Key Takeaways
- SMART goals provide a structured framework for career growth by incorporating specificity, measurability, achievability, relevance, and time-bound deadlines.
- By setting SMART goals, professionals gain clarity, focus, and motivation, driving higher levels of performance and commitment.
- Implementing SMART goals aligns individual objectives with broader career aspirations, optimizing time management, resource allocation, and positioning professionals for advancements and new opportunities.
In today’s fast-paced and competitive work environment, professionals are constantly striving for growth and advancement in their careers. Whether you’re a fresh graduate embarking on your professional journey or an experienced employee looking to climb the corporate ladder, setting goals is paramount to achieving career success. However, not all goals are created equal. That’s where SMART goals come into play.
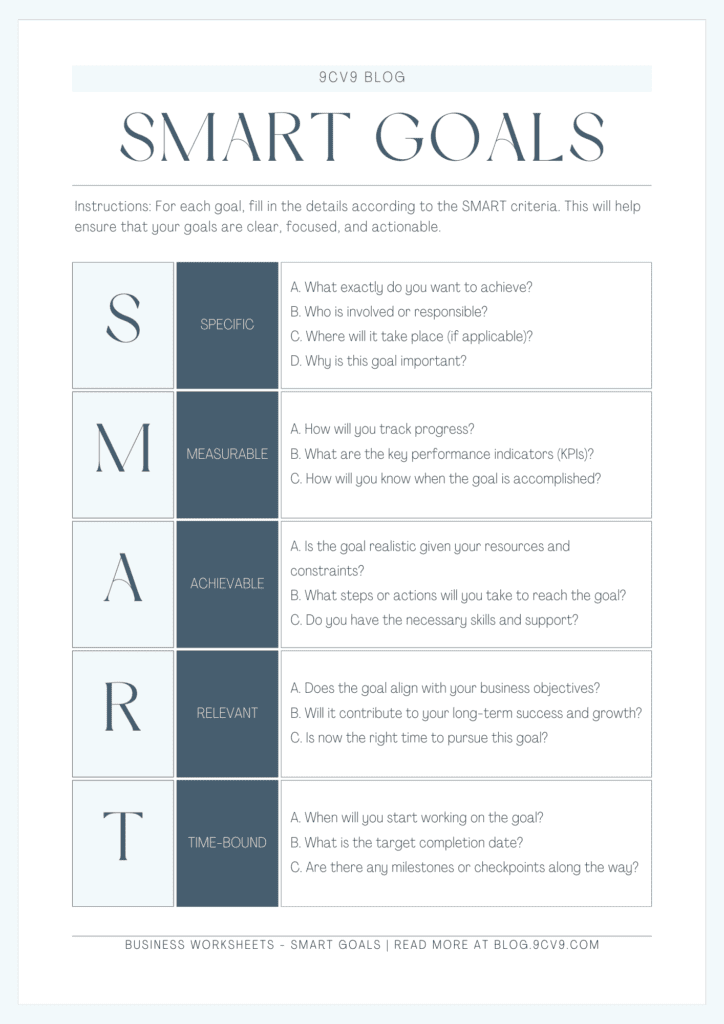
SMART goals, an acronym for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-Bound, have gained significant recognition as a powerful framework for goal setting and achievement. This approach provides a structured and strategic method to navigate the intricacies of career growth in the workplace.
This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the importance of SMART goals for career advancement and how they can revolutionize your professional journey. We will explore the numerous benefits of setting SMART goals, delve into their connection with professional development, discuss strategies for effective goal setting, and provide insights on overcoming common challenges along the way.
Why SMART Goals are Essential for Career Growth in the Workplace
- Benefits of SMART Goals for Career Growth
- SMART Goals and Professional Development
- Strategies for Setting SMART Goals in the Workplace
- Overcoming Challenges in Implementing SMART Goals
1. Benefits of SMART Goals for Career Growth

Setting SMART goals provides numerous benefits that are instrumental in driving career growth and success in the workplace.
By embracing this structured approach, professionals can unlock their full potential and achieve their professional aspirations.
Let’s explore the key benefits of SMART goals and understand how they contribute to career advancement.
- Improved Clarity and Focus: One of the primary advantages of setting SMART goals is the enhanced clarity and focus they bring to your career journey. SMART goals require specificity, meaning that they are clearly defined and leave no room for ambiguity. When you have a well-defined goal, such as “Increase sales by 20% within six months,” you gain a clear direction and purpose in your work. This clarity helps you prioritize tasks, make informed decisions, and stay focused on activities that align with your career objectives.
Example: Imagine you’re a marketing professional aiming for career growth. By setting a SMART goal like “Attain Google Analytics certification within three months,” you have a specific target to focus on. This goal not only enhances your skills but also demonstrates your commitment to professional growth, making you a valuable asset to your organization and boosting your chances of career advancement.
- Enhanced Performance and Motivation: SMART goals have a direct impact on performance and motivation levels in the workplace. When goals are specific and measurable, individuals can track their progress and see tangible results. The ability to measure progress and witness achievements fuels motivation and inspires individuals to strive for greater success. SMART goals provide a sense of purpose and a roadmap for personal growth, which ultimately leads to increased job satisfaction and productivity.
Example: Consider a sales representative who sets a SMART goal of “Secure 10 new clients by the end of the quarter.” This goal provides a clear target and enables the salesperson to monitor their progress. As they achieve milestones and witness their client base expanding, their motivation and confidence soar. This heightened motivation can drive them to surpass their initial goal and reach even greater heights in their sales career.
Also, if you are looking to find a remote sales role, our top guide “How to find a Remote or Hybrid Sales Role: A Comprehensive Guide” has got your back.
- Progress Tracking and Accountability: SMART goals incorporate the crucial elements of measurability and time-bound deadlines. These components enable individuals to track their progress effectively and hold themselves accountable. By setting measurable milestones and timelines, professionals can evaluate their achievements, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary adjustments to stay on track. Regular progress tracking promotes self-reflection and provides opportunities for course correction, leading to continuous growth and development.
Example: Suppose you aspire to become a project manager and set a SMART goal of “Lead at least two small-scale projects independently within six months.” Throughout the project timeline, you monitor your progress, milestones achieved, and lessons learned. This tracking allows you to showcase your project management skills and provides evidence of your ability to handle complex assignments. It also serves as a record of your accomplishments, which can be invaluable when seeking career advancement opportunities.
- Increased Alignment with Career Objectives: SMART goals require relevance, ensuring that your goals align with your broader career objectives. When your goals are in sync with your professional aspirations, they serve as stepping stones towards your desired career path. Setting relevant goals helps you make purposeful decisions, take on projects that contribute to your long-term objectives, and create opportunities for personal and professional growth.
Example: Let’s say you’re an aspiring human resources professional with a long-term goal of becoming an HR manager. To align with this objective, you set a SMART goal of “Complete a certification program in human resources within one year.” This goal not only enhances your knowledge and skills in your field but also positions you as a qualified candidate for future HR management roles. By setting relevant goals, you lay a solid foundation for your desired career trajectory.
Also, better yet, read up on our HR guide to be better at hiring.
- Enhanced Time Management and Resource Allocation: SMART goals require time-bound deadlines, which compel individuals to manage their time effectively. The time element in SMART goals acts as a catalyst for prioritization and efficient resource allocation. When you have specific timeframes for your goals, you can allocate resources, plan tasks, and organize your workflow accordingly. This level of time management fosters productivity, prevents procrastination, and optimizes your ability to meet deadlines.
Example: Suppose you’re an entrepreneur launching a new e-commerce venture. You set a SMART goal of “Build and launch the online store within three months.” With a clear deadline in mind, you can allocate resources, such as hiring web developers or organizing product inventory, to ensure timely execution. The time-bound nature of SMART goals drives you to utilize your time effectively, resulting in the successful launch of your online store and establishing a solid foundation for business growth.
SMART goals offer a multitude of benefits for career growth in the workplace.
They enhance clarity and focus, fuel motivation and performance, facilitate progress tracking and accountability, align with career objectives, and improve time management and resource allocation.
By embracing SMART goals, professionals can unlock their full potential, pave the way for continuous growth, and seize new opportunities for career advancement.
In addition, read our amazing guide on “How to Set Goals and Achieve Success in the Workplace”.
2. SMART Goals and Professional Development

SMART goals play a pivotal role in driving professional development and propelling individuals towards career success.
By utilizing this goal-setting framework, professionals can identify areas for improvement, enhance their skills, and expand their knowledge and expertise.
In this section, we will explore how SMART goals contribute to professional development and discuss specific ways in which they can be leveraged for growth.
- Skills Enhancement: Setting SMART goals allows individuals to focus on specific skills they want to improve or acquire. By identifying the skills that are most relevant to their career growth, professionals can set goals that target those areas. Whether it’s developing leadership abilities, enhancing technical expertise, or improving communication skills, SMART goals provide a structured approach for skill enhancement.
Example: Let’s say you’re a software engineer seeking career growth in the field of artificial intelligence. A SMART goal you could set is “Complete an online machine learning course and implement a machine learning model in a real-world project within six months.” This goal allows you to focus on enhancing your machine learning skills and gaining hands-on experience, both of which are essential for advancing your career in AI.
- Networking and Relationship Building: SMART goals can also be leveraged to foster networking and build valuable professional relationships. By setting goals that involve connecting with industry peers, attending relevant conferences or events, or actively engaging in online communities, professionals can expand their network and establish meaningful connections. These connections can provide mentorship opportunities, collaborations, and access to new career prospects.
Example: Suppose you’re a marketing professional aiming to expand your network in the digital marketing industry. A SMART goal you could set is “Attend three industry-specific conferences and connect with at least five industry leaders within the next year.” This goal prompts you to actively participate in networking events, engage in conversations, and establish connections with influential figures in your field. These relationships can open doors to new opportunities, such as job offers, partnerships, or speaking engagements.
- Promotions and Advancements: SMART goals play a crucial role in positioning individuals for promotions and career advancements. By setting goals aligned with the desired role or position, professionals can showcase their abilities, expertise, and commitment to growth. SMART goals demonstrate ambition, dedication, and a proactive approach, making individuals more attractive candidates for higher-level positions.
Example: Imagine you’re a sales manager aspiring to be promoted to a regional sales director role. A SMART goal you could set is “Achieve a 25% increase in regional sales revenue within the next fiscal year.” This goal not only highlights your leadership and strategic skills but also demonstrates your ability to drive tangible business results. By achieving this goal, you showcase your readiness for a higher-level role, increasing your chances of securing a promotion.
- Continuous Learning and Professional Growth: SMART goals promote a mindset of continuous learning and professional growth. By setting goals that require ongoing skill development, staying updated with industry trends, or acquiring new certifications, professionals can ensure they remain competitive and adaptable in their respective fields. SMART goals provide the framework for structured learning, enabling individuals to stay ahead in their careers.
Example: Suppose you’re a project manager looking to enhance your project management skills. A SMART goal you could set is “Complete a Project Management Professional (PMP) certification within the next nine months.” This goal compels you to engage in focused study, attend training courses, and pass the certification exam. By achieving this goal, you not only enhance your project management abilities but also demonstrate your commitment to professional growth and increase your marketability in the job market.
SMART goals are instrumental in driving professional development.
They enable individuals to enhance their skills, expand their network, position themselves for promotions and advancements, and foster a mindset of continuous learning.
By leveraging the power of SMART goals, professionals can navigate their career paths with purpose, constantly evolve, and seize new opportunities for growth and success.
3. Strategies for Setting SMART Goals in the Workplace

Setting SMART goals in the workplace is a strategic process that requires careful planning and consideration.
By employing effective strategies, professionals can ensure that their goals are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
In this section, we will explore practical strategies for setting SMART goals in the workplace and provide examples to illustrate their implementation.
- Specificity and Clarity: To set effective SMART goals, it is crucial to be specific and clear about what you want to achieve. Vague or general goals can lead to confusion and lack of focus. Instead, identify the precise outcome or objective you aim to accomplish. Be clear about the actions required and the expected results.
Strategy:
- Clearly define the goal: State exactly what you want to achieve, avoiding ambiguous language. For example, instead of saying “Improve customer satisfaction,” specify the goal as “Increase customer satisfaction ratings by 10% within six months.”
- Break it down: If the goal is complex, break it down into smaller, more manageable tasks. This allows for a clear understanding of the steps required to achieve the overall goal.
Example: Let’s say you’re a project manager working on a software development project. Instead of setting a vague goal like “Deliver a successful project,” a specific and clear goal would be “Complete the development phase, conduct thorough testing, and deliver a bug-free software solution within the specified timeline.”
- Measurability and Achievability: Measurable goals provide a way to track progress and determine success. It is important to establish criteria or metrics that can be objectively measured. Additionally, goals should be challenging yet realistic. Setting unattainable goals can lead to frustration and demotivation, while easily achievable goals may not push you to reach your full potential.
Strategy:
- Define metrics: Identify specific metrics or indicators that will be used to measure progress and success. This could include numbers, percentages, or other quantifiable measures.
- Assess feasibility: Consider the available resources, skills, and time required to achieve the goal. Ensure that the goal is achievable within the given constraints.
Example: Suppose you’re a sales representative aiming to increase your sales revenue. Instead of setting a general goal like “Increase sales,” a measurable and achievable goal would be “Achieve a 15% increase in sales revenue compared to the previous quarter by acquiring two new clients and upselling to existing clients.”
- Relevance and Time-Bound: SMART goals should be relevant to your career objectives and aligned with the broader goals of your organization. Additionally, goals should have a specific timeframe or deadline. Time-bound goals create a sense of urgency and help prioritize tasks.
Strategy:
- Align with career objectives: Ensure that your goals are relevant to your long-term career aspirations and contribute to your professional development.
- Set deadlines: Determine specific timelines for the completion of each goal. This helps maintain focus and accountability.
Example: Let’s consider a marketing manager who wants to enhance their digital marketing skills. A relevant and time-bound goal could be “Complete a Google Ads certification course within two months to develop advanced skills in online advertising and improve campaign performance.”
- Flexibility and Adaptability: While it is important to set specific goals, it is equally important to remain flexible and adaptable. Circumstances may change, and adjustments may be necessary along the way. Embrace a growth mindset that allows for modifications to goals as needed.
Strategy:
- Review and adjust: Regularly review your progress and reassess your goals. If necessary, make adjustments or modifications to accommodate changes in circumstances or priorities.
Example: Suppose you’re a human resources professional aiming to improve employee engagement. Initially, you set a goal to implement a new employee recognition program within three months. However, after receiving feedback from the team, you realize that a different approach is needed. In this case, it is important to be flexible and adapt your goal to align with the feedback and ultimately improve employee engagement.
Employing effective strategies is crucial for setting SMART goals in the workplace.
By being specific and clear, incorporating measurability and achievability, ensuring relevance and time-bound deadlines, and embracing flexibility, professionals can set goals that drive success, promote growth, and contribute to overall career advancement.
Utilize these strategies to empower yourself in setting SMART goals that propel your professional journey forward.
4. Overcoming Challenges in Implementing SMART Goals

Implementing SMART goals in the workplace comes with its fair share of challenges.
It’s important to acknowledge and address these challenges to ensure successful goal implementation and maximize the benefits of this goal-setting framework.
In this section, we will explore common challenges faced when implementing SMART goals and provide strategies to overcome them, along with relevant examples.
- Lack of Clarity or Direction: One of the key challenges in implementing SMART goals is a lack of clarity or direction. Without a clear understanding of the desired outcome or the steps required to achieve it, employees may struggle to set specific and actionable goals.
Strategy:
- Seek clarification: Engage in open and transparent communication with managers or team leaders to gain clarity on organizational goals, priorities, and expectations. This will help align individual goals with the broader objectives of the company.
- Collaborate with peers: Foster a collaborative environment where employees can share ideas, seek feedback, and work together to define specific goals that align with their roles and responsibilities.
Example: Imagine you’re a team member in a marketing department. The challenge lies in defining specific goals that contribute to the overall marketing strategy. By engaging in discussions with your team members and manager, you can gain a clear understanding of the marketing objectives and define individual SMART goals, such as “Increase website traffic by 20% through content marketing initiatives within six months.”
- Unrealistic or Overwhelming Goals: Setting goals that are unrealistic or overwhelming can lead to demotivation and a sense of failure. It is important to strike a balance between challenging goals and ones that are attainable within the given constraints.
Strategy:
- Break goals into smaller milestones: Divide larger goals into smaller, achievable milestones. This allows for a sense of progress and prevents employees from feeling overwhelmed.
- Set realistic timelines: Assess the available resources, workload, and other commitments to determine a realistic timeline for goal achievement.
Example: Suppose you’re a project manager tasked with implementing a new software system. Instead of setting an overwhelming goal like “Complete the entire project within two weeks,” break it down into smaller, realistic goals such as “Gather user requirements and finalize project scope within the first week.”
- Lack of Resources or Support: Implementing SMART goals requires adequate resources, support, and collaboration from stakeholders. Limited resources or a lack of support can hinder goal achievement and make the implementation process challenging.
Strategy:
- Communicate resource needs: Clearly communicate resource requirements to managers or relevant stakeholders. This includes requesting additional budget, tools, or personnel needed to accomplish the goals.
- Seek support and collaboration: Engage in open communication with colleagues and superiors to gain their support and collaboration. This can involve seeking assistance, delegating tasks, or forming cross-functional teams to achieve common goals.
Example: Let’s say you’re a sales representative aiming to expand into a new market. The challenge lies in accessing market research data and securing additional budget for marketing initiatives. By communicating the need for market research resources and presenting a compelling business case to management, you can overcome these challenges and receive the necessary support to achieve your SMART goals.
- Lack of Accountability and Monitoring: Without proper accountability and monitoring, SMART goals can lose their effectiveness. It’s crucial to establish mechanisms to track progress, provide feedback, and hold individuals accountable for goal achievement.
Strategy:
- Establish regular check-ins: Schedule periodic meetings or check-ins to review progress, discuss challenges, and provide feedback. This ensures that individuals stay on track and receive necessary guidance.
- Use technology tools: Leverage technology tools, such as project management software or goal-tracking apps, to monitor progress, set reminders, and maintain transparency.
Example: Suppose you’re a team leader responsible for a customer service team. Implement regular performance reviews or weekly team meetings where individuals can share their progress, discuss challenges, and receive feedback on their SMART goals. This creates a culture of accountability and keeps everyone focused on their objectives.
- Lack of Flexibility and Adaptability: Sometimes, unforeseen circumstances or changes in priorities may require adjustments to the initially set SMART goals. A lack of flexibility and adaptability can hinder progress and limit the effectiveness of goal implementation.
Strategy:
- Embrace agility: Foster a culture that encourages adaptability and flexibility. Encourage employees to reassess goals when necessary and make appropriate adjustments based on changing circumstances.
- Communicate changes: If modifications to goals are required, openly communicate the reasons and the revised expectations to all relevant stakeholders.
Example: Consider a software development team working on a project with evolving requirements. In such cases, it is important to embrace flexibility and allow for adjustments in the goals. By communicating changes and collaboratively revising the SMART goals to align with the evolving project scope, the team can ensure successful goal implementation.
Implementing SMART goals in the workplace may come with challenges, but with the right strategies in place, these challenges can be overcome.
By addressing issues related to clarity, setting realistic goals, securing necessary resources, establishing accountability, and embracing flexibility, organizations and individuals can navigate the implementation process effectively and reap the benefits of SMART goal-setting to drive success and growth.
Conclusion
SMART goals are essential for career growth in the workplace.
This goal-setting framework provides individuals with a structured approach to defining and achieving their career objectives.
By incorporating the principles of specificity, measurability, achievability, relevance, and time-bound deadlines, professionals can unlock their full potential and pave the way for continuous growth and success.
Through the benefits of SMART goals, individuals gain clarity and focus.
They know exactly what they want to achieve and can develop a roadmap to reach their desired outcomes. SMART goals fuel motivation and performance by providing a clear target to strive for, pushing individuals to challenge themselves and go beyond their comfort zones.
This sense of purpose drives productivity and commitment, resulting in higher levels of achievement.
Moreover, SMART goals facilitate progress tracking and accountability.
The ability to measure progress against specific metrics enables individuals to assess their performance and make necessary adjustments along the way.
Regular check-ins and feedback sessions provide opportunities for growth and development, ensuring that professionals stay on track towards their goals.
Aligning individual goals with broader career objectives is crucial for sustained career growth.
SMART goals allow professionals to make intentional choices that align with their long-term aspirations.
By setting goals that are relevant to their desired roles, industries, and personal growth, individuals can strategically position themselves for promotions, advancements, and new opportunities.
Effective time management and resource allocation are critical for career success, and SMART goals promote both.
By setting deadlines and establishing time-bound goals, professionals can optimize their time and prioritize tasks accordingly.
This level of time management prevents procrastination and ensures efficient utilization of resources, ultimately driving productivity and goal achievement.
While implementing SMART goals may come with its challenges, they can be overcome with the right strategies.
Through open communication, collaboration, and a growth mindset, individuals can address challenges such as lack of clarity, unrealistic goals, resource constraints, accountability, and the need for adaptability.
In today’s dynamic and competitive workplace, SMART goals provide a roadmap for individuals to navigate their career paths with purpose and intention.
By embracing this goal-setting framework, professionals can continuously improve their skills, expand their knowledge, build meaningful relationships, and position themselves for career growth and advancement.
In essence, SMART goals are not just a set of letters, but a powerful tool for unlocking the full potential of individuals in the workplace.
They provide the foundation for career growth, foster a culture of continuous learning and development, and empower professionals to seize new opportunities and achieve their professional aspirations.
So, take the first step today, set your SMART goals, and embark on a journey of growth, success, and fulfillment in your career.
If your company needs HR, hiring, or corporate services, you can use 9cv9 hiring and recruitment services. Book a consultation slot here, or send over an email to [email protected].
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your hiring manager and C-level suite friends and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the 9cv9 Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.
To get access to top-quality guides, click over to 9cv9 Blog.
People Also Ask
What are examples of SMART goals for work?
- Increase sales revenue by 10% in the next quarter through targeted marketing campaigns and enhanced customer retention strategies.
- Complete project XYZ within the specified timeline, delivering high-quality results while adhering to the allocated budget.
- Improve customer satisfaction ratings by 15% by implementing a comprehensive feedback system and addressing key pain points.
- Acquire three new major clients by the end of the year through proactive networking, targeted prospecting, and persuasive sales presentations.
- Enhance leadership skills by attending leadership development workshops and actively seeking opportunities to lead cross-functional projects.
What are the five SMART goals with examples?
- Specific: Increase website traffic by 20% within three months through content marketing and SEO optimization.
- Measurable: Achieve a customer satisfaction rating of 90% or higher based on post-purchase surveys by the end of the year.
- Achievable: Complete a professional certification program within six months by dedicating 10 hours per week for studying and coursework.
- Relevant: Increase social media engagement by 50% in order to strengthen brand awareness and drive customer interactions.
- Time-bound: Launch a new product by the end of Q3, following a defined product development timeline and conducting market research.
What is a SMART goal for leadership?
Develop effective communication skills by attending a leadership communication training course and implementing improved communication strategies within the team to enhance collaboration, trust, and overall team performance.































![Writing A Good CV [6 Tips To Improve Your CV] 6 Tips To Improve Your CV](https://blog.9cv9.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/2020-06-02-2-100x70.png)


