Key Takeaways
- Enhanced Data Accuracy: Address Verification Software (AVS) ensures precise address data, minimizing errors in customer records and operational processes.
- Streamlined Operations: AVS automates address validation, optimizing workflows and improving efficiency across various industries.
- Future-proof Solutions: Embrace the evolving landscape of AVS, leveraging innovations like machine learning and blockchain for secure and efficient address verification.
In today’s hyper-connected digital landscape, accurate address data is the cornerstone of successful business operations across various industries.
Whether it’s ensuring timely deliveries, preventing fraudulent transactions, or complying with regulatory requirements, the importance of precise addresses cannot be overstated.
However, the sheer volume and complexity of address data pose significant challenges for businesses seeking to maintain data accuracy.
Enter Address Verification Software (AVS), a powerful solution designed to streamline address validation processes and enhance data quality.
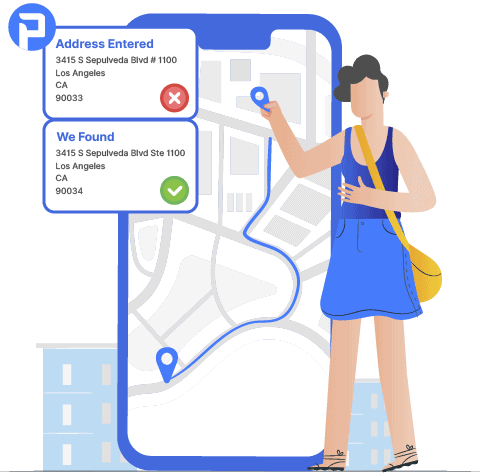
In this comprehensive guide, we delve deep into the world of address verification software, shedding light on its functionalities, benefits, and practical applications.
Understanding Address Verification Software
At its core, Address Verification Software (AVS) is a sophisticated toolset designed to standardize, validate, and enhance address data.
By leveraging advanced algorithms and data validation techniques, AVS ensures that address information is accurate, consistent, and up-to-date.
This not only improves operational efficiency but also minimizes errors and mitigates risks associated with inaccurate addresses.
How Address Verification Software Works
Address Verification Software operates through a multi-step process that begins with data collection from various sources such as customer input forms, databases, and third-party data providers.
Once the data is collected, AVS employs a series of validation techniques including address standardization, validation, geocoding, and mapping to ensure data accuracy and completeness.
Furthermore, AVS seamlessly integrates with existing systems and workflows, allowing businesses to incorporate address verification into their operations with ease.
Features and Capabilities of Address Verification Software
Address Verification Software offers a plethora of features and capabilities designed to meet the diverse needs of businesses across industries.
From real-time address validation and batch processing to international address verification and customizable options, AVS provides a comprehensive solution for addressing data quality challenges.
Additionally, advanced reporting and analytics functionalities offer valuable insights into address data, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and optimize their processes.
Use Cases and Applications
The versatility of Address Verification Software makes it applicable across a wide range of industries and use cases.
Whether it’s e-commerce and online retail, financial services and banking, logistics and supply chain management, or government and public services, AVS plays a crucial role in enhancing operational efficiency, improving customer experience, and reducing costs.
From address validation during checkout processes to address cleansing in CRM systems, the applications of AVS are limitless.
Challenges and Considerations
While Address Verification Software offers numerous benefits, businesses must also be aware of potential challenges and considerations associated with its implementation.
Data privacy and security concerns, handling of incomplete or ambiguous addresses, integration complexities with legacy systems, and cost considerations are some of the key factors that businesses need to address when deploying AVS.
Best Practices for Implementing Address Verification Software
To maximize the benefits of Address Verification Software, businesses should follow best practices for implementation.
This includes assessing business needs and goals, choosing the right AVS provider, conducting thorough testing and evaluation, training staff, and ensuring regular maintenance and updates.
By following these best practices, businesses can ensure a smooth and successful deployment of AVS.
Future Trends and Innovations
Looking ahead, the future of Address Verification Software is bright, with emerging trends and innovations poised to further enhance its capabilities.
Advancements in machine learning and AI, integration with IoT and smart city initiatives, blockchain technology for secure address verification, and predictive analytics for address accuracy forecasting are just a few of the exciting developments on the horizon.
Address Verification Software represents a powerful solution for businesses seeking to maintain data accuracy, streamline operations, and stay ahead in today’s competitive marketplace.
By understanding the functionalities, benefits, and best practices associated with AVS, businesses can unlock new levels of efficiency and productivity while delivering exceptional customer experiences.
Join us as we embark on a journey to explore the world of Address Verification Software and discover its transformative potential.
Before we venture further into this article, we like to share who we are and what we do.
About 9cv9
9cv9 is a business tech startup based in Singapore and Asia, with a strong presence all over the world.
With over eight years of startup and business experience, and being highly involved in connecting with thousands of companies and startups, the 9cv9 team has listed some important learning points in this overview of What is Address Verification Software and How It Works.
If your company needs recruitment and headhunting services to hire top-quality employees, you can use 9cv9 headhunting and recruitment services to hire top talents and candidates. Find out more here, or send over an email to [email protected].
Or just post 1 free job posting here at 9cv9 Hiring Portal in under 10 minutes.
What is Address Verification Software and How It Works
- Understanding Address Verification Software
- How Address Verification Software Works
- Features and Capabilities of Address Verification Software
- Use Cases and Applications
- Challenges and Considerations
- Best Practices for Implementing Address Verification Software
- Future Trends and Innovations
1. Understanding Address Verification Software
In the digital age, the accuracy of address data is crucial for businesses across various sectors, from e-commerce giants to financial institutions and logistics companies.
Address Verification Software (AVS) emerges as a pivotal tool in ensuring data quality and operational efficiency. Let’s delve deep into what Address Verification Software is and how it works.

What is Address Verification Software (AVS)?
- Definition: AVS is a sophisticated software solution designed to validate, standardize, and enhance address data to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Importance: Inaccurate addresses can lead to undelivered packages, failed transactions, and compliance issues, costing businesses time and money.
- Functionality: AVS employs advanced algorithms and validation techniques to verify the authenticity and correctness of address information.
Key Components of Address Verification Software:
- Data Collection:
- AVS collects address data from various sources, including customer input forms, databases, and third-party data providers.
- Example: An e-commerce platform captures address information during the checkout process.
- Address Standardization:
- AVS standardizes address formats to ensure consistency and uniformity across different datasets.
- Example: Converting “St.” to “Street” and “Ave” to “Avenue” to maintain a standardized format.
- Address Validation:
- AVS verifies the accuracy and existence of addresses by cross-referencing them with authoritative databases.
- Example: Checking whether a given address matches the official postal records.
- Geocoding and Mapping:
- AVS enhances spatial accuracy by assigning geographic coordinates to addresses and visualizing them on maps.
- Example: Plotting delivery routes based on geocoded addresses to optimize logistics operations.
- Integration with Existing Systems:
- AVS seamlessly integrates with CRM, ERP, and other business systems to automate address verification processes.
- Example: Automatically validating addresses entered into a customer relationship management (CRM) system.
Benefits of Address Verification Software:
- Improved Data Quality: AVS ensures that address data is accurate, consistent, and up-to-date, leading to better decision-making and operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: By minimizing errors in address data, AVS helps businesses deliver products and services promptly, enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Cost Reduction: Preventing failed deliveries, fraudulent transactions, and compliance penalties saves businesses money in the long run.
- Streamlined Operations: Automation of address validation processes reduces manual effort and speeds up workflows, allowing businesses to focus on core activities.
Real-Life Applications of Address Verification Software:
- E-commerce and Retail: AVS ensures accurate delivery addresses, reduces shipping errors, and enhances the overall shopping experience for customers.
- Example: An online retailer uses AVS to validate shipping addresses before processing orders, minimizing delivery delays.
- Financial Services: Banks and financial institutions utilize AVS to verify customer addresses for identity verification and fraud prevention purposes.
- Example: A bank validates the address provided by a customer during account opening to ensure compliance with Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Management: AVS optimizes route planning, reduces delivery costs, and improves delivery accuracy for logistics companies.
- Example: A courier service uses AVS to geocode addresses and optimize delivery routes, reducing fuel consumption and vehicle wear and tear.
- Government and Public Services: Government agencies use AVS to maintain accurate address databases for census, taxation, and emergency response purposes.
- Example: A municipality utilizes AVS to validate addresses in its database before sending out property tax bills to residents.
Address Verification Software is a vital tool for businesses seeking to maintain data accuracy, streamline operations, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
By understanding its functionalities, benefits, and real-life applications, businesses can leverage AVS to stay competitive in today’s fast-paced digital world.
2. How Address Verification Software Works
Address Verification Software (AVS) operates through a systematic process aimed at validating, standardizing, and enhancing address data to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Let’s explore the intricacies of how AVS functions and its key components.
Data Collection:
- Sources: AVS collects address data from various sources, including:
- Customer input forms on websites and mobile apps.
- Databases containing customer records and transactional data.
- Third-party data providers offering access to comprehensive address databases.
- Example: An e-commerce platform captures shipping addresses entered by customers during the checkout process.

Address Standardization:
- Uniform Format: AVS standardizes address formats to ensure consistency and adherence to postal guidelines.
- Correction of Abbreviations: Converts abbreviated terms such as “St.” to “Street” and “Ave” to “Avenue” for uniformity.
- Example: Transforming “123 Main St.” to “123 Main Street” to maintain a standardized format across all records.
Address Validation:
- Verification Algorithms: AVS utilizes sophisticated algorithms to verify the accuracy and existence of addresses.
- Cross-Referencing: Compares address data against authoritative databases, such as postal records and geographic information systems (GIS).
- Example: Checking whether the address “1600 Amphitheatre Parkway, Mountain View, CA” matches the official records maintained by the United States Postal Service.
Geocoding and Mapping:
- Geographic Coordinates: AVS assigns latitude and longitude coordinates to addresses for precise location identification.
- Mapping Integration: Visualizes addresses on maps to facilitate route planning, spatial analysis, and visualization.
- Example: Plotting customer addresses on a map to optimize delivery routes for a logistics company, reducing travel time and fuel costs.
Integration with Existing Systems:
- Seamless Integration: AVS integrates with CRM, ERP, and other business systems to automate address verification processes.
- Real-Time Validation: Validates addresses in real-time as they are entered into customer-facing or internal systems.
- Example: Automatically verifying addresses entered by customers during account registration in a banking application, ensuring data accuracy and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Batch Processing:
- Scalability: AVS supports batch processing for large volumes of address data, enabling efficient validation of entire datasets.
- Scheduled Processing: Allows businesses to schedule address validation jobs at regular intervals to keep data up-to-date.
- Example: A retail chain uploads a spreadsheet containing thousands of customer addresses for batch processing to ensure data accuracy before launching a marketing campaign.
Reporting and Analytics:
- Insights: AVS provides reporting and analytics capabilities to track address validation results and identify trends.
- Data Quality Metrics: Metrics such as accuracy rates and error frequencies help businesses assess the quality of their address data.
- Example: Generating a monthly report highlighting the percentage of addresses validated successfully and identifying areas for improvement in data quality processes.
Address Verification Software operates through a comprehensive process encompassing data collection, standardization, validation, geocoding, mapping, integration, batch processing, and reporting.
By leveraging advanced algorithms and integration capabilities, AVS ensures that businesses maintain accurate and reliable address data, leading to improved operational efficiency, enhanced customer experiences, and better decision-making.
3. Features and Capabilities of Address Verification Software
Address Verification Software (AVS) offers a wide array of features and capabilities designed to enhance data quality and streamline address validation processes.
Let’s explore the key features that make AVS indispensable for businesses across various industries.
Real-time Address Validation:
- Instant Verification: AVS validates addresses in real-time as they are entered into web forms, applications, or databases.
- Immediate Feedback: Provides instant feedback to users, alerting them to any errors or discrepancies in the address data.
- Example: An e-commerce website verifies the shipping address entered by a customer during the checkout process, ensuring accuracy and reducing the risk of delivery errors.
Batch Processing for Large Datasets:
- Scalability: AVS supports batch processing, allowing businesses to validate large volumes of address data efficiently.
- Automated Processing: Batch processing enables businesses to upload entire datasets for validation without manual intervention.
- Example: A marketing agency uploads a list of customer addresses for a direct mail campaign, ensuring that all addresses are validated before sending out promotional materials.
International Address Verification:
- Global Coverage: AVS supports address validation for international addresses across multiple countries and regions.
- Localized Data: Utilizes country-specific address formats and postal standards to ensure accurate validation.
- Example: An international e-commerce platform verifies addresses from customers worldwide, including different countries with diverse address formats and postal regulations.
Customization Options and Flexibility:
- Configurable Rules: AVS allows businesses to customize validation rules and criteria based on their specific requirements.
- Address Formats: Supports customization of address formats to accommodate regional variations and specific business needs.
- Example: A shipping company configures AVS to prioritize certain address validation criteria based on delivery routes and service level agreements with customers.
Reporting and Analytics:
- Insights: AVS provides reporting and analytics tools to track address validation results and performance metrics.
- Data Quality Metrics: Metrics such as validation success rates, error frequencies, and address completeness help businesses assess and improve data quality.
- Example: A logistics company generates monthly reports to monitor the accuracy of address data, identify trends, and optimize delivery operations based on analytics insights.
Integration with Existing Systems:
- Seamless Integration: AVS integrates with CRM, ERP, e-commerce platforms, and other business systems to automate address validation processes.
- API Integration: Provides API integration for easy incorporation into existing workflows and applications.
- Example: An insurance company integrates AVS with its customer management system to validate addresses during policy applications, ensuring accurate customer records and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Address Verification Software offers a rich set of features and capabilities designed to meet the diverse needs of businesses seeking to maintain data accuracy and streamline address validation processes.
Whether it’s real-time validation, batch processing, international address support, customization options, reporting and analytics, or seamless integration, AVS empowers businesses to enhance operational efficiency, improve customer experiences, and make informed decisions based on accurate address data.
4. Use Cases and Applications
Address Verification Software (AVS) finds applications across diverse industries, playing a crucial role in enhancing data accuracy, improving operational efficiency, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Let’s explore some key use cases and real-world applications of AVS:
E-commerce and Online Retail:
- Shipping Address Verification: AVS validates shipping addresses entered by customers during the checkout process, reducing delivery errors and ensuring timely order fulfillment.
- Example: An online retailer uses AVS to verify the accuracy of shipping addresses to prevent package misdeliveries and enhance the overall customer experience.
- Address Cleansing: AVS identifies and corrects inaccuracies in customer address data stored in e-commerce databases, improving data quality and reducing shipping delays.
- Example: An e-commerce platform runs regular address validation checks to cleanse and update customer address records, ensuring accurate shipping information for future orders.

Financial Services and Banking:
- Identity Verification: AVS verifies customer addresses during account opening and transaction processes to prevent identity theft and fraudulent activities.
- Example: A bank utilizes AVS to validate the addresses provided by customers during account registration, ensuring compliance with Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations.
- Risk Management: AVS helps financial institutions assess the risk associated with customer addresses by detecting inconsistencies and irregularities in address data.
- Example: An insurance company employs AVS to evaluate the risk associated with insuring properties based on the accuracy and location of the addresses provided by policyholders.
Logistics and Supply Chain Management:
- Route Optimization: AVS optimizes delivery routes by validating addresses, geocoding them, and identifying the most efficient routes for transportation.
- Example: A logistics company uses AVS to geocode delivery addresses and optimize delivery routes, reducing fuel costs and improving delivery efficiency.
- Inventory Management: AVS ensures accurate address data for warehouse locations and distribution centers, facilitating efficient inventory management and order fulfillment.
- Example: A retail chain utilizes AVS to validate and standardize addresses for its warehouse locations, enabling accurate inventory tracking and management.
Government and Public Services:
- Census and Demographic Analysis: AVS assists government agencies in validating addresses for census purposes and analyzing demographic data.
- Example: A national statistical office uses AVS to validate addresses collected during the census enumeration process, ensuring accurate population counts and demographic analysis.
- Emergency Response: AVS enables emergency services to validate and locate addresses quickly during emergency situations, such as natural disasters or medical emergencies.
- Example: A fire department utilizes AVS to validate addresses and ensure prompt response times during emergency calls for fire and rescue operations.
Healthcare and Pharmaceutical:
- Patient Data Management: AVS validates patient addresses in healthcare systems to ensure accurate medical records and facilitate communication with patients.
- Example: A hospital utilizes AVS to verify patient addresses during registration and appointment scheduling, reducing communication errors and improving patient care.
- Prescription Delivery: AVS validates patient addresses for prescription delivery services, ensuring accurate medication deliveries and patient satisfaction.
- Example: A pharmacy chain uses AVS to verify patient addresses before shipping prescription medications, minimizing delivery errors and ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations.
Address Verification Software offers versatile solutions for a wide range of industries and use cases, including e-commerce, financial services, logistics, government, healthcare, and more.
By leveraging AVS, businesses and organizations can enhance data accuracy, improve operational efficiency, mitigate risks, and deliver superior customer experiences across various touchpoints.
Stay tuned as we delve deeper into the transformative impact of AVS in addressing the diverse needs of businesses worldwide.
5. Challenges and Considerations
Address Verification Software (AVS) offers numerous benefits, but businesses must also navigate various challenges and considerations when implementing and using this technology.
Let’s explore some of the key challenges and considerations associated with AVS:
Data Privacy and Security Concerns:
- Sensitive Information: AVS processes sensitive address data, raising concerns about data privacy and security.
- Example: An e-commerce platform must ensure that customer address data is encrypted and protected against unauthorized access to comply with data protection regulations like GDPR.
- Third-party Data Providers: AVS may rely on third-party data providers for address validation, posing risks related to data ownership and compliance.
- Example: A financial institution must carefully evaluate the privacy policies and data security measures of third-party AVS providers before integrating their services.
Handling of Incomplete or Ambiguous Addresses:
- Data Completeness: AVS may struggle to validate addresses that are incomplete or contain missing information, leading to validation errors.
- Example: An online form with missing apartment numbers or incorrect street names may result in failed address validation, requiring manual intervention to correct.
- Ambiguity in Address Data: AVS may encounter ambiguity in address data, such as similar street names or misspelled addresses, affecting validation accuracy.
- Example: Two streets with similar names (e.g., “Main Street” and “Main Avenue”) in the same area may cause confusion during address validation, requiring additional validation checks.
Integration Complexities with Legacy Systems:
- Legacy Systems Compatibility: Integrating AVS with legacy systems may pose challenges due to differences in data formats and compatibility issues.
- Example: An organization using outdated ERP software may face difficulties integrating AVS due to incompatible data formats, requiring custom development or middleware solutions.
- Data Migration: Migrating existing address data to AVS-compatible formats can be complex and time-consuming, requiring careful planning and execution.
- Example: A retail chain transitioning to a new AVS platform must ensure seamless migration of customer address data from legacy systems to maintain data integrity and continuity of operations.
Cost Considerations and ROI Analysis:
- Initial Investment: Implementing AVS requires upfront investment in software licenses, integration, training, and maintenance.
- Example: A small e-commerce startup must evaluate the initial cost of implementing AVS against the potential benefits in terms of improved data accuracy and operational efficiency.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Businesses need to assess the ROI of implementing AVS by quantifying the benefits in terms of cost savings, revenue generation, and customer satisfaction.
- Example: A logistics company measures the reduction in delivery errors and fuel costs achieved through AVS implementation to determine the ROI of the investment.
Address Verification Software offers valuable solutions for businesses seeking to enhance data accuracy and streamline address validation processes.
However, businesses must carefully consider and address challenges related to data privacy and security, handling of incomplete or ambiguous addresses, integration complexities with legacy systems, and cost considerations.
By proactively addressing these challenges and considerations, businesses can maximize the benefits of AVS while minimizing risks and ensuring successful implementation and utilization of this technology.
6. Best Practices for Implementing Address Verification Software
Implementing Address Verification Software (AVS) requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing management to maximize its benefits and ensure successful integration into existing business processes.
Here are some best practices to consider when implementing AVS:
Assessing Business Needs and Goals:
- Identify Use Cases: Understand the specific use cases and scenarios where AVS will be utilized within your organization.
- Example: A retail company may use AVS for validating shipping addresses during online orders and updating customer address records in the CRM system.
- Define Objectives: Clearly define the objectives and expected outcomes of implementing AVS, such as improving data accuracy, reducing delivery errors, or enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Example: An e-commerce platform aims to reduce shipping errors by 20% within the first six months of implementing AVS.
Choosing the Right AVS Provider:
- Evaluate Features: Assess the features, capabilities, and compatibility of different AVS providers to ensure they meet your business requirements.
- Example: Compare AVS providers based on real-time validation, batch processing, international address support, and integration options.
- Consider Data Quality: Evaluate the accuracy and reliability of address validation results provided by AVS providers to ensure high data quality standards.
- Example: Request sample validation reports from AVS providers and compare the accuracy rates and error frequencies of validated addresses.
Conducting Thorough Testing and Evaluation:
- Pilot Testing: Conduct pilot tests or trials of AVS with a small subset of address data to evaluate its effectiveness and performance.
- Example: Test AVS on a sample of customer addresses to assess its validation accuracy and identify any issues or limitations.
- User Feedback: Gather feedback from end-users and stakeholders during the testing phase to identify usability issues and areas for improvement.
- Example: Survey customer service representatives and logistics staff to gather feedback on the ease of use and effectiveness of AVS in their daily workflows.
Training Staff and Ensuring Adoption:
- Training Programs: Provide comprehensive training programs for staff members who will be using AVS to ensure they understand its features, functionalities, and best practices.
- Example: Conduct interactive training sessions for customer service representatives on how to use AVS for address validation during customer interactions.
- Promote Adoption: Encourage widespread adoption of AVS by highlighting its benefits, demonstrating its value through success stories, and incentivizing its use.
- Example: Recognize and reward employees who effectively use AVS to improve data accuracy and streamline address validation processes.
Regular Maintenance and Updates:
- Stay Up-to-date: Keep abreast of updates, patches, and new features released by the AVS provider to ensure optimal performance and data accuracy.
- Example: Schedule regular meetings with the AVS provider to discuss upcoming updates and enhancements and plan for their implementation.
- Monitor Performance: Continuously monitor the performance of AVS, track key metrics such as validation success rates and error frequencies, and address any issues promptly.
- Example: Set up automated alerts for validation failures and errors and assign dedicated staff members to investigate and resolve them in a timely manner.
Implementing Address Verification Software requires careful planning, evaluation, and ongoing management to ensure its successful integration and utilization within your organization.
By following best practices such as assessing business needs, choosing the right AVS provider, conducting thorough testing, training staff, and ensuring regular maintenance and updates, businesses can maximize the benefits of AVS and achieve their objectives of improving data accuracy, streamlining operations, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
7. Future Trends and Innovations
Address Verification Software (AVS) continues to evolve rapidly, driven by advancements in technology and changing business needs.
Let’s explore some of the future trends and innovations shaping the landscape of AVS:
Advancements in Machine Learning and AI:
- Predictive Address Verification: Machine learning algorithms can predict and verify addresses based on historical data patterns, reducing the need for manual validation.
- Example: An e-commerce platform uses AI-powered address verification to predict and validate addresses based on user behavior and historical order data.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP techniques can interpret and validate addresses entered in natural language format, improving accuracy and reducing errors.
- Example: An address validation system uses NLP to understand and validate addresses entered in free-text fields, such as customer feedback forms or online surveys.
Integration with IoT and Smart City Initiatives:
- Smart Address Validation: AVS integrates with Internet of Things (IoT) devices and smart city infrastructure to validate addresses in real-time based on location data.
- Example: Smart streetlights equipped with sensors validate addresses of nearby buildings and infrastructure, ensuring accuracy and enabling smart city applications.
- Geolocation-based Validation: AVS leverages GPS data from IoT devices to verify addresses and improve location accuracy, especially in remote or rural areas.
- Example: Delivery drones use GPS-enabled AVS to validate delivery addresses and navigate to precise locations for package delivery.
Blockchain Technology for Secure Address Verification:
- Immutable Records: Blockchain technology ensures the immutability and integrity of address validation records, enhancing security and trust.
- Example: A blockchain-based AVS platform stores address validation results on a decentralized ledger, providing tamper-proof records for auditing and compliance purposes.
- Decentralized Identity Verification: Blockchain enables decentralized identity verification, allowing individuals to control and verify their addresses securely without relying on centralized authorities.
- Example: Individuals use blockchain-based digital wallets to store and verify their addresses, providing a secure and privacy-enhanced method for identity verification.
Predictive Analytics for Address Accuracy Forecasting:
- Address Data Modeling: Predictive analytics models analyze historical address data to forecast address accuracy and identify potential errors or inconsistencies.
- Example: A logistics company uses predictive analytics to forecast address accuracy based on factors such as population density, infrastructure development, and historical delivery patterns.
- Error Prevention Strategies: Predictive analytics insights enable businesses to proactively implement error prevention strategies and address validation rules to minimize validation errors.
- Example: An e-commerce platform adjusts its address validation rules based on predictive analytics insights to prevent common errors and improve data accuracy during checkout.
The future of Address Verification Software is marked by exciting trends and innovations that promise to further enhance accuracy, efficiency, and security.
Advancements in machine learning and AI, integration with IoT and smart city initiatives, blockchain technology for secure address verification, and predictive analytics for address accuracy forecasting are just some of the key trends shaping the future of AVS.
By embracing these innovations, businesses can stay ahead of the curve and unlock new opportunities for improving data quality, optimizing operations, and delivering superior customer experiences.
Conclusion
Address Verification Software (AVS) stands as a cornerstone technology in the ever-evolving landscape of data management and operational efficiency.
Throughout this comprehensive exploration of AVS, we’ve uncovered its intricacies, functionalities, and transformative potential across various industries.
From its fundamental role in validating, standardizing, and enhancing address data to its practical applications in e-commerce, financial services, logistics, government, healthcare, and beyond, AVS emerges as a powerful solution for businesses seeking to maintain data accuracy and streamline operations.
We’ve delved into the key components of AVS, including real-time address validation, batch processing, international address support, customization options, reporting and analytics, and seamless integration with existing systems.
These features empower businesses to enhance data quality, improve customer experiences, and make informed decisions based on accurate address data.
Moreover, we’ve explored the challenges and considerations associated with implementing AVS, from data privacy and security concerns to handling incomplete or ambiguous addresses, integration complexities, and cost considerations.
By proactively addressing these challenges and following best practices such as assessing business needs, choosing the right AVS provider, conducting thorough testing, training staff, and ensuring regular maintenance and updates, businesses can maximize the benefits of AVS while minimizing risks.
Looking ahead, the future of AVS is marked by exciting trends and innovations, including advancements in machine learning and AI, integration with IoT and smart city initiatives, blockchain technology for secure address verification, and predictive analytics for address accuracy forecasting.
These developments promise to further enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and security of AVS, enabling businesses to stay ahead of the curve and unlock new opportunities for growth and innovation.
In essence, Address Verification Software represents not just a tool for data validation, but a catalyst for organizational excellence, enabling businesses to navigate the complexities of the modern digital landscape with confidence and precision.
As businesses continue to harness the transformative power of AVS, they will undoubtedly pave the way for a future defined by data-driven insights, operational efficiency, and unparalleled customer experiences.
If your company needs HR, hiring, or corporate services, you can use 9cv9 hiring and recruitment services. Book a consultation slot here, or send over an email to [email protected].
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your hiring manager and C-level suite friends and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the 9cv9 Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.
To get access to top-quality guides, click over to 9cv9 Blog.
People Also Ask
What are the key components of Address Verification Software?
Address Verification Software comprises data collection, standardization, validation, geocoding, mapping, and integration functionalities.
How does Address Verification Software enhance data accuracy?
AVS employs advanced algorithms to validate and standardize address data, reducing errors and ensuring consistency across databases.
What industries benefit from Address Verification Software?
E-commerce, logistics, finance, healthcare, government, and retail sectors leverage AVS for improved operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
What role does real-time validation play in Address Verification Software?
Real-time validation instantly verifies addresses as they are entered, ensuring accuracy during customer transactions and data entry processes.
Can Address Verification Software handle international addresses?
Yes, AVS supports international address validation, accommodating diverse address formats and postal standards across countries and regions.
How does Address Verification Software integrate with existing systems?
AVS seamlessly integrates with CRM, ERP, e-commerce platforms, and other business systems, automating address validation processes.
What challenges should businesses consider when implementing Address Verification Software?
Data privacy, incomplete addresses, integration complexities, and cost considerations are key challenges businesses may encounter when implementing AVS.
What are the benefits of batch processing in Address Verification Software?
Batch processing allows businesses to validate large volumes of address data efficiently, ensuring data accuracy and compliance.
How does Address Verification Software contribute to cost reduction?
By minimizing errors and streamlining processes, AVS reduces costs associated with failed deliveries, fraudulent transactions, and manual data entry.
What future trends can we expect in Address Verification Software?
Advancements in machine learning, IoT integration, blockchain technology, and predictive analytics will shape the future of AVS, enhancing accuracy and efficiency.
Can Address Verification Software help with compliance requirements?
Yes, AVS assists businesses in complying with regulatory requirements by ensuring accurate address data and data privacy standards.
What are the customization options available in Address Verification Software?
AVS offers configurable validation rules, address formats, and integration options, allowing businesses to tailor the software to their specific needs.
How does Address Verification Software support inventory management?
By ensuring accurate addresses for warehouse locations and distribution centers, AVS facilitates efficient inventory tracking and order fulfillment.
What role does reporting and analytics play in Address Verification Software?
Reporting and analytics tools in AVS provide insights into address validation results, helping businesses track data quality metrics and make informed decisions.
How does Address Verification Software contribute to customer satisfaction?
By ensuring accurate deliveries, reducing shipping errors, and enhancing data quality, AVS improves customer experiences and builds trust.
Can Address Verification Software be used for emergency response purposes?
Yes, AVS assists emergency services in validating and locating addresses quickly during critical situations, such as natural disasters or medical emergencies.
What challenges does Address Verification Software face with incomplete addresses?
Incomplete addresses may pose validation challenges, requiring additional data validation techniques or manual intervention to ensure accuracy.
What are the security considerations when using Address Verification Software?
Businesses must prioritize data security and privacy when implementing AVS, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations and safeguarding customer information.
How does Address Verification Software contribute to fraud prevention?
By validating addresses and detecting inconsistencies, AVS helps businesses prevent fraudulent transactions and identity theft, reducing financial risks.
What role does machine learning play in the future of Address Verification Software?
Machine learning algorithms enable predictive address verification and continuous improvement of validation accuracy, driving innovation in AVS technology.































![Writing A Good CV [6 Tips To Improve Your CV] 6 Tips To Improve Your CV](https://blog.9cv9.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/2020-06-02-2-100x70.png)


