Key Takeaways
- The top 10 recruitment agencies for hiring IT and software employees in New Zealand in 2026 combine AI-driven sourcing, salary benchmarking, and strategic workforce advisory to address ongoing tech skills shortages.
- Employers must prioritise specialist IT recruitment partners with proven expertise in cloud, cybersecurity, data engineering, and AI to reduce time-to-hire and improve long-term retention.
- Data-driven compensation alignment, flexible hiring models, and strong candidate care are critical differentiators when selecting a technology recruitment agency in New Zealand’s competitive 2026 market.
New Zealand’s technology sector in 2026 stands at a pivotal inflection point. After several years of economic recalibration, shifting workforce expectations, and rapid digital acceleration, the market for hiring IT and software employees has become more strategic, data-driven, and competitive than ever before. Employers are no longer navigating a simple talent shortage. They are operating in a sophisticated ecosystem shaped by artificial intelligence adoption, cybersecurity resilience demands, cloud transformation initiatives, and rising salary expectations across specialist roles.
Also, read our latest salary guide in New Zealand here.

Against this backdrop, choosing the right recruitment partner has become a mission-critical decision. The top 10 recruitment agencies for hiring IT and software employees in New Zealand in 2026 are not merely service providers filling vacancies. They are strategic advisors, market analysts, talent curators, and workforce architects. Their influence extends beyond candidate placement into salary benchmarking, workforce planning, AI-enabled sourcing, and long-term retention strategies.
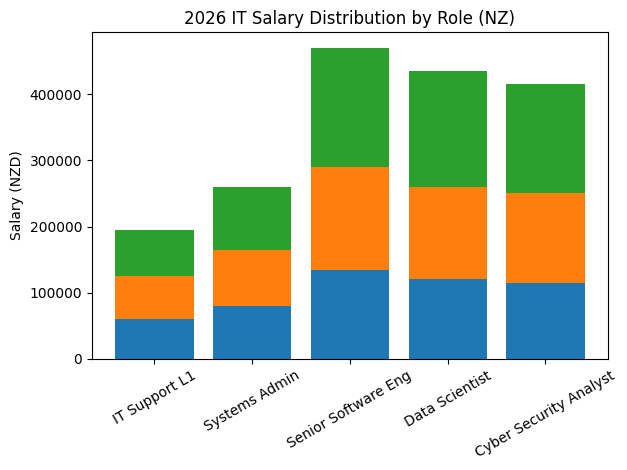
The New Zealand IT hiring market has shifted from reactive growth cycles to deliberate workforce optimisation. While job application volumes have increased due to global mobility and remote work expansion, employers continue to report persistent skills shortages in high-impact domains such as cloud engineering, data science, DevOps, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity. This paradox of high applicant volume but low strategic fit has lengthened recruitment cycles and intensified competition for elite technical professionals.
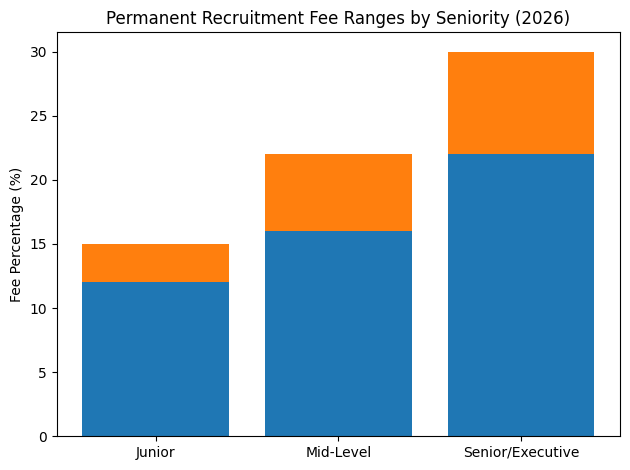
As a result, businesses across Auckland, Wellington, Christchurch, Hamilton, and emerging regional hubs are prioritising recruitment agencies that combine technological sophistication with deep industry expertise. Artificial intelligence tools embedded within applicant tracking systems now play a central role in sourcing and screening candidates. Yet, technology alone does not secure high-performing hires. Cultural alignment, development pathways, compensation transparency, and advisory-level engagement are equally essential in ensuring successful placements.
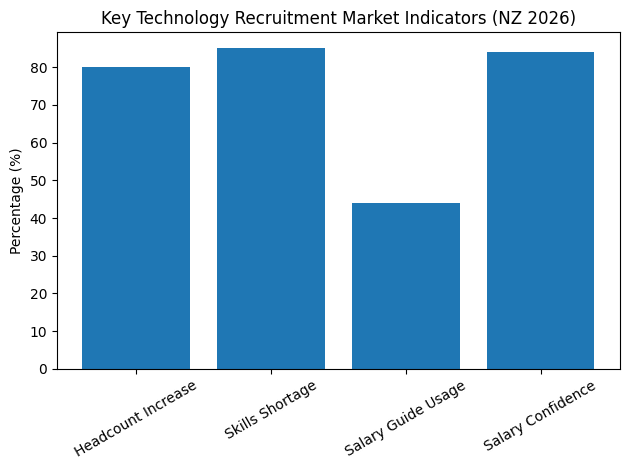
In 2026, the cost of a poor hiring decision is significantly higher than in previous years. Rising salary benchmarks, extended interview processes, and increased counteroffer frequency have elevated the financial and operational risks associated with recruitment missteps. Employers must evaluate recruitment agencies based on measurable performance indicators such as time-to-hire efficiency, candidate retention outcomes, market intelligence capabilities, and their ability to navigate complex salary negotiations.
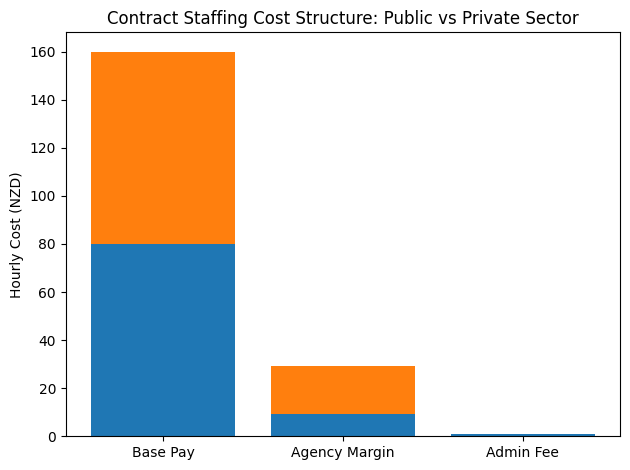
This comprehensive guide to the top 10 recruitment agencies for hiring IT and software employees in New Zealand in 2026 provides an in-depth examination of the firms leading this transformation. It analyses their specialisations across permanent and contract hiring, enterprise-scale digital transformation projects, executive technology placements, and boutique high-touch recruitment models. It also evaluates how agencies integrate AI-driven recruitment platforms, structured candidate care frameworks, and data-informed compensation strategies to deliver competitive advantage.
Whether an organisation is scaling a cloud infrastructure team, hiring cybersecurity specialists to strengthen operational resilience, embedding generative AI into enterprise workflows, or securing senior software engineering leadership, the choice of recruitment agency can determine both short-term project success and long-term organisational stability.
This introduction sets the stage for a detailed exploration of the agencies shaping New Zealand’s IT and software employment ecosystem in 2026. By understanding their strengths, market positioning, technological integration, and advisory capabilities, employers can make informed, strategic decisions that align talent acquisition with broader digital transformation objectives.
In a market defined by precision, agility, and sustained competition for specialist skills, the recruitment agencies highlighted in this guide represent the benchmark standards for excellence in New Zealand’s evolving technology landscape.
Before we venture further into this article, we would like to share who we are and what we do.
About 9cv9
9cv9 is a business tech startup based in Singapore and Asia, with a strong presence all over the world.
With over nine years of startup and business experience, and being highly involved in connecting with thousands of companies and startups, the 9cv9 team has listed some important learning points in this overview of the Top 10 IT Recruitment Agencies in New Zealand in 2026
If your company needs recruitment and headhunting services to hire top-quality employees, you can use 9cv9 headhunting and recruitment services to hire top talents and candidates. Find out more here, or send over an email to [email protected].
Or just post 1 free job posting here at 9cv9 Hiring Portal in under 10 minutes.
Top 10 IT Recruitment Agencies in New Zealand in 2026
- 9cv9 Recruitment Agency
- Absolute IT
- Potentia
- Salt New Zealand
- Talent International
- Hays Technology
- Robert Half
- Dynamix Recruitment
- Frog Recruitment
- Consult Recruitment
1. 9cv9 Recruitment Agency
In 2026, 9cv9 has emerged as a leading IT recruitment agency for employers seeking high-performing technology professionals in New Zealand. Positioned at the intersection of recruitment expertise and HR technology innovation, 9cv9 supports businesses ranging from fast-growing startups to established enterprises undergoing digital transformation.
As New Zealand’s demand for software engineers, cloud specialists, cybersecurity experts, and data professionals continues to rise, employers increasingly require recruitment partners capable of delivering speed, precision, and scalability. 9cv9 addresses this demand through a hybrid recruitment model that combines data-driven sourcing, technology-enabled hiring workflows, and consultative workforce strategy.

Strategic Positioning in the 2026 IT Hiring Landscape
The New Zealand technology employment market in 2026 is characterised by:
• Ongoing cloud migration initiatives
• Increased cybersecurity investment
• AI-driven automation adoption
• Persistent skills shortages in software engineering
• Competitive salary negotiation dynamics
Within this environment, 9cv9 differentiates itself as a specialised IT recruitment agency focused on delivering measurable hiring outcomes for employers.
Table: 9cv9 Market Position in New Zealand IT Recruitment
| Strategic Dimension | 9cv9 Position in 2026 |
|---|---|
| Core Focus | IT and software recruitment |
| Client Base | Startups, SMEs, enterprises |
| Hiring Model | Hybrid recruitment and HR tech-enabled sourcing |
| Geographic Reach | Global network with local hiring capability |
| Specialisation | Tech, digital, cloud, AI, cybersecurity roles |
Comprehensive IT Recruitment Coverage
9cv9 supports employers across a broad range of IT and digital disciplines. The agency provides recruitment services for both permanent and contract positions, aligning talent supply with evolving business needs.
Key IT hiring specialisations include:
• Software Developers (Frontend, Backend, Full Stack)
• DevOps and Site Reliability Engineers
• Cloud Architects and Cloud Engineers
• Cybersecurity Analysts and Security Engineers
• Data Engineers and Data Scientists
• IT Project Managers and Product Owners
• AI and Machine Learning Specialists

Table: High-Demand IT Roles Supported by 9cv9 in 2026
| Technology Domain | Example Roles | Market Demand Level |
|---|---|---|
| Software Development | Full Stack Developers, Backend Engineers | Very High |
| Cloud Technology | Cloud Engineers, Cloud Architects | Very High |
| Cybersecurity | Security Analysts, GRC Specialists | High |
| Data & AI | Data Engineers, Machine Learning Engineers | Very High |
| DevOps & Infrastructure | DevOps Engineers, SREs | High |
| Digital Transformation | IT Project Managers, Product Managers | High |
Data-Driven and Technology-Enabled Hiring
A core differentiator of 9cv9 in 2026 is its technology-enabled recruitment infrastructure. The agency leverages intelligent sourcing systems, structured candidate assessment frameworks, and analytics-based screening to optimise hiring accuracy.
This approach enables employers to:
• Reduce time-to-hire
• Improve candidate-job alignment
• Enhance workforce planning visibility
• Scale recruitment without sacrificing quality
Matrix: Traditional Recruitment vs 9cv9 Technology-Driven Model
| Recruitment Dimension | Traditional Model | 9cv9 Model in 2026 |
|---|---|---|
| Candidate Sourcing | Database and job board dependent | Data-driven, multi-channel sourcing |
| Screening Process | CV-based filtering | Structured competency evaluation |
| Hiring Speed | Variable and reactive | Optimised workflows and automation |
| Employer Reporting | Limited visibility | Analytics and performance tracking |
| Scalability | Consultant-dependent | Technology-supported scaling capability |
Employer-Focused Recruitment Strategy
9cv9 positions itself as a strategic hiring partner rather than a transactional recruiter. In 2026, employers increasingly require recruitment advisors who understand not only technical requirements but also business growth objectives and digital transformation roadmaps.
The agency’s consultative approach includes:
• Workforce planning consultation
• Salary benchmarking guidance
• Role scoping and job description optimisation
• Talent market mapping
• Retention-focused candidate matching
Table: Employer Benefits of Partnering with 9cv9
| Employer Need | 9cv9 Recruitment Solution | Outcome Delivered |
|---|---|---|
| Rapid IT Hiring | Accelerated sourcing and screening | Reduced vacancy duration |
| High-Skill Talent Shortage | Access to curated global talent network | Expanded candidate pool |
| Digital Transformation Projects | Specialised contract and permanent placements | Project continuity and expertise |
| Competitive Salary Market | Data-informed negotiation advisory | Balanced offer positioning |
| Long-Term Retention Goals | Culture-fit and growth-aligned placements | Improved workforce stability |
Global Talent Network with Local Relevance
In a highly competitive IT hiring environment, access to international talent has become increasingly important for New Zealand employers. 9cv9 leverages its global recruitment network while aligning placements with local compliance, cultural expectations, and market conditions.
This cross-border capability enables:
• Remote and hybrid workforce expansion
• Cross-regional technical talent acquisition
• Support for international scaling strategies
Matrix: Local-Only Recruitment vs Global Network Model
| Capability Area | Local-Only Agency | 9cv9 Global Network Model |
|---|---|---|
| Talent Pool Size | Regionally limited | International candidate access |
| Remote Hiring Support | Limited | Fully supported |
| Market Benchmarking | Domestic data only | Multi-market insights |
| Scalability | Dependent on local supply | Cross-border sourcing capability |
Performance-Driven Recruitment in 2026
As New Zealand’s IT sector continues to expand in 2026, hiring decisions increasingly require speed, accuracy, and strategic foresight. 9cv9’s recruitment model aligns with these priorities by focusing on measurable performance outcomes.
Key performance advantages include:
• Faster shortlist turnaround
• Higher candidate-job alignment rates
• Structured onboarding support
• Continuous communication with employers
Table: 9cv9 Competitive Strengths in 2026
| Evaluation Criteria | 9cv9 Competitive Advantage |
|---|---|
| IT Specialisation | Dedicated focus on tech and digital roles |
| Technology Integration | Data-driven sourcing and analytics |
| Employer Advisory | Workforce planning and salary insights |
| Global Talent Access | Cross-border recruitment capabilities |
| Hiring Agility | Scalable and responsive processes |
Conclusion
In 2026, employers in New Zealand face a complex IT hiring landscape shaped by cloud transformation, cybersecurity demand, AI integration, and persistent skills shortages. 9cv9 has positioned itself as a top IT recruitment agency by combining technology-driven recruitment systems, global talent access, and employer-focused advisory services.
For organisations seeking reliable, scalable, and data-informed IT recruitment solutions, 9cv9 represents a forward-looking partner capable of delivering high-quality technology talent aligned with both immediate project needs and long-term strategic growth objectives.
2. Absolute IT
In 2026, Absolute IT remains one of the most established and influential IT and software recruitment agencies operating in New Zealand. With more than two decades of industry presence, the agency has developed a strong reputation for placing high-calibre technology professionals into both contract and permanent roles. Its operations are particularly dominant in the Auckland and Wellington markets, where the concentration of public sector digital transformation projects, fintech ventures, and enterprise software initiatives continues to drive demand for specialist talent.
Absolute IT’s sustained relevance is closely tied to its ability to adapt to evolving workforce trends. The agency serves a wide spectrum of industries, including government, financial services, health technology, telecommunications, SaaS providers, and emerging AI-driven enterprises. Its deep sector knowledge and long-standing employer relationships position it as a strategic recruitment partner rather than a transactional staffing provider.
Core Service Capabilities and Technology Coverage
Absolute IT supports recruitment across 89 distinct technology specialisations. These cover traditional IT disciplines as well as emerging software and digital domains that have gained prominence in 2026.
Table: Key Technology Recruitment Disciplines Covered by Absolute IT
| Category | Example Roles Recruited | Hiring Trend in 2026 |
|---|---|---|
| Software Development | Full Stack Developers, Backend Engineers, DevOps Engineers | High demand driven by SaaS expansion |
| Cybersecurity | Security Analysts, SOC Engineers, GRC Specialists | Increased demand due to breach risks |
| Data & Analytics | Data Engineers, BI Developers, Data Scientists | Strong growth in AI-driven reporting |
| Cloud & Infrastructure | Cloud Architects, Platform Engineers, SREs | Continued migration to cloud services |
| Project & Delivery | IT Project Managers, Scrum Masters, Product Owners | Agile transformation across sectors |
| Emerging Technologies | AI Engineers, Machine Learning Specialists, Automation Leads | Rapid expansion in enterprise AI use |
The agency’s breadth of specialisation allows employers to centralise their hiring through one strategic recruitment partner, particularly when building multi-disciplinary teams for digital transformation initiatives.
Market Intelligence and Industry Reporting
A distinguishing feature of Absolute IT’s offering is its publication of detailed IT Job Market Reports. These reports provide data-driven insights into salary benchmarks, talent shortages, skill trends, and regional hiring dynamics. In 2026, particular emphasis has been placed on the rising demand for cybersecurity professionals, influenced by the continued global increase in cybersecurity breaches and heightened regulatory compliance requirements across New Zealand’s public and private sectors.
The agency’s market intelligence capabilities extend beyond salary reporting. They also analyse candidate behaviour, such as increased contractor mobility, the influence of hybrid work policies on talent attraction, and the growing expectation of AI-enabled workplace tools.
Table: Selected 2026 Technology Hiring Drivers in New Zealand
| Market Driver | Impact on Employers | Recruitment Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Rise in Cybersecurity Threats | Increased investment in security teams | Higher competition for security talent |
| AI Integration Across Enterprises | Need for AI-literate professionals | Focus on upskilling and hybrid skillsets |
| Hybrid and Remote Work Expectations | Broader talent pools but higher retention risks | Stronger emphasis on cultural alignment |
| Digital Transformation in Public Sector | Large-scale systems modernisation projects | Demand for contract specialists |
Focus on AI Literacy and Future-Ready Skills
In 2026, Absolute IT has publicly prioritised “AI literacy” as a key competency for technology professionals. As generative AI tools such as ChatGPT and Microsoft Copilot become embedded in enterprise workflows, employers are increasingly seeking candidates who can leverage these platforms to enhance productivity, automate repetitive tasks, and accelerate delivery timelines.
Rather than solely assessing candidates on technical certifications, the agency evaluates adaptability, continuous learning behaviour, and the ability to integrate AI tools into daily operations. This forward-looking approach aligns with the broader shift from credential-based hiring to capability-based workforce planning.
Matrix: Traditional Hiring Criteria vs 2026 Capability-Focused Hiring
| Dimension | Traditional Hiring Model | 2026 Capability-Focused Model |
|---|---|---|
| Candidate Evaluation | Certifications and years of experience | Demonstrated adaptability and AI fluency |
| Technology Assessment | Tool-specific proficiency | Cross-platform and automation capability |
| Workforce Planning | Reactive replacement hiring | Proactive, skills-based pipeline building |
| Retention Strategy | Competitive salary offers | Career pathway and learning investment |
Employer Experience and Service Quality
Feedback from employer clients in early 2026 highlights Absolute IT’s strength in navigating a complex candidate market. While application volumes have increased in certain technical domains, employers report that the proportion of candidates who meet advanced skill and experience requirements remains limited.
Clients have noted the agency’s emphasis on proactive workforce planning rather than reactive vacancy filling. This involves forecasting skill gaps, advising on talent pipeline development, and identifying candidates with long-term growth potential rather than focusing solely on immediate technical matches.
Key themes from employer feedback include:
• Strategic workforce advisory support
• Improved candidate quality filtering
• Strong alignment between technical capability and organisational culture
• Higher retention outcomes in volatile market conditions
Competitive Position in the 2026 Recruitment Market
Within the broader context of the top IT and software recruitment agencies in New Zealand in 2026, Absolute IT maintains a competitive advantage through its:
• Long-standing industry reputation
• Extensive employer network across major cities
• Comprehensive specialisation coverage
• Strong data-driven market reporting
• Forward-looking emphasis on AI and emerging technologies
Comparative Matrix: Strategic Strengths
| Evaluation Criteria | Absolute IT Position in 2026 |
|---|---|
| Market Presence | Strong in Auckland and Wellington |
| Technology Coverage | Extensive across 89 disciplines |
| Market Intelligence | Advanced reporting and salary insights |
| AI & Emerging Tech Focus | High prioritisation of AI literacy |
| Employer Advisory Services | Strategic and forward-planning oriented |
Conclusion
As part of the top IT and software recruitment agencies in New Zealand in 2026, Absolute IT continues to demonstrate resilience, adaptability, and strategic foresight. Its ability to combine in-depth market intelligence with practical hiring solutions positions it as a leading partner for organisations navigating the complexities of technology talent acquisition.
In an environment defined by rapid technological change, cybersecurity challenges, and AI-driven transformation, Absolute IT’s future-oriented recruitment model reflects the broader evolution of IT hiring across New Zealand.
3. Potentia
In 2026, Potentia stands as the largest locally owned technology recruitment agency in New Zealand, with established hubs in Auckland, Wellington, Christchurch, and Dunedin. Over a 20-year operational history, the agency has delivered more than 5,000 successful placements across contract and permanent technology roles. Its long-term presence in the domestic market has enabled it to develop strong relationships with enterprise organisations, high-growth startups, and public sector agencies.
Potentia’s positioning within the top IT and software recruitment agencies in New Zealand in 2026 is reinforced by its commitment to building sustainable technology capability within the country. Rather than focusing solely on immediate vacancy fulfilment, the agency promotes long-term workforce development and skills progression across the national tech ecosystem.
National Footprint and Service Coverage
Potentia’s multi-city presence enables it to support both regional and metropolitan technology hiring strategies. This geographic reach is increasingly important in 2026, as hybrid work models and distributed engineering teams become standard practice across New Zealand.
Table: Potentia Operational Presence and Market Focus
| Location | Primary Market Focus | Typical Client Profile |
|---|---|---|
| Auckland | Enterprise technology, SaaS, fintech | Large corporates, scale-ups, tech startups |
| Wellington | Government digital transformation, cybersecurity | Public sector agencies, consultancies |
| Christchurch | Engineering, embedded systems, innovation hubs | Product development firms, hardware-tech firms |
| Dunedin | Emerging tech, regional innovation initiatives | Startups, research-driven organisations |
This regional distribution allows Potentia to match specialised technology talent with opportunities beyond the traditional Auckland-centric hiring market.
Cultural Framework: Kaupapa Potentia
A distinctive element of Potentia’s recruitment methodology is its internal philosophy referred to as “Kaupapa Potentia.” This framework integrates core values such as Manaakitanga, which emphasises elevating others through supportive engagement, and Whanaungatanga, which focuses on building meaningful relationships and pursuing professional mastery.
These principles are embedded into candidate assessment, client advisory services, and long-term workforce planning. The agency evaluates not only technical competence but also cultural alignment, leadership potential, and the candidate’s ability to contribute positively to organisational environments.
Matrix: Technical Fit vs Cultural Alignment in Potentia’s Model
| Evaluation Dimension | Technical Assessment Focus | Cultural Assessment Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Skills Verification | Role-specific expertise and platform knowledge | Commitment to collaboration and shared values |
| Experience Validation | Project complexity and operational impact | Team contribution and leadership behaviour |
| Long-Term Potential | Adaptability to new technologies | Alignment with organisational purpose |
| Hiring Outcome Goal | Immediate technical delivery | Sustainable team performance and retention |
Specialisation in High-Growth Technology Roles
Potentia is recognised for its expertise in recruiting for complex and high-growth technical disciplines that are central to New Zealand’s digital infrastructure expansion in 2026.
Key specialisations include:
• Senior Site Reliability Engineers (SRE)
• Embedded Systems Development Engineers
• Data Engineers and Data Platform Architects
• Cloud Infrastructure and DevOps Professionals
• Product Engineering and Systems Integration Specialists
The agency has placed candidates into mission-critical projects, including advanced race management software systems developed for global sporting events such as the America’s Cup. These roles require precision engineering, high system resilience, and strong cross-functional collaboration, reflecting the level of complexity Potentia is capable of supporting.
Table: High-Growth IT Recruitment Areas in 2026
| Specialisation Area | Market Demand Level | Strategic Importance to Employers |
|---|---|---|
| Site Reliability Engineering | Very High | Ensures uptime and resilience of cloud systems |
| Embedded Development | High | Supports hardware-integrated software innovation |
| Data Engineering | Very High | Enables AI, analytics, and business intelligence |
| DevOps & Platform Engineering | High | Accelerates digital transformation initiatives |
| Systems Architecture | High | Guides enterprise technology roadmaps |
Industry Recognition and Service Quality
In 2025, Potentia received industry recognition through the Recruitment, Consulting & Staffing Association (RCSA), where it was awarded a “Rising Star” honour, specifically highlighting the contributions of Ryan Bevens. The judging panel acknowledged the agency’s strategic thinking, operational insight, and ability to elevate recruitment standards across the technology sector.
The agency’s strong client and candidate satisfaction is further reflected in its 4.8 average Google rating in 2026. Feedback consistently references the team’s deep understanding of both technical constraints and human factors within the hiring process. This dual awareness enables Potentia to manage candidate expectations, advise employers on realistic market conditions, and mitigate risk associated with complex technical placements.
Table: Indicators of Service Quality in 2026
| Service Indicator | Evidence of Performance | Market Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Industry Awards | RCSA Rising Star recognition (2025) | Enhanced brand credibility |
| Client Satisfaction | 4.8 average Google rating | High repeat business and referrals |
| Market Insight Capability | Operational understanding of talent shortages | Reduced hiring cycle times |
| Cultural Integration Approach | Kaupapa Potentia framework | Improved retention and team cohesion |
Strategic Position Within New Zealand’s IT Recruitment Sector
Among the top IT and software recruitment agencies in New Zealand in 2026, Potentia differentiates itself through a combination of local ownership, strong regional reach, cultural integration, and deep technical specialisation. Its recruitment methodology balances immediate technical delivery with long-term workforce sustainability.
Comparative Strategic Matrix
| Evaluation Criteria | Potentia Position in 2026 |
|---|---|
| Ownership Structure | Largest locally owned tech recruiter |
| Geographic Coverage | Nationwide presence across four major hubs |
| Cultural Integration | Embedded values-driven recruitment framework |
| High-Growth Technical Focus | Strong expertise in SRE, embedded, and data roles |
| Industry Recognition | Award-winning and highly rated by clients |
Conclusion
As New Zealand’s technology market continues to expand in 2026, driven by cloud transformation, data engineering growth, and resilient infrastructure requirements, Potentia maintains a prominent role in shaping the national IT workforce. Its commitment to cultural alignment, grassroots talent development, and high-impact technical recruitment ensures that it remains a key contributor to the country’s evolving digital economy.
4. Salt New Zealand
In 2026, Salt New Zealand operates as part of a global digital recruitment network, supporting organisations across technology, software engineering, digital transformation, and emerging AI-driven business functions. The agency has established a strong footprint within the New Zealand market by combining international reach with local market insight.
Salt differentiates itself from many traditional IT recruitment agencies through its strategic advisory capability. Beyond sourcing software developers, data engineers, and digital specialists, the firm provides executive-level consulting focused on AI fluency, workforce transformation, and long-term talent strategy. This broader scope positions Salt among the top IT and software recruitment agencies in New Zealand in 2026.
National and Global Positioning
As part of an international recruitment group, Salt leverages global talent intelligence while maintaining dedicated local consulting teams. This hybrid model allows the agency to respond to domestic hiring trends while drawing upon international best practices in psychometric evaluation, candidate experience, and executive advisory services.
Table: Salt New Zealand Market Positioning
| Strategic Dimension | Salt New Zealand Position in 2026 |
|---|---|
| Ownership Structure | Global digital recruitment network |
| Core Focus | IT, digital, and technology recruitment |
| Advisory Capability | Executive AI and talent strategy consulting |
| Sector Strength | Medical-tech, research, enterprise digital projects |
| Candidate Retention Focus | High emphasis on long-term placement stability |
Salt Advisory: Executive AI Fluency and Talent Strategy
A defining feature of Salt’s offering in 2026 is the Salt Advisory service. This initiative is designed to support C-suite leaders and senior executives in navigating artificial intelligence integration, digital workforce planning, and technology transformation strategies.
As AI tools and automation platforms become embedded in enterprise operations, leadership teams increasingly require guidance on workforce capability development. Salt Advisory addresses this need by delivering:
• AI literacy coaching for senior executives
• Talent mapping aligned with digital transformation roadmaps
• Workforce restructuring advisory
• Succession planning for digital leadership roles
Matrix: Traditional Recruitment Model vs Salt Advisory Model
| Dimension | Traditional Recruitment Model | Salt Advisory Model in 2026 |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Service | Vacancy-based candidate sourcing | Strategic talent and AI workforce advisory |
| Executive Engagement | Limited to role briefings | Ongoing leadership coaching and planning |
| AI Integration Focus | Role-specific technical hiring | Enterprise-wide AI fluency strategy |
| Workforce Planning Horizon | Short-term recruitment cycles | Long-term digital capability transformation |
Performance Metrics and Measurable Outcomes
Salt New Zealand reports a 97 percent retention rate for placed candidates, reflecting its structured assessment processes and long-term alignment strategies. This performance indicator suggests a strong focus on cultural compatibility, role clarity, and candidate readiness.
A core component of Salt’s methodology includes rigorous psychometric testing protocols. These assessments help identify behavioural alignment, leadership attributes, and resilience under operational pressure. Combined with its “face-to-face” engagement philosophy, the agency seeks to create a human-centred recruitment process even within highly technical environments.
Table: Key Performance Indicators in 2026
| Performance Metric | Reported Outcome | Strategic Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Candidate Retention Rate | 97 percent | Strong alignment and long-term stability |
| Medical-Tech Role Fill Rate | 94 percent | Capability in complex niche hiring |
| Project-Based Retention Outcome | 100 percent in recent 2-year project | High operational consistency |
| Net Promoter Score (NPS) | +68 | Strong client satisfaction and advocacy |
Sector Expertise: Partnership with Aotearoa Clinical Trials Network
Salt has maintained a long-term partnership with the Aotearoa Clinical Trials network since 2017. Through this collaboration, the agency has supported complex medical-technology recruitment requirements, achieving a 94 percent fill rate for highly specialised roles.
Medical-tech hiring in 2026 requires interdisciplinary expertise, blending software engineering, data science, regulatory compliance knowledge, and clinical research understanding. Salt’s ability to deliver consistent results in this niche reflects its experience in managing technically demanding and operationally critical placements.
Table: Medical-Tech Recruitment Capabilities
| Capability Area | Application in Clinical Trials Sector |
|---|---|
| Data Systems Recruitment | Clinical data platforms and analytics systems |
| Cybersecurity Expertise | Protection of patient data and research integrity |
| Regulatory Awareness | Compliance-focused technical placements |
| 24/7 Operational Staffing | Continuous research and trial support functions |
Client Experience and Service Quality
Client feedback from the research and medical sectors highlights Salt’s structured communication, timely updates, and candidate-centred approach. Long-term partners emphasise the agency’s ability to manage complex, round-the-clock operational requirements through creative sourcing strategies.
In a recent two-year project, Salt reportedly achieved a 100 percent fill and retention rate, demonstrating its capacity to maintain workforce stability in high-pressure environments. The project’s +68 Net Promoter Score further indicates strong satisfaction among stakeholders.
Matrix: Elements Driving High Retention
| Retention Driver | Salt’s Operational Approach |
|---|---|
| Candidate Screening | Psychometric and behavioural evaluation |
| Client Communication | Structured updates and proactive issue resolution |
| Cultural Alignment | Emphasis on people-first recruitment philosophy |
| Complex Project Management | Creative sourcing for 24/7 operational needs |
Strategic Position in the 2026 IT Recruitment Landscape
Within the competitive field of top IT and software recruitment agencies in New Zealand in 2026, Salt distinguishes itself through its integration of recruitment execution and executive advisory services. The agency’s ability to support AI strategy at the leadership level, while simultaneously delivering measurable placement outcomes, reinforces its market relevance.
Comparative Strategic Overview
| Evaluation Criteria | Salt New Zealand Position in 2026 |
|---|---|
| Global Network Strength | Strong international backing |
| Executive Advisory Services | Advanced AI fluency and talent strategy support |
| Retention Metrics | 97 percent placement retention |
| Sector Expertise | Medical-tech and research-focused recruitment |
| Client Satisfaction | High NPS and long-term partnerships |
Conclusion
As New Zealand’s digital economy accelerates in 2026, driven by artificial intelligence adoption, regulatory compliance demands, and advanced software engineering requirements, Salt New Zealand continues to expand its role beyond conventional recruitment. Its blend of global reach, strategic advisory capability, rigorous assessment methodology, and measurable performance outcomes positions it as a leading agency for organisations seeking both technical talent and forward-looking workforce guidance.
5. Talent International

In 2026, Talent International is recognised as one of the most established global technology recruitment organisations operating within New Zealand. With reported annual revenues ranging between 100 million and 500 million dollars, the agency operates at significant scale while maintaining a strong presence in key international markets across Asia-Pacific, Europe, and North America.
Within New Zealand, Talent International plays a prominent role among the top IT and software recruitment agencies by supporting organisations with complex, mid-level to executive technology hiring requirements. Its reputation is built on a combination of global delivery capability, ethical leadership, and long-term investment in workforce development.
Global Scale with Local Market Integration
Despite its global reach, Talent International is widely regarded for preserving a strong local culture within each regional market it operates in. In New Zealand, this approach translates into recruitment teams that are deeply embedded in the local technology ecosystem while benefiting from international best practices, tools, and talent networks.
This balance enables the agency to deliver consistent recruitment outcomes for multinational enterprises, government departments, and fast-growing local organisations that require access to both domestic and global talent pools.
Table: Talent International Global and Local Positioning
| Dimension | Talent International Position in 2026 |
|---|---|
| Revenue Scale | 100M–500M global revenue range |
| Geographic Reach | Multi-continent global operations |
| New Zealand Market Presence | Established and locally embedded teams |
| Recruitment Scope | Mid-level to executive technology roles |
| Operating Philosophy | Ethical leadership and people-first culture |
Talent RISE Foundation and Workforce Inclusion
A defining characteristic of Talent International’s broader impact is its Talent RISE foundation. This initiative is dedicated to supporting disadvantaged and underrepresented youth by providing pathways into technology careers. Through structured programs, mentorship, and employment opportunities, Talent RISE contributes to long-term skills development within the global and local technology workforce.
In the context of New Zealand’s ongoing technology skills shortage in 2026, this foundation aligns closely with national workforce development priorities. It reflects a strategic commitment to building future talent pipelines rather than relying solely on experienced hires.
Matrix: Recruitment Delivery vs Social Impact Strategy
| Focus Area | Traditional Recruitment Model | Talent International Model |
|---|---|---|
| Workforce Supply | Existing experienced professionals | Combination of experienced and emerging talent |
| Community Investment | Limited or indirect | Direct through Talent RISE programs |
| Long-Term Skills Development | Employer-led training | Foundation-supported career pathways |
| Employer Value Proposition | Speed and scale | Sustainability and social responsibility |
Specialisation in High-Value Technology Roles
Talent International is particularly active in recruiting for mid-level to senior technology professionals, including leadership and executive roles. In 2026, its strongest areas of specialisation align with technologies that underpin enterprise digital transformation initiatives.
Key focus areas include:
• Cloud engineering and cloud architecture
• Data engineering and advanced analytics
• Technology leadership and digital transformation roles
• Enterprise systems and platform modernisation
These roles are critical for organisations migrating to cloud-native environments, implementing data-driven decision-making frameworks, and scaling digital platforms across distributed teams.
Table: Priority Technology Recruitment Domains
| Technology Domain | Typical Roles Recruited | Strategic Importance in 2026 |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Technology | Cloud Engineers, Cloud Architects | Enables scalability and infrastructure modernisation |
| Data Engineering | Data Engineers, Analytics Leads | Supports AI, automation, and insight-driven operations |
| Technology Leadership | CTOs, Heads of Engineering, Digital Directors | Guides enterprise digital strategy |
| Enterprise Platforms | Systems Architects, Integration Specialists | Ensures system stability and interoperability |
Organisational Culture and Employee Engagement
One of the most frequently cited differentiators of Talent International is its internal culture. Employees and candidates consistently describe the organisation as maintaining a family-style working environment, even within a high-volume and high-pressure recruitment industry.
This culture is characterised by ethical leadership, strong internal engagement, and a sense of shared purpose. Such an environment contributes directly to service quality, as consultants are better positioned to build long-term relationships with both candidates and clients.
Table: Cultural Attributes and Operational Impact
| Cultural Attribute | Operational Outcome |
|---|---|
| Ethical Leadership | High trust with candidates and clients |
| Family-Oriented Environment | Strong employee retention and engagement |
| Community Involvement | Positive employer and brand reputation |
| Purpose-Driven Recruitment | Deeper alignment with client values |
Candidate and Client Experience
Verified feedback from senior recruitment professionals within New Zealand highlights Talent International’s ability to engage candidates and clients in a meaningful and authentic manner. Reviewers consistently reference the organisation’s passion for recruitment, commitment to community initiatives through Talent RISE, and its ability to operate effectively at scale without losing a human touch.
This balance is particularly notable in the executive and senior technology recruitment space, where trust, discretion, and long-term alignment are essential to successful outcomes.
Matrix: Candidate Experience in High-Volume vs Relationship-Led Recruitment
| Experience Factor | High-Volume Recruitment Model | Talent International Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Candidate Engagement | Transactional | Relationship-focused |
| Communication Style | Process-driven | Personal and consultative |
| Career Guidance | Limited | Long-term career development focus |
| Community Contribution | Minimal | Active through Talent RISE |
Strategic Position Among Top IT Recruitment Agencies in 2026
Within the competitive landscape of top IT and software recruitment agencies in New Zealand in 2026, Talent International differentiates itself through its combination of global scale, ethical culture, executive-level recruitment capability, and genuine social impact initiatives.
Comparative Strategic Overview
| Evaluation Criteria | Talent International Position in 2026 |
|---|---|
| Global Scale | Large multinational recruitment organisation |
| Local Market Integration | Strong New Zealand-based teams |
| Social Impact | Dedicated foundation supporting disadvantaged youth |
| Senior-Level Recruitment | Strong focus on mid-level to executive roles |
| Cultural Reputation | Family-oriented and values-driven organisation |
Conclusion
As New Zealand’s technology sector continues to mature in 2026, organisations increasingly seek recruitment partners that can deliver both scale and substance. Talent International’s ability to combine global reach with a strong local culture, alongside its investment in future talent through the Talent RISE foundation, positions it as a trusted and forward-thinking leader in the country’s IT and software recruitment ecosystem.
6. Hays Technology
In 2026, Hays continues to operate as one of the most influential global recruitment organisations within New Zealand’s technology employment landscape. Through its specialist division, Hays Technology, the firm plays a critical role in supporting public sector agencies, large enterprises, and multinational corporations undertaking complex digital transformation initiatives.
Hays Technology is widely recognised as a preferred recruitment partner for large-scale contract hiring and project-based workforce deployment. Its extensive infrastructure, global talent networks, and mature training systems allow it to manage high-volume and technically demanding assignments that smaller boutique agencies may struggle to support.
Strategic Position in Public Sector and Enterprise Recruitment
Hays Technology maintains a particularly strong footprint in New Zealand’s public sector and enterprise markets. Government agencies and major corporates often require rapid scaling of technology teams for fixed-term transformation programs, cybersecurity upgrades, and cloud migration initiatives.
The agency’s structured compliance processes and contractor management systems are designed to align with procurement standards typically associated with government and regulated industries.
Table: Hays Technology Core Market Segments in 2026
| Client Segment | Typical Recruitment Needs | Strategic Importance to Sector |
|---|---|---|
| Public Sector Agencies | Large-scale project teams, cybersecurity staff | Supports national digital modernisation |
| Financial Services | DevOps engineers, cloud security specialists | Ensures regulatory compliance and resilience |
| Enterprise Corporations | Platform engineers, cloud architects, SREs | Drives infrastructure transformation |
| Infrastructure Projects | Contract-based technical specialists | Enables time-bound digital initiatives |
Specialisation in High-Demand Technology Domains
In 2026, Hays Technology remains a primary provider for contract and project-based roles in high-growth areas such as DevOps, cloud transformation, and cybersecurity. These disciplines are central to enterprise resilience and digital agility across New Zealand’s economy.
Key focus areas include:
• DevOps engineering and continuous delivery specialists
• Cloud transformation architects and migration experts
• Cybersecurity analysts and governance professionals
• Infrastructure and platform engineering contractors
Table: High-Volume Contract Recruitment Areas
| Technology Discipline | Market Demand Level | Typical Engagement Type |
|---|---|---|
| DevOps & CI/CD | Very High | Project-based and rolling contracts |
| Cloud Migration | Very High | Multi-phase transformation programs |
| Cybersecurity | High | Risk mitigation and compliance-focused projects |
| Platform Engineering | High | Infrastructure modernisation initiatives |
Market Resilience and Financial Stability
Financial performance data from 2025–2026 demonstrates Hays Technology’s relative resilience during broader market contraction. While overall net recruitment fees in New Zealand declined by approximately 30 percent during that period, the technology division proved significantly more stable.
Across the Australia and New Zealand region, technology-related fees decreased by only 8 percent, representing a considerably smaller contraction compared to other industry sectors. This performance highlights the sustained demand for technology professionals even during economic volatility.
Matrix: Sector Performance Comparison 2025–2026
| Sector Category | Net Fee Change (%) | Relative Stability Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Overall NZ Recruitment | -30% | Significant contraction |
| ANZ Technology Division | -8% | Core pillar of stability |
| Non-Technology Sectors | Sharper declines | Higher exposure to market slowdown |
This comparative stability reinforces Hays Technology’s importance within the broader recruitment portfolio and reflects the ongoing prioritisation of digital transformation investments by both public and private organisations.
Internal Training and Recruitment Capability
One of Hays Technology’s frequently cited strengths is its internal consultant training infrastructure. The organisation is known for structured onboarding programs, particularly for professionals new to technology recruitment. This training focus enhances consultant competency in understanding complex technical requirements, market rate benchmarking, and contractor lifecycle management.
An internal review from January 2026 described the agency as maintaining a relaxed yet high-performance culture. Employees highlighted the scale of operations as a competitive advantage, enabling the firm to support transformation programs that require substantial recruitment coordination across multiple stakeholders.
Table: Operational Strengths and Service Delivery Impact
| Operational Strength | Impact on Clients and Candidates |
|---|---|
| Structured Training Programs | Improved consultant technical literacy |
| Global Infrastructure | Capacity for large-scale hiring campaigns |
| High-Performance Culture | Strong delivery against transformation timelines |
| Contractor Management Systems | Compliance and payroll reliability for long-term projects |
Large-Scale Project Capability
A defining characteristic of Hays Technology in 2026 is its ability to deliver workforce solutions for enterprise-scale digital programs. These projects often involve multi-year cloud transformation roadmaps, cybersecurity overhauls, and infrastructure modernisation efforts requiring coordinated contractor deployment.
Matrix: Boutique Agency vs Global Provider Capability
| Capability Dimension | Boutique Agency Model | Hays Technology Model |
|---|---|---|
| Volume Handling | Limited project capacity | High-volume, multi-team scaling |
| Geographic Coverage | Localised focus | National and international reach |
| Compliance Infrastructure | Basic systems | Advanced governance frameworks |
| Enterprise Program Support | Selective support | Full transformation lifecycle coverage |
Strategic Position Among Top IT Recruitment Agencies in 2026
Within the competitive landscape of top IT and software recruitment agencies in New Zealand in 2026, Hays Technology is positioned as a large-scale, enterprise-focused provider with strong resilience during market fluctuations. Its global infrastructure, structured consultant training, and deep connections with public sector and enterprise clients enable it to operate as a primary recruitment partner for large digital transformation programs.
Comparative Strategic Overview
| Evaluation Criteria | Hays Technology Position in 2026 |
|---|---|
| Global Reach | Extensive international operations |
| Public Sector Integration | Strong government and enterprise relationships |
| Contract Recruitment Scale | High-volume, project-based capability |
| Market Resilience | Technology division remained comparatively stable |
| Training and Culture | Structured learning and high-performance focus |
Conclusion
As digital transformation remains a national priority across government agencies and large enterprises in 2026, Hays Technology continues to serve as a foundational recruitment partner within New Zealand’s IT and software employment ecosystem. Its demonstrated financial resilience, ability to manage complex contract programs, and strong training infrastructure position it as a dependable provider for organisations undertaking large-scale technology initiatives.
7. Robert Half

In 2026, Robert Half remains one of the most internationally recognised recruitment firms operating in New Zealand. Known for its analytical, research-backed approach to talent acquisition, the organisation plays a significant role in shaping hiring strategies across the technology, finance, and professional services sectors.
Within the context of the top IT and software recruitment agencies in New Zealand in 2026, Robert Half stands out for its structured market intelligence tools, diversified hiring models, and strong post-placement engagement practices. Its recruitment services span permanent placements, contract staffing, and project consulting solutions tailored to time-sensitive business initiatives.
Data-Driven Recruitment and Market Intelligence
A central pillar of Robert Half’s brand positioning is its annual Salary Guide, which is widely referenced by employers when determining compensation strategies. In New Zealand, approximately 44 percent of hiring managers use this guide as a primary benchmarking instrument when assessing market rates for technology and digital roles.
The Salary Guide provides granular data on remuneration trends across disciplines such as software engineering, cybersecurity, cloud infrastructure, and IT leadership. In a market characterised by skill shortages and economic fluctuations, such data-driven insight supports informed hiring decisions.
Table: Robert Half Salary Intelligence Utilisation in New Zealand
| Market Insight Tool | Employer Adoption Rate | Strategic Impact on Hiring Decisions |
|---|---|---|
| Salary Guide | 44% of hiring managers | Informs compensation benchmarking |
| Market Trend Reporting | Broad industry usage | Supports workforce planning |
| Skills Demand Analysis | High in tech sector | Identifies emerging technical priorities |
Comprehensive Recruitment Models
Robert Half’s recruitment model extends beyond traditional permanent hiring. In 2026, organisations increasingly require flexible staffing structures that can accommodate evolving business priorities, digital transformation programs, and short-term project requirements.
The agency supports three primary engagement models:
• Permanent recruitment for long-term organisational growth
• Contract placements for short-term and specialist roles
• Project consulting for defined, outcome-driven initiatives
Matrix: Recruitment Engagement Models in 2026
| Engagement Type | Typical Use Case | Business Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Permanent Hiring | Core software engineering teams | Long-term capability building |
| Contract Staffing | Cloud migration, cybersecurity projects | Flexibility and rapid deployment |
| Project Consulting | ERP implementations, system integrations | Outcome-focused delivery and expertise |
Operational Intelligence and Market Sentiment
In 2026, Robert Half’s research indicates that 80 percent of technology leaders expect the broader economic outlook to positively influence salary settings. This optimism reflects sustained investment in digital capability despite broader economic uncertainties.
However, the agency also highlights a critical behavioural factor: 42 percent of employers report increased willingness to raise salary offers when faced with urgent hiring needs. This suggests that while long-term compensation planning is influenced by macroeconomic conditions, immediate operational demands often accelerate offer negotiations.
Table: Technology Hiring Sentiment and Compensation Drivers
| Insight Metric | Reported Percentage | Interpretation for Employers |
|---|---|---|
| Tech leaders expecting positive salary impact | 80% | Strong confidence in digital investment |
| Increased offer flexibility due to urgency | 42% | Talent scarcity driving premium offers |
| Continued demand for tech talent | High | Persistent skills shortage in core domains |
These insights reinforce Robert Half’s positioning as a strategic advisor capable of guiding employers through dynamic salary negotiations and competitive offer structuring.
Post-Placement Care and Candidate Experience
A distinguishing feature of Robert Half’s service model in 2026 is its emphasis on post-placement follow-up. Verified candidate reviews frequently reference the agency’s proactive communication after successful placements, including regular check-ins to assess job satisfaction and workplace integration.
This ongoing engagement reflects a relationship-driven approach that extends beyond transactional recruitment. Candidates report feeling valued as professionals, rather than simply being treated as placements within a hiring process.
Matrix: Traditional Placement Model vs Robert Half Post-Placement Model
| Service Dimension | Traditional Recruitment Model | Robert Half Approach in 2026 |
|---|---|---|
| Post-Placement Contact | Limited or none | Regular structured check-ins |
| Candidate Support | Issue-based response | Proactive communication |
| Work-Life Consideration | Minimal discussion | Personal circumstances acknowledged |
| Long-Term Relationship | Transactional | Ongoing professional partnership |
Strategic Position in New Zealand’s Technology Recruitment Ecosystem
Among the top IT and software recruitment agencies in New Zealand in 2026, Robert Half distinguishes itself through its integration of market research, flexible hiring models, and consistent candidate care. Its data-led advisory capability appeals to hiring managers seeking evidence-based decision-making, while its relationship-focused follow-up strengthens retention outcomes.
Comparative Strategic Overview
| Evaluation Criteria | Robert Half Position in 2026 |
|---|---|
| Market Intelligence | Strong salary benchmarking leadership |
| Recruitment Flexibility | Permanent, contract, and project consulting |
| Economic Insight Reporting | Advanced tech hiring sentiment analysis |
| Candidate Experience | Structured post-placement engagement |
| Brand Recognition | Globally established staffing firm |
Conclusion
As New Zealand’s technology workforce continues to evolve in 2026, organisations require recruitment partners capable of combining analytical precision with human-centred engagement. Robert Half’s data-driven salary intelligence, flexible engagement structures, and strong post-placement communication framework position it as a reliable and strategically valuable player within the country’s IT and software recruitment landscape.
8. Dynamix Recruitment
In 2026, Dynamix Recruitment has strengthened its reputation as one of the most candidate-focused recruitment agencies operating in New Zealand. Following a standout performance at the 2025 Recruitment, Consulting & Staffing Association awards, where it secured titles for Outstanding Medium Agency and Excellence in Candidate Care, Dynamix has emerged as a differentiated player within the competitive IT and technical recruitment landscape.
While operating at a mid-sized scale, the agency has achieved national visibility through its distinctive service philosophy and structured operational safeguards. Its approach blends technical placement expertise with a strong emphasis on loyalty, safety, and long-term relationship management.
Distinctive Recruitment Philosophy: The “Wolf Pack” Model
Dynamix Recruitment operates under what it describes as a “wolf pack” philosophy. This model centres on loyalty, protection, collaboration, and collective success. Rather than focusing solely on rapid placements, the agency positions itself as an advocate for both candidates and client organisations.
This philosophy translates into proactive communication, transparent processes, and a commitment to safeguarding candidate wellbeing throughout the employment lifecycle.
Matrix: Transactional Recruitment vs Wolf Pack Philosophy
| Recruitment Dimension | Transactional Model | Dynamix Wolf Pack Model |
|---|---|---|
| Candidate Relationship | Vacancy-driven engagement | Long-term professional partnership |
| Client Support | Role-specific delivery | Ongoing advisory and workforce alignment |
| Communication Approach | Reactive updates | Proactive, consistent engagement |
| Retention Strategy | Limited post-placement involvement | Continuous follow-up and support |
Award Recognition and Industry Standing
Dynamix Recruitment’s dual recognition at the 2025 RCSA Awards significantly elevated its profile within New Zealand’s recruitment sector. The awards for Outstanding Medium Agency and Excellence in Candidate Care reflect peer-reviewed acknowledgment of operational standards, ethical recruitment practice, and service innovation.
These accolades position Dynamix as a benchmark for candidate engagement within the broader list of top IT and software recruitment agencies in New Zealand in 2026.
Table: Industry Recognition and Service Validation
| Award Category | Year Awarded | Strategic Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Outstanding Medium Agency | 2025 | Demonstrates operational excellence |
| Excellence in Candidate Care | 2025 | Validates candidate-first service model |
| Industry Peer Recognition | Ongoing | Reinforces market credibility |
Process-Driven Recruitment and Safety Standards
A defining feature of Dynamix Recruitment’s methodology is its rigorous pre-placement process. The agency incorporates mandatory NZQA-aligned drug screening protocols and structured health and safety “toolbox talks” into its onboarding framework. These measures ensure that candidates are not only technically capable but also compliant with operational safety standards.
In industries where technology intersects with industrial environments, infrastructure projects, or regulated sectors, such safeguards significantly reduce risk exposure for employers.
Table: Structured Candidate Screening Framework
| Screening Component | Purpose | Employer Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| NZQA Drug Screening | Verifies compliance with workplace safety norms | Reduces operational and legal risk |
| Health & Safety Toolbox Talks | Reinforces on-site safety awareness | Enhances workforce readiness |
| Technical Qualification Review | Confirms skills and certifications | Ensures capability alignment |
| Wellness Checks | Monitors candidate wellbeing | Improves retention and engagement |
Candidate Care and Continuous Support
The RCSA judges’ citation for Dynamix’s Excellence in Candidate Care award emphasised the agency’s commitment to candidate-first experiences. From the initial consultation to final placement and beyond, Dynamix integrates structured communication touchpoints designed to maintain transparency and trust.
In addition to safety protocols, the agency has implemented wellness checks and upskilling initiatives. These programs provide candidates with access to skill enhancement opportunities and career progression pathways, aligning recruitment with long-term professional development.
Matrix: Elements of Excellence in Candidate Care
| Care Dimension | Operational Execution by Dynamix |
|---|---|
| Initial Engagement | Detailed role briefing and expectation setting |
| Transparent Communication | Clear timelines and process updates |
| Wellness Monitoring | Ongoing wellbeing check-ins |
| Upskilling Opportunities | Access to training and capability development |
| Post-Placement Follow-Up | Continued support after role commencement |
Strategic Position in the 2026 IT Recruitment Landscape
Within the broader context of New Zealand’s IT and software recruitment market in 2026, Dynamix Recruitment differentiates itself through its balanced focus on operational safety, ethical practice, and candidate wellbeing. While many agencies compete on speed and scale, Dynamix has built its competitive advantage around quality, compliance, and sustained relationships.
Comparative Strategic Overview
| Evaluation Criteria | Dynamix Recruitment Position in 2026 |
|---|---|
| Industry Awards | Dual RCSA recognition for excellence |
| Candidate Care Focus | Award-winning, structured engagement model |
| Safety and Compliance | Mandatory screening and toolbox talks |
| Organisational Philosophy | Loyalty-driven, protective recruitment model |
| Market Differentiation | High trust and ethical reputation |
Conclusion
As New Zealand’s technology and infrastructure sectors continue to evolve in 2026, organisations increasingly seek recruitment partners who prioritise both technical competency and workforce safety. Dynamix Recruitment’s award-winning candidate care framework, structured compliance processes, and loyalty-driven service philosophy position it as a distinctive and trusted agency within the country’s competitive IT recruitment ecosystem.
9. Frog Recruitment

In 2026, Frog Recruitment continues to strengthen its position as a premium boutique recruitment firm within New Zealand’s competitive IT and professional hiring landscape. Known for its personalised approach and consistently high client satisfaction ratings, Frog Recruitment has built a strong reputation among employers seeking quality over volume.
With an outstanding 4.99 out of 5.0 rating on Seek, the agency stands out for its service precision, communication standards, and long-term relationship management. Within the broader ecosystem of top IT and software recruitment agencies in New Zealand in 2026, Frog Recruitment differentiates itself through attention to detail and high-touch engagement rather than scale alone.
Boutique Positioning and Client Service Excellence
Frog Recruitment has earned multiple awards for Excellence in Client Service and Candidate Experience, reflecting a structured commitment to transparency, responsiveness, and accountability. As a boutique agency, it operates with smaller consultant teams, enabling deeper familiarity with client business models, hiring needs, and team culture.
This close engagement model allows Frog to deliver refined candidate shortlists aligned not only with technical requirements but also with organisational fit.
Table: Boutique Recruitment Model vs Large-Scale Agency Model
| Recruitment Dimension | Large-Scale Agency Model | Frog Recruitment Boutique Model |
|---|---|---|
| Candidate Volume Focus | High throughput | Quality-focused shortlists |
| Client Interaction | Structured but standardised | Personalised and consultative |
| Decision-Making Speed | Process-driven | Agile and relationship-led |
| Customisation Level | Moderate | High degree of tailoring |
Service Continuity and High-Pressure Environments
One of Frog Recruitment’s key strengths in 2026 is its ability to maintain service continuity in demanding and fast-paced hiring scenarios. This includes temporary staffing and urgent contract placements, where response times and candidate quality are critical.
High-pressure temporary recruitment environments often require:
• Rapid candidate sourcing and screening
• Clear communication of short-term expectations
• Immediate onboarding coordination
• Continuous client updates
Frog Recruitment’s high-touch communication model enables the agency to deliver quality placements even when timelines are compressed.
Table: Temporary Recruitment Performance Indicators
| Performance Factor | Frog Recruitment Approach | Client Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Response Time | Rapid candidate identification | Reduced downtime for employers |
| Communication Frequency | Proactive updates | Increased client confidence |
| Candidate Screening | Detailed capability and culture assessment | Higher applicant quality |
| Placement Stability | Strong matching precision | Reduced turnover in temp roles |
High-Touch Communication as a Core Differentiator
Feedback from employers in early 2026 highlights Frog Recruitment’s attentiveness and consistent communication. Clients report that consultants take the time to understand operational realities, team dynamics, and long-term business objectives before presenting candidate shortlists.
This consultative approach reduces the likelihood of misalignment and increases hiring efficiency, particularly in specialised technology roles where technical nuance matters.
Matrix: Communication-Centric Recruitment Model
| Communication Element | Operational Execution at Frog Recruitment |
|---|---|
| Initial Consultation | In-depth needs analysis and business mapping |
| Candidate Briefing | Clear role expectations and employer insights |
| Ongoing Updates | Regular progress communication |
| Post-Submission Feedback | Transparent candidate and client feedback loop |
| Relationship Maintenance | Continuous engagement beyond placement |
Candidate Experience and Applicant Quality
Frog Recruitment’s award recognition for Candidate Experience is closely linked to its respectful and transparent engagement model. Employers consistently report receiving highly relevant applicants whose skills and experience align closely with advertised requirements.
The agency’s approach minimises common frustrations such as inconsistent communication or candidate “ghosting.” By maintaining strong two-way dialogue, Frog ensures that both candidates and employers remain informed throughout the hiring lifecycle.
Table: Drivers of High Applicant Quality
| Quality Driver | Recruitment Practice | Resulting Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Deep Business Understanding | Tailored role scoping and requirement mapping | Better skills alignment |
| Active Candidate Engagement | Clear communication of expectations | Stronger commitment from applicants |
| Detailed Screening | Competency and behavioural assessment | Reduced mismatch risk |
| Ongoing Relationship Building | Trust-based engagement | Repeat business and referrals |
Strategic Position Among Top IT Recruitment Agencies in 2026
In the 2026 New Zealand IT and software recruitment market, Frog Recruitment occupies a strategic niche as a high-performing boutique provider. While larger global firms dominate large-scale enterprise contracts, Frog excels in delivering personalised service, superior communication, and carefully curated candidate pools.
Comparative Strategic Overview
| Evaluation Criteria | Frog Recruitment Position in 2026 |
|---|---|
| Agency Scale | Boutique, high-touch provider |
| Client Service Awards | Multiple recognitions for excellence |
| Candidate Experience | Award-winning and highly rated |
| Temp Recruitment Capability | Strong performance in high-pressure roles |
| Market Reputation | 4.99/5.0 Seek rating |
Conclusion
As hiring complexity increases in 2026, many New Zealand employers seek recruitment partners capable of combining speed with precision. Frog Recruitment’s boutique structure, communication-driven methodology, and award-winning service standards position it as a trusted and highly rated agency within the country’s IT and professional recruitment landscape. Its ability to consistently deliver quality candidates in both permanent and temporary environments reinforces its standing among the top technology recruitment agencies operating in New Zealand.
10. Consult Recruitment

In 2026, Consult Recruitment is widely regarded as a high-performing specialist agency within New Zealand’s IT and digital recruitment landscape. Recognised for its “Best Contribution to the NZ Tech Sector” accolade, the firm has established itself as a consultative recruitment partner rather than a transactional staffing provider.
Consult Recruitment’s reputation is built on deep integration with modern recruitment technologies, agile placement strategies, and a strong ability to deliver talent for high-value digital transformation initiatives. As part of the broader group of top IT and software recruitment agencies in New Zealand in 2026, the agency continues to serve mid-sized enterprises, corporate clients, and technology-driven organisations requiring precision and speed in hiring.
Technology Integration and Scalable Delivery
A defining feature of Consult Recruitment’s operational model is its integration with modern recruitment platforms such as JobAdder. Leveraging cloud-based applicant tracking and workflow automation systems enables the agency to scale its services according to client demand without sacrificing candidate experience or communication quality.
This technological alignment enhances:
• Real-time candidate tracking
• Transparent hiring pipelines
• Faster shortlisting cycles
• Improved reporting and analytics for clients
Table: Technology-Enabled Recruitment Infrastructure
| Operational Capability | Enabled Through Modern Software Systems | Employer Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Candidate Pipeline Tracking | Centralised applicant management | Clear visibility into recruitment progress |
| Workflow Automation | Automated screening and follow-ups | Reduced administrative delays |
| Data Reporting | Hiring metrics and performance insights | Evidence-based workforce planning |
| Scalable Delivery | Cloud-based collaboration tools | Ability to manage multiple high-value contracts |
Agile Placement Strategy in High-Value IT Roles
Consult Recruitment specialises in IT and digital roles, particularly in complex, high-impact contract engagements. In 2026, the agency frequently manages senior-level contract assignments such as Senior Project Managers, Cloud Transformation Leads, and Digital Program Directors, with daily contract rates exceeding 1,100 NZD.
This focus reflects the growing demand for experienced leaders capable of delivering enterprise-wide digital transformation programs across government agencies and private sector organisations.
Matrix: Agile Placement Approach
| Recruitment Dimension | Traditional Model | Consult Recruitment Agile Model |
|---|---|---|
| Role Scoping | Static job descriptions | Collaborative refinement with stakeholders |
| Candidate Identification | Database-driven search | Targeted sourcing aligned to business strategy |
| Contract Negotiation | Standardised rate discussions | Market-informed, value-based positioning |
| Placement Timeline | Sequential process | Parallel evaluation and rapid shortlisting |
Table: High-Value IT Contract Focus Areas in 2026
| Role Type | Typical Daily Rate Range (NZD) | Strategic Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Senior Project Manager | 1,100+ | Oversees digital transformation delivery |
| Cloud Transformation Lead | 1,100–1,300 | Guides infrastructure modernisation |
| Program Director | 1,200+ | Manages enterprise-wide change initiatives |
| Digital Portfolio Manager | 1,100+ | Aligns technology investment with strategy |
Industry Contribution and Market Impact
Consult Recruitment’s recognition for Best Contribution to the NZ Tech Sector underscores its broader influence beyond direct placements. The agency’s involvement in supporting innovation, digital workforce growth, and collaborative partnerships across New Zealand’s technology ecosystem has contributed to its strong industry standing.
This recognition suggests that the firm is viewed not only as a service provider but also as an active participant in strengthening the national technology sector.
Table: Strategic Contribution Indicators
| Contribution Area | Observable Impact in 2026 |
|---|---|
| Technology Sector Support | Recruitment for digital transformation roles |
| Industry Collaboration | Partnerships with tech-enabled organisations |
| Workforce Development | Access to senior contract expertise |
| Recruitment Technology Use | Modern, scalable hiring infrastructure |
Client Experience and Long-Term Partnership
Client feedback from late 2025 highlights Consult Recruitment’s responsiveness, market knowledge, and collaborative approach. Long-term clients report working with the agency as primary recruitment partners for extended periods, reflecting sustained trust and satisfaction.
Key themes in employer feedback include:
• High responsiveness and consistent communication
• Strong understanding of sector-specific requirements
• Quality candidate placement in specialised roles
• Willingness to listen and adapt to evolving business needs
Matrix: Partnership-Oriented Recruitment Model
| Partnership Element | Consult Recruitment Execution |
|---|---|
| Responsiveness | Rapid turnaround on candidate shortlists |
| Market Insight | Up-to-date rate benchmarking and demand data |
| Collaborative Planning | Alignment of recruitment with business goals |
| Quality Assurance | Focused screening for senior-level expertise |
Strategic Position in the 2026 IT Recruitment Landscape
Within the competitive environment of New Zealand’s IT and software recruitment sector in 2026, Consult Recruitment distinguishes itself through its agile contract delivery model, high-value placement capability, and technology-enabled recruitment infrastructure. Its ability to manage senior digital leadership contracts and integrate seamlessly with client systems reinforces its role as a strategic hiring partner.
Comparative Strategic Overview
| Evaluation Criteria | Consult Recruitment Position in 2026 |
|---|---|
| Technology Integration | Strong alignment with modern recruitment tools |
| High-Value Contract Focus | Senior IT leadership roles with premium rates |
| Industry Recognition | Awarded for contribution to NZ tech sector |
| Client Partnership Strength | Long-term, consultative relationships |
| Agile Hiring Capability | Fast, collaborative placement strategy |
Conclusion
As New Zealand’s digital economy continues to expand in 2026, organisations increasingly require recruitment partners capable of managing complex, high-value technology engagements. Consult Recruitment’s agile methodology, scalable technology infrastructure, and partnership-driven service model position it as a trusted and strategically important agency within the country’s evolving IT and digital hiring ecosystem.
Strategic Analysis of the Technology Recruitment Landscape in New Zealand: 2026 Performance and Agency Benchmarking
In 2026, the technology recruitment market in Aotearoa New Zealand has entered a phase of strategic recalibration. The rapid, reactive hiring cycles that defined the post-pandemic expansion years have given way to a more deliberate, capability-driven workforce strategy. Organisations are no longer prioritising rapid headcount growth at any cost. Instead, they are refining their hiring models to focus on resilience, long-term capability building, and precision talent acquisition.
Business confidence is recovering after sustained economic pressure, yet the labour market remains structurally constrained. Approximately 85 percent of businesses report ongoing skills shortages in high-impact domains such as artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, cloud engineering, and data engineering. At the same time, the average cost per new technology hire has nearly doubled to NZD 23,860, fundamentally altering the risk profile of hiring decisions.
Recruitment agencies in 2026 are therefore expected to operate not merely as administrative intermediaries but as strategic workforce advisors capable of navigating complexity, salary inflation, and evolving technical requirements.
Macro-Economic Foundations of the 2026 Recruitment Market
The fiscal environment underpinning the 2026 recruitment landscape is defined by cautious optimism. Around 84 percent of technology employers anticipate that broader economic conditions will positively influence salary-setting decisions. Wage growth has stabilised at approximately 2 percent, easing the volatility that previously constrained hiring budgets.
However, this stabilisation coexists with a surge in candidate activity. Job advertisement volumes remain below historical peaks, yet the number of applications per role has increased significantly. This influx is driven by both domestic job mobility and offshore professionals seeking entry into New Zealand’s technology ecosystem.
The result is a structural paradox: higher application volumes but limited availability of “strategic fits” who combine deep technical expertise with organisational alignment and adaptability.
Table: Macro-Economic Indicators Influencing IT Recruitment in 2026
| Economic Indicator | 2026 Status | Recruitment Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Employer Salary Confidence | 84% positive outlook | Increased flexibility in competitive offers |
| Wage Growth Rate | ~2% | Stabilised but cautious compensation adjustments |
| Average Cost per Tech Hire | NZD 23,860 | Higher scrutiny in hiring decisions |
| Application Volume per Vacancy | Increasing | Greater screening burden for hiring managers |
| Persistent Skills Shortage Reporting | 85% of businesses | Continued reliance on specialist recruiters |
Lengthening Recruitment Cycles and Strategic Screening
The complexity of modern IT hiring is reflected in extended recruitment timelines. In 2026, the average hiring cycle for technology roles ranges between 50.3 days and 86 days for niche or leadership positions. Employers are implementing additional interview stages, technical assessments, and cultural evaluations to mitigate risk.
While 76 percent of tech leaders report that compensation offers are broadly aligned with required skills and experience, 62 percent identify elevated salary expectations as a key obstacle to finalising placements. This dynamic underscores the importance of recruitment partners who can manage candidate expectations and negotiate strategically.
Matrix: 2026 Recruitment Complexity Drivers
| Complexity Factor | Operational Consequence | Agency Advisory Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| High Application Volume | Increased screening workload | Structured candidate filtering frameworks |
| Niche Technical Demand | Extended time-to-hire | Specialist sourcing expertise |
| Salary Expectation Inflation | Offer negotiation challenges | Market benchmarking and advisory capability |
| Cultural Fit Emphasis | Multi-stage interview processes | Behavioural and values-based assessment |
| Rising Cost-per-Hire | Greater financial risk per placement | Retention-focused matching strategies |
Core Market Indicators and Workforce Intentions
The following consolidated table outlines the quantitative benchmarks defining New Zealand’s technology recruitment landscape in 2026.
Table: Core Technology Recruitment Benchmarks for 2026
| Market Metric | 2026 Estimated Value | Primary Trend Direction |
|---|---|---|
| Organisations Planning Headcount Increase | 80.0% | Increasing |
| Employers Using Online Salary Guides | 44.0% | Stable |
| Median Cost per Technology Hire | NZD 23,860 | Increasing |
| Average Recruitment Cycle | 50.3 – 86.0 days | Lengthening |
| Businesses Reporting Skills Shortage | 85.0% | Stable |
| Targeted Salary Negotiation Increase | 11% – 15% | Strategic |
| Wage Growth Projection | ~2.0% | Decelerating |
These metrics demonstrate that while economic sentiment is improving, structural talent constraints continue to define the recruitment landscape.
Geographic Redistribution and Infrastructure Growth
The labour market is also undergoing geographic redistribution. Traditional talent hubs such as Auckland and Wellington remain dominant, yet recruitment demand is increasingly distributed across secondary regions supported by remote-first work models and infrastructure expansion.
The national data centre market is growing at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 9.9 percent. Auckland retains an estimated 82.95 percent share of data centre hotspots, but regions such as Hamilton and Christchurch are emerging as alternative technology nodes due to infrastructure resilience and cost optimisation strategies.
Table: Regional Technology Ecosystem Trends in 2026
| Region | Strategic Role in 2026 Tech Market | Recruitment Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Auckland | Primary data centre and enterprise hub | Highest concentration of specialist roles |
| Wellington | Government and cybersecurity focus | Public sector digital transformation hiring |
| Hamilton | Emerging infrastructure expansion | Growth in cloud and operations roles |
| Christchurch | Regional innovation and engineering expansion | Increased demand for platform and systems talent |
Agency Benchmarking in a Strategic Hiring Era
The evolution of the recruitment agency’s role is one of the defining features of 2026. Organisations now evaluate agencies on several advanced criteria beyond fill rates:
• Capability in managing niche technical searches
• Salary benchmarking and negotiation advisory
• Retention-focused placement strategies
• Technology-enabled screening processes
• Geographic sourcing flexibility
Matrix: 2026 Agency Benchmarking Framework
| Evaluation Criteria | Traditional Benchmark (Pre-2024) | 2026 Strategic Benchmark |
|---|---|---|
| Fill Rate | Primary KPI | Balanced with retention and quality metrics |
| Time-to-Hire | Speed-focused | Speed plus long-term suitability |
| Salary Advisory | Limited benchmarking | Data-driven negotiation support |
| Candidate Experience | Process-oriented | Relationship and brand-aligned engagement |
| Workforce Planning Contribution | Minimal | Strategic workforce mapping and forecasting |
Conclusion: A Market Defined by Precision and Partnership
The technology recruitment landscape in New Zealand in 2026 is neither contractionary nor expansionary in a simplistic sense. It is instead characterised by disciplined growth, heightened scrutiny, and strategic recalibration. Employers remain committed to expanding digital capability, with 80 percent planning headcount increases, yet they are operating within a market where skills scarcity and rising hiring costs demand precision.
Recruitment agencies that thrive in this environment will be those capable of delivering consultative insight, structured screening methodologies, geographic flexibility, and long-term workforce alignment. The era of reactive volume hiring has passed. In its place stands a recruitment ecosystem defined by strategic partnership, operational intelligence, and measured, capability-led growth.
The Financial Mechanics of Talent Acquisition in New Zealand’s Technology Sector: 2026 Cost Structures and Pricing Models
In 2026, the economic structure of technology recruitment in New Zealand has evolved toward transparent, logic-based pricing frameworks. Employers are increasingly demanding clarity around fee structures, return on investment, and long-term value alignment. As the median cost per technology hire approaches NZD 23,860, organisations are scrutinising recruitment expenditure more closely than in previous growth cycles.
The traditional contingency “pay on placement” model remains common among small-to-medium enterprises. However, larger corporations, government agencies, and high-growth technology startups are progressively adopting retained search and subscription-based recruitment models. These structures prioritise exclusivity, candidate quality, and strategic workforce access rather than speed alone.
Recruitment Pricing Models in 2026
Technology recruitment agencies now operate under three dominant commercial frameworks:
Table: Recruitment Commercial Models in 2026
| Pricing Model | Primary Users | Strategic Advantage | Risk Allocation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contingency (Pay on Placement) | SMEs and cost-sensitive employers | No upfront cost | Agency absorbs sourcing risk |
| Retained Search | Enterprises and executive hiring | Priority access and deeper candidate mapping | Shared risk with upfront investment |
| Subscription / Embedded | High-growth startups and scaling firms | Continuous talent pipeline and workforce planning | Long-term partnership model |
The shift toward retained and subscription models reflects an environment where elite technology talent is scarce, and employers are willing to invest earlier in the search process to secure strategic advantage.
Placement Fee Structures for Permanent Technology Roles
Permanent placement fees in 2026 are typically calculated as a percentage of the candidate’s first-year gross annual salary. This calculation excludes bonuses and statutory contributions such as KiwiSaver. Market rates have stabilised into defined tiers based on role seniority and complexity.
Table: Permanent Recruitment Fee Benchmarks – Technology Roles (2026)
| Role Seniority Tier | Standard Fee Percentage | Niche / Hard-to-Fill Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Junior / Entry Level | 12.0% – 15.0% | Up to 18.0% |
| Mid-Level Specialist | 16.0% – 22.0% | Up to 25.0% |
| Senior / Lead / Executive | 22.0% – 30.0% | 33.0% and above |
Agencies typically build flexibility into these ranges to accommodate negotiation. For example:
• A single senior software engineer earning NZD 150,000 may generate a placement fee between NZD 22,500 and NZD 37,500.
• Volume hiring agreements can reduce a standard 25 percent fee to 18–20 percent for individual placements.
• Multi-role hiring campaigns may secure fee reductions to 15–18 percent when exclusivity is granted.
Matrix: Fee Drivers in Permanent Technology Recruitment
| Pricing Variable | Impact on Fee Percentage | Strategic Consideration for Employers |
|---|---|---|
| Role Scarcity | Increases toward upper-tier rates | Hard-to-fill cybersecurity or AI roles |
| Salary Band | Higher salary increases total fee value | Executive and specialist hires |
| Volume Commitment | Enables negotiated reductions | Multi-hire or scaling initiatives |
| Exclusivity | Often lowers fee percentage | Reduces agency competition |
| Replacement Guarantee Period | May adjust pricing slightly | Risk mitigation component |
Contract and Temporary Staffing Markup Analysis
The contract technology market in 2026 operates under two distinct pricing environments: public sector frameworks and private sector consultancy margins.
Public sector recruitment is heavily influenced by the All-of-Government (AoG) External Recruitment Services framework, which imposes strict caps on agency margins. Private sector engagements, by contrast, operate under market-driven pricing conditions.
Table: Contract Staffing Pricing Comparison (2026 Example)
| Pricing Element | Public Sector (AoG Framework) | Private Sector (Standard) |
|---|---|---|
| Contractor Base Pay (Example) | NZD 80.00 per hour | NZD 80.00 per hour |
| Agency Markup / Margin | 11.5% (NZD 9.20) | 25.0% (NZD 20.00) |
| Admin / Managed Service Fee | 1.0% (NZD 0.80) | Included in margin |
| Total Hourly Charge Rate | NZD 90.00 per hour | NZD 100.00 per hour |
For long-term engagements, the financial impact becomes substantial. Over a 65-week contract, the difference between public sector and private sector pricing can exceed NZD 25,000 per contractor.
Financial Implications for Agencies
The capped margins under the AoG framework have significantly influenced agency operational strategy. To maintain profitability while complying with regulated pricing structures, agencies have increasingly:
• Invested in automation and applicant tracking systems
• Streamlined onboarding and payroll processes
• Reduced administrative overhead through digital workflows
• Leveraged data analytics for more precise candidate matching
Matrix: Profitability Strategies Under Margin Constraints
| Operational Lever | Purpose | Financial Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Recruitment Automation | Reduce consultant administrative load | Improved margin preservation |
| Centralised Contractor Payroll | Increase efficiency | Lower operational cost per contractor |
| Data-Driven Sourcing | Improve match accuracy | Reduced replacement and churn risk |
| Volume Framework Agreements | Secure predictable revenue streams | Greater financial stability |
Cost Sensitivity and Strategic Negotiation
In a competitive hiring climate, employers have become more strategic in negotiating recruitment fees. Agencies respond by structuring pricing packages that balance flexibility with sustainability.
Negotiation strategies commonly include:
• Tiered discounts based on hiring volume
• Reduced fees for exclusivity agreements
• Performance-based rebate clauses
• Extended guarantee periods in exchange for higher percentages
However, given the rising average cost per hire and lengthening recruitment cycles, agencies must protect margin integrity to sustain high-quality sourcing capabilities.
Conclusion: Financial Transparency as a Competitive Differentiator
The financial mechanics of talent acquisition in New Zealand’s technology sector in 2026 reflect a mature and highly scrutinised marketplace. Employers are increasingly analytical in evaluating recruitment expenditure, while agencies must balance competitive pricing with operational sustainability.
Transparent fee structures, logic-based commission tiers, and structured contract markups have become central to agency differentiation. In an environment where elite technology talent commands premium compensation and extended search cycles, recruitment economics are no longer secondary considerations. They are strategic levers that directly influence hiring success, organisational resilience, and long-term workforce performance.
Technological Integration: The AI Paradigm in Recruitment in New Zealand, 2026
By 2026, artificial intelligence has transitioned from an experimental enhancement to a core operational infrastructure within New Zealand’s technology recruitment ecosystem. Approximately 78 percent of recruitment agencies now utilise AI-driven systems to streamline administrative processes, enhance candidate matching precision, and improve data visibility across hiring pipelines.
In a market defined by lengthening recruitment cycles and rising cost-per-hire metrics, AI integration is no longer optional. Agencies that fail to adopt intelligent automation risk falling behind in efficiency, scalability, and candidate engagement.
Table: AI Adoption in Recruitment Agencies – 2026 Snapshot
| AI Adoption Indicator | 2026 Estimated Level | Operational Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Agencies Using AI for Admin Reduction | 78% | Reduced manual screening workload |
| AI-Driven Candidate Matching | Widespread | Higher shortlisting accuracy |
| Conversational AI Engagement Tools | Increasing adoption | Faster candidate response times |
| ATS-Integrated Intelligence Systems | Rapid growth | Improved real-time data synchronisation |
The Emergence of Intelligent Sourcing Platforms
One of the most influential developments in the New Zealand recruitment technology market has been the introduction of Adder Intelligence in late 2025. By 2026, its integration across agencies has significantly altered recruiter workflows.
Operating within existing applicant tracking systems, the platform enhances decision-making through two primary features:
Smart Summary
This function consolidates historical candidate interactions, communication records, and skill progression into a unified intelligence profile. Without requiring manual prompts, it generates real-time recommendations regarding candidate-role alignment. Recruiters benefit from immediate visibility into match strength, reducing evaluation time.
Smart Sync
Smart Sync analyses unstructured recruiter notes, call logs, and engagement activity. It automatically updates candidate profiles and surfaces high-potential individuals who may not have recently applied but are suitable for new opportunities. This proactive resurfacing mechanism addresses one of the largest inefficiencies in legacy ATS databases: underutilised talent pools.
Matrix: Traditional ATS vs AI-Enhanced ATS in 2026
| Capability Dimension | Traditional ATS Model | AI-Enhanced Model with Adder Intelligence |
|---|---|---|
| Candidate Profile Updates | Manual entry required | Automated real-time synchronisation |
| Historical Interaction Use | Limited reference | Integrated predictive match analysis |
| Passive Talent Surfacing | Reactive search | Proactive AI-triggered recommendations |
| Recruiter Time Allocation | Admin-heavy | Strategic engagement-focused |
Agencies adopting AI-powered workflows report reductions in time-to-hire of up to 67 percent, particularly for mid-level technical roles where structured competency data is abundant.
Expansion of AI-Native Recruitment Platforms
Beyond ATS-integrated intelligence tools, AI-native platforms such as Manatal and iSmartRecruit 2.0 have introduced conversational AI chatbots and 24/7 digital engagement tools.
These systems operate across messaging platforms including WhatsApp and Facebook, enabling automated candidate communication, interview scheduling, and screening question responses.
Reported outcomes include:
• Candidate response rate increases of approximately 46 percent
• Faster interview scheduling turnaround
• Reduced recruiter dependency on manual follow-up
• Enhanced engagement with passive candidates
Table: AI-Native Engagement Impact Metrics
| Engagement Metric | Performance Improvement (2026) |
|---|---|
| Candidate Response Rate | +46% |
| Screening Automation Efficiency | Significant reduction in manual review |
| Interview Scheduling Speed | Accelerated by chatbot workflows |
| Passive Candidate Activation | Increased through 24/7 outreach |
Candidate Adaptation to AI Screening
The proliferation of AI-driven screening tools has significantly altered candidate behaviour. As automated CV parsing and algorithmic ranking systems become standard, job applicants must now optimise their applications to navigate digital gatekeeping mechanisms.
Leading agencies such as Absolute IT and Salt advise candidates on specific “AI-proofing” strategies to ensure visibility within automated systems.
Core AI-Proofing Techniques in 2026
Keyword Mirroring
Precise alignment with terminology used in job advertisements has become essential. Candidates must explicitly reference required platforms, frameworks, and methodologies such as Snowflake, Kubernetes, DevOps, Azure, or Python to pass automated screening thresholds.
Formatting Simplification
Complex CV designs, multi-column layouts, graphics, and embedded tables often disrupt parsing accuracy. Clean, single-column formats with clearly defined headings and consistent typography have become standard practice.
Quantifiable Impact Statements
AI engines increasingly prioritise measurable outcomes. Statements such as “reduced latency by 15 percent” or “automated deployment pipelines saving 10 hours per week” are weighted more heavily than qualitative descriptions of responsibilities.
Matrix: Traditional CV Optimisation vs AI-Optimised CV Strategy
| CV Strategy Element | Traditional Focus | AI-Optimised Approach in 2026 |
|---|---|---|
| Keyword Usage | General skills listing | Precise job description alignment |
| Visual Design | Creative or stylised layouts | Minimalist, parser-friendly formatting |
| Achievement Description | Narrative-based responsibilities | Metrics-driven performance statements |
| Skills Section Structure | Broad competency categories | Exact platform and tool references |
Operational Implications for Recruitment Agencies
The AI paradigm has reshaped agency value propositions. Recruiters are no longer solely evaluated on network depth or relationship management. They must now demonstrate:
• Technological fluency in AI-enabled sourcing tools
• Data interpretation capability
• Ethical governance of automated screening
• Transparency in algorithm-driven shortlisting
Agencies that effectively combine AI automation with human judgment achieve a dual advantage: improved efficiency and stronger candidate trust.
Table: AI Integration Benefits for Agencies in 2026
| Strategic Outcome | AI Contribution |
|---|---|
| Reduced Administrative Burden | Automation of data entry and screening |
| Faster Talent Identification | Predictive matching algorithms |
| Improved Candidate Experience | 24/7 chatbot communication |
| Enhanced Database Utilisation | Intelligent resurfacing of dormant candidates |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational overhead per placement |
Conclusion: AI as Foundational Infrastructure
In New Zealand’s 2026 recruitment landscape, artificial intelligence is no longer positioned as a differentiator alone; it has become foundational infrastructure. Agencies leveraging AI-enhanced sourcing, predictive analytics, and conversational engagement tools operate with measurable speed and efficiency advantages.
At the same time, candidates must navigate algorithm-driven gatekeeping systems by adapting CV strategy and keyword precision. The future of recruitment is therefore defined not by automation alone, but by the intelligent integration of AI systems with strategic human oversight. The agencies that master this balance will shape the next phase of New Zealand’s technology talent acquisition ecosystem.
Salary Benchmarking and Role-Specific Demand in New Zealand’s Technology Sector, 2026
In 2026, New Zealand’s technology salary landscape reflects stabilisation following several years of rapid wage acceleration. Most employers are implementing moderate annual salary increases in the range of 3 to 5 percent, aligning with broader economic adjustments and decelerating wage growth trends.
However, this stability is not uniform across all roles. High-impact disciplines such as artificial intelligence, data engineering, cloud architecture, and cybersecurity continue to command aggressive counteroffers and accelerated salary negotiations. These domains remain structurally constrained by limited domestic talent supply and sustained enterprise investment.
While median salary growth has moderated, competition for specialised skills remains intense, particularly in Auckland and Wellington, which continue to function as primary hiring hubs for technology and digital transformation projects.
2026 Salary Guide: IT and Software Roles
The following salary benchmarks reflect 2026 placement data across Auckland and Wellington. Figures represent base salary only and exclude bonuses, equity incentives, and KiwiSaver contributions.
Table: 2026 Salary Percentiles for IT and Software Roles (NZD)
| Position Title | 25th Percentile | 50th Percentile | 75th Percentile |
|---|---|---|---|
| IT Support Level 1 | 60,000 | 65,000 | 70,000 |
| IT Support Level 2 | 72,000 | 75,000 | 80,000 |
| Systems Administrator | 80,000 | 85,000 | 95,000 |
| Application Support | 65,000 | 75,000 | 95,000 |
| Senior Software Engineer | 135,000 | 155,000 | 180,000 |
| Data Scientist | 120,000 | 140,000 | 175,000 |
| Cyber Security Analyst | 115,000 | 135,000 | 165,000 |
Interpretation of Salary Percentiles
• The 25th percentile represents professionals with foundational or early-stage competency.
• The 50th percentile reflects experienced practitioners meeting standard market expectations.
• The 75th percentile indicates highly experienced specialists with advanced certifications, niche technical depth, or leadership capability.
The widening gap between the 50th and 75th percentiles in advanced roles such as Senior Software Engineer, Data Scientist, and Cyber Security Analyst demonstrates the premium placed on expertise and strategic impact.
Matrix: Salary Compression vs Skill Scarcity in 2026
| Role Category | Salary Growth Stability | Scarcity Level | Counteroffer Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| IT Support Roles | Moderate (3–5%) | Low–Moderate | Limited |
| Systems Administration | Stable | Moderate | Occasional |
| Senior Software Engineering | Strong at upper quartile | High | Frequent |
| Data Science | High variance | Very High | Aggressive |
| Cybersecurity | High variance | Very High | Aggressive |
Emerging Specialisations and High-Demand Skills
The first half of 2026 has seen a resurgence of enterprise-scale transformation programs, particularly within Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) modernisation and national data transformation initiatives. This resurgence has triggered concentrated demand in several specialised domains.
Cloud Architects and Engineers
Organisations accelerating artificial intelligence deployment and infrastructure modernisation are actively recruiting cloud professionals certified in Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services. These roles require expertise in scalable architecture design, security integration, and hybrid-cloud orchestration.
Generative AI Engineers
A newly defined category in many organisations, Generative AI Engineers are responsible for embedding large language models and automation frameworks into internal workflows. Responsibilities include prompt engineering, API integration, governance oversight, and AI compliance strategy.
Site Reliability Engineering and DevOps Professionals
Demand for SRE and DevOps specialists continues to expand, particularly those with automation expertise using tools such as Terraform and Snowflake. Employers prioritise candidates capable of building repeatable, resilient deployment environments that reduce system downtime and operational risk.
Table: Emerging High-Impact Technology Roles in 2026
| Emerging Specialisation | Key Competencies Required | Strategic Importance to Employers |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Architect | Azure, AWS, infrastructure-as-code, security design | AI readiness and scalability |
| Generative AI Engineer | LLM integration, API design, automation governance | Enterprise AI deployment |
| SRE / DevOps Engineer | Terraform, CI/CD pipelines, reliability engineering | Operational stability and automation |
| Data Transformation Lead | ERP integration, data migration, analytics platforms | Business intelligence modernisation |
Regional Influence on Salary Dynamics
Auckland remains the dominant salary benchmark driver due to its concentration of enterprise headquarters and data centre infrastructure. Wellington continues to influence cybersecurity and public sector digital transformation remuneration trends.
However, increasing adoption of remote-first hiring models is narrowing regional pay gaps for certain high-demand roles. Employers are increasingly benchmarking salaries based on skill scarcity rather than physical location alone.
Strategic Implications for Employers and Agencies
The stabilised yet selectively competitive salary environment of 2026 requires careful workforce planning. Employers must balance internal equity with market-driven counteroffer pressures. Recruitment agencies play a key advisory role in:
• Benchmarking salary expectations accurately
• Managing candidate counteroffer risk
• Advising on total compensation packages
• Identifying retention-sensitive skill clusters
Conclusion: A Stabilised but Skill-Selective Salary Market
The 2026 technology salary landscape in New Zealand reflects measured recovery and disciplined compensation growth. While entry-level and support roles follow moderate adjustment patterns, advanced technical disciplines continue to command premium compensation.
As AI, cloud transformation, and cybersecurity remain strategic priorities, employers must adopt targeted salary strategies that align with skill scarcity and long-term digital transformation objectives. The organisations that successfully integrate data-driven benchmarking with flexible negotiation tactics will maintain a competitive advantage in securing high-impact technology talent.
Candidate Dynamics in New Zealand’s Technology Sector: The Shift from “Job Hugging” to Strategic Mobility in 2026
In 2026, the technology workforce in New Zealand has transitioned from defensive employment behaviour to what can be described as strategic mobility. During the economic uncertainty of 2024, many professionals adopted a “job hugging” mindset, choosing stability over career progression due to concerns about redundancy and hiring slowdowns.
By contrast, 2026 reflects renewed confidence. Approximately 61 percent of technology professionals are actively considering a career move, even though 85 percent report being initially satisfied in their current roles. This signals a fundamental change: mobility is no longer driven by dissatisfaction alone, but by long-term career optimisation.
Table: Workforce Sentiment Indicators in 2026
| Workforce Indicator | 2026 Percentage | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Professionals Considering a Job Move | 61% | Increased confidence and career recalibration |
| Professionals Reporting Initial Job Happiness | 85% | Satisfaction does not eliminate mobility |
| Employers Expecting Retention Challenges | 67% | Rising cost-of-living pressures influencing decisions |
The modern technology professional is increasingly selective, evaluating roles based on progression potential, skill relevance, organisational stability, and long-term earning trajectory rather than short-term security alone.
Cultural Alignment Versus Compensation
Compensation continues to function as the primary engagement trigger in recruitment conversations. Competitive salary packages remain essential for attracting candidates into the hiring funnel. However, data from 2026 highlights that pay alone does not secure retention.
Culture, broadly defined as professional development, managerial support, recognition frameworks, and clarity of progression, now plays a decisive role in long-term workforce stability.
Matrix: Compensation Versus Cultural Drivers in 2026
| Decision Factor | Role in Attraction | Role in Retention |
|---|---|---|
| Base Salary | Primary hook | Secondary to growth opportunities |
| Bonus and Incentives | Competitive differentiator | Moderate impact |
| Development Planning | Influential | Critical |
| Leadership Quality | Moderate initial importance | High long-term impact |
| Recognition and Support | Enhances employer brand | Core retention driver |
Compensation Sensitivity and Cost-of-Living Pressure
Approximately 67 percent of employers expect rising living costs to increase retention challenges. While wage growth has stabilised at moderate levels, many technology professionals perceive that salary adjustments are not fully aligned with inflationary pressures.
This perception gap creates heightened vulnerability to counteroffers and external recruitment approaches. In particular, mid-level software engineers, data professionals, and cybersecurity specialists are more likely to respond to competing salary packages if internal adjustments lag behind market benchmarks.
Table: Compensation Sensitivity Factors in 2026
| Retention Pressure Driver | Impact on Workforce Stability |
|---|---|
| Inflation Perception | Increased job market exploration |
| External Counteroffers | Higher acceptance rates |
| Limited Internal Salary Reviews | Reduced organisational loyalty |
| Transparent Salary Benchmarking | Improved retention when aligned |
The Value of Development and Career Roadmaps
One of the most notable behavioural trends in 2026 is the willingness of certain professionals to accept lower base compensation in exchange for structured career development. Some candidates report readiness to accept pay reductions of up to 30 to 40 percent if provided with a clear six-to-twelve-month progression roadmap.
This indicates a strategic recalibration in career planning. Professionals are prioritising skill expansion, leadership exposure, and long-term earning potential over immediate remuneration.
Matrix: Short-Term Pay Versus Long-Term Value
| Career Evaluation Dimension | Short-Term Salary Focus | Development-Focused Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Immediate Income | Maximised | Potentially reduced |
| Skill Expansion | Limited in static roles | Accelerated via structured development |
| Promotion Visibility | Uncertain | Defined progression pathway |
| Long-Term Earning Potential | Stable but capped | Higher through capability growth |
Flexibility as a Competitive Retention Tool
Workplace flexibility remains a critical factor in recruitment and retention. Approximately 50 percent of businesses now offer enhanced flexibility arrangements, including hybrid and remote-first options, to secure preferred candidates.
Flexibility is no longer treated as an optional benefit but as a baseline expectation in many technology disciplines. Professionals increasingly evaluate commute time, autonomy, and work-life integration as part of total compensation.
Additionally, 59 percent of businesses report that aligning compensation more precisely with role requirements has significantly improved their success in securing top-tier talent. This suggests that transparent role evaluation and structured pay benchmarking are effective retention levers.
Persistent Drivers of Turnover
Despite compensation alignment and flexibility initiatives, cultural weaknesses continue to drive voluntary exits. The most frequently cited reasons for turnover in 2026 include:
• Uninspiring organisational culture
• Poor management practices
• Lack of recognition
• Absence of meaningful progression pathways
Table: Primary Turnover Drivers in Technology Roles (2026)
| Turnover Cause | Strategic Risk to Employers |
|---|---|
| Poor Management | High team-level instability |
| Unclear Career Progression | Increased external job exploration |
| Limited Recognition | Reduced engagement |
| Cultural Misalignment | Accelerated voluntary attrition |
Conclusion: Strategic Mobility as the New Normal
The 2026 technology workforce in New Zealand is defined not by fear-based job retention but by informed, strategic mobility. Professionals are actively evaluating their long-term positioning, balancing compensation, cultural alignment, development potential, and flexibility.
For employers and recruitment agencies, this shift requires a recalibrated retention strategy. Competitive pay remains essential for attraction, but sustained engagement depends on leadership quality, transparent progression frameworks, and authentic organisational culture.
In this new environment, organisations that integrate salary benchmarking, development planning, and flexible work design will be best positioned to secure and retain high-impact technology talent.
Strategic Outlook and Future Considerations for New Zealand’s Technology Recruitment Market in 2026
As New Zealand progresses through the latter half of 2026, the technology recruitment landscape is expected to remain measured and strategic rather than reactive. The volatility that defined earlier post-pandemic expansion cycles has been replaced by disciplined workforce planning and controlled headcount growth.
Many Kiwi technology companies have expanded internationally, entering offshore markets to secure growth capital and diversified revenue streams. This outward movement has reshaped local recruitment expectations. Employers must now operate with a global mindset, benchmarking talent, compensation, and skill availability against international standards. At the same time, demand for region-specific capabilities in cybersecurity, regulatory compliance, infrastructure resilience, and operational continuity has intensified.
The resulting environment is one where strategic foresight, not speed alone, determines hiring success.
Table: Defining Characteristics of the Late-2026 Recruitment Market
| Market Characteristic | Strategic Implication for Employers |
|---|---|
| Measured Headcount Expansion | Focus on quality over quantity |
| Global Talent Competition | Increased benchmarking against offshore markets |
| Persistent Skills Shortages | Continued reliance on specialist recruitment |
| Regional Cybersecurity Demand | Elevated salary and retention pressure |
| AI Integration in Recruitment | Operational efficiency as baseline expectation |
Investment in Long-Term Talent Pipelines
Organisations that perform strongly in 2026 are those shifting from immediate vacancy-filling toward long-term pipeline cultivation. Rather than reacting to sudden departures, forward-thinking employers are mapping future skill requirements and investing in internal development frameworks.
Key elements of this strategy include:
• Graduate and early-career development programs
• Structured internal upskilling in AI and cloud technologies
• Succession planning for critical technical leadership roles
• Continuous engagement with passive candidate networks
Matrix: Reactive Hiring vs Pipeline-Based Strategy
| Hiring Model Dimension | Reactive Approach | Pipeline-Based Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Workforce Planning Horizon | Immediate vacancy focus | 12–24 month skills forecasting |
| Candidate Engagement | Transactional | Ongoing relationship building |
| Skills Development | External hiring dependency | Internal capability expansion |
| Risk Exposure | High disruption during attrition | Reduced through proactive planning |
Leveraging Specialised Advisory at Board Level
The evolving complexity of AI integration, cybersecurity governance, and digital transformation has elevated the role of recruitment agencies beyond operational delivery. Leading organisations increasingly seek agencies capable of offering boardroom-level advisory services related to talent architecture and workforce infrastructure.
This includes:
• AI capability mapping across enterprise functions
• Strategic workforce modelling
• Executive succession planning
• Infrastructure resilience hiring strategy
Agencies that combine market intelligence with executive advisory expertise are positioned to become strategic partners rather than transactional suppliers.
Table: Strategic Advisory Capabilities in 2026
| Advisory Function | Organisational Impact |
|---|---|
| AI Workforce Strategy | Future-proofed digital transformation plans |
| Talent Infrastructure Planning | Improved alignment between hiring and growth |
| Leadership Succession Advisory | Reduced executive transition risk |
| Market Intelligence Benchmarking | Evidence-based compensation alignment |
Adoption of Data-Driven Benchmarking
Data-driven salary benchmarking remains one of the most critical risk mitigation tools in 2026. Employers that align compensation with both national averages and role-specific percentile data reduce the likelihood of counteroffers and voluntary exits.
This benchmarking process increasingly integrates:
• National salary guide data
• Regional variance analysis
• Skill scarcity premiums
• Internal equity audits
Matrix: Compensation Strategy and Retention Risk
| Compensation Approach | Retention Risk Level | Market Competitiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Below Market Benchmark | High | Weak |
| Market Median Alignment | Moderate | Stable |
| 75th Percentile for Scarce Roles | Low | Strong |
| Performance-Linked Variable Model | Balanced | Flexible and adaptive |
The Convergence of AI Efficiency and Human-Centric Care
The defining characteristic of leading recruitment agencies in 2026 is their ability to balance automation with human connection. Artificial intelligence tools such as Adder Intelligence have redefined operational efficiency, reducing administrative burden and accelerating candidate matching.
Simultaneously, agencies that emphasise loyalty, candidate protection, and long-term relationship management continue to differentiate themselves. For example, Dynamix Recruitment has demonstrated how a loyalty-driven philosophy can coexist with structured compliance and modern screening systems.
Matrix: Technology-Driven Efficiency vs Human-Centric Engagement
| Competitive Dimension | AI-Driven Advantage | Human-Centric Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Time-to-Hire | Accelerated through automation | Improved through trust-based communication |
| Candidate Screening Accuracy | Algorithmic match precision | Cultural alignment validation |
| Administrative Efficiency | Reduced manual workload | Higher engagement quality |
| Retention Outcomes | Data-informed alignment | Loyalty and support-driven stability |
Future Considerations for Employers and Agencies
Looking ahead, several themes are likely to define the remainder of 2026 and beyond:
• Increased demand for AI governance and regulatory expertise
• Heightened competition for cybersecurity and resilience specialists
• Continued globalisation of talent sourcing
• Greater integration between workforce analytics and executive decision-making
Organisations that succeed will treat recruitment not as a cost centre but as strategic infrastructure. Similarly, agencies that integrate technological sophistication with candidate advocacy and advisory depth will maintain competitive relevance.
Conclusion: A Market Defined by Strategic Discipline
The New Zealand technology recruitment market in late 2026 is characterised by deliberation, data-driven decision-making, and long-term workforce alignment. The era of reactive, volume-driven hiring has been replaced by measured capability building.
The agencies and employers that lead in this environment will be those capable of combining advanced AI-enabled recruitment systems with authentic, human-centred engagement models. Strategic pipeline investment, compensation benchmarking precision, and advisory-level partnership will ultimately determine which organisations secure sustainable advantage in an increasingly competitive digital economy.
Conclusion
As New Zealand advances through 2026, the technology recruitment market has clearly transitioned into a new era defined by precision, partnership, and performance. The days of reactive, high-volume hiring have given way to a more deliberate, capability-focused model. Employers are no longer simply seeking recruitment agencies that can deliver CVs quickly. Instead, they are prioritising strategic partners capable of navigating skills shortages, managing salary inflation, leveraging AI-driven recruitment systems, and safeguarding long-term workforce stability.
The top 10 recruitment agencies for hiring IT and software employees in New Zealand in 2026 reflect this evolution. Each agency profiled throughout this analysis represents a distinct response to the modern hiring environment. Some excel in large-scale enterprise and public sector transformation programs. Others differentiate themselves through boutique, high-touch candidate care models. Several combine global reach with local cultural alignment. A growing number integrate advanced artificial intelligence tools into their sourcing, screening, and engagement processes.
Collectively, these agencies illustrate the multifaceted nature of today’s technology recruitment ecosystem.
The Strategic Importance of Specialisation in IT and Software Recruitment
In 2026, technology hiring is no longer a generic function. Cloud engineering, cybersecurity, AI implementation, DevOps automation, ERP transformation, and data infrastructure modernisation all require nuanced domain expertise. Employers that attempt to generalise their recruitment strategy risk prolonged time-to-hire cycles, elevated cost-per-hire metrics, and increased turnover.
Specialist IT recruitment agencies bring several measurable advantages:
• Deep understanding of technical skill stacks and emerging technologies
• Access to curated talent pools across cloud, AI, data, and security disciplines
• Up-to-date salary benchmarking across Auckland, Wellington, and emerging regional hubs
• Experience navigating counteroffers and candidate mobility dynamics
• Advisory capability aligned with digital transformation objectives
As the average recruitment cycle extends beyond 50 days for specialised roles and salary expectations continue to fluctuate within competitive bands, the value of expertise has become central to hiring success.
Balancing Technology Integration with Human-Centric Recruitment
One of the most defining characteristics of the 2026 recruitment market is the convergence of AI-powered efficiency and human-centred engagement. Artificial intelligence tools embedded within applicant tracking systems, automated sourcing platforms, and conversational chatbots have significantly improved operational speed and candidate identification accuracy.
However, automation alone does not secure top-tier talent. Technology professionals remain highly sensitive to culture, leadership quality, and career progression clarity. While compensation acts as the initial attractor, long-term retention depends on development pathways, management capability, and authentic organisational alignment.
The top IT recruitment agencies in New Zealand have recognised this dual requirement. They invest in intelligent sourcing platforms while simultaneously maintaining structured candidate care programs, advisory-level employer consultation, and transparent communication practices.
This balance is critical in a market where 61 percent of tech professionals are considering new opportunities despite high baseline job satisfaction levels.
Salary Benchmarking and Cost Efficiency as Competitive Advantages
In 2026, salary transparency and benchmarking precision have become strategic differentiators. Employers face a stabilised but selectively competitive compensation environment. While general wage growth has moderated to approximately 2 percent, high-demand roles in AI, data engineering, cybersecurity, and cloud architecture continue to command premium remuneration and aggressive counteroffers.
The top recruitment agencies provide employers with:
• Percentile-based salary benchmarking
• Market-informed negotiation strategies
• Insight into candidate expectation trends
• Risk mitigation frameworks to reduce post-offer attrition
With the median cost per technology hire approaching NZD 23,860, organisations cannot afford misaligned offers or extended vacancy gaps. Strategic salary positioning and data-driven compensation modelling are no longer optional; they are operational necessities.
Global Expansion and Local Skill Specificity
The international expansion of New Zealand-based technology companies has introduced a more global mindset into local recruitment. Employers now compete not only within Auckland and Wellington but also against offshore markets offering remote opportunities.
Yet at the same time, region-specific skill demands remain critical. Cybersecurity compliance, infrastructure resilience, and data sovereignty requirements necessitate locally grounded expertise. The best recruitment agencies in 2026 are those capable of combining global talent access with nuanced understanding of New Zealand’s regulatory and operational landscape.
This hybrid capability enables:
• Remote workforce scaling
• Cross-border talent acquisition
• Regionally compliant cybersecurity hiring
• Infrastructure-aligned cloud engineering placements
Why Agency Selection Matters More Than Ever
Selecting the right recruitment partner in 2026 directly influences organisational agility, digital transformation outcomes, and long-term workforce sustainability. The top 10 recruitment agencies highlighted in this blog represent varying strengths:
• Enterprise-scale delivery and public sector frameworks
• Boutique, high-engagement service models
• AI-driven recruitment innovation
• Executive-level advisory capability
• Contract staffing infrastructure under government frameworks
• High-value senior technology placement expertise
Each agency contributes differently to New Zealand’s technology hiring ecosystem. The optimal choice for an employer depends on organisational size, industry sector, urgency of hiring needs, and long-term workforce strategy.
A single startup seeking its first cloud architect may require a different recruitment model than a government agency launching a multi-year cybersecurity overhaul. Understanding these distinctions is essential for maximising return on recruitment investment.
The Future of IT and Software Recruitment in New Zealand
Looking beyond 2026, several structural trends will continue shaping the recruitment landscape:
• Increased integration of AI governance and compliance roles
• Continued demand for generative AI engineering expertise
• Greater emphasis on internal upskilling pipelines
• Expansion of hybrid and remote-first employment frameworks
• Data-driven performance measurement within recruitment partnerships
Agencies that remain adaptive, technologically advanced, and culturally aligned will continue to lead the market. Employers that treat recruitment as a strategic function rather than a transactional necessity will secure a sustained competitive advantage in talent acquisition.
Final Perspective
The technology recruitment market in New Zealand in 2026 is disciplined, competitive, and data-driven. Skills shortages persist. Candidate mobility is strategic rather than reactive. Salary benchmarking requires precision. AI tools have redefined operational efficiency. Cultural alignment determines retention outcomes.
Against this backdrop, the top 10 recruitment agencies for hiring IT and software employees in New Zealand in 2026 stand out not merely for their placement volumes, but for their strategic insight, technological sophistication, and commitment to candidate and client success.
For organisations seeking to build resilient digital infrastructure, scale AI capability, modernise enterprise systems, or secure cybersecurity expertise, choosing the right recruitment partner is a decision with long-term operational consequences. The agencies profiled throughout this guide represent the benchmark standards for excellence, adaptability, and performance in New Zealand’s evolving technology employment ecosystem.
Ultimately, the most successful employers in 2026 will be those who align their hiring strategy with agencies that combine intelligence, integrity, and innovation.
If you find this article useful, why not share it with your hiring manager and C-level suite friends and also leave a nice comment below?
We, at the 9cv9 Research Team, strive to bring the latest and most meaningful data, guides, and statistics to your doorstep.
To get access to top-quality guides, click over to 9cv9 Blog.
To hire top talents using our modern AI-powered recruitment agency, find out more at 9cv9 Modern AI-Powered Recruitment Agency.
People Also Ask
What are the top IT recruitment agencies in New Zealand in 2026?
The top IT recruitment agencies in New Zealand in 2026 are firms specializing in software, cloud, cybersecurity, AI, and data hiring. They combine market intelligence, salary benchmarking, and AI-driven sourcing to help employers secure high-demand tech talent efficiently.
Why should companies use specialist IT recruitment agencies in New Zealand?
Specialist IT recruitment agencies understand technical skill stacks, salary trends, and talent shortages. They reduce time-to-hire, improve candidate quality, and help employers compete in a tight technology labor market.
How much do IT recruitment agencies charge in New Zealand?
Permanent placement fees typically range from 12% to 30% of first-year base salary. Contract staffing margins vary, especially between public and private sectors, depending on complexity and exclusivity agreements.
Are IT recruitment agencies worth the cost in 2026?
Yes. With the average cost per tech hire rising significantly, agencies help reduce hiring mistakes, shorten recruitment cycles, and improve retention, delivering stronger long-term ROI.
What roles are most in demand in New Zealand’s tech sector in 2026?
Cloud architects, DevOps engineers, data engineers, cybersecurity analysts, AI specialists, and senior software engineers are among the most sought-after roles.
How long does it take to hire IT employees in New Zealand in 2026?
The average recruitment cycle ranges from 50 to 86 days for specialized roles, depending on skill scarcity and salary alignment.
Do recruitment agencies help with salary benchmarking?
Yes. Leading agencies provide percentile-based salary data aligned with Auckland, Wellington, and regional benchmarks to ensure competitive offers.
What is the average salary for a senior software engineer in NZ in 2026?
Senior software engineers typically earn between NZD 135,000 and NZD 180,000, depending on experience, certifications, and location.
How competitive is the IT job market in New Zealand in 2026?
The market remains highly competitive, with persistent skills shortages in AI, cybersecurity, and cloud engineering despite increased candidate applications.
Do agencies use AI in recruitment processes?
Most agencies now use AI-driven sourcing tools, applicant tracking systems, and automated screening to improve candidate matching and reduce administrative workload.
Can recruitment agencies help hire remote IT talent?
Yes. Many agencies source both local and international candidates, supporting remote and hybrid hiring strategies.
What is the difference between contingency and retained search models?
Contingency means paying only upon placement, while retained search involves upfront fees for exclusive, high-priority hiring assignments.
Which cities have the strongest tech hiring demand in NZ?
Auckland and Wellington remain primary hubs, while Christchurch and Hamilton are emerging growth regions for infrastructure and digital projects.
How do agencies reduce time-to-hire for tech roles?
They use pre-qualified talent pools, AI matching tools, structured screening, and proactive sourcing to accelerate hiring cycles.
What industries rely most on IT recruitment agencies in NZ?
Government, fintech, SaaS companies, healthcare technology, and enterprise corporations frequently rely on specialist IT recruiters.
Are cybersecurity professionals difficult to hire in 2026?
Yes. Cybersecurity talent remains scarce due to high demand for compliance, risk management, and infrastructure resilience expertise.
How can startups benefit from IT recruitment agencies?
Startups gain access to curated talent, salary guidance, and scalable hiring strategies without building large in-house HR teams.
Do agencies support contract and project-based hiring?
Yes. Many agencies provide contract staffing for cloud migrations, ERP implementations, and cybersecurity upgrades.
What factors influence IT salary negotiations in 2026?
Skill scarcity, role urgency, economic outlook, and cost-of-living pressures significantly influence compensation discussions.
How important is cultural fit in IT recruitment?
Cultural alignment is critical for retention. While salary attracts candidates, development opportunities and leadership quality drive long-term stability.
Are tech professionals open to changing jobs in 2026?
Yes. Around 61% of tech professionals are considering new opportunities despite reporting general job satisfaction.
What benefits attract top IT talent in New Zealand?
Competitive salary, flexible work options, structured development plans, and clear progression pathways are top attractors.
How does AI impact candidate screening?
AI tools prioritize keyword alignment, measurable achievements, and structured CV formatting to assess candidate suitability efficiently.
What is the cost difference between public and private sector contract hiring?
Public sector frameworks often cap agency margins, resulting in lower overall contractor costs compared to private sector engagements.
How do agencies handle counteroffers?
Agencies prepare candidates early, provide salary benchmarking, and guide negotiation strategies to reduce counteroffer risks.
Do IT recruitment agencies offer executive search services?
Yes. Many provide executive-level hiring for CTOs, digital directors, and senior technology leaders.
What makes a recruitment agency stand out in 2026?
Data-driven sourcing, AI integration, strong candidate care, salary intelligence, and strategic workforce advisory distinguish top agencies.
Is remote work still a major factor in tech hiring?
Yes. Hybrid and remote flexibility remain critical for attracting and retaining top IT professionals.
How can employers choose the right IT recruitment agency?
Employers should assess industry specialization, client testimonials, fee transparency, AI capabilities, and advisory expertise.
Will tech hiring continue growing beyond 2026?
Yes. Ongoing digital transformation, AI adoption, and cybersecurity investment indicate sustained long-term demand for IT talent in New Zealand.
Sources
Robert Half
- Absolute IT
- HCAMag
- Robert Walters
- Borderless AI
- Talent International
- Staffing Industry
- Mordor Intelligence
- GiiG Hire
- Juicebox
- Dover
- New Millennia
- New Zealand Government Procurement
- IT Brief
- iSmartRecruit
- SourceForge
- Find Recruitment
- HeroHunt
- Potentia
- RCSA
- Salt
- Indeed
- Hire Overseas
- Industry Connect
- NZ Hi-Tech Awards
- Hays
- Alcor BPO
- Horner Recruitment
- Dynamix Recruitment
- Clutch
- Frog Recruitment
- Seek
- JobAdder
- Wanderlog
- Envision RPO




