Key Takeaways
- Gender discrimination and harassment remain significant issues in the workplace, impacting many women’s professional lives.
- Organizations can take steps to address and prevent sexist behavior, such as developing clear policies, providing training and education, fostering a culture of inclusion, encouraging reporting, and holding perpetrators accountable.
- By creating a more equitable and respectful workplace, organizations can improve their business outcomes and contribute to a better future for women in the workplace.
Gender Discrimination in the workplace is a pervasive issue that affects individuals and organizations around the world.
Despite progress toward gender equality in recent years, many individuals still experience sexism and discrimination on the job.
From pay inequity to harassment, sexist behavior can take many forms and have serious consequences for those impacted.
To shed light on the prevalence of sexist behavior in the workplace, we’ve compiled a list of top statistics that you need to know.
These statistics highlight the challenges that individuals face when it comes to gender inequality at work and the importance of addressing these issues head-on.
From the gender pay gap to the prevalence of sexual harassment, these statistics reveal the harsh realities of sexism in the workplace.
They show that progress toward gender equality has been slow and that there is still much work to be done to create a more inclusive and equitable workplace for all.
Whether you’re an employer, employee, or simply someone who cares about social justice, understanding the statistics around sexist behavior in the workplace is crucial.
By raising awareness and taking action to address these issues, we can work towards a more just and equal world for all.
Before we venture further into this article, we like to share who we are and what we do.
About 9cv9
9cv9 is a business tech startup based in Singapore with a strong presence all over the world.
With over six years of startup and business experience, and being highly involved in connecting with thousands of companies and startups, the 9cv9 team has listed some important learning points in this overview of gender discrimination in the workplace statistics you need to know.
If your company needs recruitment and headhunting services, you can use 9cv9 headhunting and recruitment services to hire top talents and candidates. Find out more here, or send over an email to [email protected].
Gender Discrimination in the Workplace Statistics You Need to Know in 2023
- Females over 45 are nearly twice as likely to experience sexist behavior as compared to their younger counterparts
- 12% of females above 45 admitted to being impacted by sexist behaviors at work
- A further 5% of women have also experienced sexual harassment in the workplace
- Nearly a third (30%) of those females over 45 experience bullying in the workplace
- 21% experience inappropriate comments and 18% experience offensive comments
- Women hold 41 (8.2%) of CEO positions at those S&P 500 companies
- Women make up more than a quarter (28%) of all members of the 118th Congress
- About 42% of working women in the United States say they have faced discrimination on the job
- 38% of women in the technology field feel that gender discrimination staggers growth
- 60% of these women attribute not wanting to be a top executive to excessive stress and pressure
- One-in-four working women (25%) say they have earned less than a man who was doing the same job
- 23% of employed women say they have been treated as if they were not competent because of their gender
- 16% say they have experienced repeated small slights at work because of their gender
- 15% of working women say they have received less support from senior leaders than a man who was doing the same job
- 10% of women say they are passed over for the most important assignments because of their gender
1. Females over 45 are nearly twice as likely to experience sexist behavior as compared to their younger counterparts
(HR News)
Recent studies have revealed that age plays a significant role in the prevalence of sexist behavior in the workplace.
In particular, females over the age of 45 are nearly twice as likely to experience sexist behavior as compared to their younger counterparts.
This statistic highlights the fact that ageism and sexism are often intertwined, and that older women may face unique challenges in the workplace that are not faced by younger women.
There are several reasons why females over 45 may be more likely to experience sexist behavior in the workplace.
One factor may be that they are more likely to occupy positions of power or authority, which can make them targets of discrimination and harassment.
Additionally, older women may be perceived as less competent or less valuable than their younger colleagues, which can lead to unfair treatment and marginalization.
2. 12% of females above 45 admitted to being impacted by sexist behaviors at work
(HR News)
Firstly, as women age, they may face additional challenges in the workplace that are not faced by their younger counterparts.
For example, they may be more likely to be overlooked for promotions or opportunities, or they may be subjected to ageist or sexist comments from colleagues or superiors.
Additionally, as women age, they may be more likely to experience stereotypes or assumptions about their abilities or value to the organization.
Secondly, the intersection of age and gender can compound the impact of sexism in the workplace.
Thirdly, the fact that only 12% of females above 45 have admitted to being impacted by sexist behaviors at work may indicate a larger problem of underreporting.
Many individuals, particularly women, may feel uncomfortable reporting incidents of sexism or harassment due to fear of retaliation, disbelief, or a lack of support from their colleagues or superiors.
This can create a culture of silence that perpetuates the problem and makes it difficult to address.
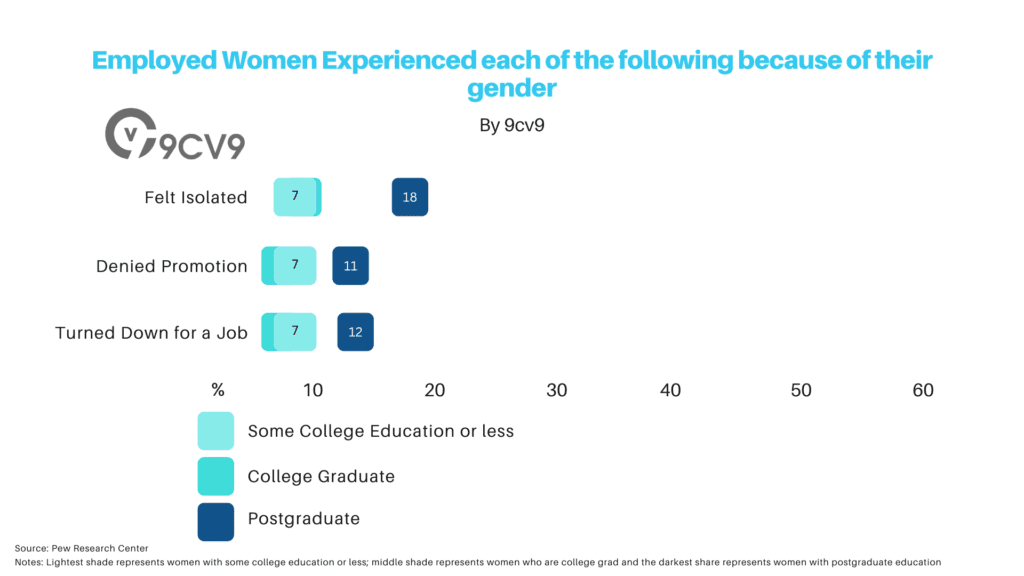
3. A further 5% of women have also experienced sexual harassment in the workplace
(HR News)
The fact that a further 5% of women have experienced sexual harassment in the workplace is a disturbing and troubling statistic.
Sexual harassment is a form of sexism and gender-based violence that can have serious physical, emotional, and professional consequences for the individuals who experience it.
Sexual harassment can take many forms, from unwanted touching and comments to sexual assault and coercion.
It is a violation of an individual’s rights and dignity and can create a hostile work environment that can be difficult to navigate.
There are several reasons why women may be more likely to experience sexual harassment in the workplace.
One factor may be the power dynamics that exist in many workplaces, with men often occupying positions of authority and influence.
This can create an environment where sexual harassment is tolerated or even normalized.
Additionally, social norms and stereotypes around gender can contribute to the prevalence of sexual harassment.
Women may be perceived as objects or sexual beings, rather than as professionals or colleagues, which can lead to inappropriate and harmful behavior.
The fact that a further 5% of women have experienced sexual harassment in the workplace underscores the need for employers to take proactive steps to prevent and address this issue.
This can include initiatives such as training on sexual harassment prevention, creating a reporting and response mechanism for incidents of harassment, and ensuring that all employees are aware of their rights and responsibilities.
4. Nearly a third (30%) of those females over 45 experience bullying in the workplace
(HR News)
The fact that nearly a third (30%) of females over the age of 45 experience bullying in the workplace is a deeply concerning and alarming statistic.
Workplace bullying can take many forms, including verbal abuse, intimidation, exclusion, and sabotage, and can have serious consequences for the mental and physical health of those who experience it.
There are several reasons why women over the age of 45 may be more likely to experience workplace bullying.
One factor may be ageism or discrimination based on age, which can create a hostile work environment for older workers. This can include being excluded from opportunities, subjected to negative stereotypes or assumptions, or facing microaggressions and other forms of disrespectful behavior.
Another factor may be sexism or discrimination based on gender, which can manifest as bullying or harassment in the workplace. Women may be perceived as less competent or valuable than their male colleagues or may be subjected to gender-based stereotypes or assumptions that contribute to a toxic work environment.
Additionally, women over the age of 45 may be more likely to be in positions of authority or leadership, which can make them targets of bullying from colleagues or subordinates who feel threatened by their success or expertise.
5. 21% experience inappropriate comments and 18% experience offensive comments
(HR News)
The fact that 21% of employees report experiencing inappropriate comments and 18% report experiencing offensive comments highlights the prevalence of workplace harassment and the urgent need for employers to take action to prevent and address this issue.
Inappropriate comments can take many forms, from sexist or racist jokes to unwelcome comments about an individual’s appearance or personal life.
These types of comments can contribute to a hostile work environment, making it difficult for employees to feel safe and comfortable in their jobs.
Offensive comments, meanwhile, can include derogatory or insulting remarks about an individual’s race, gender, sexual orientation, religion, or other personal characteristics.
These comments can be deeply hurtful and can contribute to a culture of discrimination and bias in the workplace.
6. Women hold 41 (8.2%) of CEO positions at those S&P 500 companies
(Catalyst)
The fact that women currently hold only 41 (8.2%) of CEO positions at S&P 500 companies is a sobering reminder of the persistent gender inequality that exists in corporate America.
Despite progress in recent years, women continue to be significantly underrepresented in leadership positions across industries, with the highest echelons of corporate leadership remaining stubbornly male-dominated.
There are several factors that contribute to the lack of women in CEO positions.
One of the most significant is gender bias, which can manifest in many different ways, from unconscious assumptions about leadership qualities to outright discrimination in hiring and promotion decisions.
Additionally, women face significant structural barriers to advancement in many organizations, including a lack of access to mentorship and sponsorship opportunities, implicit bias in performance evaluations and feedback, and a lack of support for work-life balance and caregiving responsibilities.
7. Women make up more than a quarter (28%) of all members of the 118th Congress
(Pew Research)
The fact that women make up more than a quarter (28%) of all members of the 118th Congress is a significant milestone for gender representation in politics.
While there is still a long way to go towards achieving gender parity in government, this progress is a step in the right direction toward creating a more inclusive and representative democracy.
Having more women in Congress brings diverse perspectives and experiences to the table, helping to ensure that policies and legislation take into account the needs and concerns of all Americans, regardless of gender.
This is particularly important when it comes to issues such as reproductive rights, equal pay, and access to healthcare, where women’s voices and perspectives have historically been underrepresented.
The fact that women now make up more than a quarter of Congress is a testament to the hard work and dedication of women leaders and advocates, as well as the broader movement for gender equality.
It is also a reminder that there is still much work to be done to achieve true gender parity in politics and other areas of society.
8. About 42% of working women in the United States say they have faced discrimination on the job
(Pew Research)
The fact that about four-in-ten working women (42%) in the United States say they have faced discrimination on the job highlights the ongoing challenges and barriers that women face in the workplace.
Discrimination can take many forms, including unequal pay, limited opportunities for advancement, sexual harassment, and bias and stereotyping based on gender or other personal characteristics.
The impact of discrimination can be profound, both on individuals and on society as a whole.
Women who experience discrimination may face lower wages, reduced career opportunities, and lower job satisfaction, while organizations that fail to address discrimination may suffer from decreased productivity, employee turnover, and reputational damage.
9. 38% of women in the technology field feel that gender discrimination staggers growth
(Women in Tech)
The fact that 38% of women in the technology field feel that gender discrimination staggers growth highlights the ongoing challenges and barriers that women face in this industry.
Despite progress in recent years, the technology field continues to be male-dominated, and women often face discrimination, bias, and microaggressions in the workplace.
This discrimination can take many forms, from unequal pay and limited opportunities for advancement to implicit bias in hiring and promotion decisions.
These barriers can have a significant impact on women’s career growth and advancement, as well as on their overall job satisfaction and well-being.
To address gender discrimination in the technology field, it is important for employers to take proactive steps to create a culture of inclusion and respect.
This can include initiatives such as diversity and inclusion training, policies and procedures to prevent and address discrimination and harassment, and transparent and fair hiring and promotion practices.
It is also important for women in the technology field to support each other and speak out against discrimination when it occurs.
This can include participating in mentorship and networking programs, joining advocacy organizations or support groups, and sharing their experiences and insights with others in the industry.
10. 60% of these women attribute not wanting to be a top executive to excessive stress and pressure
(Fintech Finance News)
The fact that 60% of these women attribute not wanting to be a top executive to excessive stress and pressure highlights the challenges and trade-offs that women in leadership positions often face.
While women have made progress in breaking through the glass ceiling and reaching high-level positions in many industries, the demands and expectations of these roles can be daunting and overwhelming.
Leadership positions often require long hours, high levels of responsibility, and intense pressure to perform.
This can create significant stress and burnout, particularly for women who may also be juggling family responsibilities and other obligations outside of work.
To address these challenges, it is important for employers to prioritize work-life balance and support the well-being of their employees, particularly those in leadership positions.
This can include initiatives such as flexible scheduling, telecommuting options, and mental health support programs.
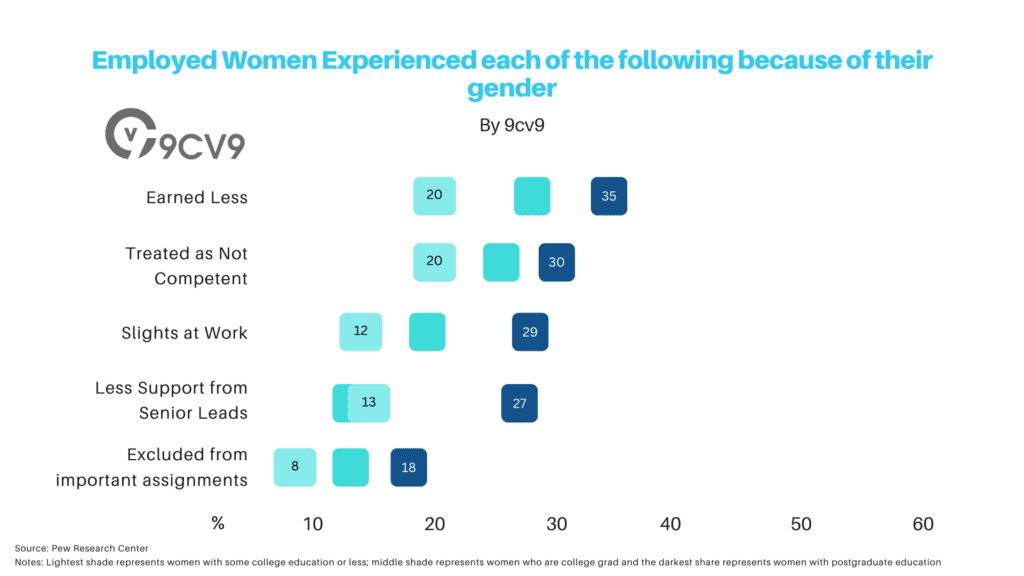
11. One-in-four working women (25%) say they have earned less than a man who was doing the same job
(Pew Research)
On the contrary, one-in-twenty working men (5%) say they have earned less than a female peer.
The fact that one-in-four working women (25%) say they have earned less than a man who was doing the same job highlights the persistent gender pay gap that exists in many industries and workplaces.
Despite progress in recent years, women continue to earn less than men on average, even when they hold the same jobs and possess the same qualifications and experience.
This gender pay gap can have significant impacts on women’s financial security and overall well-being, as well as on the broader economy and society as a whole.
When women are paid less than men for doing the same work, it undermines the principles of fairness and equality that are fundamental to a just and democratic society.
12. 23% of employed women say they have been treated as if they were not competent because of their gender
(Pew Research)
The fact that 23% of employed women say they have been treated as if they were not competent because of their gender highlights the persistence of gender stereotypes and bias in many workplaces.
These stereotypes can create significant barriers for women in achieving their full potential and advancing in their careers, even when they possess the skills, knowledge, and experience necessary to succeed.
On the contrary, only 6% of men say they have been treated as if they were not competent because of their gender, showing a difference of around 4 times between the sexes.
When women are treated as if they are not competent or are subject to other forms of gender-based bias and discrimination, it can have a profound impact on their self-esteem, confidence, and motivation.
It can also limit their opportunities for advancement and contribute to a workplace culture that is hostile or unwelcoming to women.
13. 16% say they have experienced repeated small slights at work because of their gender
(Pew Research)
The fact that 16% of women say they have experienced repeated small slights at work because of their gender highlights the insidious nature of gender bias and discrimination in the workplace.
These small slights, also known as microaggressions, can include comments, gestures, or behaviors that are subtle but still convey bias or prejudice.
On the contrary, only 5% of men say they have been treated as if they were not competent because of their gender, showing a difference of around 3 times between the sexes.
While these slights may seem small in isolation, they can add up over time and create a hostile or unwelcoming environment for women in the workplace.
They can also contribute to feelings of isolation, frustration, and dissatisfaction, which can ultimately impact women’s job performance and career advancement.
14. 15% of working women say they have received less support from senior leaders than a man who was doing the same job
(Pew Research)
The fact that 15% of working women say they have received less support from senior leaders than a man who was doing the same job highlights the persistent gender bias and discrimination that exists in many workplaces.
When women are denied the same level of support as their male counterparts, it can hinder their ability to perform at their best and advance in their careers.
On the contrary, only 7% of men say they have been treated as if they were not competent because of their gender, showing a difference of around 2 times between the sexes.
The lack of support from senior leaders can take many forms, such as fewer opportunities for mentorship or sponsorship, lower salaries, or being passed over for promotion in favor of male colleagues.
This can create a demoralizing and demotivating environment for women, making it difficult for them to thrive and succeed.
15. 10% of women say they are passed over for the most important assignments because of their gender
(Pew Research)
The fact that 10% of women say they are passed over for the most important assignments because of their gender highlights the ongoing issue of gender bias and discrimination in the workplace.
When women are not given the same opportunities as men to work on high-profile projects or to take on leadership roles, it can hinder their ability to advance in their careers and reach their full potential.
On the contrary, only 5% of men say they have been treated as if they were not competent because of their gender, showing a difference of around 2 times between the sexes.
There are many reasons why women may be passed over for important assignments due to their gender.
For example, some managers may have unconscious biases that lead them to view men as more capable or competent than women, even if this is not the case.
Additionally, women may be seen as less committed to their careers if they have caregiving responsibilities or if they take time off to have children, which can result in them being overlooked for important assignments.
Consequences of Gender Discrimination in the Workplace
Gender Discrimination in the workplace can have a range of negative consequences for those who experience it, as well as for organizations as a whole.
Some of the consequences of Gender Discrimination in the workplace may include:
- Decreased job satisfaction: Women who experience sexist behavior in the workplace may feel undervalued, disrespected, and unsupported, which can lead to decreased job satisfaction and motivation.
- Increased turnover: When women feel that they are not respected or valued in their workplace, they may be more likely to leave their jobs, leading to increased turnover and higher recruitment costs for the organization.
- Decreased productivity: Women who are subjected to sexist behavior may be less productive as a result of stress, anxiety, and decreased motivation.
- Damage to organizational reputation: If instances of sexist behavior become public, it can damage the reputation of the organization, leading to decreased trust and support from customers, investors, and the general public.
- Legal consequences: In some cases, sexist behavior in the workplace can lead to legal consequences, such as discrimination lawsuits or fines for non-compliance with workplace harassment laws.
It is important for organizations to take a proactive approach to address and prevent sexist behavior in the workplace.
This can include implementing policies and procedures to address harassment and discrimination, providing training and education to employees and managers, and creating a culture that values diversity and inclusion.
By taking these steps, organizations can help to create a more supportive and equitable workplace for all employees.
Strategies for addressing Gender Discrimination in the workplace
Addressing sexist behavior in the workplace requires a multi-faceted approach that involves a combination of policies, procedures, and cultural changes.
Here are some strategies that organizations can implement to address and prevent sexist behavior in the workplace:
- Develop and communicate clear policies: Organizations should have clear policies in place that outline what constitutes sexist behavior and the consequences of engaging in such behavior. These policies should be communicated to all employees and enforced consistently.
- Provide training and education: Organizations should provide regular training and education to employees and managers on issues related to sexism, harassment, and discrimination. This can help to increase awareness and understanding of these issues and empower employees to speak out and take action when they witness or experience sexist behavior.
- Foster a culture of inclusion: Organizations should work to create a culture that values diversity and inclusion. This can include promoting and celebrating diversity in hiring and promotions, creating opportunities for employees from diverse backgrounds to share their perspectives, and actively working to eliminate biases and stereotypes in the workplace.
- Encourage reporting and provide support: Employees who experience sexist behavior should feel comfortable reporting it and should be provided with support and resources to address the situation. Organizations can provide channels for reporting, such as a dedicated hotline or anonymous reporting tool, and ensure that employees who report are protected from retaliation.
- Hold perpetrators accountable: Organizations must take allegations of sexist behavior seriously and investigate them thoroughly. Perpetrators should be held accountable for their actions, and organizations should take appropriate disciplinary action, up to and including termination.
By implementing these strategies, organizations can work to create a more equitable and respectful workplace for all employees.
Conclusion
The statistics on sexist behavior in the workplace are alarming and demonstrate that gender discrimination and harassment continue to be significant issues that impact many women’s professional lives.
From experiencing discriminatory treatment and pay inequality to being passed over for important assignments and receiving less support from senior leaders, women continue to face numerous challenges in the workplace due to their gender.
However, there are strategies that organizations can implement to address and prevent sexist behavior in the workplace.
These include developing clear policies, providing training and education, fostering a culture of inclusion, encouraging reporting and providing support, and holding perpetrators accountable.
By working to create a more equitable and respectful workplace, organizations can not only improve the lives of their employees but also enhance their business outcomes.
Research shows that organizations with diverse and inclusive workforces are more innovative, productive, and successful than those that lack diversity.
It’s time for all organizations to recognize the importance of addressing sexist behavior in the workplace and take action to create a more equitable and inclusive environment for all employees.
By doing so, we can create a better future for women in the workplace and beyond.
If you find this article useful, why not share it among your recruitment, human resource business partner, and talent acquisition counterparts hiring in Malaysia, and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the 9cv9 Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guide, and statistics to your doorstep.
Sources:































![Writing A Good CV [6 Tips To Improve Your CV] 6 Tips To Improve Your CV](https://blog.9cv9.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/2020-06-02-2-100x70.png)


