High-Concurrency CI/CD in 2026
The DevOps software ecosystem in 2026 increasingly demands:
Parallel Execution at Scale
Modern architectures require multiple simultaneous builds, tests, and deployment pipelines.
Infrastructure as Code Complexity
Terraform, Kubernetes manifests, and multi-environment provisioning introduce long-running workflows.
Reproducible Build Environments
Consistency across staging and production is critical for reducing deployment errors.
Developer-Centric CI/CD Tools
Teams prioritize intuitive user interfaces and rapid onboarding experiences.
CircleCI aligns with these requirements by offering high concurrency limits, container-based isolation, and scalable compute allocation.
Architecture and Concurrency Capabilities
CircleCI’s infrastructure is optimized for concurrent job execution. Instead of fixed pipeline limits, the platform allocates credits that teams consume based on resource usage and runtime.
Core CircleCI Capabilities in 2026
| Capability Area | Description | Operational Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Parallel Job Execution | Multiple jobs running simultaneously | Faster pipeline completion |
| Credit-Based Compute Model | Pay for resources consumed rather than fixed minutes | Flexible scaling |
| Containerized Runners | Reproducible Docker-based build environments | Consistent deployments |
| GitHub Integration | Native repository and webhook automation | Seamless CI trigger management |
| Configurable Resource Classes | Adjustable CPU and memory allocations | Optimized workload performance |
Concurrency Comparison Matrix
| Plan Tier | Maximum Concurrency | Target Team Profile | Resource Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free | 30x concurrency | Startups and small engineering teams | Basic |
| Performance | 80x concurrency | Growing DevOps teams | Enhanced |
| Scale | Custom | Enterprise-grade CI/CD operations | Extensive |
Pricing and Compute Model in 2026
CircleCI’s pricing structure centers on credit consumption rather than traditional minute-based billing. This approach enables teams to tailor performance according to workload intensity.
CircleCI Pricing and Compute Tiers (2026)
| Plan | Price (2026) | Included Credits per Month | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free | $0 | 30,000 credits | 30x concurrency, basic runners |
| Performance | $15 per user per month | 30,000 credits included | 80x concurrency, larger resource classes |
| Scale | $2,000+ per month | Custom allocation | 24/7 support, largest resource classes |
Credit Usage Efficiency Matrix
| Workload Type | Credit Consumption Pattern | Recommended Tier |
|---|---|---|
| Simple App Testing | Low to Moderate | Free or Performance |
| Microservices Parallel Builds | High | Performance |
| Infrastructure as Code (IaC) | Very High | Scale |
| Enterprise Release Pipelines | Custom | Scale |
Enterprise Strengths in 2026
High-Speed Pipeline Execution
CircleCI is widely recognized for reducing build and test cycle times through aggressive parallelization.
Developer-Friendly User Interface
Teams frequently cite the platform’s clean UI and intuitive configuration model as superior to legacy CI systems.
GitHub-Centric Workflows
CircleCI integrates seamlessly with GitHub repositories, simplifying webhook configuration and automated build triggers.
Modern CI/CD Philosophy
Compared to traditional tools such as Jenkins, CircleCI offers a more streamlined, cloud-native experience.
Operational Limitations and Considerations
Long-Running Infrastructure Jobs
Complex Terraform-based infrastructure pipelines can experience extended execution times, especially when managing multi-region or multi-environment provisioning.
Limited Native Stage Segmentation
There is no built-in mechanism to easily divide certain infrastructure-heavy stages without custom configuration.
Monitoring Dashboard Scope
While individual pipeline visibility is strong, some organizations seek improved centralized dashboards for holistic project health monitoring.
User Experience and Industry Feedback
Engineering teams consistently highlight CircleCI’s automation capabilities and GitHub integration as primary reasons for adoption. Automated test execution after each code push significantly reduces manual effort and increases deployment frequency.
Commonly Reported Advantages
Efficient Continuous Testing
Automatic test runs reduce regression risks.
Ease of Integration
GitHub compatibility streamlines onboarding.
Modern Interface
User experience surpasses many legacy CI/CD tools.
Commonly Reported Challenges
Infrastructure Execution Time
Complex Terraform workflows can extend pipeline duration.
Project-Level Monitoring
Centralized performance visibility could be enhanced.
Comparative Positioning in the 2026 DevOps Software Market
| Evaluation Criteria | CircleCI Position in 2026 | Market Average Position |
|---|---|---|
| CI/CD Performance Speed | Very High | Moderate |
| Concurrency Scalability | Advanced | Limited to Moderate |
| Credit-Based Flexibility | High | Mixed Billing Models |
| Full DevOps Lifecycle Coverage | Moderate | Expanding |
| Infrastructure Workflow Support | Strong but Custom | Variable |
| Enterprise Support | Tier-Based | Tier-Based |
Strategic Role Among the Top DevOps Software Platforms in 2026
Within the broader ranking of top DevOps software platforms in 2026, CircleCI holds a distinctive role as the high-performance concurrency specialist. It does not attempt to replace planning or issue-tracking systems; instead, it focuses on delivering scalable, reliable, and fast CI/CD automation.
Organizations that require parallelized workflows, reproducible environments, and GitHub-integrated automation frequently position CircleCI as a core component of their DevOps architecture. While improvements in centralized monitoring and infrastructure stage management remain areas for enhancement, its speed, scalability, and developer-centric design ensure that CircleCI remains one of the leading CI/CD platforms globally in 2026.
8. Google Cloud DevOps (Cloud Build and Cloud Deploy)

In 2026, Google Cloud’s DevOps ecosystem, centered around Cloud Build and Cloud Deploy, represents one of the most modern serverless CI/CD solutions in the global DevOps software landscape. Designed with a Kubernetes-first philosophy, Google Cloud DevOps prioritizes container-native development, microservices scalability, and seamless integration with managed cloud services.
Unlike traditional CI/CD platforms that require dedicated runners or fixed monthly capacity, Google Cloud Build operates on a fully consumption-based pricing model. This pay-as-you-go approach eliminates upfront infrastructure commitments, aligning DevOps costs directly with usage patterns. For organizations building primarily within the Google Cloud Platform (GCP), this creates a highly elastic and cloud-optimized delivery pipeline.
Strategic Context: Serverless DevOps in 2026
The DevOps software market in 2026 increasingly favors:
Serverless Automation
Engineering teams seek to eliminate CI server maintenance and infrastructure overhead.
Kubernetes-Native Deployments
Container orchestration platforms such as Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) dominate production workloads.
Usage-Based Pricing Models
Enterprises prefer cost structures that scale with actual compute consumption rather than fixed capacity tiers.
Discounted Compute for Non-Critical Workloads
Spot-based infrastructure is widely adopted for CI/CD runners and testing pipelines.
Google Cloud DevOps aligns with these priorities by combining Cloud Build’s serverless automation with discounted Spot VM infrastructure for non-critical workloads.
Platform Architecture and Core Components
Google Cloud DevOps integrates multiple services to create a streamlined CI/CD workflow.
Core Components of Google Cloud DevOps
| Component | Primary Function | Kubernetes-Native Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Build | Serverless CI automation | Native container build support |
| Cloud Deploy | Progressive delivery and release management | Direct integration with GKE |
| Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) | Container orchestration | Managed Kubernetes infrastructure |
| Cloud Run | Serverless container execution | Automatic scaling and traffic splitting |
| Identity and IAM | Access management | Centralized cloud governance |
This tightly coupled ecosystem simplifies container-based deployment pipelines within Google Cloud environments.
Pricing Model and Cost Efficiency in 2026
Cloud Build follows a pay-as-you-go pricing structure based on compute resources consumed during builds. There are no fixed monthly subscription fees for the CI/CD service itself, making it attractive for teams with variable workload intensity.
In 2026, Google Cloud Spot VMs offer substantial discounts ranging from 60 percent to 91 percent off standard on-demand pricing. These discounted instances are commonly used for CI/CD runners, integration tests, and other non-critical build tasks where temporary interruption is acceptable.
Google Cloud Build Performance and Cost Factors
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Pricing Model | Pay-as-you-go consumption-based billing |
| Infrastructure | Fully serverless build execution |
| Integration Depth | Native integration with GKE and Cloud Run |
| Cost Optimization | Spot VM discounts up to 91 percent |
| Support Options | $29 per month or 3 percent of total cloud spend |
Spot VM Utilization Matrix
| Workload Type | Recommended Compute Model | Cost Efficiency Potential |
|---|---|---|
| Standard CI Builds | On-Demand Serverless | Moderate |
| Integration Testing Pipelines | Spot VMs | High |
| Nightly Batch Testing | Spot VMs | Very High |
| Production Deployment Validation | On-Demand | Stability Focused |
Enterprise Strengths in 2026
True Serverless CI/CD
Cloud Build eliminates the need to provision or maintain dedicated build servers. Engineering teams can focus on writing code rather than managing infrastructure capacity.
Deep Kubernetes and Cloud Run Integration
The platform integrates directly with Google Kubernetes Engine and Cloud Run, enabling seamless container deployment and traffic management.
Elastic Cost Control
The consumption-based pricing model aligns expenses with actual build activity, making it suitable for organizations with fluctuating CI/CD demands.
Spot-Based Compute Savings
Using Spot VMs for non-critical workloads significantly reduces operational costs while maintaining high throughput.
Operational Challenges and Limitations
GCP-Centric Integration
Google Cloud DevOps is optimized primarily for workloads within GCP. Integration with external cloud providers or hybrid infrastructure environments may require additional customization.
YAML Configuration Complexity
Build configurations are YAML-based and can become extensive, especially in monorepo architectures with multi-step workflows.
Debugging and Documentation Gaps
Complex build failures may require additional troubleshooting due to limited granular documentation for advanced multi-stage pipelines.
User Experience and Industry Feedback
Teams operating fully within Google Cloud frequently describe Cloud Build as an efficient and streamlined serverless CI/CD solution. The elimination of infrastructure maintenance is widely regarded as a major advantage.
Commonly Reported Benefits
Reduced Infrastructure Overhead
No need to manage build servers or runner capacity.
Strong Kubernetes Alignment
Native compatibility with GKE simplifies container-based deployments.
Scalable Cost Structure
Pay-as-you-go pricing supports dynamic engineering workloads.
Commonly Reported Limitations
Limited Multi-Cloud Flexibility
Cross-platform integrations can be restrictive.
Complex Configuration Management
Large YAML files may reduce readability in complex repositories.
Comparative Positioning in the 2026 DevOps Software Market
| Evaluation Criteria | Google Cloud DevOps Position | Market Average Position |
|---|---|---|
| Serverless CI/CD Architecture | Very High | Moderate |
| Kubernetes-Native Integration | Advanced | Expanding |
| Multi-Cloud Flexibility | Limited | Moderate |
| Cost Elasticity | High | Variable |
| Spot Compute Optimization | Industry-Leading | Emerging |
| Configuration Simplicity | Moderate | Moderate |
Strategic Role Among the Top DevOps Software Platforms in 2026
Within the global ranking of top DevOps software platforms in 2026, Google Cloud DevOps occupies a specialized leadership role in serverless, Kubernetes-first CI/CD. It excels in environments fully committed to Google Cloud infrastructure, where its deep service integration and elastic pricing provide strong operational advantages.
Organizations prioritizing container-native development, scalable build automation, and cost-efficient compute through Spot VM usage frequently adopt Cloud Build and Cloud Deploy as core components of their DevOps architecture. While its GCP-centric design may limit multi-cloud flexibility, its serverless efficiency and Kubernetes alignment solidify its position as a leading CI/CD solution in the 2026 DevOps ecosystem.
9. CloudBees (Enterprise Jenkins)
In 2026, CloudBees continues to lead the market for enterprise-grade Jenkins-based DevOps platforms. Positioned as the commercial evolution of Jenkins, CloudBees provides centralized governance, secure controls, and large-scale orchestration capabilities required by highly regulated industries such as banking, financial services, healthcare, and government.
While many modern DevOps platforms focus on developer simplicity or cloud-native automation, CloudBees emphasizes enterprise governance, compliance enforcement, and operational scalability. For organizations managing thousands of pipelines across global engineering teams, CloudBees serves as the preferred solution for maintaining control, auditability, and structured DevOps operations at scale.
Strategic Context: Enterprise DevOps Governance in 2026
The DevOps software ecosystem in 2026 reflects a growing divide between lightweight CI/CD tools and enterprise governance platforms. Large organizations require:
Centralized Pipeline Management
Unified control across thousands of projects and distributed teams.
Regulatory Compliance Alignment
Audit trails, policy enforcement, and role-based access control.
Secure Multi-Tenant Environments
Isolated project environments within shared infrastructure.
Scalable Jenkins Compatibility
Continuation of Jenkinsfile-based pipelines with enterprise enhancements.
CloudBees addresses these needs by extending Jenkins with enterprise-level capabilities while preserving compatibility with existing Jenkins ecosystems.
Enterprise Jenkins Architecture
CloudBees provides a hardened, scalable version of Jenkins with centralized management and policy enforcement layers. It supports distributed controllers, team-based isolation, and standardized governance models.
Core Enterprise Capabilities of CloudBees CI
| Capability Area | Description | Enterprise Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Centralized Governance | Unified control across multiple Jenkins controllers | Improved compliance and visibility |
| Role-Based Access Control | Fine-grained permissions for teams and projects | Enhanced security posture |
| Team-Based Project Isolation | Multi-tenant pipeline separation | Reduced cross-team interference |
| Certified Plugin Management | Curated and validated plugin ecosystem | Stability and security assurance |
| Scalable Pipeline Execution | Distributed build infrastructure | High concurrency across enterprise workloads |
Performance and Capability Ratings in 2026
CloudBees maintains strong performance ratings across enterprise evaluation criteria, particularly in scalability and integration.
CloudBees CI Performance Ratings (2026)
| Capability Area | Rating (Out of 5.0) |
|---|---|
| Scalability | 4.8 |
| Integration | 4.8 |
| Compliance | 4.5 |
| Developer Experience (DevX) | 4.7 |
| Continuous Delivery Orchestration | 3.5 |
These ratings reflect CloudBees’ strength in managing complex, large-scale DevOps operations, though its CD orchestration capabilities are often supplemented with additional tooling in highly advanced delivery ecosystems.
Scalability and Multi-Tenant Operations
CloudBees is particularly well suited for organizations managing thousands of engineers and projects. Its distributed architecture allows enterprises to maintain performance consistency while enforcing global governance standards.
Enterprise Scalability Comparison Matrix
| Evaluation Criteria | CloudBees Position | Typical CI/CD Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Large-Scale Pipeline Management | Very High | Moderate |
| Multi-Team Isolation | Advanced | Limited |
| Compliance Policy Enforcement | Enterprise-Grade | Variable |
| Plugin Ecosystem Stability | Certified and Curated | Community-Based |
| Operational Complexity | High | Low to Moderate |
Governance and Compliance Leadership
In heavily regulated sectors such as banking and finance, governance is not optional. CloudBees offers centralized audit logs, compliance reporting frameworks, and enforced pipeline policies that align with regulatory standards.
Organizations benefit from:
Controlled Plugin Usage
Only certified plugins are permitted within enterprise environments.
Audit-Ready Logs
Comprehensive tracking of user actions and pipeline changes.
Policy Enforcement
Standardized pipeline templates ensure adherence to security protocols.
Operational Maturity Requirements
While CloudBees provides powerful enterprise controls, it requires a higher degree of operational maturity compared to cloud-native CI/CD platforms. Skilled DevOps engineers are often necessary to manage distributed controllers, optimize pipeline configurations, and maintain infrastructure resilience.
Common Operational Considerations
| Consideration Area | Impact on Organization |
|---|---|
| Skilled Resource Demand | Requires experienced Jenkins administrators |
| Onboarding Speed | Slower compared to SaaS-native CI/CD tools |
| Infrastructure Management | Requires internal operational oversight |
| Governance Overhead | Structured but resource-intensive |
User Experience and Industry Feedback
Enterprise users consistently highlight CloudBees’ scalability and governance strengths. In regulated environments, its ability to maintain strict access controls and enforce compliance policies is a primary advantage.
Commonly Reported Strengths
Robust Governance Controls
Critical for financial and regulatory compliance.
Scalable Jenkinsfile Support
Preserves existing pipeline investments while enhancing manageability.
Multi-Tenant Architecture
Supports large engineering organizations with structured isolation.
Commonly Reported Challenges
Operational Complexity
Effective management requires skilled DevOps teams.
Slower Onboarding
Compared to fully managed SaaS platforms, setup and configuration demand more time and expertise.
Comparative Positioning in the 2026 DevOps Software Market
| Evaluation Criteria | CloudBees Position in 2026 | Market Average Position |
|---|---|---|
| Enterprise Governance | Industry-Leading | Moderate |
| Jenkins Ecosystem Compatibility | Full | Partial or None |
| Multi-Project Scalability | Very High | Moderate |
| Developer Simplicity | Moderate | High (SaaS Tools) |
| Compliance Readiness | Advanced | Variable |
| Cloud-Native Simplicity | Moderate | High |
Strategic Role Among the Top DevOps Software Platforms in 2026
Within the global ranking of top DevOps software platforms in 2026, CloudBees occupies a critical niche as the enterprise governance and scalability standard. It does not compete primarily on ease of use or serverless simplicity; instead, it delivers structured control for large-scale, regulated organizations that cannot compromise on compliance and auditability.
For enterprises managing thousands of pipelines and engineers, particularly in banking and financial services, CloudBees remains the preferred platform for secure, centralized DevOps orchestration. Although it requires operational maturity and skilled administration, its robust governance framework and enterprise-grade scalability solidify its role as a cornerstone of regulated DevOps environments in 2026.
10. Octopus Deploy
In 2026, Octopus Deploy remains one of the most respected deployment automation platforms in the DevOps ecosystem. Unlike platforms that focus primarily on source control or CI build execution, Octopus Deploy specializes in release orchestration, particularly for complex, multi-environment deployment strategies.
Octopus Deploy is widely adopted by organizations that require structured release management across development, staging, testing, and production environments. Its ability to integrate with leading CI servers such as Jenkins, Azure DevOps, and other build systems positions it as a critical “last mile” deployment solution within enterprise DevOps toolchains.
Strategic Context: Deployment Orchestration in 2026
The DevOps landscape in 2026 increasingly differentiates between build automation and release orchestration. As applications grow more distributed and multi-tiered, deployment complexity rises significantly.
Organizations commonly require:
Multi-Environment Promotion
Controlled progression of releases across dev, QA, staging, and production.
Variable Management Across Environments
Secure and scalable injection of environment-specific configuration values.
Rollback Capabilities
Fast recovery from failed deployments.
Hybrid Infrastructure Support
Ability to deploy across on-premises, cloud, and containerized systems.
Octopus Deploy addresses these needs by focusing specifically on deployment workflow orchestration rather than CI pipeline execution.
Core Capabilities and Deployment Architecture
Octopus Deploy functions as a deployment automation layer that integrates with existing build servers. Once artifacts are produced by CI systems, Octopus manages packaging, configuration, environment targeting, and release promotion.
Key Functional Capabilities of Octopus Deploy
| Capability Area | Description | Operational Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-Environment Management | Structured deployment across dev, test, staging, prod | Controlled release promotion |
| Variable Injection | Centralized management of environment-specific values | Reduced scripting complexity |
| Release Promotion Workflows | One-click progression between environments | Faster and safer deployments |
| Rollback Functionality | Re-deployment of previous stable versions | Rapid incident recovery |
| CI Tool Integration | Seamless connection to Jenkins, Azure DevOps, and others | Flexible DevOps toolchain compatibility |
Universal Deployment Patterns
Octopus Deploy supports diverse deployment targets, including:
Traditional Virtual Machines
Cloud Infrastructure (AWS, Azure, GCP)
Kubernetes Clusters
Windows and Linux Servers
On-Premise Data Centers
Deployment Target Compatibility Matrix
| Infrastructure Type | Native Support | Enterprise Usage Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| On-Premise Servers | Yes | Regulated industries with data residency |
| Public Cloud (AWS/Azure) | Yes | Scalable cloud-native deployments |
| Kubernetes | Yes | Containerized microservices environments |
| Hybrid Infrastructure | Yes | Mixed cloud and on-premise operations |
Pricing Structure in 2026
Octopus Deploy offers both cloud-hosted and on-premise server licensing models. Pricing reflects enterprise-grade deployment orchestration capabilities.
Octopus Deploy Pricing Plans (2026)
| Plan Type | Deployment Model | Price (2026) |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Professional | Cloud | $4,170 per year |
| Cloud Enterprise | Cloud | $23,400 per year |
| Server Professional | On-Premise | $1,920 per year |
| Server Enterprise | On-Premise | $14,400 per year |
Cloud vs On-Premise Comparison Matrix
| Evaluation Criteria | Cloud Plans | Server Plans |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Management | Managed by Octopus | Managed by Organization |
| Scalability | Elastic | Infrastructure-Dependent |
| Data Residency Control | Moderate | Full Control |
| Compliance Customization | Standard Enterprise | Advanced Enterprise |
| Maintenance Overhead | Low | Higher |
Enterprise Strengths in 2026
Advanced Multi-Environment Control
Octopus Deploy excels in managing complex environment hierarchies. Teams can define lifecycle rules that automatically control how releases move through various stages of validation.
Seamless Variable Management
One of Octopus Deploy’s standout features is its structured variable injection system. Environment-specific configuration values can be defined centrally, eliminating the need for custom scripting or manual overrides.
Simplified Rollback Mechanisms
In production-critical systems, the ability to redeploy a stable version quickly is essential. Octopus Deploy provides straightforward rollback capabilities, enhancing release reliability.
CI/CD Toolchain Compatibility
Octopus integrates easily with CI tools such as Jenkins and Azure DevOps, making it a complementary deployment layer rather than a full pipeline replacement.
User Experience and Industry Feedback
Organizations managing multi-tier deployment environments frequently highlight Octopus Deploy’s clarity and control over release orchestration. The ability to promote releases between environments with minimal friction is often cited as a core advantage.
Commonly Reported Strengths
Environment Promotion Efficiency
Structured release pipelines reduce manual errors.
Reduced Scripting Complexity
Built-in variable management minimizes custom deployment scripts.
Reliable Rollback Options
Deployment failures can be mitigated quickly.
Commonly Reported Challenges
Perceived Cost
For smaller teams, annual licensing fees may appear high relative to simpler deployment tools.
Specialized Focus
Octopus Deploy concentrates on release orchestration and typically requires integration with external CI systems.
Comparative Positioning in the 2026 DevOps Software Market
| Evaluation Criteria | Octopus Deploy Position in 2026 | Market Average Position |
|---|---|---|
| Release Orchestration Depth | Industry-Leading | Moderate |
| Multi-Environment Management | Advanced | Limited to Moderate |
| CI Integration Flexibility | High | Variable |
| Rollback Simplicity | Strong | Basic to Moderate |
| Cost Accessibility | Enterprise-Focused | Mixed |
| Full CI/CD Lifecycle Coverage | Specialized (Deployment-Focused) | Broad but Shallow |
Strategic Role Among the Top DevOps Software Platforms in 2026
Within the broader ranking of top DevOps software platforms in 2026, Octopus Deploy holds a specialized yet essential position as the release orchestration expert. It is particularly valuable for organizations operating complex, multi-tier applications where controlled promotion and configuration management are critical.
Rather than replacing CI systems, Octopus Deploy complements them by focusing exclusively on the deployment and release stages of the DevOps lifecycle. For enterprises managing hybrid infrastructure and regulated environments, its structured variable management and lifecycle-based deployment workflows justify its investment.
As software delivery pipelines continue to grow in complexity in 2026, Octopus Deploy remains a leading choice for organizations seeking disciplined, reliable, and scalable release automation.
Strategic Analysis of the Global DevOps Software Ecosystem: Market Dominance, Technical Paradigms, and the 2026 Competitive Landscape
Executive Overview of the Global DevOps Market in 2026
By 2026, the global DevOps software ecosystem has evolved into one of the most critical infrastructure layers underpinning the digital economy. Once viewed as a cultural transformation within software engineering teams, DevOps has become an industrialized, capital-intensive discipline directly influencing enterprise resilience, operational efficiency, and shareholder value.
The global DevOps market is projected to reach approximately USD 19.57 billion in 2026, expanding at a compound annual growth rate of 21.33 percent. This sustained growth signals more than increased software tool adoption. It reflects a structural transformation in how organizations treat software delivery as a strategic asset. Software velocity is now directly correlated with competitive positioning, revenue scalability, and capital efficiency.
In 2026, enterprises operate within increasingly complex multi-cloud infrastructures, face near-zero tolerance for downtime, and deploy AI-native workloads that demand elastic automation. As a result, DevOps toolchains have undergone significant consolidation, shifting toward unified platforms that emphasize developer experience (DevEx), automation intelligence, and operational autonomy.
The Macro-Economic Trajectory of DevOps from 2018 to 2026
To fully understand the 2026 DevOps landscape, it is essential to examine the historical capital flows and structural growth patterns that shaped the industry.
In 2018, the global DevOps market was valued at USD 3,709.1 million. Over the subsequent eight years, the sector experienced a sustained CAGR of approximately 19.1 percent. This growth was initially concentrated in North America, which accounted for 49.32 percent of global market share during the early expansion phase.
However, by 2026, geographic dynamics have shifted considerably. While North America remains the largest single regional market, Asia-Pacific has emerged as the fastest-growing region, with projected growth rates ranging between 24.1 percent and 28 percent. This acceleration is driven by rapid cloud adoption among small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), along with substantial venture capital inflows into SaaS ecosystems across India and Southeast Asia.
Global DevOps Market Size and Regional Dynamics
| Metric | Value (USD Billion / Percentage) |
|---|---|
| Global Market Size (2025) | 16.13 |
| Global Market Size (2026 Projection) | 19.57 |
| North American Market Share (Historical) | 49.32% |
| Asia-Pacific Projected Growth Rate | 24.1% – 28% |
| Expected Global Market Size (2031) | 51.43 |
The projected expansion to USD 51.43 billion by 2031 underscores the continued acceleration of DevOps as a core enterprise investment category.
Component-Level Market Distribution in 2026
The DevOps market in 2026 is dominated by software solutions, which account for approximately 59.65 percent of total revenue. Services, while essential, represent a smaller share of total market value.
This dominance of software platforms is attributed to several factors:
Reduced Capital Expenditure
Cloud-native DevOps platforms minimize upfront infrastructure costs, shifting organizations toward operational expenditure models.
Automated Regulatory Compliance
Integrated compliance and security modules enable automated audit trails, vulnerability scanning, and policy enforcement.
Toolchain Consolidation
Enterprises are moving away from fragmented tool ecosystems in favor of unified DevOps platforms offering end-to-end lifecycle visibility.
Market Share by Component in 2026
| Component Type | Revenue Share (%) |
|---|---|
| Software Solutions | 59.65% |
| Services | 40.35% |
Enterprise Adoption Patterns and Revenue Distribution
Large enterprises account for approximately 64.05 percent of total DevOps revenue in 2026. These organizations have transitioned from experimentation to optimization, focusing on reducing toolchain sprawl and consolidating workflows into integrated platforms.
Enterprise Segment Revenue Distribution
| Organization Size | Revenue Share (%) |
|---|---|
| Large Enterprises | 64.05% |
| SMEs | 35.95% |
Large organizations prioritize:
Unified Platform Governance
Centralized dashboards from code commit to production monitoring.
Regulatory and Security Controls
Built-in DevSecOps automation to manage compliance requirements.
Operational Observability
Integrated metrics tracking including DORA performance indicators.
Conversely, SMEs are emerging as one of the fastest-growing segments. With a projected CAGR of 21.2 percent through 2031, SMEs are adopting cloud-native architectures from inception. Unlike large enterprises burdened by legacy migrations, smaller organizations often implement microservices, container orchestration, and pay-as-you-grow pricing models from the outset.
Regional Competitive Landscape in 2026
The DevOps ecosystem in 2026 is characterized by a multipolar regional structure.
North America
Remains the largest revenue generator due to enterprise IT budgets and mature SaaS adoption.
Asia-Pacific
Exhibits the highest growth rate, fueled by startup ecosystems, digital transformation initiatives, and government-backed cloud modernization programs.
Europe
Demonstrates strong regulatory-driven DevOps adoption, particularly around data privacy and compliance frameworks.
Regional Growth Comparison Matrix
| Region | Market Maturity | Growth Rate Trend | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | Mature | Moderate | Enterprise IT modernization |
| Asia-Pacific | Expanding | High | SME cloud adoption, SaaS investment |
| Europe | Mature | Moderate-High | Compliance automation, digital sovereignty |
Technical Paradigms Shaping the 2026 DevOps Ecosystem
The 2026 DevOps competitive landscape is influenced by several dominant technical paradigms:
Unified DevSecOps Platforms
Enterprises prefer single-application ecosystems that integrate source control, CI/CD, security scanning, and monitoring.
AI-Driven Automation
Machine learning models assist in deployment verification, anomaly detection, and predictive rollback.
Kubernetes-First Architectures
Container orchestration underpins modern infrastructure strategies.
Serverless CI/CD
Pay-as-you-go automation models reduce operational overhead.
Platform Engineering
Internal developer platforms provide standardized workflows and reduce cognitive load for engineering teams.
Technical Paradigm Influence Matrix
| Technical Paradigm | Market Influence Level | Enterprise Adoption Trend |
|---|---|---|
| AI-Driven DevOps | High | Rapidly Increasing |
| Kubernetes-Native CI/CD | High | Standardizing |
| Serverless Automation | Moderate-High | Growing |
| Toolchain Consolidation | Very High | Accelerating |
| Platform Engineering | High | Expanding |
Competitive Landscape and Capital Efficiency
In 2026, competition within the DevOps market is defined less by isolated feature differentiation and more by ecosystem breadth, integration depth, and cost alignment with enterprise financial models.
Capital efficiency has become a primary metric. Organizations increasingly evaluate DevOps investments through the lens of:
Deployment Frequency
Lead Time Reduction
Infrastructure Cost Optimization
Change Failure Rate Improvement
The shift from fragmented toolchains to unified platforms is directly linked to reduced operational friction and improved return on investment.
Strategic Outlook Toward 2031
Looking forward, the DevOps market is expected to more than double in size by 2031. Key growth accelerators include:
AI-native development workflows
Automated compliance frameworks
Multi-cloud orchestration standardization
Expansion of SME digital transformation
The democratization of DevOps within SMEs represents one of the most significant structural shifts. These organizations are avoiding legacy technical debt and building directly on scalable, cloud-native foundations. Their adoption of pay-as-you-grow pricing models ensures that operational expenditure aligns closely with revenue expansion.
Conclusion: The Industrialization of Software Delivery
The global DevOps software ecosystem in 2026 reflects the industrialization of software delivery. What began as a cultural practice emphasizing collaboration between development and operations has evolved into a capital-intensive strategic discipline central to enterprise competitiveness.
With a projected market size of USD 19.57 billion and strong double-digit growth rates across regions, DevOps now functions as a core economic infrastructure layer. The shift toward unified platforms, AI-driven automation, and cloud-native architectures signals a market entering maturity while continuing to expand at scale.
In this environment, software delivery velocity is no longer a technical metric alone. It is a defining indicator of market resilience, operational efficiency, and long-term enterprise value creation.
Technical Evolution: From Automation to Agentic Autonomy in the 2026 DevOps Ecosystem
Executive Overview of the Agentic Shift
The defining technical transformation of the 2026 DevOps software landscape is the progression from rule-based automation toward agentic AI-driven autonomy. While automation characterized the early and mid-2020s DevOps era, 2026 represents a pivotal inflection point in which intelligent systems actively reason, predict, and execute operational decisions without direct human instruction.
By 2025, approximately 76 percent of DevOps teams had already integrated AI components into their CI/CD pipelines. However, these implementations were largely assistive, providing dashboards, static recommendations, and anomaly alerts. In 2026, the paradigm has shifted decisively toward autonomous agents embedded within the software delivery chain.
From Passive Monitoring to Autonomous Remediation
Traditional DevOps automation focused on predefined scripts and threshold-based triggers. If CPU utilization exceeded a specific limit, a scaling rule executed. If a test failed, a notification was sent. The model was reactive and required continuous human oversight.
In contrast, agentic AI systems in 2026 introduce predictive analysis and contextual reasoning. These systems:
Detect early indicators of memory leaks before they escalate into outages
Forecast disk or CPU exhaustion based on historical usage patterns
Automatically trigger remediation workflows
Adjust scaling policies dynamically
Initiate rollback sequences if anomaly confidence thresholds are exceeded
Agentic DevOps Capability Matrix
| Capability Area | Traditional Automation | Agentic AI Autonomy |
|---|---|---|
| Monitoring | Threshold-based alerts | Predictive anomaly detection |
| Remediation | Predefined scripts | Context-aware self-healing workflows |
| Deployment Validation | Static rule evaluation | Machine-learning-based verification |
| Capacity Planning | Manual forecasting | Predictive infrastructure modeling |
| Incident Escalation | Human triage required | Autonomous decision routing |
The shift to agentic AI reduces cognitive load on operations teams and significantly improves system resilience.
The Rise of Platform Engineering and Internal Developer Platforms
Parallel to the rise of agentic AI, Platform Engineering has emerged as a structural redesign of DevOps operations. By 2026, approximately 80 percent of software development organizations rely on internal developer platforms (IDPs) to abstract infrastructure complexity.
IDPs provide standardized interfaces through which developers can provision infrastructure, deploy services, and manage configurations without directly interacting with underlying cloud primitives.
Core Characteristics of Internal Developer Platforms
| Feature Category | Description | Operational Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Golden Paths | Curated deployment templates | Standardized engineering practices |
| Self-Service Provisioning | Automated environment creation | Reduced dependency on DevOps tickets |
| Policy Enforcement | Embedded security and compliance rules | Consistent governance |
| Observability Integration | Built-in logging and monitoring | Unified visibility |
| Infrastructure Abstraction | Simplified service catalogs | Lower cognitive overhead for developers |
Quantifiable Impact of IDP Adoption
The operational benefits of IDP implementation are measurable:
Environment setup times have been reduced from days to minutes
Inbound DevOps ticket volume has decreased by approximately 40 percent
Operational toil has been significantly reduced
Operational Impact of AI and Platform Engineering in 2026
| Performance Metric | Traditional Automation Impact | AI-Driven / Agentic Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Incident Resolution Time (MTTR) | 15% – 20% reduction | 30% – 50% reduction |
| Infrastructure Cost Optimization | 5% – 10% savings | 20% – 40% savings |
| Deployment Frequency | 2x – 5x increase | 10x – 30x increase |
| Operational Toil Reduction | 25% reduction | 70% reduction |
These metrics illustrate that the move from automation to autonomy produces exponential improvements rather than incremental gains.
Deployment Frequency and Autonomy
In earlier DevOps cycles, automation enabled organizations to deploy two to five times more frequently than legacy release models. Agentic AI systems in 2026 now support ten to thirty times higher deployment frequency in high-maturity engineering environments.
Autonomous verification engines continuously validate deployment health and dynamically adjust traffic routing. This dramatically lowers change failure rates while maintaining velocity.
Infrastructure Economics: FinOps and GreenOps Integration
The transition to agentic autonomy coincides with the formal integration of FinOps and GreenOps principles into DevOps strategy. Cloud spending has evolved into one of the top five expense categories on corporate profit and loss statements. As a result, engineering leaders increasingly evaluate architectural decisions through financial and environmental lenses.
FinOps Integration in DevOps
AI-driven platforms optimize infrastructure usage by:
Identifying underutilized compute instances
Recommending rightsizing strategies
Forecasting cost anomalies
Automating spot instance utilization
GreenOps Alignment
Sustainability objectives are now embedded into engineering policies. Agentic systems can:
Shift workloads to energy-efficient regions
Optimize compute density
Reduce idle resource waste
Measure carbon impact per deployment
FinOps and GreenOps Influence Matrix
| Strategic Dimension | Automation Era Approach | Agentic AI Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Visibility | Monthly reporting dashboards | Real-time predictive cost modeling |
| Resource Optimization | Manual rightsizing | Autonomous workload balancing |
| Carbon Footprint Control | Static reporting | Dynamic energy-aware workload shifts |
| Budget Governance | Reactive cost reviews | Proactive anomaly prevention |
The Broader Competitive Implications
The evolution toward agentic autonomy reshapes competitive dynamics within the DevOps software ecosystem. Platforms that embed predictive intelligence directly into CI/CD pipelines and infrastructure orchestration engines gain measurable differentiation.
Organizations adopting agentic DevOps architectures achieve:
Faster recovery from incidents
Higher deployment velocity
Lower operational overhead
Improved cost-to-performance ratios
Reduced engineering burnout
This technical transformation also redefines the role of DevOps engineers. Rather than manually orchestrating pipelines and responding to alerts, engineers increasingly design guardrails, supervise AI agents, and optimize system intelligence.
Conclusion: DevOps as an Autonomous Economic Engine
In 2026, DevOps has evolved beyond scripted automation into a semi-autonomous operational model. Agentic AI systems actively manage infrastructure health, optimize deployment pipelines, and align engineering output with financial and sustainability objectives.
Platform Engineering amplifies this transformation by providing standardized, self-service golden paths that dramatically reduce operational friction. Together, agentic AI and internal developer platforms redefine DevOps as an intelligent economic engine rather than a collection of automation scripts.
This shift marks a fundamental inflection point in software delivery maturity. Organizations that successfully implement agentic autonomy will not only accelerate software velocity but also achieve superior capital efficiency, operational resilience, and long-term strategic advantage in the digital economy.
Comparative Analysis of Artifact Management Costs: The JFrog Consumption Model in 2026
Executive Overview of Artifact Management Economics
Within the broader DevOps software ecosystem, artifact management represents one of the most underestimated cost centers. While organizations often focus on CI/CD licensing, AI capabilities, and infrastructure compute, artifact repositories generate recurring storage and data transfer expenses that scale with engineering velocity.
In 2026, artifact management platforms such as JFrog exemplify the financial complexity of consumption-based pricing models. As build frequency increases and microservices architectures proliferate, artifact volumes grow exponentially. Without proactive cost monitoring, storage and egress charges can significantly impact total DevOps expenditure.
Understanding the Artifact System-of-Record Market
Artifact repositories function as the system of record for binaries, container images, libraries, and build outputs. They serve as central distribution hubs between development, testing, staging, and production environments.
Key Artifact Management Cost Drivers
| Cost Driver | Description | Financial Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Consumption | Total GB stored in repository | Recurring monthly charges |
| Data Egress | Transfer of artifacts across regions or environments | Incremental bandwidth costs |
| Build Frequency | Number of CI/CD cycles per day | Exponential growth in artifact volume |
| Artifact Size | Average size per build | Direct multiplier of storage costs |
| Retention Policies | Duration artifacts are stored | Long-term cost accumulation |
The JFrog Pricing Structure in 2026
JFrog’s pricing begins at a base subscription rate of 150 USD per month for the Pro tier. However, this base fee includes a limited data allowance. Additional storage and transfer usage is billed at tiered rates, typically beginning at 1.25 USD per GB beyond the included threshold.
Mathematical Cost Model for Artifact Management
The monthly cost of artifact management can be estimated using the following model:
C_monthly = P_base + (G_total − G_included) × R_tier
Where:
C_monthly represents the total monthly cost
P_base represents the base subscription price (150 USD for Pro)
G_total represents the total storage and transfer volume in GB
G_included represents the included allowance (25 GB for Pro)
R_tier represents the applicable tier rate (1.25 USD per GB in the first tier)
Practical Cost Scenario: 10-Developer Team
Consider a development team with the following characteristics:
10 developers
50 builds per day
Average artifact size of 200 MB
Step-by-Step Consumption Breakdown
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Builds per day | 50 |
| Artifact size per build | 200 MB |
| Daily artifact generation | 10,000 MB (10 GB) |
| Monthly artifact generation | 400 GB (approx.) |
| Included allowance | 25 GB |
| Billable volume | 375 GB |
| Rate per GB | 1.25 USD |
Cost Calculation
Base subscription: 150 USD
Billable overage: 375 GB × 1.25 USD = 468.75 USD
Total monthly cost: 618.75 USD
Annual cost: 7,425.00 USD
Annual Artifact Cost Projection Matrix
| Team Size | Daily Builds | Artifact Size | Monthly Usage (GB) | Annual Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 Devs | 30 | 150 MB | ~135 GB | ~2,400 |
| 10 Devs | 50 | 200 MB | ~400 GB | 7,425 |
| 25 Devs | 100 | 250 MB | ~1,875 GB | ~28,000+ |
| 50 Devs | 150 | 300 MB | ~6,750 GB | ~100,000+ |
The exponential nature of artifact growth becomes evident as team size and deployment velocity increase.
Hidden Cost Multipliers in CI/CD Pipelines
Artifact storage costs are often compounded by additional factors:
Frequent CI pipeline retries
Multi-region replication for disaster recovery
Long artifact retention periods
Container image layering inefficiencies
Parallel branch builds
These hidden multipliers can inflate total costs by 20 percent to 40 percent beyond baseline projections.
Artifact Cost Risk Matrix
| Risk Factor | Impact Level | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Unlimited Retention Policies | High | Enforce lifecycle expiration rules |
| Excessive Branch Builds | Moderate | Limit parallel build redundancy |
| Multi-Region Replication | High | Optimize replication policies |
| Large Monorepo Artifacts | High | Modularize artifact packaging |
| Unmonitored Egress | Very High | Implement real-time cost dashboards |
The Rise of FinOps in Artifact Management
The quantitative reality of artifact management expenses has accelerated the formal adoption of FinOps practices within DevOps organizations.
FinOps introduces financial accountability into engineering workflows by:
Monitoring storage growth in real time
Setting cost alerts for egress thresholds
Optimizing retention and cleanup policies
Aligning artifact lifecycle decisions with business priorities
FinOps Impact on Artifact Economics
| Financial Dimension | Without FinOps | With FinOps Governance |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Growth Rate | Uncontrolled | Actively managed |
| Cost Predictability | Low | High |
| Budget Alignment | Reactive | Proactive |
| Annual Cost Escalation | Exponential | Controlled |
Strategic Implications for DevOps Leaders in 2026
Artifact management is no longer a marginal operational expense. As CI/CD frequency increases and AI-driven development accelerates build cycles, artifact volume expands proportionally.
Organizations must treat artifact repositories as financial infrastructure components rather than passive storage systems. Without structured governance, artifact costs can rival or exceed CI/CD licensing fees.
Key Strategic Considerations
Integrate artifact cost tracking into DevOps dashboards
Implement lifecycle retention policies by default
Use compression and deduplication where possible
Align artifact replication with business continuity needs
Model annual artifact growth in financial planning cycles
Conclusion: Artifact Management as a Strategic Cost Center
In the 2026 DevOps ecosystem, artifact management represents a hidden yet critical financial lever. The JFrog pricing example illustrates how seemingly modest base subscription fees can scale significantly when combined with storage and data transfer consumption.
As engineering teams accelerate deployment frequency and adopt AI-enhanced workflows, artifact volume growth becomes inevitable. The integration of FinOps discipline into DevOps governance is therefore essential to maintain cost transparency, prevent uncontrolled budget expansion, and sustain long-term capital efficiency.
Artifact management is no longer a background technical function. It is a measurable economic variable within the modern software delivery lifecycle.
Market Segmentation and Industry Adoption Benchmarks in the 2026 DevOps Ecosystem
Executive Overview of Industry-Specific DevOps Adoption
By 2026, the global DevOps software ecosystem is no longer defined solely by horizontal technology adoption. Instead, it is increasingly segmented by vertical industry requirements. Each sector prioritizes specific DevOps platform capabilities based on regulatory intensity, operational complexity, uptime demands, and data governance standards.
The maturation of DevSecOps, agentic automation, and platform engineering has allowed industry-specific deployment patterns to emerge. Financial institutions, healthcare providers, manufacturers, and e-commerce enterprises now implement DevOps strategies aligned with sector-driven performance benchmarks rather than generic software velocity metrics.
Industry Adoption and Performance Impact in 2026
| Industry Sector | Primary Focus Area | Release Acceleration | Key Impact Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| BFSI (Finance) | Compliance and Security | 29% Faster | 75% Hybrid Cloud Adoption |
| Healthcare | Data Privacy and Security | 28.1% CAGR | 60% MTTR Reduction |
| Manufacturing | OT and IT Convergence | 19.8% CAGR | 30% Sales Increase |
| E-Commerce | Scalability and Speed | 30% Growth | 99.99% Uptime |
These figures demonstrate that DevOps maturity in 2026 is closely tied to measurable operational and financial outcomes.
BFSI Sector: Compliance-as-Code and Hybrid Governance
The Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance sector remains one of the most regulated segments in the global economy. In 2026, compliance automation is the dominant DevOps priority for financial institutions.
Compliance-as-Code
Financial organizations increasingly embed policy enforcement, access control rules, and audit logging directly into CI/CD pipelines. Infrastructure provisioning scripts now include regulatory controls by default, eliminating manual review bottlenecks.
Hybrid Cloud Standardization
Approximately 75 percent of financial workloads operate within hybrid cloud architectures, combining on-premises data centers with public cloud platforms. DevOps platforms capable of enforcing governance across distributed environments are essential.
Performance Impact in BFSI
| Performance Dimension | Measured Improvement in 2026 |
|---|---|
| Release Acceleration | 29% Faster Deployment Cycles |
| Audit Trail Automation | Near-Real-Time Reporting |
| Security Policy Enforcement | Embedded in Pipelines |
| Hybrid Cloud Coverage | 75% of Workloads |
In highly regulated environments, DevOps investments are justified primarily by risk mitigation rather than pure velocity. Automated audit trails and secure multi-tenant governance reduce compliance exposure while maintaining release speed.
Healthcare Sector: Shift-Left Security and Data Privacy
Healthcare has emerged as one of the fastest-growing DevOps adoption sectors, with a CAGR of 28.1 percent in 2026. Data sensitivity and regulatory mandates drive technical priorities.
Shift-Left Security
Healthcare organizations integrate vulnerability scanning, compliance validation, and data protection policies directly into early development stages. Rather than testing for compliance after deployment, security is enforced at commit time.
Regulatory Alignment
Automated checks aligned with HIPAA requirements and GAMP4 validation frameworks are embedded within CI/CD workflows. This automation significantly reduces human error and accelerates release validation.
Operational Impact in Healthcare
| Performance Dimension | Measured Outcome in 2026 |
|---|---|
| MTTR Reduction | 60% Decrease |
| Compliance Validation Rate | 99% Pipeline Enforcement |
| Release Validation Automation | Fully Embedded |
| SaaS Reliability Improvement | Significant |
Healthcare DevOps strategies prioritize incident response efficiency and regulatory confidence over aggressive deployment frequency. The 60 percent reduction in mean time to recovery reflects the impact of integrated security validation.
Manufacturing Sector: OT and IT Convergence
In manufacturing, the convergence of Operational Technology (OT) and Information Technology (IT) defines the DevOps transformation strategy. With a projected CAGR of 19.8 percent, the sector increasingly leverages DevOps to bridge factory systems and digital platforms.
Key Focus Areas
Integration of IoT sensor data with enterprise systems
Automated firmware and edge device updates
Predictive maintenance pipelines
Real-time operational analytics
Business Impact in Manufacturing
| Performance Dimension | Measured Outcome in 2026 |
|---|---|
| Revenue Impact | 30% Sales Increase |
| Deployment Automation | Factory-to-Cloud Sync |
| Infrastructure Modernization | Accelerated Adoption |
| Operational Visibility | End-to-End Monitoring |
DevOps in manufacturing directly influences production optimization and supply chain responsiveness. The linkage between software deployment and sales growth highlights DevOps as a revenue driver rather than merely a cost center.
E-Commerce Sector: Scalability and Uptime Excellence
E-commerce remains one of the most performance-sensitive industries in 2026. Revenue is tightly coupled to uptime, latency, and deployment frequency.
Primary DevOps Objectives
Elastic scalability during peak demand
Continuous feature deployment
Zero-downtime release strategies
High availability architecture
Operational Benchmarks in E-Commerce
| Performance Dimension | Measured Outcome in 2026 |
|---|---|
| Platform Growth | 30% Year-over-Year |
| Uptime Target | 99.99% Availability |
| Deployment Frequency | High Cadence |
| Infrastructure Elasticity | Dynamic Scaling |
DevOps automation, combined with agentic scaling and predictive infrastructure management, ensures near-zero downtime. A 99.99 percent uptime benchmark is now a competitive baseline rather than a premium differentiator.
Comparative Industry Benchmark Matrix
| Industry | Regulatory Intensity | Deployment Speed Priority | Automation Depth | Financial Impact Alignment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BFSI | Very High | Moderate | High | Risk Mitigation |
| Healthcare | Very High | Moderate | High | Reliability & Compliance |
| Manufacturing | Moderate | Balanced | Moderate-High | Revenue Optimization |
| E-Commerce | Moderate | Very High | Very High | Direct Revenue Growth |
Emerging Cross-Industry Trends in 2026
Several cross-sector patterns define the 2026 DevOps landscape:
Compliance-as-Code as Standard Practice
Policy enforcement is embedded into CI/CD pipelines across regulated industries.
Shift-Left Security Adoption
Security testing now begins at commit rather than pre-production.
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Governance
Enterprises require unified visibility across distributed infrastructures.
Operational Metrics as Executive KPIs
Deployment frequency, MTTR, and uptime are board-level performance indicators.
Strategic Conclusion
The 2026 DevOps software ecosystem reflects a mature, vertically segmented market where industry context dictates platform priorities. Financial institutions emphasize compliance automation and hybrid governance. Healthcare prioritizes data privacy and rapid incident recovery. Manufacturing leverages DevOps for operational efficiency and revenue acceleration. E-commerce focuses on scalability and uptime resilience.
Across all sectors, DevOps has transitioned from a purely technical practice to a sector-specific strategic capability. Adoption benchmarks increasingly tie directly to measurable business outcomes, including compliance adherence, revenue growth, operational resilience, and cost optimization.
As industry segmentation deepens, DevOps platforms that offer configurable governance frameworks, AI-driven automation, and sector-aligned compliance modules will define competitive advantage in the evolving 2026 digital economy.
The Future of DevOps Software: Strategic Trends Shaping the Competitive Landscape Toward 2030
Executive Outlook: DevOps as Intelligent Infrastructure
As the global DevOps software market accelerates toward the end of the decade, the competitive definition of the top DevOps platforms is shifting from feature depth to systemic intelligence, sustainability alignment, and economic automation. The projected expansion of global public cloud spending to approximately 723.4 billion USD by 2025 signals not only growth in infrastructure consumption but also increased scrutiny over operational efficiency, environmental impact, and capital allocation.
By 2030, DevOps platforms will no longer be evaluated solely on deployment velocity or integration breadth. Instead, leading tools will differentiate through carbon awareness, autonomous remediation, serverless abstraction, and financial governance embedded directly into engineering workflows.
GreenOps: Carbon Efficiency as a Core DevOps Metric
The rapid growth in cloud infrastructure spending has introduced sustainability as a measurable performance criterion. As energy consumption from hyperscale data centers increases, enterprises are incorporating carbon impact into DevOps decision-making processes.
GreenOps represents the convergence of environmental accountability and engineering efficiency. By 2030, leading DevOps platforms are expected to integrate carbon intensity indicators alongside traditional performance metrics such as deployment frequency and mean time to recovery.
GreenOps Evaluation Metrics
| Metric Category | Traditional DevOps Focus | GreenOps-Enhanced Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Performance Measurement | DORA Metrics | DORA + Carbon Intensity Metrics |
| Infrastructure Optimization | Cost Efficiency | Cost + Energy Efficiency |
| Scaling Decisions | Load-Based | Load + Energy Source Optimization |
| Deployment Scheduling | Business Priority | Business + Carbon-Aware Scheduling |
Emerging GreenOps Capabilities by 2030
Predictive carbon-aware workload scheduling
Automatic migration to lower-intensity cloud regions
Real-time carbon footprint dashboards
Energy-efficient artifact storage optimization
As regulatory pressure and ESG reporting standards expand, DevOps teams will increasingly be evaluated on both performance and environmental footprint.
The Acceleration of NoOps and Serverless DevOps
Another defining trend leading into 2030 is the continued abstraction of infrastructure management. The NoOps model, once considered aspirational, is becoming increasingly practical for specific workloads.
By 2026, the Serverless DevOps segment is growing at approximately 19.8 percent annually. Instead of provisioning virtual machines or container clusters, development teams deploy discrete functions executed within managed environments.
Comparative Infrastructure Evolution
| Operational Model | Infrastructure Responsibility | Operational Effort Level | Target Workloads |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Ops | Full Server Management | High | Legacy Applications |
| DevOps Automation | Scripted Provisioning | Moderate | Microservices |
| Serverless DevOps | Managed Runtime Environments | Low | Event-Driven Applications |
| NoOps (Emerging) | Fully Abstracted Operations | Minimal | Stateless, Elastic Workloads |
Operational Implications of the NoOps Shift
Reduced infrastructure maintenance overhead
Automatic horizontal scaling
Lower operational staffing requirements
Increased dependency on cloud provider reliability
While NoOps will not eliminate operations entirely, it will redefine the role of DevOps engineers from system operators to platform architects and policy designers.
The Evolution from AI-Assisted to AI-Autonomous Systems
Perhaps the most transformative trend shaping DevOps through 2030 is the transition from AI assistance to AI autonomy.
In earlier phases, AI systems provided code suggestions, anomaly alerts, and dashboard insights. By the end of the decade, next-generation DevOps tools will actively:
Patch security vulnerabilities without human review
Reconfigure infrastructure for cost optimization
Rewrite inefficient pipeline stages
Rebalance traffic to prevent performance degradation
Continuously refactor infrastructure-as-code templates
AI Capability Evolution Timeline
| Phase | AI Role in DevOps | Human Involvement Level |
|---|---|---|
| AI-Assisted (2023–2025) | Recommendations and Alerts | High |
| AI-Integrated (2026–2027) | Predictive Remediation | Moderate |
| AI-Autonomous (2028–2030) | Self-Healing and Optimization | Policy Oversight Only |
The Role of Humans in Autonomous DevOps
As autonomy increases, engineers transition toward governance and oversight roles. Human responsibility will focus on:
Defining guardrails and compliance policies
Setting cost thresholds and sustainability targets
Auditing AI decision-making frameworks
Managing cross-platform architectural strategy
This shift aligns DevOps more closely with strategic enterprise planning rather than operational firefighting.
Convergence of FinOps, GreenOps, and DevOps
By 2030, DevOps will not operate as an isolated engineering function. It will converge structurally with FinOps and GreenOps disciplines.
Integrated Economic and Environmental Governance
| Governance Dimension | 2026 State | 2030 Projection |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Monitoring | Dashboard Reporting | Autonomous Budget Enforcement |
| Carbon Tracking | Post-Deployment Reports | Real-Time Carbon-Aware Scheduling |
| Resource Allocation | Manual Optimization | Self-Optimizing Infrastructure |
| Policy Compliance | CI/CD Embedded Checks | Continuous Autonomous Enforcement |
Competitive Implications for DevOps Vendors
To remain competitive toward 2030, leading DevOps platforms must:
Embed sustainability analytics into core dashboards
Offer serverless-first pipeline architectures
Develop AI agents capable of autonomous remediation
Integrate cost optimization as a default pipeline stage
Provide unified governance across hybrid and multi-cloud systems
Platforms unable to evolve beyond automation into autonomous, sustainability-aware orchestration risk obsolescence in an increasingly performance- and efficiency-driven market.
Strategic Conclusion: DevOps as an Autonomous, Sustainable Operating System
The future of DevOps software extends beyond faster builds and cleaner pipelines. By 2030, DevOps platforms will function as autonomous operating systems for digital enterprises, balancing performance, cost efficiency, environmental impact, and regulatory compliance simultaneously.
GreenOps will embed carbon accountability into deployment metrics. The NoOps model will abstract infrastructure management for scalable workloads. AI-autonomous systems will actively maintain, secure, and optimize delivery pipelines without manual intervention.
In this evolving landscape, the definition of the top DevOps tools will shift fundamentally. Success will depend not only on technical capability but on the ability to operate as intelligent, self-optimizing ecosystems aligned with both financial discipline and environmental responsibility.
DevOps is transitioning from an automation framework to an autonomous, sustainability-aware economic engine that will shape enterprise competitiveness throughout the remainder of the decade.
Conclusion
The global landscape of DevOps software in 2026 represents a defining moment in the evolution of enterprise technology. What began as a cultural methodology centered around collaboration between development and operations teams has matured into a sophisticated, AI-enhanced, multi-billion-dollar software category that directly shapes business resilience, scalability, and economic performance. The top 10 DevOps software platforms in the world in 2026 are no longer evaluated solely on CI/CD capabilities or automation depth. They are assessed as strategic infrastructure ecosystems capable of enabling unified platform engineering, agentic AI autonomy, and sustainable operational governance.
The Maturity of the DevOps Market in 2026
By 2026, the DevOps market has transitioned from fragmented tooling to consolidated, intelligent platforms. Enterprises and startups alike now recognize DevOps software as a core operational backbone rather than a supporting utility. Market growth exceeding USD 19 billion reflects more than adoption; it signals a structural shift in how organizations build, deploy, secure, and scale software-driven products.
The top DevOps software tools in 2026 share several defining characteristics:
Unified lifecycle management from planning to monitoring
Integrated DevSecOps controls embedded within pipelines
AI-driven automation and predictive remediation
Cloud-native and Kubernetes-first architectures
Consumption-based pricing models aligned with business scale
Strong platform engineering alignment
Organizations that embrace these capabilities consistently outperform peers in deployment velocity, incident recovery time, and infrastructure cost optimization.
From Toolchains to Unified DevOps Platforms
One of the most important conclusions drawn from the 2026 DevOps ecosystem is the decline of fragmented toolchains. In the early 2020s, enterprises often stitched together separate tools for version control, CI/CD, artifact management, security scanning, and monitoring. This led to integration complexity, governance blind spots, and rising operational costs.
The top DevOps software platforms in 2026 emphasize consolidation. Unified platforms reduce integration overhead, standardize workflows, and offer centralized governance. This shift toward platform engineering models enables teams to focus on product innovation rather than pipeline maintenance.
Organizations that move toward internal developer platforms and standardized “golden paths” report measurable improvements:
Reduced environment setup time
Lower inbound DevOps support tickets
Faster release cycles
Improved compliance automation
The Competitive Differentiator: AI Maturity
In 2026, artificial intelligence is no longer a marketing feature; it is a core evaluation criterion for DevOps software selection. The transition from AI-assisted suggestions to AI-autonomous operations defines the current competitive landscape.
Leading DevOps platforms now:
Automatically detect deployment anomalies
Trigger rollbacks without manual approval
Predict infrastructure exhaustion before outages occur
Optimize cloud resource allocation in real time
Continuously enforce security and compliance policies
This agentic AI layer reduces operational toil by up to 70 percent in mature organizations. The impact extends beyond engineering productivity; it improves business continuity and lowers total cost of ownership.
As a result, when evaluating the best DevOps software in 2026, organizations increasingly prioritize AI maturity over feature quantity.
Governance and Scalability for Large Enterprises
For large enterprises, governance, compliance, and scalability remain central concerns. Financial institutions, healthcare providers, and regulated industries demand audit-ready pipelines and secure multi-tenant isolation.
The top DevOps platforms serving enterprise customers focus on:
Role-based access control
Compliance-as-code automation
Hybrid and multi-cloud governance
Certified plugin ecosystems
Centralized observability and reporting
In highly regulated sectors, DevOps software must operate as both an innovation engine and a compliance enforcement framework. This dual function is a defining trait of leading platforms in 2026.
Developer Experience and Serverless Simplicity for SMEs
While enterprise governance drives one segment of the market, startups and small to medium-sized enterprises prioritize speed, flexibility, and developer experience.
The best DevOps tools for startups in 2026 emphasize:
Serverless CI/CD pipelines
Pay-as-you-grow pricing
Low infrastructure management overhead
High concurrency and rapid scaling
Seamless Git-based workflows
Serverless DevOps adoption continues to grow, enabling smaller teams to deploy frequently without managing servers or clusters. This shift supports faster innovation cycles and capital-efficient scaling.
Total Cost of Ownership and FinOps Integration
Another critical takeaway from analyzing the top 10 DevOps software platforms in 2026 is the growing importance of total cost of ownership. Consumption-based pricing models, artifact storage costs, AI credit usage, and cloud egress fees can significantly impact budgets.
Organizations now integrate FinOps practices into DevOps decision-making. Real-time cost visibility, predictive budget alerts, and automated resource optimization are essential capabilities.
The most competitive DevOps platforms provide:
Transparent pricing structures
Granular usage dashboards
Automated cost optimization
Artifact lifecycle management tools
Without financial governance, DevOps scalability can quickly become economically inefficient. In 2026, economic efficiency is as important as technical capability.
GreenOps and Sustainability as Emerging Metrics
As global cloud spending rises, sustainability considerations increasingly influence DevOps strategy. Organizations now evaluate platforms based on their ability to support carbon-efficient compute usage and optimized infrastructure allocation.
Future-ready DevOps platforms are expected to integrate:
Carbon intensity reporting
Energy-efficient workload scheduling
Sustainable infrastructure recommendations
This convergence of DevOps, FinOps, and GreenOps marks the beginning of a more holistic engineering governance model.
The Characteristics of Elite DevOps Performers
Elite DevOps organizations in 2026 share several measurable characteristics:
Multiple deployments per day
Mean time to recovery under one hour
High automation coverage
Low change failure rates
Strong alignment between engineering and business metrics
These high-performing teams are statistically more likely to achieve strategic organizational goals. The correlation between DevOps maturity and business success is no longer theoretical; it is quantifiable.
Future Outlook: DevOps Toward 2030
Looking ahead, the top DevOps software platforms will continue evolving toward greater autonomy and abstraction. Infrastructure management will become increasingly invisible, with AI agents handling scaling, remediation, and optimization tasks.
By 2030, the best DevOps tools will likely:
Operate as autonomous systems with minimal manual intervention
Continuously optimize cost and performance
Embed sustainability metrics into deployment pipelines
Provide real-time governance across global cloud footprints
The role of DevOps engineers will shift further toward policy definition, architectural oversight, and AI governance rather than manual pipeline troubleshooting.
Final Perspective
The top 10 DevOps software platforms in the world in 2026 represent more than technical tools. They function as strategic enablers of digital transformation, economic resilience, and operational excellence. Organizations that approach DevOps platform selection as a long-term architectural investment rather than a short-term feature comparison are better positioned to compete in an increasingly software-defined economy.
In this mature and rapidly evolving ecosystem, success is measured not simply by faster builds or more frequent deployments. It is defined by resilience, scalability, governance, economic discipline, and intelligent autonomy. The future of DevOps belongs to platforms that unify these dimensions into a cohesive, adaptive, and sustainable delivery engine for the modern enterprise.
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your hiring manager and C-level suite friends and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the 9cv9 Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.
To get access to top-quality guides, click over to 9cv9 Blog.
To hire top talents using our modern AI-powered recruitment agency, find out more at 9cv9 Modern AI-Powered Recruitment Agency.
People Also Ask
What are the top 10 DevOps software tools in the world in 2026?
The top 10 DevOps software in 2026 include leading platforms offering unified CI/CD, DevSecOps, AI automation, and cloud-native scalability for enterprises and startups.
Which DevOps platform is best for enterprises in 2026?
Enterprise DevOps platforms in 2026 prioritize governance, compliance, hybrid cloud support, and scalability to manage large teams and regulated environments.
What is the best DevOps tool for startups in 2026?
Startups prefer DevOps tools with serverless CI/CD, easy onboarding, AI-assisted coding, and pay-as-you-go pricing for fast and cost-efficient growth.
How is AI changing DevOps software in 2026?
AI enables predictive monitoring, automated rollbacks, security patching, and cost optimization, transforming DevOps from manual automation to autonomous operations.
What features should I look for in DevOps software in 2026?
Key features include CI/CD automation, integrated security, AI-driven insights, artifact management, scalability, compliance controls, and cost transparency.
What is DevSecOps and why is it important in 2026?
DevSecOps embeds security directly into development pipelines, reducing vulnerabilities early and ensuring compliance across cloud and hybrid environments.
Are unified DevOps platforms better than multiple tools?
Unified DevOps platforms reduce integration complexity, improve visibility, and lower operational overhead compared to fragmented toolchains.
How much does DevOps software cost in 2026?
DevOps software costs vary by tier and usage, with pricing models based on users, compute minutes, storage, and AI credits.
What is serverless DevOps in 2026?
Serverless DevOps removes infrastructure management by running CI/CD workflows on managed cloud services, reducing operational effort.
Which DevOps tools support Kubernetes natively?
Most top DevOps platforms in 2026 provide Kubernetes-native integration for container orchestration and scalable deployments.
What is the role of platform engineering in DevOps?
Platform engineering standardizes development workflows through internal developer platforms, reducing setup time and operational complexity.
How do DevOps tools improve deployment frequency?
Automated pipelines, AI validation, and containerized workflows enable multiple deployments per day with minimal manual intervention.
What are DORA metrics in DevOps?
DORA metrics measure deployment frequency, lead time, MTTR, and change failure rate to assess DevOps performance.
Is DevOps software suitable for small businesses?
Yes, modern DevOps tools offer scalable pricing and simplified workflows designed for SMEs and growing startups.
How does DevOps software improve MTTR?
AI monitoring and automated rollback capabilities reduce incident resolution time and improve system resilience.
What is artifact management in DevOps?
Artifact management stores and distributes build outputs like binaries and containers, ensuring consistency across environments.
How does FinOps relate to DevOps in 2026?
FinOps integrates financial governance into DevOps to optimize cloud spending and monitor consumption-based costs.
What is GreenOps in DevOps platforms?
GreenOps focuses on carbon-efficient computing, enabling teams to track and reduce environmental impact in cloud deployments.
Can DevOps tools handle multi-cloud environments?
Leading DevOps platforms in 2026 provide hybrid and multi-cloud orchestration with centralized governance.
What is agentic AI in DevOps?
Agentic AI systems autonomously detect issues, optimize resources, and execute remediation workflows without manual intervention.
How do DevOps tools support compliance in regulated industries?
They automate audit trails, enforce policy-as-code, and integrate security scanning into CI/CD pipelines.
What is the difference between CI and CD?
Continuous Integration automates code testing and builds, while Continuous Deployment automates release to production.
Which DevOps software offers the best developer experience?
Platforms emphasizing intuitive UI, Git integration, AI assistance, and fast onboarding rank highest for developer experience.
How scalable are modern DevOps platforms?
Top DevOps software supports thousands of pipelines, distributed teams, and global cloud infrastructure.
What industries benefit most from DevOps in 2026?
Finance, healthcare, manufacturing, and e-commerce see measurable gains in compliance, uptime, and release speed.
How does DevOps reduce operational toil?
Automation and AI-driven workflows eliminate repetitive tasks, reducing manual intervention and support tickets.
Is Jenkins still relevant in 2026?
Enterprise Jenkins-based platforms remain relevant for large organizations requiring deep customization and governance.
What is the future of DevOps software beyond 2026?
DevOps platforms are evolving toward fully autonomous, AI-driven systems with integrated cost and sustainability controls.
How do DevOps tools improve software quality?
Automated testing, security scanning, and AI-based validation ensure stable, reliable releases.
Why is choosing the right DevOps software critical in 2026?
The right platform impacts deployment speed, compliance, cost efficiency, and long-term scalability in a software-driven economy.
Sources
Mordor Intelligence
Forrester
RealVNC
Geeks Solutions
Fortune Business Insights
Spacelift
Technavio
Wildnet Edge
Khired Networks
GetDX
GitLab
Siit
Atlassian
Tekpon
Capterra
Gartner
GitHub
GitHub Docs
Microsoft Azure
MicroAge
Constellation Research
TrustRadius
G2
Amazon Web Services
Cloudomation
CircleCI
Google Cloud
Medium
DigitalOcean
GetApp
JFrog
CloudRepo
Gart Solutions
eSparkBiz
SkyQuest































![Writing A Good CV [6 Tips To Improve Your CV] 6 Tips To Improve Your CV](https://blog.9cv9.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/2020-06-02-2-100x70.png)


