Key Takeaways
- Explore the versatility: ACH payments offer cost-effective, secure, and efficient ways to transfer funds electronically.
- Optimize your processes: Learn best practices for seamless ACH payment acceptance to streamline operations and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Stay compliant: Understand regulatory requirements and implement robust security measures to ensure smooth ACH payment processing while maintaining compliance.
In today’s fast-paced digital economy, the landscape of financial transactions is constantly evolving.
Among the myriad of payment methods available to businesses and consumers alike, ACH payments stand out as a reliable and efficient solution.
But what exactly are ACH payments, and how can businesses leverage their potential to streamline their operations and enhance customer satisfaction?
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the world of ACH payments, demystifying their intricacies and providing actionable insights on how businesses can seamlessly integrate them into their payment processing systems.
Whether you’re a small startup or a large enterprise, understanding ACH payments is essential for staying competitive and meeting the evolving needs of your customers.
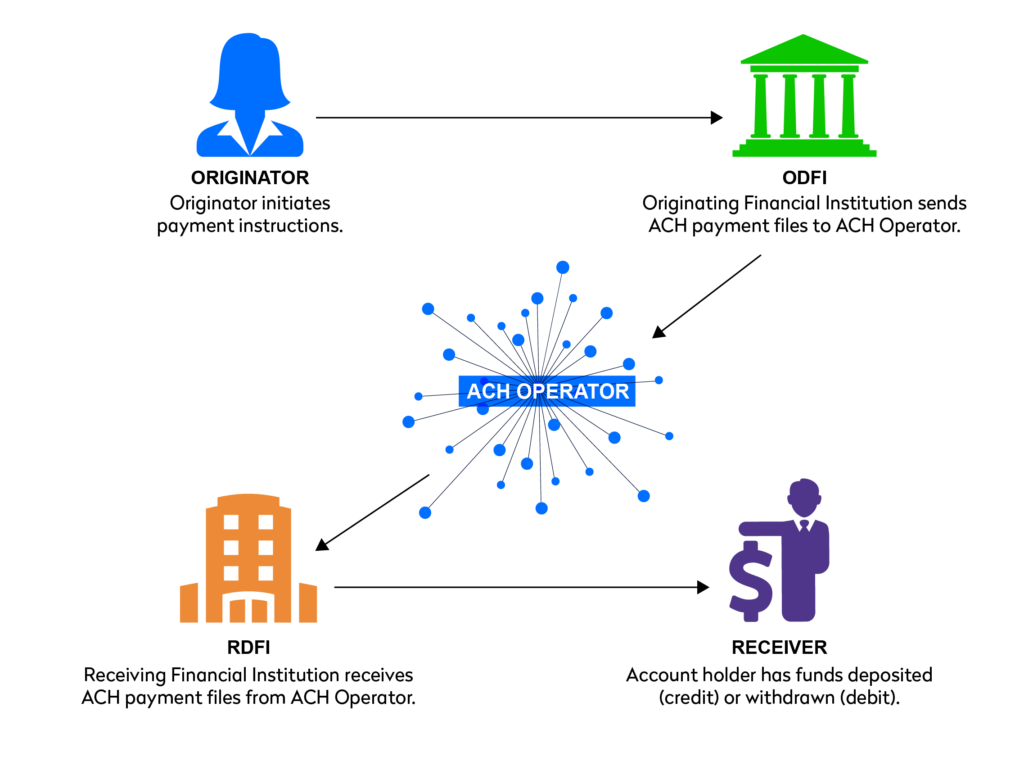
But first, let’s address the fundamental question: What are ACH payments?
ACH, which stands for Automated Clearing House, is a secure electronic network that facilitates various types of financial transactions, including direct deposits, bill payments, and business-to-business transfers.
Unlike traditional paper checks or wire transfers, ACH payments enable funds to be transferred electronically between bank accounts, offering a faster, more convenient, and cost-effective alternative.
Now, you might be wondering how exactly ACH payments work and why they’re gaining traction in today’s digital economy.
The ACH network operates under the governance of NACHA (National Automated Clearing House Association), ensuring the smooth and secure transfer of funds between financial institutions across the United States.
Whether it’s payroll processing, recurring billing, or vendor payments, ACH offers unparalleled efficiency and reliability, making it the preferred choice for businesses looking to streamline their payment workflows.
But the benefits of ACH payments extend beyond efficiency.
By accepting ACH payments, businesses can reduce transaction costs, minimize the risk of fraud, and improve cash flow management.
With faster processing times and enhanced security features, ACH payments empower businesses to focus on what truly matters: delivering exceptional products and services to their customers.
In this guide, we’ll explore the various types of ACH payments, including direct deposits, direct payments, and person-to-person transfers, providing insights into how each method can be leveraged to meet specific business needs.
Additionally, we’ll discuss the steps involved in accepting ACH payments, from setting up a merchant account to choosing the right payment processor and integrating ACH capabilities into existing payment systems.
But embracing ACH payments isn’t without its challenges.
From compliance and regulatory requirements to security concerns and payment rejections, businesses must navigate a complex landscape to fully capitalize on the benefits of ACH.
That’s why we’ll also provide practical tips and best practices for overcoming common obstacles and ensuring a seamless ACH payment experience for both businesses and customers alike.
So whether you’re a budding entrepreneur looking to streamline your payment processes or an established enterprise seeking to stay ahead of the curve, this guide is your ultimate resource for unlocking the full potential of ACH payments.
Join us on this journey as we explore the ins and outs of ACH payments and discover how they can revolutionize the way you do business.
Before we venture further into this article, we like to share who we are and what we do.
About 9cv9
9cv9 is a business tech startup based in Singapore and Asia, with a strong presence all over the world.
With over eight years of startup and business experience, and being highly involved in connecting with thousands of companies and startups, the 9cv9 team has listed some important learning points in this overview of What are ACH Payments and How to Accept Them.
If your company needs recruitment and headhunting services to hire top-quality employees, you can use 9cv9 headhunting and recruitment services to hire top talents and candidates. Find out more here, or send over an email to hello@9cv9.com.
Or just post 1 free job posting here at 9cv9 Hiring Portal in under 10 minutes.
What are ACH Payments and How to Accept Them
- Understanding ACH Payments
- Types of ACH Payments
- Benefits of Accepting ACH Payments
- How to Accept ACH Payments
- Security Measures for ACH Payments
- Compliance and Regulations
- Common Challenges and Solutions
- Best Practices for ACH Payment Acceptance
1. Understanding ACH Payments
In this section, we’ll delve into the fundamentals of ACH payments, unraveling their complexities and shedding light on why they’re becoming increasingly popular in today’s digital age.
What is ACH?
- Definition: ACH, short for Automated Clearing House, is an electronic network that facilitates financial transactions in the United States. It serves as the backbone for various types of electronic payments, including direct deposits, bill payments, and business-to-business transfers.
- Operational Framework: ACH operates under the governance of the National Automated Clearing House Association (NACHA), ensuring the secure and efficient transfer of funds between financial institutions across the country.
How ACH Payments Work
- The ACH Network: ACH payments involve the electronic transfer of funds between bank accounts through the ACH network. This network acts as an intermediary, facilitating communication between originating and receiving financial institutions.
- Example: When an employer initiates direct deposit payroll for its employees, the payroll processor sends the payment instructions to its bank, which then transmits the funds through the ACH network to the employees’ bank accounts.
- Difference from Other Payment Methods: Unlike credit card transactions that involve card networks like Visa or Mastercard, ACH payments bypass these networks and rely solely on the ACH infrastructure. This distinction often results in lower transaction fees and longer processing times compared to credit card payments.
Benefits of ACH Payments
- Cost-effectiveness: ACH payments typically incur lower processing fees compared to credit card transactions, making them an attractive option for businesses looking to reduce payment processing costs.
- Example: A small business processing a high volume of transactions can significantly lower its payment processing expenses by leveraging ACH payments instead of credit cards.
- Faster Processing Time: While ACH payments may not be as instantaneous as credit card transactions, they generally offer faster processing times compared to traditional paper checks, with funds typically clearing within 1-2 business days.
- Example: A utility company can collect monthly bill payments from its customers more efficiently through ACH, allowing for quicker reconciliation and improved cash flow management.
- Enhanced Security: ACH payments are highly secure, utilizing encryption and authentication protocols to safeguard sensitive financial information throughout the transaction process.
- Example: A large corporation can securely transfer funds to its suppliers or vendors without the risk of interception or unauthorized access, reducing the likelihood of payment fraud.
Understanding ACH payments is essential for businesses looking to optimize their payment processing workflows and capitalize on the numerous benefits that electronic payments offer.
By leveraging the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and security of ACH payments, businesses can streamline their financial operations and enhance customer satisfaction in today’s increasingly digital marketplace.
2. Types of ACH Payments
In this section, we’ll explore the various types of ACH payments, each serving specific purposes and offering unique benefits for businesses and consumers alike.
Direct Deposit
- Definition: Direct deposit allows employers to electronically deposit employees’ salaries or wages directly into their bank accounts, eliminating the need for paper checks.
- Benefits:
- Convenience: Employees no longer need to visit a bank to deposit their paychecks, as funds are automatically transferred into their accounts.
- Efficiency: Direct deposit streamlines payroll processes for employers, reducing administrative costs and potential errors associated with paper checks.
- Example: A large corporation implements direct deposit for its employees, enabling seamless payroll processing and improving overall workforce satisfaction.
Direct Payments
- Definition: Direct payments, also known as ACH debits, allow businesses to initiate electronic transfers from their customers’ bank accounts for various purposes, such as bill payments, subscription renewals, or one-time purchases.
- Benefits:
- Predictability: Businesses can schedule recurring payments, ensuring timely collection of funds without relying on customers to initiate payments.
- Cost Savings: Direct payments often incur lower transaction fees compared to credit card payments, reducing processing expenses for businesses.
- Example: A subscription-based service provider sets up automatic monthly withdrawals from its customers’ bank accounts, ensuring uninterrupted access to its services while minimizing billing-related inquiries.
Business-to-Business (B2B) Payments
- Definition: B2B payments involve the electronic transfer of funds between businesses for goods or services rendered. ACH payments offer a cost-effective and efficient alternative to traditional methods such as checks or wire transfers.
- Benefits:
- Speed: B2B payments via ACH typically clear within 1-2 business days, accelerating payment cycles and improving cash flow for both buyers and suppliers.
- Reduced Risk: ACH payments mitigate the risks associated with paper checks, such as fraud, lost or stolen checks, and potential delays in processing.
- Example: A manufacturing company pays its suppliers electronically using ACH transfers, streamlining the procurement process and enhancing supplier relationships through prompt payment.
Person-to-Person (P2P) Payments
- Definition: P2P payments enable individuals to transfer funds electronically to friends, family members, or acquaintances using their bank accounts. Popular P2P payment platforms leverage the ACH network to facilitate these transactions.
- Benefits:
- Convenience: P2P payments offer a convenient way for individuals to split bills, repay debts, or send gifts without the need for cash or checks.
- Accessibility: P2P payment apps and platforms are widely accessible, allowing users to initiate transactions anytime, anywhere, using their smartphones or computers.
- Example: Friends share expenses for a group dinner by using a P2P payment app to transfer funds directly from their bank accounts to the organizer, eliminating the hassle of collecting cash or writing checks.
Understanding the various types of ACH payments empowers businesses and consumers to leverage electronic payment solutions that best suit their needs.
Whether it’s streamlining payroll processes, facilitating B2B transactions, or simplifying personal finances, ACH payments offer a versatile and efficient means of transferring funds securely and conveniently in today’s digital world.
3. Benefits of Accepting ACH Payments
Accepting ACH payments offers numerous advantages for businesses of all sizes, from improved cash flow management to enhanced customer satisfaction.
Let’s explore the key benefits in detail:
Cost-effectiveness
- Lower Transaction Fees: ACH payments typically incur lower processing fees compared to credit card transactions, making them an attractive option for businesses looking to minimize payment processing expenses.
- Reduced Processing Costs: By shifting from paper-based payment methods to electronic ACH transfers, businesses can lower administrative costs associated with printing and mailing checks.
- Example: A small business processing a high volume of transactions can significantly reduce its payment processing expenses by leveraging ACH payments instead of credit cards, leading to substantial cost savings over time.
Faster Processing Time
- Quicker Clearing and Settlement: ACH payments typically clear within 1-2 business days, providing faster access to funds compared to traditional paper checks, which may take several days to clear.
- Improved Cash Flow: Faster processing times enable businesses to receive payments more promptly, enhancing cash flow management and liquidity.
- Example: A utility company can collect monthly bill payments from its customers more efficiently through ACH, allowing for quicker reconciliation and improved cash flow management, particularly during peak billing periods.
Enhanced Security
- Encryption and Authentication: ACH payments utilize advanced encryption and authentication protocols to safeguard sensitive financial information throughout the transaction process, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or fraud.
- Reduced Risk of Fraud: Compared to paper-based payment methods, such as checks, ACH payments offer greater security and protection against fraudulent activities, mitigating the risk of payment fraud.
- Example: A large corporation can securely transfer funds to its suppliers or vendors without the risk of interception or unauthorized access, reducing the likelihood of payment fraud and ensuring secure transactions.
Streamlined Payment Processes
- Automated Payment Processing: ACH payments enable businesses to automate recurring payments, such as payroll processing, subscription renewals, and invoicing, streamlining payment workflows and reducing manual intervention.
- Improved Efficiency: By integrating ACH payment capabilities into existing payment systems or accounting software, businesses can streamline payment processes and eliminate the need for manual data entry.
- Example: A subscription-based service provider can automate monthly subscription renewals for its customers using ACH payments, reducing administrative overhead and ensuring seamless billing cycles.
Accessibility and Convenience
- Wider Reach: ACH payments are accessible to a broader audience, including individuals without access to traditional banking services or credit cards, enhancing customer accessibility and inclusivity.
- Convenience for Customers: Offering ACH payment options provides customers with a convenient and hassle-free way to make payments, particularly for recurring expenses or subscription services.
- Example: A nonprofit organization accepts donations via ACH payments, allowing supporters to contribute funds directly from their bank accounts, offering a convenient alternative to traditional payment methods like credit cards or checks.
Accepting ACH payments offers a multitude of benefits for businesses, ranging from cost savings and faster processing times to enhanced security and convenience for both businesses and customers.
By leveraging the efficiency and reliability of ACH payments, businesses can streamline their payment processes, improve cash flow management, and deliver a superior payment experience to their customers, ultimately driving growth and success in today’s digital economy.
4. How to Accept ACH Payments
Accepting ACH payments requires businesses to set up the necessary infrastructure and integrate ACH capabilities into their payment processing systems.
Let’s explore the step-by-step process of accepting ACH payments, along with relevant examples:
Setting Up an ACH Merchant Account
- Choose a Financial Institution: Select a bank or financial institution that offers ACH processing services and inquire about setting up an ACH merchant account.
- Submit Application: Complete the application process for an ACH merchant account, providing necessary documentation and information about your business.
- Approval and Setup: Once approved, work with the financial institution to set up your ACH merchant account and establish the necessary connections for processing ACH transactions.
- Example: A small e-commerce business applies for an ACH merchant account with its bank to enable customers to make purchases using ACH payments, expanding payment options and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Choosing the Right ACH Payment Processor
- Research and Compare: Conduct research to identify ACH payment processors that meet your business needs in terms of pricing, features, and customer support.
- Evaluate Fees and Pricing: Compare the fees and pricing structures of different ACH payment processors, considering factors such as transaction fees, monthly service fees, and any additional charges.
- Consider Integration Options: Choose an ACH payment processor that offers seamless integration with your existing payment systems or e-commerce platforms.
- Example: A subscription-based software company selects an ACH payment processor that offers competitive transaction fees and integrates seamlessly with its subscription management platform, allowing for automated billing and payment processing.
Integrating ACH Payments into Your Business
- Online Platforms: Integrate ACH payment capabilities into your website or online checkout process, allowing customers to select ACH as a payment option and securely enter their bank account information.
- Point-of-Sale Systems: If you operate a brick-and-mortar store, ensure that your point-of-sale (POS) system supports ACH payments, allowing customers to pay using their bank accounts in-person.
- Invoicing Software: Use invoicing software that supports ACH payments to send invoices to customers and enable them to make payments directly from their bank accounts.
- Example: A rental property management company integrates ACH payment functionality into its online tenant portal, allowing tenants to pay rent electronically using their bank accounts, simplifying the payment process for both tenants and property managers.
Security Measures for ACH Payments
- Encryption and Data Security: Implement robust encryption protocols to secure sensitive financial information transmitted during ACH transactions, protecting against unauthorized access or data breaches.
- ACH Authorization Requirements: Ensure compliance with ACH authorization requirements by obtaining explicit consent from customers before initiating ACH transactions and maintaining accurate records of authorization.
- Fraud Prevention Tips: Implement fraud prevention measures, such as monitoring transaction activity for suspicious behavior, verifying customer information, and using multi-factor authentication.
- Example: A healthcare provider implements stringent security measures to protect patient payment information during ACH transactions, including encryption, secure authentication, and regular monitoring for fraudulent activity.
Accepting ACH payments requires businesses to navigate the setup process, choose the right payment processor, integrate ACH capabilities into their systems, and implement robust security measures.
By following these steps and leveraging the flexibility and convenience of ACH payments, businesses can expand their payment options, streamline payment processing, and enhance the overall customer experience.
5. Security Measures for ACH Payments
Ensuring the security of ACH payments is paramount for businesses and financial institutions alike.
Implementing robust security measures helps safeguard sensitive financial information, mitigate the risk of fraud, and maintain trust with customers.
Let’s explore the essential security measures for ACH payments:
Encryption and Data Security
- Utilize SSL Encryption: Implement Secure Socket Layer (SSL) encryption to secure data transmitted between the customer’s browser and your website during ACH transactions, protecting against interception and unauthorized access.
- Data Masking: Mask sensitive information, such as bank account numbers and routing numbers, to prevent unauthorized users from viewing or accessing this information.
- Secure Storage: Store customer data in encrypted databases or secure servers with restricted access to authorized personnel only.
- Example: An e-commerce platform uses SSL encryption to protect customer payment information entered during checkout, ensuring that sensitive data is securely transmitted and stored to prevent unauthorized access.
ACH Authorization Requirements
- Obtain Explicit Consent: Obtain explicit authorization from customers before initiating ACH transactions, ensuring that they understand and consent to the terms of the transaction.
- Maintain Records: Maintain accurate records of ACH authorizations, including the date, time, and method of consent, to provide evidence of customer consent in case of disputes or inquiries.
- Compliance with Regulations: Ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, such as the Electronic Fund Transfer Act (EFTA) and the NACHA Operating Rules, governing ACH transactions and consumer protection.
- Example: A subscription-based service provider obtains explicit consent from customers before initiating recurring ACH payments, maintaining detailed records of authorization to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements.
Fraud Prevention Measures
- Transaction Monitoring: Implement real-time transaction monitoring systems to detect suspicious activity, such as unusual transaction patterns or high-risk transactions, and flag potential fraudulent transactions for further review.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Require multi-factor authentication for account access and transaction authorization, adding an extra layer of security to verify the identity of users.
- Fraud Detection Tools: Utilize fraud detection tools and algorithms to analyze transaction data, identify anomalies, and proactively prevent fraudulent activity.
- Example: A financial institution employs advanced fraud detection algorithms to analyze ACH transaction data, automatically flagging and investigating suspicious transactions to prevent fraudulent activity and protect customer accounts.
Regular Security Audits and Compliance Checks
- Conduct Regular Audits: Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify potential security weaknesses or vulnerabilities in your ACH payment systems and infrastructure.
- Compliance Checks: Ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and the NACHA Operating Rules, to protect customer data and maintain trust.
- Update Security Protocols: Stay informed about emerging threats and security best practices, and update security protocols and procedures accordingly to address new vulnerabilities and mitigate risks.
- Example: A financial institution conducts regular security audits and compliance checks of its ACH payment systems, ensuring that security protocols are up to date and aligned with industry standards to protect customer data and prevent security breaches.
Implementing robust security measures is essential for safeguarding ACH payments and protecting sensitive financial information from unauthorized access or fraudulent activity.
By employing encryption and data security protocols, obtaining explicit consent from customers, implementing fraud prevention measures, and conducting regular security audits, businesses and financial institutions can enhance the security of ACH payments, build trust with customers, and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements.
6. Compliance and Regulations
Compliance with regulatory requirements is crucial for businesses and financial institutions involved in processing ACH payments.
Understanding and adhering to relevant regulations helps ensure the security, integrity, and legality of ACH transactions. Let’s delve into the key compliance and regulations for ACH payments:
NACHA Rules and Guidelines
- NACHA Operating Rules: Familiarize yourself with the NACHA Operating Rules, which govern the ACH Network and establish the rights, obligations, and responsibilities of participants in ACH transactions.
- Compliance Requirements: Ensure compliance with NACHA rules and guidelines regarding transaction processing, authorization, settlement, and dispute resolution.
- ACH Network Participation: Adhere to eligibility criteria and requirements for participation in the ACH Network, including registration, accreditation, and ongoing compliance checks.
- Example: A financial institution maintains compliance with NACHA rules and guidelines by implementing appropriate controls and procedures for ACH transaction processing, ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Compliance
- Know Your Customer (KYC): Implement robust KYC procedures to verify the identity of customers and assess the risk of money laundering or terrorist financing activities associated with ACH transactions.
- AML Policies and Procedures: Develop and implement AML policies and procedures to detect, prevent, and report suspicious activity, including transaction monitoring, customer due diligence, and reporting obligations.
- Regulatory Oversight: Comply with AML regulations enforced by regulatory agencies such as the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) and ensure adherence to applicable laws and regulations governing AML compliance.
- Example: A payment processor conducts thorough KYC checks on customers and monitors ACH transactions for suspicious activity, reporting any suspicious transactions to regulatory authorities in compliance with AML regulations.
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) Compliance
- Data Security Requirements: Adhere to the PCI DSS, a set of security standards designed to protect cardholder data and prevent unauthorized access, disclosure, or misuse of sensitive payment information.
- Secure Data Handling: Implement secure data handling practices, including encryption, tokenization, and access controls, to protect ACH payment information from security breaches or data breaches.
- Compliance Validation: Validate compliance with PCI DSS requirements through regular assessments, audits, and certifications conducted by qualified security assessors (QSAs) or internal compliance teams.
- Example: An e-commerce merchant maintains PCI DSS compliance by encrypting ACH payment data during transmission and storage, implementing access controls to restrict access to sensitive information, and conducting regular security assessments to ensure compliance with PCI DSS requirements.
Consumer Protection Regulations
- Electronic Fund Transfer Act (EFTA): Comply with the EFTA, which establishes consumer rights and protections for electronic fund transfers, including ACH transactions, such as error resolution procedures, liability limits, and disclosure requirements.
- Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA): Ensure compliance with the FCRA, which regulates the collection, use, and dissemination of consumer credit information, including ACH payments processed for credit-related purposes.
- State and Federal Regulations: Stay informed about state and federal regulations governing consumer protection, privacy, and data security, ensuring compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
- Example: A financial institution provides clear and accurate disclosures to consumers regarding their rights and liabilities under the EFTA, including procedures for resolving errors or unauthorized transactions, fostering transparency and consumer trust in ACH payment services.
Compliance with regulatory requirements is essential for businesses and financial institutions involved in processing ACH payments.
By adhering to NACHA rules and guidelines, implementing AML and PCI DSS compliance measures, and ensuring compliance with consumer protection regulations, businesses can uphold the integrity, security, and legality of ACH transactions, safeguarding customer interests and maintaining trust in the financial system.
7. Common Challenges and Solutions
Despite the many benefits of ACH payments, businesses may encounter various challenges when implementing and processing ACH transactions.
Understanding these challenges and implementing effective solutions is crucial for optimizing ACH payment processing. Let’s explore some common challenges and their solutions:
Handling Payment Rejections
- Insufficient Funds: Payment rejections due to insufficient funds in the payer’s bank account are a common challenge in ACH transactions.
- Solution: Implement real-time funds verification or pre-authorization checks to ensure that sufficient funds are available before initiating ACH transactions.
- Invalid Account Information: Errors in account numbers, routing numbers, or other account information may result in payment rejections.
- Solution: Use validation tools to verify the accuracy of account information entered by customers, reducing the likelihood of payment rejections due to invalid account details.
- Communication with Customers: Communicate proactively with customers to resolve payment rejections promptly, providing guidance on updating account information or resolving issues that led to the rejection.
- Solution: Implement automated notifications or alerts to notify customers of payment rejections and provide instructions for resolving the issue.
Dealing with Chargebacks
- Unauthorized Transactions: Instances of unauthorized transactions or disputes may result in chargebacks, leading to financial losses and administrative burdens for businesses.
- Solution: Implement robust authentication and authorization protocols to verify the identity of customers and obtain explicit consent for ACH transactions, reducing the risk of unauthorized transactions and chargebacks.
- Dispute Resolution Procedures: Establish clear and efficient dispute resolution procedures to address customer inquiries, complaints, or disputes related to ACH transactions.
- Solution: Provide responsive customer support and facilitate timely resolution of disputes through transparent communication, documentation, and collaboration with customers and financial institutions.
- Fraud Prevention Measures: Implement fraud prevention measures, such as transaction monitoring and verification processes, to detect and prevent fraudulent activity that may lead to chargebacks.
- Solution: Utilize fraud detection tools and algorithms to analyze transaction data for suspicious patterns or anomalies, flagging potentially fraudulent transactions for further review and investigation.
Addressing Customer Concerns
- Security and Privacy: Customers may have concerns about the security and privacy of their financial information when making ACH payments.
- Solution: Provide transparent information about security measures and data protection protocols implemented to safeguard customer information during ACH transactions, building trust and confidence among customers.
- Ease of Use: Complex or cumbersome payment processes may deter customers from using ACH payment options.
- Solution: Streamline the payment experience by optimizing user interfaces, providing clear instructions, and offering user-friendly features that simplify the ACH payment process for customers.
- Customer Support: Prompt and responsive customer support is essential for addressing customer inquiries, resolving issues, and providing assistance with ACH payments.
- Solution: Offer multiple channels for customer support, including phone, email, and live chat, staffed by knowledgeable representatives trained to assist with ACH payment-related inquiries and concerns.
Technical Integration Challenges
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating ACH payment capabilities into existing payment systems or software platforms may pose technical challenges.
- Solution: Work with experienced developers or payment solution providers to ensure seamless integration of ACH payment functionality with your existing systems, minimizing disruptions and ensuring compatibility.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Testing and validating ACH payment integrations are essential to ensure proper functionality and compatibility with different devices, browsers, and operating systems.
- Solution: Develop comprehensive testing protocols and conduct rigorous quality assurance testing to identify and resolve any issues or bugs before deploying ACH payment solutions in production environments.
- Scalability and Performance: Ensure that ACH payment systems can scale effectively to accommodate increasing transaction volumes and maintain optimal performance under peak load conditions.
- Solution: Implement scalable infrastructure and performance optimization strategies to handle growing transaction volumes and ensure consistent performance and reliability of ACH payment processing systems.
While ACH payments offer numerous benefits, businesses may encounter various challenges when implementing and processing ACH transactions.
By understanding these challenges and implementing effective solutions such as addressing payment rejections, dealing with chargebacks, addressing customer concerns, and overcoming technical integration challenges, businesses can optimize ACH payment processing, enhance the customer experience, and maximize the benefits of electronic payments.
8. Best Practices for ACH Payment Acceptance
Implementing best practices for ACH payment acceptance is essential for businesses looking to optimize their payment processing workflows, enhance security, and improve the overall customer experience.
Let’s explore some key best practices:
Transparent Pricing and Policies
- Clear Fee Structure: Provide customers with a transparent fee structure detailing any applicable charges associated with ACH payments, such as transaction fees or processing fees.
- Example: Clearly outline ACH payment fees on your website or payment platform, ensuring transparency and helping customers make informed decisions.
- Policy Disclosures: Clearly communicate your policies regarding ACH payment processing, including terms of service, refund policies, and dispute resolution procedures.
- Example: Display policy disclosures prominently on your website or payment portal, ensuring that customers are aware of your terms and conditions before initiating ACH transactions.
Streamlined Payment Processes
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Design user-friendly interfaces for ACH payment acceptance, with clear instructions and intuitive navigation to facilitate seamless transactions.
- Example: Optimize your checkout process with simplified ACH payment options, reducing friction and making it easier for customers to complete transactions.
- Automated Workflows: Automate ACH payment processes wherever possible to streamline administrative tasks and reduce manual intervention.
- Example: Implement automated invoicing and payment scheduling systems to streamline recurring ACH payments for subscription-based services or memberships.
Regular Monitoring and Maintenance
- Transaction Monitoring: Monitor ACH transactions regularly to detect any anomalies or suspicious activity that may indicate fraudulent transactions.
- Example: Use transaction monitoring tools to review transaction data for unusual patterns or discrepancies, flagging potentially fraudulent transactions for further investigation.
- System Updates and Maintenance: Stay up to date with software updates, security patches, and system maintenance to ensure the reliability and security of your ACH payment infrastructure.
- Example: Schedule regular maintenance windows to apply software updates and security patches, minimizing downtime and ensuring optimal performance of ACH payment systems.
Compliance with Regulations
- NACHA Rules Compliance: Adhere to the rules and guidelines established by NACHA governing ACH payment processing, including transaction processing, authorization, and dispute resolution.
- Example: Ensure compliance with NACHA rules by implementing appropriate controls and procedures for ACH transaction processing and dispute resolution, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stay informed about relevant regulations and compliance requirements governing ACH payments, including consumer protection laws, data privacy regulations, and anti-money laundering (AML) regulations.
- Example: Conduct regular audits and assessments to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, updating policies and procedures as needed to align with changing regulations.
Customer Education and Support
- Educational Resources: Provide customers with educational resources and information about ACH payments, including FAQs, tutorials, and guides to help them understand the ACH payment process.
- Example: Create blog posts, videos, or webinars explaining the benefits of ACH payments, how to set up ACH payments, and common FAQs to educate customers and address their concerns.
- Responsive Customer Support: Offer responsive customer support channels, such as phone, email, or live chat, staffed by knowledgeable representatives trained to assist with ACH payment-related inquiries and issues.
- Example: Provide dedicated customer support for ACH payment inquiries, ensuring prompt and effective assistance for customers experiencing issues or seeking assistance with ACH payments.
By implementing best practices for ACH payment acceptance, businesses can enhance the efficiency, security, and reliability of their payment processing workflows while improving the overall customer experience.
From transparent pricing and streamlined payment processes to regular monitoring and compliance with regulations, adopting these best practices ensures that businesses can maximize the benefits of ACH payments while maintaining trust and confidence with customers.
Conclusion
Understanding ACH payments and how to accept them is paramount for businesses aiming to streamline their payment processing operations, enhance security, and provide a seamless payment experience for customers.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the intricacies of ACH payments, delving into their definition, benefits, types, and best practices for acceptance.
ACH payments, facilitated through the Automated Clearing House network, offer a secure, cost-effective, and efficient means of transferring funds electronically between bank accounts.
Whether it’s direct deposits for payroll processing, direct payments for bill settlements, or B2B transfers for vendor payments, ACH payments provide businesses with a versatile solution for managing their financial transactions.
By accepting ACH payments, businesses can benefit from lower transaction fees, faster processing times, enhanced security measures, and improved cash flow management.
From small startups to large enterprises, embracing ACH payments enables businesses to optimize their payment processing workflows, reduce administrative costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
However, accepting ACH payments also comes with its challenges, including handling payment rejections, dealing with chargebacks, addressing customer concerns, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Nevertheless, by implementing best practices such as transparent pricing, streamlined payment processes, regular monitoring, compliance with regulations, and providing customer education and support, businesses can overcome these challenges and maximize the benefits of ACH payments.
In today’s digital economy, where convenience, security, and efficiency are paramount, ACH payments offer businesses a competitive edge in managing their financial transactions.
By leveraging the power of ACH payments and implementing best practices for acceptance, businesses can not only streamline their payment processing operations but also build trust, foster customer loyalty, and drive growth in an increasingly digital marketplace.
In essence, ACH payments represent more than just a payment method; they signify a shift towards a more efficient, secure, and convenient way of conducting financial transactions in today’s fast-paced world.
As businesses continue to adapt to evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements, embracing ACH payments is not just an option but a necessity for staying competitive and thriving in the digital landscape.
If your company needs HR, hiring, or corporate services, you can use 9cv9 hiring and recruitment services. Book a consultation slot here, or send over an email to hello@9cv9.com.
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your hiring manager and C-level suite friends and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the 9cv9 Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.
To get access to top-quality guides, click over to 9cv9 Blog.
People Also Ask
What is an ACH payment?
ACH (Automated Clearing House) payment is an electronic funds transfer system allowing businesses to move money between bank accounts.
How do ACH payments work?
ACH payments transfer funds electronically between bank accounts using the ACH network, facilitating transactions such as direct deposits and bill payments.
What are the benefits of ACH payments?
ACH payments offer cost-effective, secure, and efficient money transfer, streamlining payment processes for businesses and providing convenience for consumers.
Are ACH payments secure?
Yes, ACH payments are secure, employing encryption and authentication protocols to safeguard sensitive financial information throughout the transaction process.
What are the different types of ACH payments?
Types of ACH payments include direct deposits, direct payments, B2B payments, and person-to-person payments, each serving specific purposes and offering unique benefits.
How long do ACH payments take to process?
ACH payments typically clear within 1-2 business days, providing faster access to funds compared to traditional paper checks.
Can I accept ACH payments as a business?
Yes, businesses can accept ACH payments by setting up an ACH merchant account with a bank or financial institution and integrating ACH payment capabilities into their payment systems.
What information do I need to accept ACH payments?
To accept ACH payments, you’ll need the customer’s bank account number, routing number, and authorization to initiate the transaction.
How do I integrate ACH payments into my website?
You can integrate ACH payment capabilities into your website using payment processing software or platforms that support ACH transactions, providing customers with a convenient payment option.
Are there fees associated with accepting ACH payments?
Yes, there may be fees associated with accepting ACH payments, including transaction fees, processing fees, and monthly service fees, depending on the payment processor and service provider.
How can I ensure compliance with ACH regulations?
Ensure compliance with ACH regulations by familiarizing yourself with NACHA rules and guidelines, implementing fraud prevention measures, and maintaining accurate records of ACH authorizations.
What should I do if an ACH payment is rejected?
If an ACH payment is rejected due to insufficient funds or invalid account information, communicate proactively with the customer to resolve the issue and update the payment details if necessary.
How can I prevent chargebacks with ACH payments?
Prevent chargebacks with ACH payments by implementing robust authentication and authorization protocols, resolving disputes promptly, and implementing fraud prevention measures.
Can I automate recurring ACH payments?
Yes, businesses can automate recurring ACH payments for subscription renewals, memberships, and recurring bills using ACH payment processing software or platforms.
How can I improve the security of ACH payments?
Improve the security of ACH payments by implementing encryption and data security protocols, obtaining explicit consent from customers before initiating transactions, and monitoring transactions for suspicious activity.
What are the best practices for accepting ACH payments?
Best practices for accepting ACH payments include transparent pricing and policies, streamlined payment processes, regular monitoring and maintenance, compliance with regulations, and providing customer education and support.
What should I do if I encounter technical integration challenges?
If you encounter technical integration challenges when accepting ACH payments, work with experienced developers or payment solution providers to ensure seamless integration with your existing systems.
Can I accept ACH payments without a merchant account?
No, businesses typically need an ACH merchant account with a bank or financial institution to accept ACH payments and process electronic fund transfers.
Are there any limits on ACH transactions?
Yes, there may be limits on ACH transactions imposed by banks or financial institutions, including daily transaction limits and maximum transaction amounts, depending on the account type and provider.